eScore
alliantenergy.comThe eScore is a comprehensive evaluation of a business's online presence and effectiveness. It analyzes multiple factors including digital presence, brand communication, conversion optimization, and competitive advantage.
Alliant Energy demonstrates a mature and effective digital presence focused on its core service territories in Iowa and Wisconsin. Content is well-aligned with the primary search intent of its customers, prioritizing critical tasks like bill payment and outage reporting. The company maintains a consistent, professional presence across its website and key social channels, and its strong domain authority is bolstered by its status as a critical infrastructure provider. However, its content strategy is less developed for capturing top-of-funnel, non-branded search queries related to broader energy topics like 'home solar options' or 'EV charging incentives', representing a missed opportunity for early customer engagement.
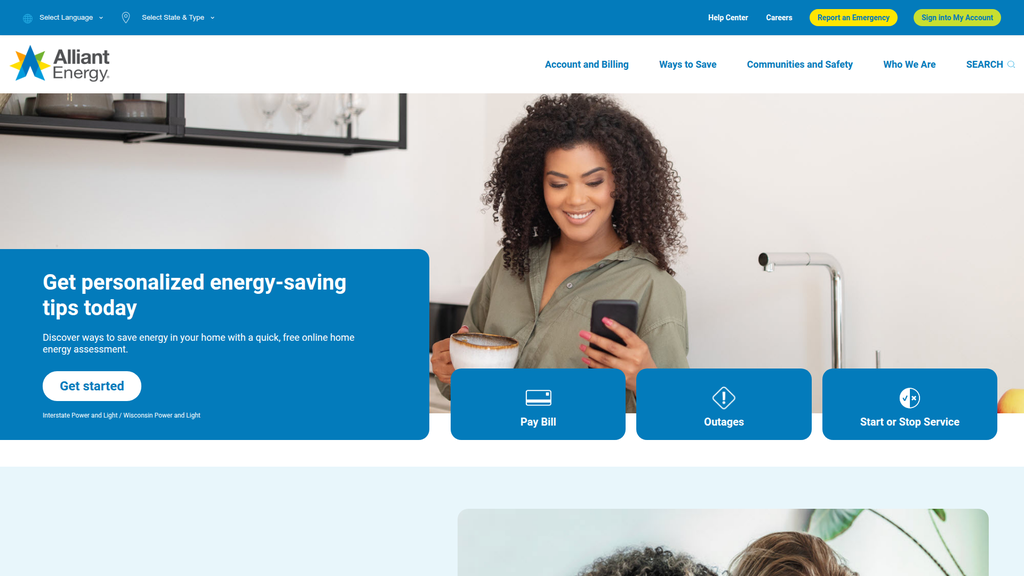
Excellent search intent alignment for core customer tasks (e.g., 'Pay Bill', 'Outages'), making the website highly functional for its existing user base.
Develop a comprehensive content strategy around non-branded, advisory keywords to capture users in the awareness and consideration stages of their energy journey, establishing Alliant as the primary resource for all energy-related decisions in its service area.
The company's brand communication is exceptionally clear, direct, and effective for its primary utilitarian functions. Messaging for residential customers is well-segmented, focusing on tangible benefits like cost savings and personalized energy tips. However, the overall brand narrative is underdeveloped; while Alliant has a compelling story around its 'Clean Energy Blueprint' and community investments, this is largely confined to news releases and not woven into a cohesive, emotionally resonant brand story on customer-facing pages. The provided analysis highlights this gap, noting the messaging is more 'transactional' than 'relational'.
Crystal-clear, task-oriented messaging and calls-to-action on the homepage that effectively guide existing customers to complete their primary goals.
Integrate the 'Clean Energy Blueprint' and community impact stories into the main customer journey to build a stronger brand narrative that moves beyond utility and fosters emotional connection and brand affinity.
Alliant Energy provides a best-in-class conversion experience for the most critical user tasks. The task-oriented homepage design significantly reduces friction and cognitive load for the majority of visitors, reflecting a deep understanding of customer needs. The mobile experience is seamless, and the information architecture is logical. The main friction point identified in the analysis is the low prominence of the 'Report an emergency' link, which could be a critical flaw during a crisis, and the lack of a prominent, dedicated accessibility statement.
The homepage design masterfully prioritizes the three most critical user tasks (Pay Bill, Outages, Start/Stop Service), creating an almost frictionless experience for the vast majority of visitors.
Implement a dynamic, high-prominence CTA for emergency reporting that activates based on system status to ensure immediate visibility during a crisis, and add a clear, public-facing Accessibility Statement to mitigate legal risk and improve usability for all customers.
As a publicly-traded (NASDAQ: LNT) and heavily regulated utility, Alliant Energy has exceptionally high intrinsic credibility. The website effectively deploys trust signals, including prominent safety information, comprehensive legal policies, and transparent financial reporting. Third-party validation comes from industry awards and a clear strategic plan for clean energy that aligns with regulatory and public expectations. The primary risk, as identified in the analysis, stems from digital compliance gaps, particularly the need for a formal accessibility audit and operational readiness for emerging data privacy laws like the ICDPA.
Inherent credibility as a regulated public utility, reinforced by transparent financial reporting and a strategic vision ('Clean Energy Blueprint') that aligns with regulator and investor expectations.
Commission a formal WCAG 2.1 AA accessibility audit and publish a dedicated statement to mitigate legal risk and reinforce the company's commitment to serving all members of its communities.
Alliant Energy's competitive advantage is profoundly strong and sustainable, anchored in its status as a regulated monopoly in its designated service territories. This creates an insurmountable moat with infinitely high switching costs for its core utility services. The company further strengthens its position through massive capital investments in infrastructure and renewable energy, which are approved by regulators and added to its rate base, ensuring a stable return. While it faces indirect competition from alternatives like rooftop solar, its ownership of the transmission and distribution grid makes it an indispensable player in the energy ecosystem.
The regulated monopoly model, which provides a captive customer base, predictable revenue, and a nearly impenetrable barrier to entry for core electricity and gas distribution services.
Develop and aggressively market a branded green energy program to counter competitor messaging (e.g., MidAmerican's '100% renewable' claim) and solidify public perception of Alliant's clean energy leadership.
Alliant Energy is poised for a rare and significant growth phase for a mature utility. This growth is not from geographic expansion but from massive, regulator-approved capital investment into its rate base, driven by an unprecedented surge in electricity demand from data centers. The company's $11.5 billion capital expenditure plan for 2025-2028 is a direct indicator of this expansion potential, underpinning a projected 11% compound annual growth in its rate base. Scalability is constrained only by the pace of regulatory approvals and the executional capacity to build out new infrastructure.
A massive, de-risked growth catalyst from contracted data center demand, which fuels an $11.5 billion, regulator-approved capital investment plan that directly drives earnings growth.
Accelerate the development of an integrated digital platform to increase adoption of value-added services (e.g., EV rates, demand response), creating new revenue opportunities and deepening customer relationships.
Alliant Energy's business model exhibits exceptional coherence and strategic alignment. The regulated rate-based revenue model provides a stable foundation, while the 'Clean Energy Blueprint' serves as a clear and focused strategy that perfectly aligns with the primary market trends of decarbonization and electrification. This strategy allows the company to invest billions in renewables and grid modernization, which simultaneously meets regulatory mandates, satisfies customer and investor ESG demands, and drives earnings growth by expanding the rate base. The model shows strong stakeholder alignment and excellent market timing, capitalizing on the surge in demand from data centers.
The strategic alignment of the 'Clean Energy Blueprint,' which allows regulator-approved capital investments in decarbonization to be the primary engine of rate base and earnings growth, satisfying all key stakeholders.
Proactively engage with regulators to propose innovative, performance-based rate designs that further align utility incentives with efficiency and customer satisfaction goals, moving beyond the traditional cost-plus model.
Within its service territory, Alliant Energy holds monopoly power, giving it a dominant market share by definition. Its pricing power is significant, albeit indirect; while rates are set by regulators, they are based on the company's proposed capital investments, giving it substantial influence over the pricing structure. The company has demonstrated strong leverage with partners, securing contracts for over 2.1 GW of new data center demand. Its market influence is demonstrated by its ability to shape regional energy policy and infrastructure development, though its brand perception in renewables lags behind some key competitors.
Monopoly control over essential infrastructure in its service territories, which grants it a captive customer base and significant leverage in negotiating with large customers and influencing regional energy development.
Invest in brand marketing to close the public perception gap with competitors on clean energy leadership, ensuring its market power is matched by its brand influence.
Business Overview
Business Classification
Regulated Public Utility
Energy Services Provider
Energy & Utilities
Sub Verticals
Electric Power Generation, Transmission & Distribution
Natural Gas Distribution
Mature
Maturity Indicators
- •
Publicly traded company (NASDAQ: LNT) with a long operational history.
- •
Operates as a regulated monopoly in defined service territories, ensuring stable revenue.
- •
Consistent dividend payouts and a stated long-term annual earnings growth target of 5-7%.
- •
Large, established asset base with significant ongoing capital expenditure plans ($11.5B for 2025-2028).
Enterprise
Steady
Revenue Model
Primary Revenue Streams
- Stream Name:
Regulated Electric Utility Sales
Description:Generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity to residential, commercial, and industrial customers in Iowa and Wisconsin at rates approved by state utility commissions.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Residential, Commercial & Industrial, Agricultural
Estimated Margin:Medium
- Stream Name:
Regulated Natural Gas Sales
Description:Distribution and transportation of natural gas to residential, commercial, and industrial customers in Iowa and Wisconsin at regulated rates.
Estimated Importance:Secondary
Customer Segment:Residential, Commercial & Industrial
Estimated Margin:Medium
- Stream Name:
Other Utility Operations & Services
Description:Includes wholesale electricity sales, steam distribution in specific areas, and potentially future revenue from energy services like EV charging infrastructure and energy management programs.
Estimated Importance:Tertiary
Customer Segment:Wholesale Markets, Large Industrial
Estimated Margin:Low
Recurring Revenue Components
Monthly residential utility bills for electricity and gas.
Recurring commercial and industrial energy supply contracts.
Pricing Strategy
Regulated Rate-Based
Regulator-Approved
Semi-transparent
Pricing Psychology
- •
Budget Billing / Levelized Payments
- •
Time-of-Use Rates (potential/emerging)
- •
Energy Efficiency Rebates & Incentives
Monetization Assessment
Strengths
- •
High predictability and stability of revenue due to the regulated monopoly model.
- •
Guaranteed rate of return on approved capital investments incentivizes infrastructure modernization and renewable energy development.
- •
Captive customer base of approximately 1 million electric and 430,000 gas customers ensures consistent demand.
Weaknesses
- •
Revenue growth is constrained by regulatory approval processes and the economic/population growth of service territories.
- •
Susceptible to political and regulatory shifts that can impact approved rates and profitability.
- •
Traditional model is based on selling more energy, which is misaligned with the societal push for energy efficiency.
Opportunities
- •
Develop new revenue streams from 'Energy-as-a-Service' models for large customers.
- •
Invest in and operate EV charging networks as a new regulated or non-regulated business line.
- •
Leverage the transition to renewables by providing grid management services for distributed energy resources (DERs).
- •
Grow the rate base through regulator-approved investments in clean energy, grid modernization, and energy storage.
Threats
- •
Customer-owned generation (rooftop solar) and battery storage reducing reliance on the utility grid (grid defection).
- •
Increased energy efficiency measures and smart home technology reducing overall energy consumption.
- •
Cybersecurity threats to grid infrastructure and operations.
- •
Regulatory model evolution to Performance-Based Regulation (PBR) could shift risk and incentive structures.
Market Positioning
Regulated Monopoly & Trusted Clean Energy Partner
Dominant/Monopoly within designated service areas in Iowa and Wisconsin.
Target Segments
- Segment Name:
Residential Customers
Description:Homeowners and renters within the service territory requiring electricity and natural gas for daily living.
Demographic Factors
Varying income levels
Urban, suburban, and rural locations
Psychographic Factors
- •
Value reliability and affordability above all.
- •
Increasingly interested in sustainability and clean energy options.
- •
Seeks convenience in billing and customer service.
Behavioral Factors
- •
Consistent, predictable energy consumption patterns.
- •
Increasing adoption of smart home devices and electric vehicles.
- •
Responds to energy-saving tips and rebate programs.
Pain Points
- •
Unexpected power outages.
- •
Unpredictable or high energy bills.
- •
Complexity in understanding energy usage and pricing.
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:Medium
- Segment Name:
Commercial & Industrial (C&I) Customers
Description:Businesses, manufacturers, data centers, and agricultural operations with significant energy needs.
Demographic Factors
Small businesses to large industrial facilities.
Key sectors: manufacturing, agriculture, data centers.
Psychographic Factors
- •
Prioritize power quality and reliability to avoid operational disruptions.
- •
Focused on cost management and budget predictability.
- •
Increasingly driven by corporate sustainability (ESG) goals.
Behavioral Factors
- •
High, often constant, energy load.
- •
Engage in long-term energy planning and contracts.
- •
Seek customized energy solutions and dedicated account management.
Pain Points
- •
Power quality issues that can damage sensitive equipment.
- •
Volatile energy costs impacting operational expenses.
- •
Meeting corporate mandates for renewable energy usage.
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:High
Market Differentiation
- Factor:
Leadership in Clean Energy Transition
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Operational Reliability & Grid Resilience
Strength:Moderate
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Customer Service & Digital Engagement Tools
Strength:Moderate
Sustainability:Temporary
- Factor:
Economic Development Partnerships
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
Value Proposition
To provide safe, reliable, and affordable energy solutions while actively leading the transition to a sustainable, clean energy future for the communities we serve.
Excellent
Key Benefits
- Benefit:
Reliable Energy Supply
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Common
Proof Elements
Ongoing grid modernization investments.
Public outage maps and restoration information.
- Benefit:
Affordable and Predictable Costs
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Common
Proof Elements
Regulated rates approved by public commissions.
Budget billing and payment assistance programs.
- Benefit:
Transition to Clean Energy
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
Public commitment to 'Clean Energy Blueprint' with specific goals.
Tangible investments in large-scale solar, wind, and battery storage projects.
- Benefit:
Tools to Manage and Save Energy
Importance:Nice-to-have
Differentiation:Common
Proof Elements
Online home energy assessments.
Personalized tips and rebate finders on the website.
Unique Selling Points
- Usp:
The 'Clean Energy Blueprint' - a comprehensive, long-term strategic plan for decarbonization, including retiring coal plants and adding significant solar and storage capacity.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
Proactive economic development partnerships, such as supporting the infrastructure for large-scale data centers.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Moderate
Customer Problems Solved
- Problem:
Need for a constant, reliable source of power for daily life and business operations.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Desire for predictable energy expenses to manage household or business budgets.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
- Problem:
Growing desire by consumers and businesses to reduce their carbon footprint.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
Value Alignment Assessment
High
The value proposition is highly aligned with the macro trends of decarbonization, electrification, and the need for a more resilient grid.
High
The proposition directly addresses the core needs of all customer segments for reliability and affordability, while also meeting the growing demand for sustainability and control over energy use.
Strategic Assessment
Business Model Canvas
Key Partners
- •
State Regulators (Iowa Utilities Board, Public Service Commission of Wisconsin).
- •
Renewable Energy Developers and Equipment Manufacturers (e.g., Vestas, First Solar).
- •
Grid Technology Providers (e.g., Siemens, Schneider Electric).
- •
Local Communities and Governments.
- •
Large industrial partners and data centers (e.g., QTS).
Key Activities
- •
Electric Power Generation & Natural Gas Distribution.
- •
Transmission and Distribution Grid Maintenance & Modernization.
- •
Regulatory Compliance and Rate Case Management.
- •
Execution of large-scale capital investment projects (e.g., solar farms, battery storage).
- •
Customer Service and Billing.
Key Resources
- •
Generation Assets (Power Plants: natural gas, solar, wind, legacy coal).
- •
Extensive Transmission and Distribution Infrastructure (the 'Grid').
- •
State-issued utility franchises and operating licenses.
- •
Skilled workforce of engineers, technicians, and line workers.
- •
Strong balance sheet and access to capital markets.
Cost Structure
- •
Capital Expenditures (CapEx) for infrastructure construction and upgrades.
- •
Fuel and Purchased Power Costs.
- •
Operational & Maintenance (O&M) Expenses.
- •
Depreciation of Assets.
- •
Financing Costs (Interest on Debt).
Swot Analysis
Strengths
- •
Regulated monopoly status provides a stable, predictable revenue stream and reduced direct competition.
- •
Clear strategic vision for clean energy transition ('Clean Energy Blueprint') provides a roadmap for future investment and growth.
- •
Strong financial position with confirmed earnings guidance and a long-term growth target.
- •
Constructive regulatory relationships that enable significant capital investment and rate base growth.
Weaknesses
- •
Business model is capital-intensive with heavy reliance on long-term assets and debt financing.
- •
Pace of innovation and adaptation can be slowed by the regulatory approval process.
- •
Legacy portfolio includes coal-fired generation assets that must be retired, incurring decommissioning costs.
Opportunities
- •
Lead the build-out of EV charging infrastructure in the service territory.
- •
Leverage federal incentives like the Inflation Reduction Act to accelerate renewable energy projects and transfer tax credits.
- •
Attract new, large-load customers like data centers and advanced manufacturing through green energy offerings.
- •
Modernize the grid to create a 'smart grid' platform that can manage two-way power flows and enable new services.
Threats
- •
Changes in regulatory frameworks or unfavorable rate case outcomes could negatively impact financial performance.
- •
Increasing frequency of extreme weather events threatens grid infrastructure and reliability.
- •
Technological disruption from distributed energy resources (DERs) could erode the traditional centralized utility model.
- •
Rising interest rates increase the cost of capital for major infrastructure projects.
Recommendations
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Customer Digital Experience
Recommendation:Accelerate development of an integrated digital platform that provides granular energy usage data, personalized savings recommendations, and seamless enrollment in new programs (e.g., EV rates, demand response).
Expected Impact:Medium
- Area:
Grid Modernization
Recommendation:Increase investment in smart grid technologies, including advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and distribution automation, to improve operational efficiency and prepare the grid for high penetration of DERs.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Regulatory Strategy
Recommendation:Proactively engage with regulators to propose innovative rate designs and performance-based mechanisms that align utility incentives with decarbonization, efficiency, and customer satisfaction goals.
Expected Impact:High
Business Model Innovation
- •
Develop a 'Grid Services' platform to manage and orchestrate customer-owned assets (solar, batteries, EVs) and create a new revenue stream from providing grid stability services.
- •
Launch a non-regulated subsidiary focused on commercial and industrial decarbonization solutions, offering services like fleet electrification, on-site solar/storage, and energy management.
- •
Explore utility-scale green hydrogen production projects, leveraging renewable generation assets to supply future industrial and transportation needs.
Revenue Diversification
- •
Establish a subscription-based EV charging service for residential and commercial customers.
- •
Offer fee-based energy consulting and ESG advisory services to large C&I customers.
- •
Invest in community solar projects where the utility acts as the developer and manager, offering subscriptions to residential customers.
Alliant Energy represents a classic example of a mature, regulated utility successfully navigating a fundamental industry transformation. Its core business model, built on the century-old principle of a regulated monopoly providing safe and reliable power, remains robust and financially stable. This foundation is evidenced by its consistent earnings, strong capital investment plans, and a captive customer base across Iowa and Wisconsin.
The critical evolution underway is the strategic pivot from a traditional power generator to a modern, clean energy partner. This is not a superficial change but a deep-seated transformation driven by their 'Clean Energy Blueprint'. This strategy correctly identifies the primary threats and opportunities facing the industry: decarbonization, decentralization, and electrification. By proactively retiring coal assets and making substantial, regulator-approved investments in solar, wind, and battery storage, Alliant Energy is transforming its largest cost center (generation) into its primary growth engine. Each new renewable facility expands the company's rate base, upon which its future earnings are based, while also aligning with customer and investor ESG expectations.
The primary strategic challenge lies in evolving the revenue model beyond the simple sale of kilowatt-hours. The current model is inherently threatened by energy efficiency and customer-sited generation. Future success will depend on their ability to transition towards a service-oriented model, leveraging their grid infrastructure as a platform. Opportunities in managing a distributed grid, providing EV infrastructure, and offering tailored energy solutions to large industrial clients are paramount for long-term growth and relevance. Alliant's ability to innovate within the constraints of the regulatory framework will be the ultimate determinant of its success in this new energy landscape.
Competitors
Competitive Landscape
Mature
Oligopoly
Barriers To Entry
- Barrier:
High Capital Costs & Infrastructure
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Regulatory Approval & Franchises
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Economies of Scale
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Technical Expertise & Grid Management
Impact:Medium
Industry Trends
- Trend:
Decarbonization and Renewable Energy Transition
Impact On Business:Requires significant capital investment in solar, wind, and storage to meet clean energy goals and customer expectations. Creates opportunities for new revenue streams and improved public perception.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Grid Modernization and Resilience
Impact On Business:Investment in smart grids, advanced metering, and hardened infrastructure is necessary to accommodate distributed energy resources (DERs), improve reliability, and mitigate climate-related risks.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Electrification of Transportation and Buildings
Impact On Business:Creates significant new load growth and revenue opportunities (e.g., EV charging programs) but also requires grid upgrades to manage increased demand.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Rise of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Impact On Business:Customer-sited generation (rooftop solar) and storage challenges the traditional utility model, reducing energy sales and requiring new grid management strategies like Virtual Power Plants (VPPs).
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Focus on Customer Affordability and Experience
Impact On Business:Amid rising energy costs, utilities are under pressure to manage bills, improve digital self-service tools, and enhance communication to maintain customer satisfaction.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Agrivoltaics (Dual-use Land for Solar & Agriculture)
Impact On Business:An innovative approach to land use for solar development that can improve community acceptance, create partnerships with the agricultural sector, and align with sustainability goals, as seen with Alliant's award-winning project.
Timeline:Near-term
Direct Competitors
- →
MidAmerican Energy Company
Service Territory Focus:Primary investor-owned utility competitor in Iowa.
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Positions itself as a leader in renewable energy, having achieved 100% renewable energy equivalent for its Iowa customers. Emphasizes low rates and a net-zero emissions goal.
Strengths
- •
Strong renewable energy brand perception, particularly in wind energy.
- •
Aggressive investment in both wind and solar projects.
- •
Consistently ranks highest for residential customer satisfaction in the Midwest Large segment according to J.D. Power.
- •
Clear and marketable 'GreenAdvantage' program providing a tangible claim of 100% renewable energy for customers.
Weaknesses
Continued reliance on a significant coal fleet, despite renewable achievements, presents a target for environmental groups.
Faces public and regulatory pressure to accelerate coal plant retirements.
Differentiators
First-mover advantage and scale in wind generation.
Aggressive marketing of its 100% renewable energy achievement.
- →
WEC Energy Group (We Energies / Wisconsin Public Service)
Service Territory Focus:Primary investor-owned utility competitor in Wisconsin.
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Positions as a reliable energy provider investing heavily in a clean energy transition, aiming to eliminate coal and grow its renewable portfolio.
Strengths
- •
Significant planned investments in new solar, wind, and battery storage projects across Wisconsin.
- •
Strong track record of getting large-scale renewable projects approved by regulators.
- •
Diversified portfolio including natural gas, which it positions as a reliability bridge fuel.
- •
Parent company (WEC Energy Group) provides significant capital and resource advantages.
Weaknesses
Public messaging on clean energy is less consolidated than MidAmerican's.
Transition to natural gas as an interim step may draw criticism from groups advocating for a direct-to-renewables path.
Differentiators
Large-scale, multi-project renewable investment strategy announced in clear phases.
Joint ownership model with other utilities (like MGE) on projects can diversify risk and capital allocation.
- →
Xcel Energy (Northern States Power Company-Wisconsin)
Service Territory Focus:Operates in parts of western and northern Wisconsin.
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:Positions as a national leader in the clean energy transition with a vision to deliver 100% carbon-free electricity.
Strengths
- •
Strong national brand recognition for clean energy leadership.
- •
Extensive experience with various renewable technologies and grid management across a multi-state territory.
- •
Offers a wide range of customer programs for energy efficiency, EVs, and renewable choice.
- •
Proactive in areas of grid modernization and beneficial electrification.
Weaknesses
Service territory in Wisconsin is less contiguous and central than Alliant's or WEC's.
As a large national player, may be perceived as less locally-focused than Wisconsin-centric utilities.
Differentiators
Early and ambitious carbon-free electricity goals.
Comprehensive suite of customer-facing programs that promote electrification and energy management.
Indirect Competitors
- →
Rooftop Solar Installers (e.g., Eagle Point Solar, All Energy Solar)
Description:Companies that install residential, commercial, and agricultural solar panel systems, allowing customers to generate their own electricity, reducing their reliance on utility-provided power.
Threat Level:High
Potential For Direct Competition:N/A - They are a direct alternative to energy consumption from the utility, eroding the traditional sales base.
- →
Community Solar Providers
Description:Third-party developers or utility-sponsored programs that allow customers to subscribe to a portion of a local solar farm and receive credits on their electricity bill, offering a solar alternative without rooftop installation.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:High, as third-party providers can disintermediate the utility's relationship with the customer for energy generation. Alliant's own community solar program is a direct response to this competitive threat.
- →
Energy Efficiency & Smart Home Tech Companies (e.g., Google Nest, Ecobee)
Description:Technology companies providing smart thermostats, energy management platforms, and IoT devices that help customers reduce their overall energy consumption and manage their load, potentially shifting them to off-peak times.
Threat Level:Low
Potential For Direct Competition:Low. The primary threat is disintermediation of the customer relationship and a reduction in overall kWh sales. However, they also represent a partnership opportunity for demand response programs.
Competitive Advantage Analysis
Sustainable Advantages
- Advantage:
Regulated Monopoly Service Territory
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable due to significant regulatory and infrastructure barriers to entry. Alliant is the incumbent provider for all customers within its defined geographical areas.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Ownership of Transmission and Distribution Infrastructure
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. Owning the 'poles and wires' is a core, defensible asset of the utility business model that all energy providers must use.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Established Community Relationships and Brand Trust
Sustainability Assessment:Moderately sustainable. Long-standing presence in Iowa and Wisconsin communities builds trust, but this can be eroded by rate hikes, poor service, or negative public perception.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
Temporary Advantages
- Advantage:
Leadership in Agrivoltaics
Estimated Duration:2-4 years
Description:Receiving awards and pioneering research in agrivoltaics, as highlighted on their news page, provides a positive PR and innovation narrative that competitors are not currently matching.
Disadvantages
- Disadvantage:
Perception Lag in Renewable Energy vs. Competitors
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately
Description:Competitor MidAmerican Energy has successfully branded itself as providing '100% renewable energy' to its Iowa customers , setting a high bar for customer perception that Alliant may struggle to match in its messaging, even with significant renewable investments.
- Disadvantage:
Regulatory Constraints on Innovation
Impact:Major
Addressability:Difficult
Description:As a regulated utility, the ability to rapidly innovate, test new pricing models, or invest in emerging technologies is constrained by the need for approval from public service commissions, potentially slowing response to market disruptors.
- Disadvantage:
Customer Satisfaction Rankings
Impact:Minor
Addressability:Easily
Description:While not ranked poorly, Alliant Energy does not lead its peer group in customer satisfaction studies, where competitor MidAmerican Energy has consistently held the top spot in the Midwest Large segment.
Strategic Recommendations
Quick Wins
- Recommendation:
Launch a targeted digital marketing campaign highlighting Alliant's specific clean energy projects and their community impact.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
- Recommendation:
Prominently feature the 'Agrivoltaics' leadership story and other innovation awards on the website homepage and in customer communications to counter competitor narratives.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
- Recommendation:
Enhance the online EV and Home Energy Assessment tools with more personalized data and savings projections to improve user engagement.
Expected Impact:Low
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Medium Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Develop and aggressively market a branded green energy program, similar to MidAmerican's 'GreenAdvantage', to provide customers with a clear, marketable renewable energy story.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Expand the community solar program offerings and streamline the waitlist/signup process to capture customer interest and defend against third-party providers.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Establish formal partnerships with smart home technology companies to offer integrated demand response programs, providing customers with bill credits for smart device usage.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Long Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Invest in utility-scale battery storage to complement solar and wind assets, enhancing grid reliability and creating a new narrative around '24/7 clean energy'.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Develop an 'Energy as a Service' (EaaS) business model for large commercial and industrial customers, offering comprehensive energy management, DER integration, and sustainability consulting.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Shift positioning from a traditional, reliable utility to an innovative and community-focused energy partner. Leverage unique strengths like agrivoltaics leadership to build a distinct brand identity that is not just about being clean, but about being a smart and sustainable partner for the communities it serves.
Differentiate through 'Sustainable Innovation and Community Integration.' While competitors focus on the scale of their renewable generation, Alliant should focus on the quality and impact of its projects. This includes leading in dual-use land strategies (agrivoltaics), pioneering new storage technologies, and deeply integrating community solar programs to make clean energy accessible to all customers, not just homeowners.
Whitespace Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Become the leading utility for comprehensive EV owner support.
Competitive Gap:While competitors offer basic EV tools, none have established a dominant position in providing end-to-end support, including managed charging programs, EV-specific rate plans, and partnerships with charger installers and auto dealers.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Develop a Virtual Power Plant (VPP) platform.
Competitive Gap:Competitors are investing in renewable generation but are slower to adopt platforms that aggregate customer-sited resources like rooftop solar, batteries, and smart appliances to provide grid services. This is a key area of grid modernization.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Offer customized energy solutions for agricultural customers.
Competitive Gap:Building on its agrivoltaics success, Alliant can create tailored energy efficiency, renewable generation (e.g., digesters), and rate programs specifically for the large agricultural sector in its territory, a segment not explicitly targeted by competitors.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:Medium
Alliant Energy operates in a mature, highly-regulated oligopolistic market where direct competition is geographically limited to service territories in Iowa and Wisconsin. Its primary competitive pressures come not from other investor-owned utilities (IOUs) poaching customers, but from comparisons in regulatory proceedings, public perception, and the race to decarbonize. The most significant competitive threats are indirect, stemming from the rise of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) like rooftop solar, which erode traditional energy sales, and third-party community solar providers that can intercept the customer relationship.
Key direct competitors, MidAmerican Energy in Iowa and WEC Energy Group in Wisconsin, are formidable. MidAmerican has established a powerful brand identity around its '100% renewable' achievement, setting a high benchmark in customer messaging that Alliant currently struggles to match. WEC Energy Group is pursuing an aggressive, large-scale investment in clean energy projects, competing for both capital and the narrative of being Wisconsin's forward-looking utility. Both competitors are actively shaping customer and regulator expectations for the pace of the clean energy transition.
Alliant's core sustainable advantage is its entrenched position as a regulated monopoly with ownership of critical infrastructure. However, its competitive disadvantages lie in the perception and messaging space. It lacks a simple, powerful clean energy narrative like MidAmerican and faces the constant challenge of innovating within a restrictive regulatory framework. The company's website reflects a solid, traditional utility focusing on self-service, safety, and corporate news, but it could more effectively weaponize its genuine innovation stories, such as its leadership in agrivoltaics, to build a more distinct and forward-thinking brand.
The strategic imperative for Alliant Energy is to shift its competitive posture from a reliable-but-traditional utility to an innovative energy partner. This involves not only continuing its investment in clean energy but also wrapping that investment in a more compelling and differentiated narrative. Key opportunities exist in dominating the EV support ecosystem, pioneering VPPs to manage the modern grid, and leveraging its unique agrivoltaics experience to build deeper ties with the agricultural community. By focusing on smart, integrated, and community-centric solutions, Alliant can carve out a competitive identity that is distinct from the sheer scale of its competitors' renewable portfolios.
Messaging
Message Architecture
Key Messages
- Message:
Get personalized energy-saving tips today.
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage Hero Banner
- Message:
Get energy programs and offers, tailored for you.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage Body
- Message:
We deliver the energy solutions and exceptional service our customers and communities count on – safely, cost-effectively, efficiently and responsibly.
Prominence:Tertiary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Company Mission (Inferred across site)
- Message:
Is an electric vehicle right for you?
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage Body
- Message:
Alliant Energy is committed to community support and clean energy advancement.
Prominence:Tertiary
Clarity Score:Medium
Location:News Center (via headlines)
The message hierarchy is logical and effective for a residential customer. The most prominent messages focus on immediate, tangible benefits like saving money and getting personalized offers. Core transactional needs ('Pay Bill', 'Outages') are also given high visual priority. The broader corporate messages about clean energy and community support are appropriately placed in the news section, though they could be better integrated into the main customer journey.
Messaging is highly consistent across the provided pages. Core customer needs and safety topics are presented uniformly in 'Suggested Topics' sections. The focus on customer empowerment through tools and personalization is a consistent thread on the homepage.
Brand Voice
Voice Attributes
- Attribute:
Helpful
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Get personalized energy-saving tips today.
- •
Discover ways to save energy in your home...
- •
Get EV insights with our online tool.
- Attribute:
Conventional
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Alliant Energy announces second quarter 2025 results.
- •
U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)...
- •
Contact Media Relations.
- Attribute:
Straightforward
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Pay Bill
- •
Outages
- •
Start or Stop Service
- •
Call 811 Before You Dig
- Attribute:
Community-Oriented
Strength:Moderate
Examples
Communities receive over $530,000 from Alliant Energy...
Enjoy stories that illuminate and inspire.
Tone Analysis
Informational & Utilitarian
Secondary Tones
Promotional
Corporate
Tone Shifts
The tone shifts from customer-centric and helpful on the homepage to formal and corporate in the 'News Releases' section, which is appropriate for the respective audiences.
Voice Consistency Rating
Good
Consistency Issues
The voice is functionally consistent, but it lacks a strong, unifying brand personality. The 'illuminate and inspire' tagline for the blog feels slightly disconnected from the otherwise very direct and utilitarian tone of the main site.
Value Proposition Assessment
Alliant Energy is a reliable energy partner that provides safe, cost-effective energy while offering personalized tools and solutions to help customers save money and navigate the future of energy.
Value Proposition Components
- Component:
Cost Savings & Efficiency
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Common
- Component:
Personalized Tools & Programs
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
- Component:
Safety & Reliability
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Common
- Component:
Future-Readiness (EVs, Renewables)
Clarity:Somewhat Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
- Component:
Community Support
Clarity:Somewhat Clear
Uniqueness:Common
Differentiation comes primarily from the emphasis on proactive, personalized digital tools ('home energy assessment', 'offers tailored for you', 'EV insights'). While other utilities offer savings programs, Alliant's messaging frames these as customized solutions, which enhances their value. The focus isn't just on providing energy, but on providing energy intelligence to the customer.
As a regulated utility, direct competition for customers is low. However, messaging positions Alliant Energy favorably against the traditional utility stereotype. They are not just a power provider but a modern, helpful partner. This positioning is crucial for regulatory relationships and public perception, especially as they pursue clean energy initiatives like their 'Clean Energy Blueprint'.
Audience Messaging
Target Personas
- Persona:
Residential Customer (Homeowner)
Tailored Messages
- •
Get personalized energy-saving tips today.
- •
Answer a few questions and get a list of energy programs and offers that match your lifestyle.
- •
Is an electric vehicle right for you?
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Media / Investors
Tailored Messages
- •
Alliant Energy announces second quarter 2025 results.
- •
Contact Media Relations.
- •
Subscribe to RSS.
Effectiveness:Effective
Audience Pain Points Addressed
- •
High energy bills
- •
Complexity of managing energy usage
- •
Uncertainty about adopting new technologies like EVs
- •
Need for immediate help with bills or outages
Audience Aspirations Addressed
- •
Saving money
- •
Living a more sustainable lifestyle
- •
Making informed decisions about energy consumption
- •
Supporting a company that invests in the local community
Persuasion Elements
Emotional Appeals
- Appeal Type:
Financial Security
Effectiveness:High
Examples
Get personalized energy-saving tips today.
Payment Assistance Options
- Appeal Type:
Safety & Peace of Mind
Effectiveness:High
Examples
- •
Electric Safety
- •
Gas Safety
- •
How to Spot a Scam
- Appeal Type:
Community Pride
Effectiveness:Medium
Examples
Communities receive over $530,000 from Alliant Energy and Alliant Energy Foundation.
Social Proof Elements
- Proof Type:
Awards and Recognition
Impact:Moderate
Examples
Kegonsa Research Center named 2025 North American Agrivoltaics Dual-Use Plan of the Year.
- Proof Type:
Community Investment
Impact:Strong
Examples
News releases detailing specific grant amounts given to communities.
Trust Indicators
- •
Prominent safety information
- •
Clear contact information for media
- •
Publicly available financial results (NASDAQ: LNT)
- •
Information on payment assistance programs
Scarcity Urgency Tactics
No itemsCalls To Action
Primary Ctas
- Text:
Get started
Location:Homepage Hero Banner (Home energy assessment)
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Pay Bill
Location:Homepage Quick Links
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Try it now
Location:Homepage Body (Personalized programs)
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Read More
Location:News Center
Clarity:Clear
The CTAs are highly effective. They are clear, concise, use action-oriented language, and are placed logically where a user would expect to take the next step. The visual design of buttons makes them stand out and encourages clicks.
Messaging Gaps Analysis
Critical Gaps
There is no dedicated messaging for Business or Industrial customers in the provided content, which is a major audience segment for any utility.
The 'Why Alliant Energy?' is underdeveloped. The homepage lacks a strong, consolidated brand story that connects their clean energy projects and community support back to customer benefits.
Contradiction Points
No itemsUnderdeveloped Areas
- •
Storytelling: The positive stories in the News Center (community grants, renewable projects) are not leveraged on the homepage. They are presented as factual announcements rather than compelling narratives about the company's impact.
- •
Clean Energy Vision: The company has goals to be net-zero by 2050 and eliminate coal by 2040. This forward-looking vision is buried in news releases and corporate reports, not woven into the primary customer-facing message.
- •
Emotional Connection: The messaging is highly functional but lacks emotional resonance. It helps customers complete tasks but does little to build a deeper brand affinity or sense of shared purpose.
Messaging Quality
Strengths
- •
Clarity and Simplicity: The messaging is exceptionally clear and easy to understand, focusing on user tasks and benefits.
- •
Task-Oriented: The site effectively guides users to complete key actions like paying bills and finding savings.
- •
Personalization Focus: The recurring theme of 'personalized' and 'tailored' offerings is a strong differentiator.
- •
Effective CTAs: Calls-to-action are direct, prominent, and compelling.
Weaknesses
- •
Overly Transactional: The homepage feels more like a dashboard for existing customers than a destination to build brand preference.
- •
Lack of Brand Narrative: The broader story of Alliant Energy's purpose, innovation, and community impact is absent from the main customer touchpoint.
- •
Siloed Information: Positive news about renewable energy and community support is confined to the news section, missing an opportunity to strengthen the brand message on the homepage.
Opportunities
- •
Integrate the 'Clean Energy Blueprint' narrative into the homepage to showcase innovation and commitment to sustainability directly to customers.
- •
Create a dedicated 'Community Impact' section on the homepage that visually summarizes key achievements from the news releases.
- •
Develop a clear messaging track and value proposition for business customers, with a prominent entry point on the homepage.
Optimization Roadmap
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Homepage Narrative
Recommendation:Introduce a new homepage module titled 'Your Energy Future' that briefly explains the Clean Energy Blueprint, linking renewable projects to benefits like stable future costs and a healthier environment.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Audience Segmentation
Recommendation:Create a clear navigational path and value proposition for 'Business Customers' on the homepage, leading to a dedicated section with tailored messaging about reliability, economic development, and commercial energy solutions.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Brand Storytelling
Recommendation:Repurpose news center content into a more engaging 'Our Impact' section on the main site, using visuals and customer-centric language to tell stories about community grants and renewable energy milestones.
Expected Impact:Medium
Quick Wins
- •
Add a sub-headline to the hero banner that connects energy savings with environmental responsibility (e.g., 'Save money and support a cleaner future').
- •
On the homepage, add a small, visually engaging block with a key statistic from the News Center (e.g., '$530,000 to local communities') that links to the full story.
- •
Change the blog CTA from 'Enjoy stories that illuminate and inspire' to a more benefit-driven CTA like 'See how we're powering our communities'.
Long Term Recommendations
- •
Develop a comprehensive content strategy that moves beyond announcements to create human-interest stories about employees, community partners, and the tangible benefits of their clean energy transition.
- •
Invest in video content to showcase large-scale renewable projects and community initiatives, making the company's purpose more tangible and emotionally resonant.
- •
Conduct persona research for business customers to tailor messaging and digital tools specifically to their unique needs and pain points.
Alliant Energy's website messaging is exceptionally effective at fulfilling its primary, utilitarian function: serving the immediate needs of its existing residential customers. The communication is clear, the hierarchy is logical, and the calls-to-action are direct and compelling, focusing on tangible benefits like cost savings and personalized programs. This task-oriented approach builds trust through usability and helpfulness.
However, the messaging strategy reveals a significant missed opportunity in brand building and market positioning. The communication is fundamentally transactional, not relational. While Alliant Energy is actively pursuing a 'Clean Energy Blueprint' and investing significantly in communities, these powerful brand stories are siloed within the corporate news section. The primary customer-facing messaging lacks a compelling, overarching narrative that would differentiate the brand, build deeper emotional connection, and position Alliant Energy as a leader in the energy transition. The current messaging positions them as a competent 'power company' but fails to elevate them to an inspiring 'energy partner for the future'.
To drive measurable business outcomes beyond customer service transactions—such as improved public perception, stronger regulatory relationships, and enhanced brand affinity—Alliant Energy must bridge the gap between its corporate actions and its customer-facing narrative. Integrating the story of their clean energy vision and community impact directly into the main customer journey is the critical next step to evolving their brand from a simple utility provider to a purpose-driven industry leader.
Growth Readiness
Growth Foundation
Product Market Fit
Strong
Evidence
- •
Operates as a regulated monopoly in its service territories (Iowa and Wisconsin), ensuring a captive customer base for core electricity and gas services.
- •
Consistently growing customer volumes for both electric and natural gas.
- •
Actively developing and promoting new offerings like community solar, EV charging programs, and energy efficiency tools in response to evolving customer preferences and policy drivers for clean energy.
Improvement Areas
- •
Increase adoption rates of value-added services (e.g., home energy assessments, EV programs) to move beyond a commodity provider to a trusted energy advisor.
- •
Enhance the product-market fit for large industrial customers, particularly data centers, by offering tailored energy solutions and infrastructure support.
- •
Improve digital customer engagement tools to provide more personalized energy insights and program recommendations.
Market Dynamics
5-7% annual EPS growth target (company specific). Industry electricity demand projected to grow 9% by 2028, a significant shift from two decades of flat consumption.
Mature & Transforming
Market Trends
- Trend:
Explosive demand from data centers, AI, and onshoring of manufacturing.
Business Impact:Creates a massive, unprecedented growth opportunity for electricity sales and requires significant investment in new generation and grid infrastructure. Alliant projects a 9-10% electric sales growth CAGR from 2025-2030, driven by data centers.
- Trend:
Decarbonization and the clean energy transition.
Business Impact:Drives the core strategic initiative, the 'Clean Energy Blueprint,' necessitating large-scale capital investment in solar, wind, and battery storage, which expands the regulated rate base.
- Trend:
Electrification of transportation and buildings.
Business Impact:Represents a long-term, sustained driver of load growth. Requires investment in grid upgrades and customer-facing programs to support EV adoption.
- Trend:
Grid modernization and resilience.
Business Impact:Requires significant capital investment to create a more intelligent, resilient, and flexible grid capable of handling distributed energy resources (DERs) and intermittent renewables.
Excellent. Alliant Energy is capitalizing on the concurrent trends of decarbonization and surging electricity demand from new sources like data centers, creating a powerful tailwind for capital investment and growth.
Business Model Scalability
Medium
Very high fixed costs (generation plants, transmission and distribution infrastructure) with relatively low variable costs. Growth is achieved by investing in the fixed asset base (rate base).
High. Once infrastructure is in place, serving additional load or customers within the service area has high-profit potential, subject to regulatory rate structures.
Scalability Constraints
- •
Growth is highly capital-intensive, requiring massive, multi-billion dollar investment programs.
- •
All significant investments and rate changes are subject to regulatory review and approval by state public utility commissions, which can be a lengthy process.
- •
Geographically constrained to existing service territories in Iowa and Wisconsin.
- •
Physical constraints of the grid and supply chain limitations for key components like transformers can delay expansion.
Team Readiness
Strong. The leadership team has a clear, articulated strategy (the 'Clean Energy Blueprint') and has demonstrated the ability to execute large-scale capital plans and secure favorable regulatory outcomes.
Traditional, functional structure typical of a mature utility. Needs to continue developing more agile, cross-functional teams to accelerate the development and deployment of new customer-centric products and services.
Key Capability Gaps
- •
Advanced data analytics and digital product management to fully leverage smart meter data for customer segmentation and personalized offerings.
- •
Business development and partnership management for non-regulated or lightly-regulated growth areas like commercial EV fleet charging or Energy-as-a-Service.
- •
Talent acquisition and retention for specialized roles in grid modernization, cybersecurity, and renewable energy project management.
Growth Engine
Acquisition Channels
- Channel:
Website & Digital Presence (for Program Adoption)
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Implement a personalization engine to deliver targeted energy-saving tips, program offers, and EV suitability content based on customer usage data and demographics.
- Channel:
Direct Customer Communication (Bills, Email)
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Segment email campaigns to promote specific programs (e.g., community solar, demand response) to customers most likely to benefit, increasing relevancy and conversion.
- Channel:
Economic Development Teams (for Large C&I Customers)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Expand the mandate of economic development teams to proactively partner with site selectors and large corporations (especially data centers) to co-develop energy infrastructure solutions, making Alliant's territory a premier destination.
Customer Journey
The primary 'conversion' is not customer acquisition, but enrollment in voluntary programs (energy efficiency, green power, etc.). The path is primarily through the website or customer service calls.
Friction Points
- •
Lack of awareness of available value-added programs and services.
- •
Complex enrollment processes for certain programs.
- •
Value proposition for new services may not be immediately clear to all customer segments.
Journey Enhancement Priorities
{'area': 'Program Discovery', 'recommendation': "Create a centralized, interactive 'Solutions Hub' on the website where customers can easily explore and compare all available programs and rates based on their needs (e.g., 'I want to save money', 'I want to be greener', 'I'm buying an EV')."}
{'area': 'Digital Onboarding', 'recommendation': 'Simplify and digitize the enrollment process for all programs, enabling one-click sign-ups where possible and providing clear feedback on enrollment status.'}
Retention Mechanisms
- Mechanism:
Regulated Monopoly Status
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Focus on improving customer satisfaction and regulatory relationships to maintain the social license to operate and secure favorable rate case outcomes.
- Mechanism:
Value-Added Programs (e.g., Energy Efficiency)
Effectiveness:Moderate
Improvement Opportunity:Increase program participation to deepen customer relationships and position Alliant as a proactive energy partner, not just a commodity provider. This also serves as a grid resource.
Revenue Economics
Driven by regulated Return on Equity (ROE) on invested capital (the 'rate base'). Growth comes from increasing the rate base through prudent, regulator-approved investments.
Not Applicable. CAC is effectively zero for core services.
High, due to the regulated, recurring revenue model. Efficiency is measured by the ability to earn the authorized rate of return.
Optimization Recommendations
- •
Aggressively pursue rate base growth by accelerating capital expenditures in the Clean Energy Blueprint (renewables, storage, grid modernization). The company plans an $11.5 billion investment from 2025-2028.
- •
Promote 'beneficial electrification' (e.g., EVs, heat pumps) to sustainably grow electricity sales (kWh) and revenue within the existing customer base.
- •
Secure timely and constructive outcomes in regulatory rate cases to ensure cost recovery and a fair return on new investments.
Scale Barriers
Technical Limitations
- Limitation:
Grid Capacity & Interconnection Queues
Impact:High
Solution Approach:Invest heavily in transmission and distribution upgrades to accommodate new large loads (data centers) and integrate vast amounts of new renewable generation.
- Limitation:
Intermittency of Renewable Energy
Impact:Medium
Solution Approach:Invest in a balanced portfolio including battery storage, flexible natural gas generation, and demand response programs to ensure grid reliability as renewable penetration increases.
Operational Bottlenecks
- Bottleneck:
Regulatory Approval Timelines
Growth Impact:Acts as a governor on the speed of investment and growth.
Resolution Strategy:Maintain proactive and collaborative relationships with regulators in Iowa and Wisconsin. Pre-file and engage in stakeholder processes to build consensus and streamline approvals.
- Bottleneck:
Supply Chain for Critical Equipment
Growth Impact:Shortages of key components like transformers and solar panels can delay project timelines and increase costs.
Resolution Strategy:Implement strategic sourcing, diversify suppliers, and safe harbor equipment where possible to mitigate supply chain risk.
- Bottleneck:
Construction & Project Management Capacity
Growth Impact:The scale of the planned capital investment requires immense project execution capabilities.
Resolution Strategy:Develop strategic partnerships with EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) firms and invest in internal project management talent and systems.
Market Penetration Challenges
- Challenge:
Customer Inertia for New Programs
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Utilize data analytics to create highly targeted marketing campaigns. Simplify enrollment and clearly communicate the financial and non-financial benefits of participation.
- Challenge:
Competition from Third-Party DER Providers
Severity:Minor
Mitigation Strategy:Offer utility-owned solutions like community solar or battery lease programs that provide customers with the benefits of DERs without the upfront cost and maintenance hassle, while also growing the rate base.
Resource Limitations
Talent Gaps
- •
Data scientists and digital experience professionals
- •
Grid architects and engineers with expertise in DER integration
- •
Regulatory strategists with experience in performance-based ratemaking
Extremely high. The 2025-2028 capital plan is $11.5 billion, funded through a mix of cash from operations, debt, and equity.
Infrastructure Needs
- •
Upgraded high-voltage transmission lines to support new renewable hubs and data centers.
- •
A modernized distribution grid with advanced metering, sensors, and automated controls.
- •
Robust IT and cybersecurity infrastructure to manage a more complex, data-intensive grid.
Growth Opportunities
Market Expansion
- Expansion Vector:
Rate Base Growth via Clean Energy Investment
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:High
Recommended Approach:Fully execute and potentially accelerate the 'Clean Energy Blueprint' by investing in utility-scale solar, wind repowering, and battery storage projects. This is the primary driver of earnings growth.
- Expansion Vector:
Data Center and Industrial Load Growth
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:High
Recommended Approach:Market Alliant's service territories as prime locations for data centers, highlighting reliable service and a clear path to 100% renewable energy. Proactively invest in the required generation and transmission infrastructure to meet this +2.1 GW of new demand.
Product Opportunities
- Opportunity:
EV Charging Infrastructure & Services
Market Demand Evidence:Rapidly growing EV adoption is a major national trend.
Strategic Fit:High. Leverages existing infrastructure and customer relationships, promotes beneficial electrification, and creates new rate-basing opportunities.
Development Recommendation:Develop a comprehensive offering including residential charger rebates, time-of-use EV charging rates, and 'make-ready' infrastructure programs for public and commercial fleet charging depots.
- Opportunity:
Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS) for C&I Customers
Market Demand Evidence:Large corporations are increasingly looking to outsource energy management to meet sustainability goals and control costs.
Strategic Fit:Medium. Moves into a less-regulated space, but builds on core competencies in energy management and large project development.
Development Recommendation:Pilot an EaaS offering for a key industrial segment (e.g., manufacturing, food processing) that combines energy supply, efficiency retrofits, on-site generation (solar/storage), and energy management software into a single service contract.
Channel Diversification
- Channel:
Automotive Dealership Partnerships
Fit Assessment:High
Implementation Strategy:Create a partnership program that provides EV dealers with information and sign-up materials for Alliant's EV rates and home charger rebates, creating a seamless customer experience at the point of vehicle purchase.
- Channel:
Smart Home Technology Integrators
Fit Assessment:Medium
Implementation Strategy:Partner with companies like Google Nest or smart home installers to integrate Alliant's demand response and time-varying rate programs directly into their platforms, automating energy savings for customers.
Strategic Partnerships
- Partnership Type:
Large Technology/Data Center Companies
Potential Partners
- •
Google
- •
QTS
- •
Microsoft
- •
Amazon Web Services
Expected Benefits:Secure long-term energy supply agreements for massive new loads, co-invest in renewable generation, and drive significant economic development and sales growth in the service territory.
- Partnership Type:
Municipalities and Community Organizations
Potential Partners
City governments in the service territory
Local community action agencies
Expected Benefits:Co-develop community solar projects, roll out public EV charging infrastructure, and partner on energy assistance and weatherization programs to build stronger community ties and regulatory goodwill.
Growth Strategy
North Star Metric
Annual Growth in Rate Base ($)
For a regulated utility, sustainable earnings growth is directly tied to the size of the capital base on which it earns a regulated return. This metric aligns investment in modernization, decarbonization, and customer needs with the primary driver of shareholder value.
Achieve an 11% compound annual growth rate in rate base through 2028, as per the company's strategic plan.
Growth Model
Capital-Led & Electrification-Driven Growth
Key Drivers
- •
Regulator-approved capital investment in clean energy and grid modernization.
- •
Organic load growth from economic development, especially data centers.
- •
Increased per-customer consumption through beneficial electrification (EVs, heat pumps).
A dual-pronged approach: 1) A highly disciplined, large-scale capital execution function focused on building new assets on time and on budget. 2) A customer-facing marketing and business development function focused on driving adoption of new electric technologies.
Prioritized Initiatives
- Initiative:
Execute the $11.5 Billion 'Data Center Growth' Capital Plan
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:2025-2028
First Steps:Secure final regulatory approvals for all planned projects. Finalize contracts with key equipment suppliers and EPC partners. Begin site preparation and construction.
- Initiative:
Launch a Comprehensive 'EV Everywhere' Program
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:12-18 Months
First Steps:File for regulatory approval of new EV-specific rates and rebate programs. Develop marketing partnerships with regional auto dealers. Launch a targeted awareness campaign to existing customers.
- Initiative:
Develop a 'Digital Energy Advisor' Platform
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:18-24 Months
First Steps:Invest in a customer data platform to consolidate usage and account information. Develop a pilot program with a small customer segment to test personalized energy insights and program recommendations via the web portal and mobile app.
Experimentation Plan
High Leverage Tests
{'test': 'Incentive Structures for Demand Response', 'hypothesis': 'A gamified, points-based incentive system will drive higher peak-hour energy reduction than a simple bill credit.'}
{'test': 'Messaging for Home Energy Assessments', 'hypothesis': "Messaging focused on 'home comfort and improved resale value' will have a higher conversion rate than messaging focused purely on 'dollar savings'."}
Track program enrollment rates, kWh sales growth from electrification, peak demand reduction (MW), customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), and regulatory metrics (e.g., authorized ROE vs. earned ROE).
Quarterly review of program performance metrics, with A/B tests on digital campaigns run on a continuous basis.
Growth Team
A centralized 'Energy Futures' or 'Strategic Growth' group that sits outside the core utility operations. This team should have distinct verticals for 1) Large Load Growth (Data Centers), 2) Electrification & New Products, and 3) Grid Modernization Strategy.
Key Roles
- •
Director of Strategic Growth
- •
Data Center Business Development Lead
- •
Product Manager, EV Solutions
- •
Regulatory Strategist, New Business Models
Invest in training for digital marketing and data analytics. Potentially acquire a small energy services or technology company to bring in new talent and capabilities. Foster a culture that allows for experimentation and managed risk-taking in developing new customer offerings.
Alliant Energy is exceptionally well-positioned for a period of sustained, high-growth, a rarity for a mature utility. The company's growth foundation is solid, with a monopoly over core services in constructive regulatory environments. Its primary growth engine is not traditional customer acquisition, but massive, regulator-approved capital investment into its rate base, which is the fundamental driver of earnings. The company's 'Clean Energy Blueprint' is the perfect strategic vehicle for this, allowing Alliant to invest billions in decarbonization—a priority for regulators, customers, and investors—thereby directly fueling growth.
The key differentiator transforming Alliant from a stable utility into a growth-oriented energy infrastructure company is the unprecedented surge in electricity demand from data centers within its service territory. This provides a clear, tangible driver for an $11.5 billion capital expenditure plan from 2025-2028, which underpins a projected 11% compound annual growth rate in its rate base. This is a powerful, de-risked growth story.
Key barriers are primarily executional and regulatory rather than competitive. The ability to manage large-scale construction projects on time and budget, navigate supply chains, and maintain positive regulatory relationships will be critical. The opportunity lies in leveraging this period of intense investment to evolve the business model. While executing on the core capital plan, Alliant must simultaneously build capabilities in customer-facing areas like EV services and digital energy management. These initiatives will create new revenue streams and, more importantly, transform the customer relationship from a passive, transactional one into an active, advisory partnership.
Strategic Recommendation:
- Execute Flawlessly: The highest priority is the disciplined execution of the $11.5 billion capital plan. This is the bedrock of the company's growth for the next five years.
- Become the Premier Data Center Partner: Double down on the economic development strategy to not just supply power to data centers, but to become a full-service energy infrastructure partner, differentiating on speed, reliability, and customized renewable solutions.
- Build the 'Utility of the Future' in Parallel: Dedicate a focused, empowered team—the 'Energy Futures' group—to aggressively develop and scale the next generation of customer-centric products, starting with a market-leading EV program. This ensures that once the current wave of capital investment crests, new avenues for growth are already mature.
Alliant Energy's challenge is not finding growth, but managing it. By maintaining executional discipline on its core investment plan while strategically building new customer-facing capabilities, the company can deliver industry-leading growth and redefine its role in the clean energy transition.
Legal Compliance
Upon live review of the website, a 'Privacy Policy' link is readily accessible in the footer. The policy is comprehensive, outlining the types of personal information collected (e.g., account information, website usage data, location information), the purposes for collection (e.g., providing service, billing, marketing), and with whom it is shared (e.g., service providers, legal authorities). It includes specific sections for residents of states with privacy laws, demonstrating an awareness of its obligations. The policy clearly identifies Alliant Energy as the data controller and provides contact information for privacy-related inquiries. However, the language could be simplified for greater public readability, as it currently uses legalistic phrasing that may be challenging for the average consumer.
A 'Terms of Use' document is accessible via a link in the website footer. The terms are clearly structured and cover standard topics such as intellectual property rights, acceptable use of the website, disclaimers of warranties, and limitations of liability. It also includes a clause regarding forward-looking statements, which is a crucial disclosure for a publicly-traded company (NASDAQ: LNT). The enforceability of these terms is standard for online agreements. The clarity is adequate for legal purposes, though like the privacy policy, it could benefit from a plain-language summary to improve user comprehension.
The website implements a cookie consent banner upon the first visit. The banner informs users about the use of cookies and provides 'Accept All' and 'Cookie Settings' options. This granular 'Cookie Settings' option is a strength, allowing users to opt-in to specific categories of cookies (e.g., Functional, Performance, Targeting) rather than forcing an all-or-nothing choice. Non-essential cookies do not appear to load before user interaction with the banner, which aligns with modern privacy standards. The mechanism is good, but lacks a prominent 'Reject All' button on the initial banner, requiring an extra click into settings to deny consent, which is a minor usability friction point but a common practice.
Alliant Energy's data protection posture is shaped by both consumer privacy laws and stringent industry regulations. The company operates in Iowa and Wisconsin, making it subject to emerging state-level privacy legislation. Notably, the Iowa Consumer Data Protection Act (ICDPA) takes effect on January 1, 2025. Given Alliant Energy serves approximately 1 million electric customers, it easily surpasses the ICDPA's applicability threshold of controlling data for 100,000+ Iowa consumers. The website's privacy policy appears to be preparing for these requirements by outlining consumer rights. As a critical infrastructure entity, the company is also subject to NERC CIP (Critical Infrastructure Protection) standards, which mandate robust cybersecurity measures to protect the Bulk Electric System (BES) and associated data, including BES Cyber System Information (BCSI). While NERC CIP primarily governs operational systems, its security principles heavily influence the protection of all company data, including customer information stored in corporate systems.
A high-level assessment of the website suggests a reasonable effort towards accessibility. The site uses clear headings, legible fonts, and adequate color contrast. Navigation is structured logically. Contact phone numbers are provided, which is a basic accessibility feature. However, a dedicated 'Accessibility' statement or link outlining commitment to standards like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) or Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) was not immediately apparent in the main footer. Without a formal statement or a full audit, it is difficult to assess full compliance with WCAG 2.1 AA standards. For instance, information about TTY/TDD services for the hearing impaired was not prominently displayed.
As a regulated public utility, Alliant Energy's legal positioning is fundamentally defined by industry-specific regulations. The company is primarily regulated by the Iowa Utilities Board (IUB) and the Public Service Commission of Wisconsin (PSCW). These state agencies oversee rates, service quality, and major infrastructure projects, and their rules dictate many of the website's necessary disclosures, such as information on payment assistance, safety procedures ('Call 811 Before You Dig'), and outage reporting. At the federal level, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) regulates interstate electricity transmission. Furthermore, compliance with NERC CIP standards for cybersecurity is mandatory and a critical risk area. The website's strong emphasis on safety and customer service programs (e.g., payment assistance) reflects a strategic effort to align with the public interest mandates of its state regulators.
Compliance Gaps
- •
The cookie consent banner lacks a one-click 'Reject All' option on the initial display.
- •
No easily discoverable, dedicated 'Accessibility Statement' in the website footer detailing commitment to ADA/WCAG standards.
- •
The privacy policy and terms of use are legally dense and could be supplemented with plain-language summaries to enhance customer trust and understanding.
- •
Forward-looking statement disclaimers are present in SEC filings but should be explicitly linked or referenced in the news/press release section where earnings are announced to fully align with safe harbor best practices.
Compliance Strengths
- •
Maintains comprehensive and easily accessible Privacy Policy and Terms of Use documents.
- •
Prominently features critical, regulator-mandated safety information (electric, gas, digging safety).
- •
Provides a granular cookie consent mechanism allowing users to select specific cookie categories.
- •
The privacy policy shows proactive awareness of forthcoming state-level regulations like the Iowa Consumer Data Protection Act.
- •
Website content clearly supports customer service mandates from state utility commissions, such as payment assistance programs.
Risk Assessment
- Risk Area:
Regulatory Non-Compliance (State PUCs)
Severity:High
Recommendation:Continuously audit website content to ensure all disclosures, forms, and customer information required by the IUB and PSCW are current and easily accessible. Failure to comply can lead to fines and mandated corrective actions.
- Risk Area:
Data Privacy Violation (ICDPA/State Laws)
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Operationalize the consumer rights outlined in the privacy policy to ensure timely and accurate responses to data access/deletion requests under the ICDPA by the January 1, 2025 deadline. Failure to do so could result in enforcement actions by the Iowa Attorney General.
- Risk Area:
Accessibility Litigation (ADA/WCAG)
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Conduct a formal WCAG 2.1 AA audit of the website and digital properties. Publish an 'Accessibility Statement' outlining the company's commitment and providing a channel for users with disabilities to report issues. This mitigates the growing risk of demand letters and litigation.
- Risk Area:
Securities Law (Forward-Looking Statements)
Severity:Low
Recommendation:Ensure that all press releases in the 'News Center' that contain financial projections or forward-looking information include a direct link to the full safe harbor statement. While a general Terms of Use disclaimer exists, direct and contemporaneous disclaimers are a stronger defense.
High Priority Recommendations
- •
Ensure all systems and internal processes are prepared to handle consumer data rights requests under the Iowa Consumer Data Protection Act before its January 1, 2025 effective date.
- •
Commission a third-party accessibility audit against WCAG 2.1 AA standards and create a public-facing Accessibility Statement to mitigate legal risk and improve usability for all customers.
- •
Review all customer-facing content and forms to confirm they meet the latest disclosure and service requirements set by the Iowa Utilities Board and the Public Service Commission of Wisconsin.
Alliant Energy's legal positioning reflects its status as a mature, publicly-traded, and heavily regulated utility. Its strategic focus is rightly on regulatory compliance and maintaining the trust of its captive customer base and state commissions (IUB and PSCW), rather than on aggressive market competition. The website's legal foundation—its Privacy Policy and Terms of Use—is solid and demonstrates awareness of emerging data privacy laws like the ICDPA. The prominent placement of safety and payment assistance information aligns directly with the public service mandates of its regulators. The company's compliance strengths lie in this alignment with its core industry obligations.
However, there are opportunities to transition from a reactive compliance posture to a more proactive legal-strategic one. The primary gaps are in digital user experience compliance, specifically concerning accessibility (ADA/WCAG) and cookie consent usability. While not immediate regulatory threats from the IUB or PSCW, these areas represent a growing source of litigation risk and impact public perception and customer trust. Addressing accessibility would not only mitigate legal risk but also reinforce the company's mission to serve all members of the communities it operates in. The most critical near-term priority is operational readiness for the ICDPA, as failure to comply by the 2025 deadline could lead to regulatory penalties. By addressing these digital compliance gaps, Alliant Energy can further solidify its position as a trusted, responsible, and legally resilient service provider.
Visual
Design System
Modern Corporate
Excellent
Advanced
User Experience
Navigation
Horizontal Top Navigation with Utility Bar
Intuitive
Excellent
Information Architecture
Logical
Clear
Light
Conversion Elements
- Element:
Key Task Buttons (Pay Bill, Outages, Start/Stop Service)
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:This is a best-in-class implementation for a utility website and requires no immediate improvement. The design directly serves the user's primary goals.
- Element:
'Sign into My Account' CTA
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:The high-contrast yellow button in the persistent top navigation bar is highly effective. No improvements are necessary.
- Element:
Content Section CTAs (e.g., 'Try it now', 'Get started')
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:The visual distinction between primary (white/yellow) and secondary (blue) CTAs is clear. Consider A/B testing copy to optimize for engagement (e.g., 'Find My Savings' instead of 'Get started').
- Element:
'Report an emergency' Link
Prominence:Low
Effectiveness:Somewhat effective
Improvement:In a crisis, this link's standard text styling could be missed. Recommend implementing a dynamic alert system where this CTA becomes a prominent, high-contrast button or banner during widespread service interruptions.
Assessment
Strengths
- Aspect:
Task-Oriented Homepage Design
Impact:High
Description:The homepage immediately presents the three most critical user tasks—Pay Bill, Outages, and Start/Stop Service—as prominent, clear, and interactive elements. This significantly reduces user friction for the majority of visitors and reflects a deep understanding of customer needs.
- Aspect:
Consistent and Trustworthy Brand Identity
Impact:High
Description:The visual design consistently uses a professional color palette (trustworthy blues, reassuring greens), clean typography, and high-quality, authentic imagery. This combination successfully projects an image of a reliable, modern, and customer-centric utility provider.
- Aspect:
Clear Information Hierarchy
Impact:Medium
Description:The site effectively uses size, color, and whitespace to guide the user's eye. From the main value proposition in the hero banner to the key tasks and secondary informational content, the user journey is logical and scannable, preventing cognitive overload.
Weaknesses
- Aspect:
Low-Prominence Emergency Reporting
Impact:Medium
Description:The 'Report an emergency' link, arguably one of the most critical functions during a crisis, is styled as a standard text link in the top utility bar. A user in a panicked state may struggle to locate it quickly, potentially increasing frustration and call center volume.
- Aspect:
Passive Content Headlines
Impact:Low
Description:Headlines for content sections like 'Alliant Energy in the News' are purely descriptive. They could be rewritten to be more engaging and user-centric (e.g., 'See How We're Powering Your Community') to encourage deeper site exploration.
- Aspect:
Dense Footer Layout
Impact:Low
Description:The footer contains a large number of links without strong visual grouping. For users who scroll to the bottom for specific information, this density can make scanning and locating the correct link more difficult than necessary.
Priority Recommendations
- Recommendation:
Implement Dynamic Emergency CTA
Effort Level:Medium
Impact Potential:High
Rationale:During a widespread outage or emergency, user anxiety is high. Modifying the 'Report an emergency' link to a prominent, high-contrast button or banner that activates based on system status will ensure immediate visibility, improve customer experience in a crisis, and potentially deflect non-critical calls.
- Recommendation:
Refine Footer Information Architecture
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Improve the scannability of the footer by grouping links into more defined categories with clear subheadings (e.g., 'For Your Home', 'About Us', 'Support'). This simple IA change will help users find information faster and reduce frustration.
- Recommendation:
Personalize Homepage Content Blocks
Effort Level:High
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:For logged-in users, dynamically change the homepage content blocks to be more relevant. For example, instead of a generic 'Get energy programs' block, show them a block specific to their eligibility or past interest. This increases engagement and the perceived value of having an online account.
Mobile Responsiveness
Excellent
The design adapts seamlessly across all major breakpoints. On mobile, the navigation collapses into an intuitive hamburger menu, and content blocks stack vertically in a logical order, maintaining hierarchy and readability.
Mobile Specific Issues
No itemsDesktop Specific Issues
No itemsThis analysis of Alliant Energy's website reveals a mature, well-executed digital presence that successfully balances brand expression with exceptional user experience. The design is strategically aligned with the needs of a utility customer base, prioritizing critical tasks and building trust through a clean, professional aesthetic.
1. Design System & Brand Identity:
The website employs a Modern Corporate design style that feels both trustworthy and current. The brand's identity is expressed consistently through a disciplined color palette, clear typography, and relatable imagery. The design system is clearly mature, with consistent component styling (buttons, links, content cards) that creates a cohesive and predictable user experience across different sections of the site. This consistency is crucial for a utility, as it builds user confidence and reinforces brand reliability.
2. Visual Hierarchy & Information Architecture:
The site's masterclass is its information architecture, particularly on the homepage. By elevating the three most common user tasks ('Pay Bill', 'Outages', 'Start or Stop Service') into a visually dominant, interactive panel, the design immediately addresses the primary intent of most visitors. This user-centric approach minimizes search time and demonstrates a clear understanding of customer priorities. The visual hierarchy throughout the rest of the page effectively guides users from primary tasks to secondary marketing messages (e.g., energy programs, EVs) without creating clutter. The cognitive load is kept remarkably light.
3. Navigation & User Flow:
Navigation is intuitive, utilizing a standard horizontal pattern that is familiar to users. The separation of primary navigation ('Account and Billing', 'Ways to Save') from utility links ('Help Center', 'Careers') is logical. The high-contrast 'Sign into My Account' button is perfectly placed and colored for maximum visibility, optimizing the flow for returning customers. User flows for key tasks are direct and unambiguous.
4. Mobile Responsiveness:
The cross-device experience is excellent. The site is fully responsive, with content and navigation adapting gracefully to smaller viewports. On mobile, key CTAs are prominent, text is readable, and interactive elements are well-spaced for touch targets. The experience feels intentionally designed for mobile, not simply adapted from desktop.
5. Conversion & CTAs:
Visual conversion elements are highly effective. Primary CTAs are impossible to miss, using color, placement, and clear language to drive action. The distinction between primary, secondary, and tertiary actions is clear, guiding the user without causing confusion. The single area for significant improvement is the low visibility of the 'Report an emergency' link, which could be a critical usability failure during a real crisis.
6. Visual Storytelling & Content:
Through its use of imagery—featuring diverse families and individuals in bright, comfortable homes, alongside forward-looking technology like EVs—the site tells a story of a modern energy partner that enables customers' lives. Content is presented in digestible, scannable chunks, respecting the user's time and attention. While the headline copy is sometimes purely functional, the overall presentation is engaging and reinforces the brand's positive positioning.
Discoverability
Market Visibility Assessment
Alliant Energy is positioned as a foundational, reliable energy provider within its Iowa and Wisconsin service territories. Digitally, they are strategically evolving this authority from a traditional utility to a forward-looking energy partner. This is evidenced by their focus on a "Clean Energy Blueprint" and significant investments in solar and renewable projects, which they actively promote. Their authority is strongest on core utility topics like safety, billing, and outages but is expanding into areas like EV adoption and energy efficiency, positioning themselves as a primary resource for customers navigating the energy transition.
As a regulated utility, Alliant Energy operates with a near-monopoly on energy delivery within its defined geographic areas, meaning traditional market share competition is minimal. However, they compete for influence and share of the energy conversation against alternative solutions like third-party solar installers and for public perception on policy and rates. Their digital visibility for branded and service-related terms (e.g., 'pay Alliant bill,' 'Alliant Energy outage') is inherently dominant. The strategic challenge lies in achieving top visibility for non-branded, advisory-focused searches such as 'Iowa solar panel incentives' or 'Wisconsin EV charging options' to capture customers early in their decision-making process.
Customer acquisition is geographically determined rather than competitively driven. Therefore, the digital potential is not in acquiring new customers from competitors but in efficiently onboarding new residents and businesses, and more importantly, driving adoption of voluntary, value-added programs. The website's emphasis on tools for energy assessments and EV insights indicates a strategy focused on deepening relationships with existing customers and increasing enrollment in programs that support grid stability and sustainability goals.
Alliant Energy's digital presence is correctly focused on its service areas in Iowa and Wisconsin. This is reflected in their news releases, which are filterable by state, and their promotion of local community solar projects. A significant opportunity exists to enhance geographic penetration through hyper-local content. This could include detailing the economic and environmental impact of specific renewable projects on local communities, providing localized guides for storm preparedness, and creating content for businesses in specific service corridors to support economic development.
The company demonstrates strong coverage of core utility functions (billing, safety, service) and has established a robust narrative around its commitment to renewable energy. Their "Clean Energy Blueprint" serves as a central pillar for content on solar, wind, and sustainability. They effectively cover topics like financial performance and community investment. The primary gap is in translating their high-level strategic initiatives (like grid modernization) into customer-centric educational content that explains the direct benefits of these investments, such as improved reliability and stable future costs.
Strategic Content Positioning
The website's content strongly serves the 'Service' and 'Loyalty' stages of the customer journey, with prominent links for bill payment, outage reporting, and account management. The push for energy efficiency tools and EV calculators addresses the 'Consideration' stage for specific energy-related decisions. However, the 'Awareness' stage is underserved. There is a strategic opportunity to create high-level educational content that captures users researching broad topics like home electrification, energy savings, or sustainability before they are even thinking about their utility's role.
While Alliant Energy publishes news about its innovative projects (e.g., agrivoltaics, energy storage), this content is largely presented as press releases. The opportunity is to elevate this into true thought leadership. This could involve creating in-depth analyses, white papers, or video interviews with their engineers on topics like 'The Future of the Midwest's Electric Grid,' 'Integrating Battery Storage at Scale,' or 'The Economic Impact of Utility-Scale Solar.' This would position them not just as a participant in the energy transition, but as a key architect of it.
Given the regulated market, the 'competition' is for mindshare. A key content gap is the lack of comprehensive, unbiased guides comparing different energy solutions from a customer's perspective. For example, creating a definitive 'Guide to Rooftop Solar vs. Community Solar in Iowa' could position Alliant as the trusted, neutral advisor, building significant brand equity and guiding customers toward solutions that integrate well with the grid. Another gap is content targeting businesses, highlighting the benefits of locating in Alliant's territory, such as stable rates, renewable energy options, and infrastructure reliability.
The brand messaging is highly consistent. The mission to deliver energy 'safely, cost-effectively, efficiently and responsibly' is reinforced through the website's structure and content. The homepage's focus on practical tools (energy assessments) and the newsroom's emphasis on community grants and renewable projects effectively support this narrative. The "Clean Energy Blueprint" provides a consistent, forward-looking theme that ties together their corporate actions and communications.
Digital Market Strategy
Market Expansion Opportunities
- •
Expand the brand's role from an energy provider to the central 'Electrification Partner' for its service area, creating definitive content hubs on transitioning to EVs, heat pumps, and electric appliances.
- •
Target economic development agencies and businesses looking to relocate by developing content that showcases the region's energy infrastructure, reliability, and access to renewable energy sources.
- •
Develop a B2B content strategy targeting large commercial and industrial customers with tailored information on specialized rates, energy efficiency programs, and sustainability partnerships.
Customer Acquisition Optimization
- •
Reframe from 'acquisition' to 'engagement and self-service adoption.' Optimize the user journey for new movers to streamline the 'Start Service' process, reducing administrative costs.
- •
Digitally market value-added programs (e.g., energy efficiency rebates, smart thermostat integration) to the existing customer base to increase participation, which helps manage overall grid demand and reduces long-term costs.
- •
Create and promote online tools that answer common, high-volume customer questions to reduce call center traffic and associated operational costs.
Brand Authority Initiatives
- •
Launch a 'Future of Energy' digital hub featuring expert interviews, project deep-dives, and forward-looking articles to establish thought leadership beyond standard press releases.
- •
Partner with Wisconsin and Iowa universities on co-authored research or webinars about the regional energy transition, leveraging third-party credibility.
- •
Create detailed, data-rich project showcases for major renewable energy installations, highlighting the technology, community benefits, and environmental impact to build public support and demonstrate expertise.
Competitive Positioning Improvements
- •
Position Alliant Energy as the trusted, long-term advisor in the face of a fragmented market of solar installers and energy startups by providing stable, reliable information.
- •
Proactively create content that frames the narrative around grid modernization, explaining how utility-scale renewables and infrastructure upgrades provide greater reliability and cost-effectiveness than uncoordinated, distributed resources alone.
- •
Develop a strong content shield around key topics like reliability, storm response, and economic impact to reinforce the unique value proposition that only a well-established utility can offer.
Business Impact Assessment
Market share for a utility is measured by influence and program adoption, not customer count. Success indicators include the percentage of customers enrolled in voluntary programs (e.g., green energy tariffs, demand response), the adoption rate of energy efficiency rebates, and website traffic to economic development sections from corporate IP addresses.
Key metrics center on digital engagement and cost reduction. These include the completion rate of the online 'Start/Stop Service' forms, usage rates of the online home energy assessment tool, and a measured decrease in call center volume for issues that can be resolved via website content or tools.
Authority can be measured by share of voice for key non-branded search terms ('Wisconsin renewable energy,' 'Iowa EV rebates'), backlinks from reputable academic, governmental, and news organizations, media mentions related to energy innovation, and engagement rates (downloads, time on page) with thought leadership content.
Success is benchmarked against other sources of energy information within the service territory. This includes tracking search result rankings for key advisory topics against solar installers and energy media outlets, analyzing social media sentiment analysis on topics like reliability and rates, and measuring the volume of direct vs. search traffic, indicating strong brand recall.
Strategic Recommendations
High Impact Initiatives
- Initiative:
Develop 'The Definitive Electrification Hub' for Iowa & Wisconsin
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Become the primary, trusted source for customers and businesses considering major investments in EVs, heat pumps, and other electric technologies, thereby guiding the future of regional energy consumption.
Success Metrics
- •
Organic search rankings for key electrification terms
- •
Traffic and engagement within the content hub
- •
Lead generation for EV charging programs and efficiency rebates
- •
Backlinks from local media and industry partners
- Initiative:
Launch a Hyper-Local Community Impact Portal
Business Impact:Medium
Market Opportunity:Increase transparency and build grassroots support for infrastructure projects by clearly communicating the local economic and environmental benefits, preempting potential opposition.
Success Metrics
- •
Geographically-targeted website traffic to project pages
- •
Positive local media mentions and social media sentiment
- •
Reduced timelines for project approvals
- •
Community engagement metrics (e.g., webinar attendance)
- Initiative:
Create a B2B Economic Development Content Program
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Attract new large-scale commercial and industrial customers to the service territory by proactively showcasing energy reliability, competitive rates, and access to renewables as a key business advantage.
Success Metrics
- •
Traffic from target industries and corporate domains
- •
Qualified leads passed to the economic development team
- •
Downloads of B2B-focused white papers and case studies
- •
Mentions in regional business publications
Transition Alliant Energy's digital market position from a 'dependable utility' to the 'essential partner in building a sustainable and prosperous future for Iowa and Wisconsin.' This strategy shifts the narrative from being a passive provider of a commodity to an active enabler of customer goals, community growth, and the regional energy transition. Every piece of content should answer not just 'what' we do, but 'why' it matters for our customers' wallets, their communities, and the environment.
Competitive Advantage Opportunities
- •
Leverage exclusive, system-level data to provide unique insights on energy usage trends and grid needs that no competitor can replicate.
- •
Utilize the direct, established relationship with nearly every home and business in the service area to become the default, most trusted source of energy information.
- •
Promote the long-term, regulated commitment to the community as a key differentiator against transient, purely commercial competitors, emphasizing reliability, accountability, and shared investment in the future.
Alliant Energy has successfully established a digital presence that serves its core function as a regulated utility while laying the groundwork for a more sophisticated strategic position. The current website is effective for existing customers, providing essential tools for account management, bill payment, and outage reporting. The company's communications, particularly around its 'Clean Energy Blueprint,' consistently reinforce a forward-looking strategy focused on sustainability and modernization.
However, the primary strategic opportunity lies in shifting the digital focus from broadcasting corporate actions to creating resonant, customer-centric value. As a regulated monopoly, Alliant Energy's competition is not for customers, but for influence, trust, and leadership in the broader energy conversation. The digital strategy must evolve from being a repository of information to becoming the definitive educational resource for energy decisions in its territory.
The key strategic imperative is to capture customers at the beginning of their decision-making journey for major energy-related investments, such as electric vehicles, solar panels, or home electrification. By creating comprehensive, authoritative content on these topics, Alliant can position itself as the indispensable partner, building immense brand equity and guiding the evolution of energy consumption in a way that benefits both the customer and the stability of the grid. This involves transforming their news of innovation into true thought leadership and leveraging their unique position of trust to provide guidance that transcends any single product or service. By focusing on market education and hyper-local community impact, Alliant Energy can solidify its role not just as a power company, but as a foundational pillar of the region's economic and environmental future.
Strategic Priorities
Strategic Priorities
- Title:
Establish Premier 'Energy Partner' Status for the Data Center Industry
Business Rationale:The analysis identifies an unprecedented surge in electricity demand from data centers (+2.1 GW) as the single largest growth driver, underpinning an $11.5B capital plan. Proactively becoming a full-service infrastructure partner, rather than a reactive power supplier, will capture maximum value and attract further investment to the region.
Strategic Impact:This initiative transforms Alliant from a regional utility into a critical infrastructure partner for the global technology industry. It de-risks a massive capital investment cycle by securing long-term demand, drives substantial rate base growth, and establishes a new core competency in serving high-intensity industrial clients.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in contracted MW from new data center customers (Target: 2.1 GW by 2030)
- •
Revenue growth from the commercial & industrial segment
- •
Reduction in the average time-to-power for new large load customers
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Market Expansion
- Title:
Launch a Comprehensive 'EV Ecosystem' Business Unit
Business Rationale:The analysis identifies a whitespace opportunity to become the leading utility for comprehensive EV support, as competitors have not yet established a dominant position. This initiative drives beneficial electrification, increases per-customer revenue, and creates a new, sticky customer relationship beyond the meter.
Strategic Impact:This transforms the business from a passive electricity provider into an active enabler of the transportation transition. It creates new revenue streams through managed charging programs and infrastructure services, while positioning the brand as a forward-thinking partner in customers' sustainability efforts.
Success Metrics
- •
Percentage of residential customers enrolled in EV-specific rates
- •
Number of commercial fleet charging depots enabled
- •
Revenue from EV charging services and infrastructure programs
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Revenue Model
- Title:
Redefine the Brand Narrative from 'Reliable Utility' to 'Sustainable Innovation Partner'
Business Rationale:Competitor analysis reveals a significant perception gap, with rivals like MidAmerican Energy successfully claiming the '100% renewable' narrative. Alliant must shift its brand positioning to counter this by highlighting its unique innovation stories (e.g., agrivoltaics, battery storage) and community integration, moving beyond generic reliability.
Strategic Impact:A stronger, differentiated brand narrative improves public and regulatory perception, which is critical for securing favorable outcomes in rate cases and project approvals. It transforms the brand from a commodity provider into a purpose-driven industry leader, building customer affinity and social license to operate.
Success Metrics
- •
Improved public perception and brand sentiment tracking scores
- •
Increase in positive media mentions related to innovation and sustainability
- •
Higher customer satisfaction scores in annual surveys (e.g., J.D. Power)
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Quick Win (0-3 months)
Category:Brand Strategy
- Title:
Develop and Monetize a Grid Services Platform for Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Business Rationale:The analysis identifies the rise of customer-owned generation (rooftop solar, batteries) as a primary threat to the traditional utility model. This initiative transforms the threat into an opportunity by creating a platform to manage, orchestrate, and monetize these assets for grid stability, creating a new service-based revenue stream.
Strategic Impact:This represents a fundamental business model pivot from a one-way energy seller to a two-way energy platform operator. It secures the utility's central role in a decentralized energy future, creates new revenue from grid services (like a Virtual Power Plant), and defers costly infrastructure upgrades.
Success Metrics
- •
Total MW of customer-owned assets enrolled in the platform
- •
Revenue generated from grid services provided by the DER portfolio
- •
Measured reduction in peak demand through demand response programs
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Long-term Vision (12+ months)
Category:Operations
- Title:
Pilot an 'Energy-as-a-Service' (EaaS) Model for High-Value Industrial Customers
Business Rationale:To diversify revenue beyond regulated sales, Alliant must explore new commercial models. An EaaS offering for large C&I customers—bundling energy supply, efficiency, on-site renewables, and management services into a single subscription—meets growing corporate demand for outsourced decarbonization solutions.
Strategic Impact:This initiative opens up a potentially non-regulated, higher-margin revenue stream and deepens relationships with the most valuable customer segment. It positions Alliant as a comprehensive decarbonization partner, defending against disintermediation and building a scalable business for the future.
Success Metrics
- •
Number of C&I customers enrolled in the pilot program
- •
Recurring revenue generated from EaaS contracts
- •
Customer-reported improvements in energy efficiency and sustainability metrics
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Long-term Vision (12+ months)
Category:Revenue Model
Alliant Energy must accelerate its transformation from a traditional regulated utility into a modern energy infrastructure and services company. The strategic focus is to flawlessly execute its massive capital investment plan driven by data center demand, while simultaneously building new, customer-centric business models in areas like EV services and grid management to ensure long-term, diversified growth.
The key competitive advantage to build is becoming the indispensable 'Energy Infrastructure Partner' for the region. This transcends simply owning the poles and wires by leveraging deep engineering expertise, regulatory skill, and community integration to deliver complex, large-scale energy solutions faster and more reliably than any competitor or new market entrant.
The primary growth catalyst is the unprecedented surge in electricity demand from the data center industry within the service territory, which provides a clear and immediate driver for an $11.5 billion, regulator-approved capital investment program and subsequent rate base growth.