eScore
evergy.comThe eScore is a comprehensive evaluation of a business's online presence and effectiveness. It analyzes multiple factors including digital presence, brand communication, conversion optimization, and competitive advantage.
Evergy's digital presence is highly effective for its core, task-oriented audience, demonstrating strong search intent alignment for transactional queries like bill payment and service initiation. The website's architecture is well-optimized for its defined local service areas in Kansas and Missouri, though its content authority is more functional than thought-leading in the broader energy conversation. The largest gap is in voice search optimization and creating deeper, educational content that captures users earlier in their informational journey.
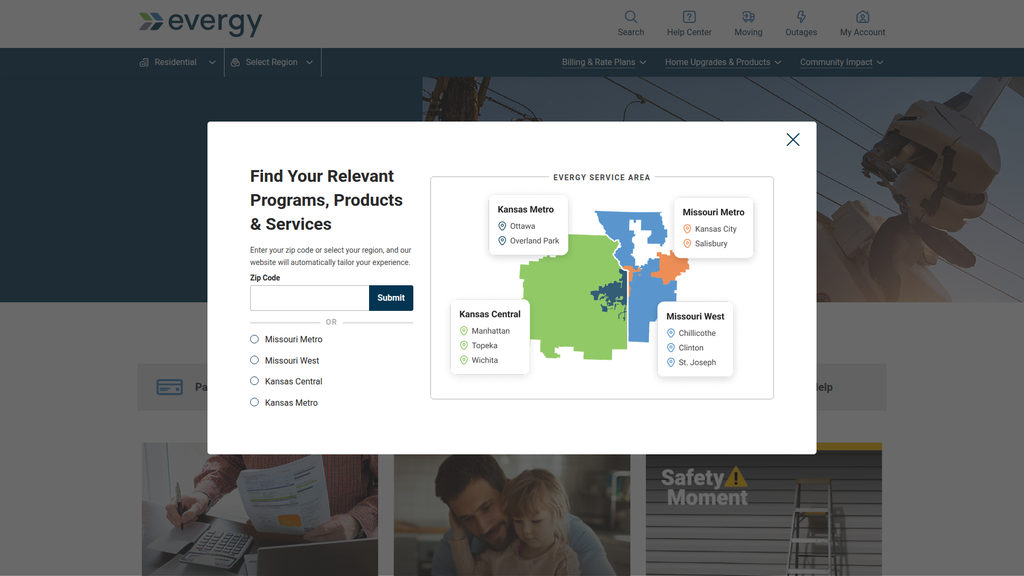
Excellent geographic targeting and tailoring of the user experience based on the customer's specific service location.
Develop a robust thought leadership content strategy around topics like home electrification and grid modernization to capture informational search traffic and build brand authority beyond basic service provision.
The brand messaging is exceptionally clear, consistent, and effective for guiding users through essential tasks, built on a strong foundation of 'Reliable, Affordable, Sustainable'. Communication is well-tailored for existing and prospective residential customers. However, the overall tone is overly functional and lacks a compelling emotional narrative that could build a deeper brand connection and humanize the utility for its 1.7 million customers.
The messaging hierarchy is highly effective, prioritizing core customer tasks ('Pay Bill', 'Report Outage') which aligns perfectly with the primary reasons for visiting the site.
Develop and integrate a cohesive brand story that weaves together reliability, sustainability, and community impact into an emotional narrative, using authentic employee and customer stories to build trust.
The site is designed around key conversions like 'Start Service' or 'Pay Bill', and these paths are generally clear. A significant strength is the robust commitment to accessibility (WCAG 2.1 AA), which expands market reach. However, the overall experience is hampered by a major friction point—an intrusive location-selection modal on the homepage—which damages the first impression and is especially disruptive on mobile devices.
A public commitment to WCAG 2.1 Level AA accessibility standards ensures the widest possible audience can complete critical tasks, mitigating legal risk and demonstrating social responsibility.
Immediately replace the intrusive homepage pop-up modal with a persistent banner or an integrated on-page element for location selection to eliminate the primary point of user friction.
As a regulated utility, Evergy's credibility is high, reinforced by a professional website that prioritizes safety information and financial assistance programs. The company demonstrates a mature legal and compliance posture, particularly regarding data privacy (CCPA/CPRA) and accessibility (ADA), which significantly mitigates risk. The primary weakness is a lack of social proof in the form of customer testimonials or detailed case studies to validate its service claims.
Strong, proactive compliance with state-level data privacy laws and a dedicated commitment to accessibility standards build significant trust and reduce legal exposure.
Incorporate customer testimonials and detailed case studies (e.g., a business benefiting from reliability, a family using energy efficiency programs) to humanize the brand and provide tangible proof of its value proposition.
Evergy's competitive advantage is exceptionally strong and sustainable, rooted in its status as a regulated monopoly with sole ownership of the transmission and distribution infrastructure in its service territory. This creates nearly insurmountable barriers to entry for direct competitors. The primary long-term threat comes not from direct competitors but from disruptive, indirect forces like customer-owned solar and battery storage, which could erode the traditional business model.
The regulated monopoly and ownership of the physical grid infrastructure provide a highly durable, long-term competitive moat that is nearly impossible for a competitor to replicate.
Accelerate the development of programs and rate structures that integrate customer-owned energy resources (solar, batteries, EVs) into grid operations, turning a potential competitive threat into a managed asset.
While geographically constrained, Evergy is positioned for significant growth in market depth due to the massive projected increase in electricity demand from data centers and the general electrification of transport and heating. The business model is designed to scale through large, regulated capital investments in its infrastructure to meet this demand. This growth, however, is entirely dependent on a slow and complex regulatory approval process for new generation and rate adjustments.
Positioned at the center of a generational demand increase for electricity, driven by data centers and electrification, providing a clear and massive opportunity for rate base growth.
Develop a dedicated 'Large Load Concierge' team to streamline the onboarding of major industrial customers like data centers, accelerating the process from inquiry to construction and revenue generation.
Evergy operates a classic and highly coherent regulated utility business model that is perfectly aligned with its market structure and stakeholder expectations. The strategy to invest heavily in grid modernization and cleaner energy sources to meet future demand is sound and timely. The model effectively aligns the interests of investors (through a regulated return on capital) and customers (through reliable service), with regulatory oversight acting as a crucial balancing mechanism.
The rate-base regulation model provides a stable and predictable framework for making the multi-billion dollar, long-term capital investments necessary to ensure grid reliability and transition to cleaner energy.
Proactively partner with regulators to pioneer performance-based ratemaking (PBR) to better align financial incentives with modern goals like energy efficiency and customer satisfaction, future-proofing the revenue model.
Evergy wields significant market power as the sole electricity provider for 1.7 million customers, giving it a near-100% market share and making it a critical engine for regional economic development. While its pricing power is controlled by regulators, its influence over the region's energy infrastructure, policy direction, and the pace of the clean energy transition is immense. This power is balanced by the critical need to maintain a positive relationship with regulators and the public.
As the sole provider of an essential service and owner of critical infrastructure, Evergy has substantial leverage and influence in shaping regional energy policy and attracting new industrial development.
Systematically leverage its market intelligence to create and publish an annual, forward-looking 'State of Energy' report for its region, solidifying its position as the definitive thought leader and trusted energy planner.
Business Overview
Business Classification
Regulated Electric Utility
Investor-Owned Utility (IOU)
Energy & Utilities
Sub Verticals
- •
Electricity Generation
- •
Power Transmission
- •
Electricity Distribution
Mature
Maturity Indicators
- •
Extensive and established infrastructure (power plants, transmission lines).
- •
Operates as a regional monopoly within a defined service area.
- •
Subject to long-standing, well-defined regulatory oversight (KCC, MPSC).
- •
Stable, predictable revenue streams based on rate cases and energy consumption.
- •
Focus on operational efficiency, grid modernization, and long-term sustainability initiatives.
Enterprise
Steady
Revenue Model
Primary Revenue Streams
- Stream Name:
Sale of Electricity (Regulated Tariffs)
Description:Core revenue from selling electricity (measured in kWh) to residential, commercial, and industrial customers at rates approved by state regulatory commissions (KCC and MPSC). Rates are structured to recover costs for generation, transmission, distribution, and a regulated return on investment.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Residential, Commercial & Industrial
Estimated Margin:Medium
- Stream Name:
Wholesale Electricity Sales
Description:Sales of excess generated power to other utilities and energy marketers in the wholesale market, facilitated through the Southwest Power Pool (SPP).
Estimated Importance:Secondary
Customer Segment:Other Utilities & Energy Marketers
Estimated Margin:Low
- Stream Name:
Transmission Services
Description:Providing other utilities access to its transmission infrastructure for a fee, with rates and terms regulated by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and managed by the SPP.
Estimated Importance:Tertiary
Customer Segment:Other Utilities
Estimated Margin:Medium
Recurring Revenue Components
- •
Monthly customer electricity bills
- •
Service availability charges
- •
Approved rate riders for specific investments (e.g., fuel adjustments, environmental upgrades)
Pricing Strategy
Rate-Base Regulation
Regulated/Mid-range
Semi-transparent
Pricing Psychology
Time-of-Use Rates: Encouraging off-peak consumption through differential pricing.
Budget Billing: Offering level payment plans to smooth out seasonal cost variations for customers.
Monetization Assessment
Strengths
- •
High predictability and stability of revenue due to regulated monopoly status.
- •
Guaranteed customer base of over 1.7 million within a defined service territory.
- •
Mechanism for cost recovery of prudent capital investments through regulatory rate cases.
Weaknesses
- •
Revenue growth is constrained by regulatory approval and regional economic growth.
- •
Complex and lengthy rate case proceedings create regulatory lag in cost recovery.
- •
Limited ability to dynamically price based on market conditions, unlike unregulated businesses.
Opportunities
- •
Develop and monetize non-regulated services (e.g., EV charging infrastructure, home energy management solutions, grid consulting).
- •
Rate design innovation to support electrification and distributed energy resources (DERs).
- •
Capitalize on federal incentives like the Inflation Reduction Act to fund renewable projects, potentially earning returns on new investments.
Threats
- •
Load defection from increased adoption of residential and commercial rooftop solar.
- •
Energy efficiency gains and demand-side management reducing overall kWh sales.
- •
Unfavorable regulatory decisions or rate case outcomes that disallow cost recovery.
Market Positioning
Regional Monopoly Focused on Reliability, Affordability, and Sustainable Energy Transition
Monopoly (Near 100% within its designated service territory in Kansas and Missouri)
Target Segments
- Segment Name:
Residential Customers
Description:Households and individuals within the service area requiring electricity for daily living. This is the largest segment by customer count (approx. 1.47 million).
Demographic Factors
Varying income levels
Urban, suburban, and rural locations across Kansas and Missouri
Psychographic Factors
- •
Value reliability and uninterrupted service.
- •
Increasingly concerned with affordability and predictable bills.
- •
Growing interest in environmental impact and renewable energy options.
Behavioral Factors
- •
Non-discretionary, essential service usage
- •
Seasonal consumption peaks (summer AC, winter heating)
- •
Growing adoption of smart home technology and electric vehicles.
Pain Points
- •
High or unpredictable energy bills
- •
Power outages, especially during severe weather
- •
Complexity in understanding rates and energy-saving programs
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:Medium
- Segment Name:
Commercial & Industrial (C&I) Customers
Description:Businesses, manufacturing facilities, schools, and government entities that are critical to the regional economy. This segment represents a significant portion of total energy sales.
Demographic Factors
- •
Small-to-medium businesses (SMBs)
- •
Large industrial manufacturing plants
- •
Data centers with high energy demand
Psychographic Factors
- •
Highly sensitive to energy costs as a major operational expense.
- •
Prioritize power quality and reliability to avoid business disruption.
- •
Driven by corporate sustainability goals (ESG) and desire for green energy solutions.
Behavioral Factors
- •
High and consistent energy consumption (load factor)
- •
Participation in demand-response programs
- •
Direct engagement with utility on complex energy needs and rate structures.
Pain Points
- •
Impact of electricity costs on global competitiveness
- •
Vulnerability of operations to power interruptions or fluctuations
- •
Meeting corporate renewable energy procurement targets
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:High
Market Differentiation
- Factor:
Regulated Monopoly Status
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Commitment to Sustainability & Clean Energy Transition
Strength:Moderate
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Operational Reliability & Grid Modernization
Strength:Moderate
Sustainability:Sustainable
Value Proposition
To provide reliable, affordable, and sustainable energy that empowers a better future for the communities we serve in Kansas and Missouri.
Excellent
Key Benefits
- Benefit:
Reliable & Uninterrupted Power Supply
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Common
Proof Elements
- •
Website hero banner: 'Committed to Reliability'
- •
Investments in grid modernization and hardening.
- •
Year-round preparation and dedicated lineworker teams.
- Benefit:
Affordable & Competitive Energy Costs
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Common
Proof Elements
- •
Website messaging: 'Passing savings on to you by cutting our costs'
- •
Information on financial assistance programs.
- •
Rate structures regulated by public commissions to ensure they are 'just and reasonable'.
- Benefit:
Sustainable & Cleaner Energy Generation
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
- •
Website messaging: 'Generating cleaner, more affordable and reliable power'
- •
Stated goal of net-zero carbon emissions by 2045.
- •
News highlighting monarch butterfly conservation and solar project approvals.
Unique Selling Points
- Usp:
Exclusive energy provider for a large, defined service area in Kansas and Missouri.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
A balanced and increasingly carbon-free energy generation portfolio, with a significant portion from wind and other renewables.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Moderate
Customer Problems Solved
- Problem:
Need for a constant, dependable source of electricity to power homes, businesses, and essential services.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Desire for energy costs to be predictable and reasonably priced.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
- Problem:
Societal and corporate demand for a transition to cleaner energy to mitigate environmental impact.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
Value Alignment Assessment
High
The value proposition directly addresses the foundational needs of a modern economy: reliable, affordable power. The added emphasis on sustainability aligns with major secular trends and regulatory pressures in the energy sector.
High
For all customer segments, reliability and affordability are paramount. The sustainability component strongly resonates with the C&I segment's ESG goals and a growing portion of the residential segment.
Strategic Assessment
Business Model Canvas
Key Partners
- •
State Regulatory Commissions (Kansas Corporation Commission, Missouri Public Service Commission).
- •
Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC).
- •
Southwest Power Pool (SPP).
- •
Fuel Suppliers (Natural Gas, Coal, Uranium).
- •
Renewable Energy Developers.
- •
Technology Vendors (Siemens, GE for grid infrastructure).
- •
Local Governments and Community Organizations.
Key Activities
- •
Electricity Generation from a diverse fuel mix (wind, solar, nuclear, gas, coal).
- •
Transmission & Distribution of electricity.
- •
Grid maintenance, modernization, and storm restoration.
- •
Regulatory compliance and rate case management.
- •
Customer service, billing, and support.
Key Resources
- •
Generation Assets (Power Plants).
- •
Transmission & Distribution Infrastructure (62,000+ miles of lines).
- •
Skilled Workforce (Engineers, Lineworkers, Technicians).
- •
Regulatory licenses to operate as a monopoly.
- •
Financial capital for large-scale infrastructure investments.
Cost Structure
- •
Capital Expenditures (CapEx) for new generation and grid modernization.
- •
Fuel and Purchased Power Costs.
- •
Operational & Maintenance (O&M) Expenses.
- •
Depreciation of Assets.
- •
Labor and Employee Benefits.
Swot Analysis
Strengths
- •
Entrenched monopoly position with a captive customer base ensures revenue stability.
- •
Diverse generation portfolio balances fuel cost volatility and reliability.
- •
Extensive, established transmission and distribution assets are a high barrier to entry.
- •
Constructive relationships with regulatory bodies, enabling recovery of investments.
Weaknesses
- •
High capital intensity requiring significant ongoing investment to maintain and upgrade aging infrastructure.
- •
Slow adaptation to market changes due to regulatory oversight and long planning cycles.
- •
Financial performance is highly dependent on outcomes of regulatory rate cases.
- •
Significant portion of generation still reliant on fossil fuels, posing transition risks.
Opportunities
- •
Lead the regional transition to renewable energy by investing heavily in solar and wind, funded via the rate base.
- •
Develop infrastructure and services to support mass electrification, especially for electric vehicles (EVs).
- •
Invest in grid modernization (smart meters, automation) to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enable new services.
- •
Surging electricity demand from new data centers and AI computing.
Threats
- •
Policy and regulatory shifts that favor decentralization or increased competition.
- •
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) like rooftop solar and battery storage reducing reliance on the central grid.
- •
Cybersecurity attacks targeting critical grid infrastructure.
- •
Increasing frequency of extreme weather events stressing grid reliability and increasing restoration costs.
Recommendations
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Digital Customer Experience
Recommendation:Expand digital self-service tools beyond bill payment to include proactive outage alerts, personalized energy usage insights, and seamless enrollment in new programs (e.g., EV rates, demand response).
Expected Impact:Medium
- Area:
Grid Modernization
Recommendation:Accelerate the deployment of Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) and grid automation technologies to improve operational efficiency, enhance reliability, and enable more sophisticated rate designs.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Regulatory Strategy
Recommendation:Proactively file for innovative rate structures and performance-based ratemaking mechanisms that decouple revenue from kWh sales, aligning utility incentives with energy efficiency and DER integration.
Expected Impact:High
Business Model Innovation
- •
Platform Orchestrator Model: Evolve from a simple electricity provider to a platform that manages and orchestrates a complex, decentralized grid. This includes managing customer-owned solar, batteries, and EV chargers to provide grid services.
- •
Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS): Develop non-regulated business lines offering comprehensive energy solutions to large C&I customers, including private solar installations, energy storage, and efficiency consulting.
- •
Infrastructure-as-a-Service: Leverage existing rights-of-way and infrastructure (e.g., utility poles, fiber optic lines) to support 5G network rollouts or community broadband initiatives through partnerships.
Revenue Diversification
- •
EV Charging Services: Build, own, and operate a network of public DC fast-charging stations, creating a new, non-regulated revenue stream.
- •
Fleet Electrification Services: Partner with commercial and municipal customers to plan, manage, and provide charging infrastructure for their vehicle fleets.
- •
Renewable Energy Credits (RECs): Monetize the RECs generated from owned renewable assets beyond what is needed for regulatory compliance by selling them on the open market.
Evergy operates a classic regulated electric utility business model, characterized by its mature, capital-intensive nature and stable, predictable revenues. Its core strength lies in its government-sanctioned monopoly over a defined service territory in Kansas and Missouri, which provides a captive customer base and a clear mechanism for recovering prudently incurred costs and earning a regulated rate of return. The company's value proposition of 'Affordable, Reliable, and Sustainable' energy is well-aligned with the fundamental needs of its residential and C&I customers and is clearly communicated.
The primary strategic challenge and opportunity for Evergy is the ongoing energy transition. The traditional model of centralized generation and one-way power flow is being disrupted by three key forces: decarbonization (the shift to renewables), decentralization (the rise of rooftop solar and battery storage), and digitalization (the need for a smarter, more responsive grid). Evergy's future success is contingent on its ability to evolve its business model to embrace these forces rather than resist them.
Key opportunities for business model evolution include moving beyond the simple sale of kilowatt-hours to become an integrated energy services platform. This involves investing heavily in grid modernization to support two-way power flows, developing new rate structures and programs that incentivize customer-sited resources like EVs and batteries, and potentially creating non-regulated business arms to capture growth in areas like public EV charging and corporate energy management. The company's 'Sustainability Transformation Plan' and investments in wind and solar are positive steps in this direction. However, this evolution is constrained by a regulatory framework designed for the 20th-century utility model. Proactive engagement with regulators to pioneer new performance-based ratemaking and revenue models will be critical to aligning Evergy's financial incentives with the future of energy. Failure to adapt risks revenue erosion from customer self-generation and being relegated to the role of a 'poles and wires' company, while more agile players capture value-added services.
Competitors
Competitive Landscape
Mature
Monopolistic
The electric utility industry is mature and highly regulated. Competition is not for residential or commercial customers within a service territory, but rather exists in the realms of capital markets, regulatory favorability, large-scale energy contracts, and the encroachment of alternative energy solutions.
Barriers To Entry
- Barrier:
High Capital Investment
Impact:High
Description:Enormous capital is required for generation facilities (power plants), transmission lines, and distribution networks. This makes it virtually impossible for new players to build competing infrastructure.
- Barrier:
Regulatory Framework and Franchises
Impact:High
Description:Utilities operate as regulated monopolies with exclusive service territories granted by state commissions (Kansas Corporation Commission and Missouri Public Service Commission). New entrants cannot legally compete for retail customers in these areas.
- Barrier:
Infrastructure Ownership
Impact:High
Description:Incumbents like Evergy own the entire 'last mile' infrastructure (poles and wires) to the customer, creating a natural monopoly.
- Barrier:
Technical Expertise and Operational Complexity
Impact:Medium
Description:Operating a stable and reliable power grid requires significant engineering and operational expertise developed over decades.
Industry Trends
- Trend:
Decarbonization and Clean Energy Transition
Impact On Business:High. Requires massive investment in renewables (solar, wind) and retirement of coal-fired plants, impacting capital planning and generation mix. Evergy aims for net-zero carbon emissions by 2045.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Electrification and Demand Growth
Impact On Business:High. Rising demand from data centers and electric vehicles (EVs) requires new generation capacity and grid modernization investments. Evergy projects needing thousands of MW of new generation in the coming years.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Grid Modernization and Resilience
Impact On Business:Medium. Investment in smart grids, advanced metering, and hardened infrastructure is necessary to improve reliability, manage distributed energy resources (DERs), and mitigate extreme weather events.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Impact On Business:Medium. The growth of rooftop solar and battery storage reduces energy sales and can introduce grid stability challenges, requiring new operational models and rate structures.
Timeline:Near-term
Direct Competitors
- →
Ameren Missouri
Service Territory:Central and Eastern Missouri, adjacent to Evergy's Missouri service area.
Target Audience Overlap:Low
Competitive Positioning:Positions as a reliable, forward-looking utility investing heavily in grid modernization and a balanced clean energy transition.
Strengths
- •
Aggressive and well-defined Integrated Resource Plan (IRP) with significant investments in renewables, natural gas, and battery storage.
- •
Proactive grid modernization efforts, including smart meter deployment and substation upgrades, enhancing reliability.
- •
Strong focus on attracting large business customers through infrastructure improvements.
Weaknesses
Faces similar pressures as Evergy regarding coal plant retirements and the need for significant capital to fund the clean energy transition.
Operates under the same Missouri Public Service Commission, facing similar regulatory pressures and scrutiny over rate increases.
Differentiators
Publicly details a multi-billion dollar grid modernization plan as a core part of its value proposition to attract business investment.
Has a clear, long-term plan that includes new nuclear generation, diversifying its future carbon-free portfolio.
- →
Kansas City Board of Public Utilities (BPU)
Service Territory:Kansas City, Kansas and Wyandotte County.
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Positions as a community-owned, not-for-profit utility providing low rates and reliable service.
Strengths
- •
As a municipal utility, it can sometimes offer lower or more stable rates by not having to generate profit for shareholders.
- •
Strong community focus and local governance structure.
- •
Offers net metering, making it attractive for customers considering rooftop solar.
Weaknesses
- •
Smaller scale and potentially fewer resources for large-scale capital projects compared to investor-owned Evergy.
- •
Faces public and political pressure regarding rate increases and operational decisions.
- •
Requires significant capital investment to maintain and upgrade its systems, similar to larger utilities.
Differentiators
Non-profit, publicly-owned model, which can appeal to customers on a cost and community basis.
Governed by an elected board, giving customers a direct line of influence not present with investor-owned utilities.
- →
Liberty Utilities (Empire District)
Service Territory:Parts of Southwest Missouri and Southeast Kansas.
Target Audience Overlap:Low
Competitive Positioning:Focuses on being a trusted local utility provider, often in smaller towns and rural areas, with a focus on safety and reliability.
Strengths
Part of the larger, diversified Algonquin Power & Utilities Corp., providing access to capital and expertise.
Operates in less dense service territories which can mean different regulatory and operational challenges.
Weaknesses
Smaller operational footprint in the region compared to Evergy and Ameren.
May lack the scale to invest in large-scale renewable generation projects independently.
Differentiators
Multi-utility focus (often providing water and natural gas in addition to electricity) in its broader corporate portfolio.
Indirect Competitors
- Name:
Rooftop Solar Installers
Examples:Sunrun, Tesla Energy, local/regional installers in KS & MO
Description:Provide homeowners and businesses the ability to generate their own electricity, reducing their reliance on and purchases from Evergy. This is often referred to as 'load defection'.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Low (in generation, not transmission/distribution)
- Name:
Energy Storage Solutions
Examples:Tesla Powerwall, Generac PWRcell, Enphase IQ Battery
Description:Enable customers to store energy (from the grid or solar panels) for use during peak hours or outages, further reducing grid dependence and potentially enabling 'islanding' from the grid.
Threat Level:Low
Potential For Direct Competition:Low
- Name:
Energy Efficiency & Management Companies
Examples:Honeywell, Siemens, numerous energy service companies (ESCOs)
Description:Offer solutions (smart thermostats, building management systems, energy audits) that help customers reduce their overall electricity consumption, thereby reducing Evergy's revenue.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Low
- Name:
Community Choice Aggregation (CCA)
Examples:Not yet prevalent in KS/MO, but a model in other states.
Description:Allow local governments to procure power on behalf of their residents, potentially from sources other than the incumbent utility. While Evergy would still provide transmission and distribution, they would lose the generation component of the service.
Threat Level:Low
Potential For Direct Competition:Medium (in generation supply)
Competitive Advantage Analysis
Sustainable Advantages
- Advantage:
Regulated Monopoly
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. The legal and regulatory framework grants exclusive rights to service a defined geographic area.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Ownership of Transmission & Distribution Infrastructure
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. The physical 'poles and wires' are a natural monopoly and prohibitively expensive for a competitor to duplicate.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Scale and Generation Capacity
Sustainability Assessment:Sustainable. Evergy's large, diverse portfolio of power plants provides operational scale and the ability to meet the demand of 1.7 million customers.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
Temporary Advantages
- Advantage:
Favorable Rate Cases
Estimated Duration:1-3 years (until the next rate case)
Description:A successful outcome in a rate case with the KCC or MPSC can provide a period of stable and predictable earnings.
- Advantage:
Leadership in Wind Energy
Estimated Duration:3-5 years
Description:Evergy has a significant amount of wind power in its portfolio, which aligns with current renewable energy goals and can be a cost advantage. However, competitors are also rapidly investing in wind and solar.
Disadvantages
- Disadvantage:
Reliance on Coal Generation
Impact:Major
Addressability:Difficult
Description:A significant portion of Evergy's generation comes from coal, which faces increasing environmental regulations, operational costs, and public pressure, requiring costly retirements and replacement.
- Disadvantage:
Challenging Regulatory Environments
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately
Description:Operating under two different state regulatory bodies (Kansas and Missouri) can be complex. Both states present regulatory challenges that can impact the timely recovery of investments and earnings.
- Disadvantage:
Negative Public Perception on Rates
Impact:Minor
Addressability:Moderately
Description:Like all utilities, Evergy faces public scrutiny over rate increases, which can influence regulatory decisions and brand sentiment.
Strategic Recommendations
Quick Wins
- Recommendation:
Enhance Digital Customer Engagement on Energy Efficiency
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
Description:Proactively communicate and simplify enrollment in energy-saving programs via the website and app. J.D. Power studies indicate that proactive communication about managing costs improves customer satisfaction.
- Recommendation:
Launch Targeted Marketing for EV Programs
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
Description:Create specific landing pages and programs for current and prospective EV owners, offering rate plan analyses, charging rebates, and location-based charger information to capture this growing demand segment.
Medium Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Develop Innovative Rate Designs for DERs
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Description:Work with regulators to create and pilot new rate structures (e.g., time-of-use, demand charges) that incentivize customers with solar and batteries to support grid stability, turning a potential threat into an asset.
- Recommendation:
Expand Utility-Owned Renewable Generation
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Description:Accelerate the development of utility-scale solar and battery storage projects within the service territory. This allows Evergy to control the generation, add it to the rate base, and meet decarbonization goals proactively.
Long Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Establish an 'Energy as a Service' (EaaS) Business Unit
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Description:Create a non-regulated or alternatively-regulated business arm that provides holistic energy solutions to large commercial and industrial customers, including managing DERs, EV fleets, and microgrids. This diversifies revenue beyond traditional kWh sales.
- Recommendation:
Invest in Grid-Scale Long-Duration Storage
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Description:As reliance on intermittent renewables grows, invest in emerging long-duration storage technologies (beyond Li-ion batteries) to ensure reliability and replace the function of retiring coal plants.
Shift positioning from a traditional 'power provider' to a 'holistic energy partner for a sustainable future.' Emphasize not just reliability and affordability, but also the company's role in enabling economic development, facilitating the clean energy transition for customers, and building a smarter, more resilient grid.
Differentiate through superior digital customer experience and by creating a platform for energy innovation. While competitors also focus on reliability, Evergy can lead in providing customers with intuitive tools to manage their energy use, connect their EVs and solar panels, and participate in new energy programs, making the grid transition feel seamless and beneficial to them.
Whitespace Opportunities
- Opportunity:
EV Fleet Management Services
Competitive Gap:Direct competitors are focused on individual EV owner programs, but few offer comprehensive charging infrastructure, management software, and optimized charging rate plans as a bundled service for commercial and municipal fleets.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Community Solar Program Expansion
Competitive Gap:While rooftop solar is growing, a large segment of the population (renters, apartment dwellers, those with unsuitable roofs) cannot participate. Expanding community solar programs allows Evergy to meet customer demand for renewables, own the generation asset, and provide access to a wider customer base.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:Medium
- Opportunity:
Residential Energy Storage Solutions
Competitive Gap:Indirect competitors sell batteries directly to consumers. Evergy could create a program to lease or finance home batteries, integrating them into a Virtual Power Plant (VPP) to provide grid services, creating a new revenue stream and enhancing grid stability.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
Evergy operates in a mature, monopolistic electric utility industry where traditional competition is non-existent within its regulated service territories in Kansas and Missouri. The competitive landscape is not defined by customer choice between providers, but by a complex interplay of regulatory oversight, capital investment strategy, operational efficiency, and the emergence of disruptive, non-traditional competitors.
Direct competitors, such as Ameren Missouri and the Kansas City BPU, operate in adjacent territories and compete primarily in the arenas of regulatory favorability and attracting large-scale economic development to their respective regions. Ameren Missouri appears particularly aggressive in its forward-looking Integrated Resource Plan and grid modernization efforts, setting a high benchmark for strategic planning.
The most significant competitive threat to Evergy comes from indirect and disruptive forces. The proliferation of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs), particularly rooftop solar and battery storage, represents a fundamental shift from the centralized utility model. These technologies allow customers to become producers, directly chipping away at Evergy's core business of selling kilowatt-hours. While the current threat level is moderate, the declining costs of these technologies pose a substantial long-term risk of 'load defection.'
Evergy's primary sustainable advantage is its ownership of the transmission and distribution infrastructure and its government-sanctioned monopoly. These are formidable barriers to entry. However, its competitive disadvantages, namely a significant reliance on legacy coal generation and navigating challenging dual-state regulations, create significant headwinds. The urgent need to decarbonize requires immense capital investment in renewables, which must be recovered through rates approved by regulators who are under public pressure to maintain affordability.
Strategic opportunities lie in transitioning the business model from a simple commodity provider to a sophisticated energy services platform. Whitespace exists in areas like managing EV fleets, expanding accessible community solar, and offering integrated home energy solutions that incorporate batteries. By embracing and integrating the technologies that threaten its traditional model, Evergy can create new revenue streams, enhance grid stability, and solidify its central role in the energy ecosystem of the future. The key to success will be proactive engagement with regulators to create frameworks that support these innovative investments, while effectively communicating the value of a modernized, clean, and reliable grid to its customers.
Messaging
Message Architecture
Key Messages
- Message:
Commitment to Reliability: We prepare year-round to provide dependable energy.
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage Hero Banner
- Message:
Affordable Energy: We pass savings on to you by cutting our costs.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage Value Proposition Section
- Message:
Sustainable Power: We are generating cleaner, more affordable and reliable power.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage Value Proposition Section
- Message:
Customer Assistance: We provide functional help for core tasks like payments, service changes, and outage reporting.
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage 'How can we help you today?' Section
- Message:
Community & Safety Focus: We are committed to safety, conservation, and appreciating our workers.
Prominence:Tertiary
Clarity Score:Medium
Location:Homepage Pods and News Section
The message hierarchy is exceptionally clear and effective for a utility. It correctly prioritizes the core customer need for reliability, followed immediately by easy access to transactional tasks (Pay Bill, Report Outage). The three brand pillars of 'Affordable,' 'Reliable,' and 'Sustainable' are given equal and prominent weight, forming a strong foundational message block.
Messaging is highly consistent across the provided content. The theme of reliability is introduced in the hero banner and reinforced in the value proposition section. The 'Start, Stop or Move' page maintains the same direct, functional, and helpful tone established on the homepage, ensuring a consistent user experience.
Brand Voice
Voice Attributes
- Attribute:
Dependable
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Committed to Reliability
- •
We prepare year-round.
- •
Reliability is a cornerstone of our operations
- Attribute:
Service-Oriented
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
How can we help you today?
- •
Pay My Bill
- •
Start, Stop or Move Your Energy Service
- Attribute:
Community-Minded
Strength:Moderate
Examples
- •
Evergy receives award for work with monarch butterfly conservation.
- •
Thank a lineworker
- •
Our lineworkers are committed to powering our communities.
- Attribute:
Straightforward
Strength:Strong
Examples
Enter your zip code or select your region...
Follow the options below.
Tone Analysis
Functional and Authoritative
Secondary Tones
- •
Reassuring
- •
Supportive
- •
Community-Focused
Tone Shifts
The tone shifts from highly functional ('Pay My Bill') to community-focused and appreciative in the 'Recent News' section ('Thank a lineworker').
It becomes encouraging and benefit-oriented in promotional pods like 'Paperless Benefits'.
Voice Consistency Rating
Excellent
Consistency Issues
No itemsValue Proposition Assessment
Evergy delivers reliable, affordable, and increasingly sustainable energy with a focus on customer service and community well-being.
Value Proposition Components
- Component:
Reliability
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Common
- Component:
Affordability
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Common
- Component:
Sustainability
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
- Component:
Customer Support (Financial Help)
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
As a regulated utility, Evergy operates in a market with limited direct competition. Differentiation is therefore less about customer acquisition from rivals and more about building public trust and regulatory goodwill. The primary differentiators are the emphasis on Sustainability and community-oriented initiatives (monarch conservation, lineworker appreciation). While 'Reliability' and 'Affordability' are table stakes for any utility, the explicit, top-level commitment to 'Sustainability' positions Evergy as a forward-thinking energy provider.
The messaging positions Evergy not as a competitor in a crowded market, but as a foundational, responsible partner to the communities it serves. The focus is on stewardship—of the grid, of customer finances, and of the environment. This positioning is appropriate for a modern utility aiming to maintain a positive public image and a strong relationship with regulatory bodies.
Audience Messaging
Target Personas
- Persona:
Existing Residential Customer
Tailored Messages
- •
Pay My Bill
- •
Report an Outage
- •
Financial Help
- •
Ways to save money
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Prospective/Moving Customer
Tailored Messages
- •
Start or Stop Service
- •
Moving within Evergy service areas...
- •
Start Service
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Community Stakeholder / Regulator
Tailored Messages
- •
Evergy receives award for work with monarch butterfly conservation.
- •
Evergy advances gas, solar projects with Kansas Corporation Commission approval.
- •
Sustainability Initiatives
Effectiveness:Somewhat Effective
Audience Pain Points Addressed
- •
Paying my bill easily
- •
Knowing what to do during an outage
- •
Managing the process of moving
- •
Concerns about high energy bills
- •
Needing financial assistance for utilities
Audience Aspirations Addressed
- •
Saving money on energy bills
- •
Supporting a company that cares about the environment
- •
Feeling safe around power lines
- •
Living in a well-supported community
Persuasion Elements
Emotional Appeals
- Appeal Type:
Peace of Mind / Security
Effectiveness:High
Examples
- •
Committed to Reliability
- •
We prepare year-round.
- •
Power Line Safety
- Appeal Type:
Relief / Support
Effectiveness:High
Examples
Financial Help
Funds available to assist with utility bills and more
- Appeal Type:
Community Pride / Goodwill
Effectiveness:Medium
Examples
Evergy receives award for work with monarch butterfly conservation.
Thank a lineworker
Social Proof Elements
- Proof Type:
Third-Party Validation / Awards
Impact:Moderate
Examples
Evergy receives award for work with monarch butterfly conservation.
- Proof Type:
Regulatory Approval
Impact:Moderate
Examples
Evergy advances gas, solar projects with Kansas Corporation Commission approval.
Trust Indicators
- •
Clear, upfront links to financial help
- •
Prominent safety information ('Power Line Safety')
- •
Transparent news updates on projects and regulatory approvals
- •
Direct and functional navigation for essential services
Scarcity Urgency Tactics
Not applicable for this business model, and appropriately absent from the messaging.
Calls To Action
Primary Ctas
- Text:
Pay My Bill
Location:Homepage 'How can we help you today?'
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Start or Stop Service
Location:Homepage 'How can we help you today?'
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Report an Outage
Location:Homepage 'How can we help you today?'
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Reliable Energy
Location:Homepage Hero Banner
Clarity:Somewhat Clear
The task-based CTAs are extremely effective. They are prominent, use simple action-oriented language, and address the most frequent reasons a customer visits a utility website. The more conceptual CTAs like 'Reliable Energy' or 'Sustainability Initiatives' are less direct but serve their purpose of guiding users to deeper content hubs. Overall effectiveness is very high.
Messaging Gaps Analysis
Critical Gaps
- •
Lack of a compelling, overarching brand narrative that ties together the themes of reliability, sustainability, and community.
- •
Minimal forward-looking messaging about innovation, such as smart grid technology, electric vehicle (EV) integration, or customer-facing energy management tools, beyond a few news items.
- •
Absence of customer stories or testimonials to humanize the brand and validate its claims of reliability and service.
Contradiction Points
No itemsUnderdeveloped Areas
The 'Sustainability' message is presented as a key pillar but lacks depth on the homepage. There's an opportunity to provide more compelling statistics or a clearer vision of the company's green energy future.
The 'Affordable' message could be strengthened with more specific proof points, such as comparisons to regional or national averages, or examples of cost-saving programs.
Messaging Quality
Strengths
- •
Exceptional Clarity: The website excels at making it easy for customers to complete core tasks.
- •
Strong Message Hierarchy: Key messages are prioritized logically and effectively.
- •
Solid Foundational Pillars: 'Affordable, Reliable, Sustainable' provides a clear and modern framework for the brand's value proposition.
- •
Consistent Voice: The dependable, service-oriented voice is maintained across different sections of the site.
Weaknesses
- •
Overly Functional: The messaging is highly transactional and lacks a strong emotional or narrative component to build a deeper brand connection.
- •
Lacks Aspirational Vision: The communication is focused on the present and past ('we are reliable') rather than painting a compelling picture of the future of energy for its customers.
- •
Generic Community Proof Points: While positive, the news items feel like a checklist of corporate responsibility rather than an integrated part of a genuine community story.
Opportunities
- •
Develop a Brand Story: Weave the individual elements (lineworkers, reliability, sustainability) into a cohesive narrative about 'powering a better future' for the communities served.
- •
Become an Energy Advisor: Position Evergy as a forward-thinking partner by creating content and tools that help customers navigate the future of energy (e.g., EV charger selection, home battery storage, smart appliance integration).
- •
Humanize the Brand: Feature authentic stories of employees and customers to add a layer of emotional connection and trust.
Optimization Roadmap
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Brand Storytelling
Recommendation:Develop a central brand narrative. For example: 'For over 100 years, we've powered Kansas and Missouri. Today, we're building a smarter, cleaner, and more reliable energy future, together.' Integrate this story throughout the site.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Sustainability Messaging
Recommendation:Elevate the 'Sustainability' pillar by adding a dynamic data point to the homepage (e.g., 'Powering your life with X% carbon-free energy today') and linking to a more visually engaging and forward-looking sustainability hub.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Social Proof
Recommendation:Incorporate a section with brief customer testimonials or case studies highlighting reliability, customer service experiences, or benefits from energy-saving programs.
Expected Impact:Medium
Quick Wins
- •
Change the 'Recent News' headline to a more narrative-driven title like 'Powering Our Communities' or 'Our Commitment in Action.'
- •
Add a sub-headline to the hero banner that connects reliability to a customer benefit, e.g., 'Committed to Reliability. Powering the moments that matter.'
- •
Make the 'Ways to save money' link more prominent and benefit-focused, such as 'See How You Can Save'.
Long Term Recommendations
- •
Create a dedicated 'Future of Energy' content section on the website to establish thought leadership around EVs, smart homes, and grid modernization.
- •
Invest in video content showcasing the work of lineworkers, engineers, and community partners to build a stronger emotional connection with the audience.
- •
Develop an integrated marketing campaign that moves beyond functional messaging to tell the brand's broader story of innovation, community, and sustainability.
Evergy's website messaging is a masterclass in functional clarity and effective information architecture for a utility provider. It flawlessly addresses the primary needs of its captive audience: paying bills, reporting outages, and managing service. The brand's voice is consistently dependable and service-oriented, which builds foundational trust. The strategic choice to highlight 'Reliability,' 'Affordability,' and 'Sustainability' as core pillars effectively positions Evergy as a modern, responsible utility.
The significant opportunity for Evergy lies in evolving its messaging from purely functional to strategically narrative. The current approach is transactional; it tells customers what Evergy does. To build deeper brand equity, the messaging must also tell them why it matters. There is a lack of a cohesive, compelling brand story that connects the dots between a reliable grid, environmental stewardship, and community vitality. While elements of this story exist—lineworker appreciation, conservation awards—they are presented as disparate facts rather than chapters in a larger narrative.
To elevate its market positioning from a mere utility to a trusted community partner and energy leader, Evergy should focus on two key areas. First, it must humanize its brand by showcasing the people behind the power and the customers it serves. Second, it must articulate a more ambitious and tangible vision for the future of energy in its region, positioning itself as an indispensable guide for customers navigating the transition to a more electrified and sustainable world. By wrapping its proven functional excellence in a more emotionally resonant and forward-looking narrative, Evergy can significantly enhance public perception, stakeholder engagement, and long-term brand loyalty.
Growth Readiness
Growth Foundation
Product Market Fit
Strong
Evidence
- •
Operates as a regulated monopoly in its designated service areas in Kansas and Missouri, ensuring a captive customer base for its core product: electricity.
- •
Electricity is an essential service, guaranteeing persistent demand irrespective of economic cycles.
- •
The company's value proposition of 'Affordability, Reliability, Sustainability' aligns with the primary expectations of both residential customers and regulators.
- •
Consistently executes on its business strategy, reporting a 7% increase in adjusted earnings per share in 2022.
Improvement Areas
- •
Enhance customer perception of value beyond basic service, focusing on energy efficiency programs, smart home integration, and EV charging solutions.
- •
Improve communication and transparency around rate increases and infrastructure investments to maintain regulatory and public support.
- •
Address criticisms regarding the pace of transition to renewable energy to better align with evolving customer and stakeholder expectations for sustainability.
Market Dynamics
Slow but accelerating; U.S. electricity demand is rising for the first time in decades, driven by data centers, onshoring, and electrification. Evergy specifically projects 2-3% annual demand growth, potentially rising to 4-5%.
Mature
Market Trends
- Trend:
Electrification of Everything
Business Impact:Significant long-term demand growth from EVs, heat pumps, and industrial processes. This represents the primary organic growth vector for utilities.
- Trend:
Massive Load Growth from Data Centers & AI
Business Impact:Unprecedented increase in demand from large industrial customers. Evergy has a 12.2 GW pipeline of large-load customers, with 1.1 GW already under construction.
- Trend:
Decarbonization and Energy Transition
Business Impact:Requires massive capital investment to transition from coal to renewables and natural gas, creating opportunities for rate base growth but also significant regulatory and execution risk.
- Trend:
Grid Modernization and Resiliency
Business Impact:Aging infrastructure necessitates significant investment in smart grids, automation, and hardening, which can be recovered through rates and improve reliability.
- Trend:
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Business Impact:Growth of rooftop solar and battery storage presents both a challenge to the traditional utility model and an opportunity to create new services for grid management.
Excellent. After years of flat demand, the confluence of electrification and new industrial load (data centers) creates a generational opportunity for growth in the utility sector.
Business Model Scalability
Medium
Extremely high fixed costs associated with generation plants and grid infrastructure. Scaling requires massive, lumpy capital expenditures, not incremental user acquisition costs.
High, but constrained by regulation. Once infrastructure is built, the cost of delivering an additional kilowatt-hour is low, but the rate of return on that infrastructure is capped by regulators.
Scalability Constraints
- •
Regulatory Approval Cycle: All major investments and rate changes must be approved by the Kansas Corporation Commission and Missouri Public Service Commission, a slow and uncertain process.
- •
Capital Intensity: Scaling generation and transmission requires billions in capital. Evergy plans a $17.5 billion investment from 2025-29.
- •
Long Lead Times: Planning, permitting, and constructing new power plants and transmission lines can take many years.
Team Readiness
Experienced in managing a regulated utility, focusing on operational execution, financial stability, and regulatory affairs. Appears capable of executing the current capital investment plan.
Traditional, hierarchical structure typical of a utility, optimized for reliability and operational efficiency rather than rapid innovation or agile growth.
Key Capability Gaps
- •
Innovative Product Development: Need for talent in developing and marketing new energy services (e.g., EV fleet management, demand response programs) to commercial and industrial customers.
- •
Big Data & Analytics: Deeper expertise required to leverage smart grid data for predictive maintenance, load forecasting, and personalized customer offerings.
- •
Partnership and M&A: Enhanced capabilities to forge complex partnerships with technology companies, EV manufacturers, and large industrial clients to co-develop energy solutions.
Growth Engine
Acquisition Channels
- Channel:
New Business Attraction (Economic Development)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Actively partner with state and local economic development agencies to attract energy-intensive industries (e.g., data centers, advanced manufacturing) to the service territory. Develop specialized 'large-load' tariffs and infrastructure plans to secure these major customers.
- Channel:
New Construction Hookups
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Partner with homebuilders to promote all-electric homes and pre-wire for EV charging, thereby locking in future electricity demand. Forecasts for the KC metro area show household growth of over 200,000 by 2050.
- Channel:
Electrification Conversion (e.g., Gas to Electric)
Effectiveness:Low
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Develop targeted marketing campaigns and rebates for converting from natural gas appliances (furnaces, water heaters) to electric heat pumps, especially in partnership with HVAC installers.
Customer Journey
The 'conversion' path is the mandatory process of starting, stopping, or moving service. The website provides a clear, functional path for these necessary transactions.
Friction Points
- •
Lack of proactive communication during outages (though improving with new tech).
- •
Complex billing for customers on time-of-use or demand rates.
- •
Limited self-service options for complex issues, requiring calls to customer service.
Journey Enhancement Priorities
{'area': 'Outage Communications', 'recommendation': 'Implement automated, personalized outage alerts via SMS/app with estimated restoration times and causes, leveraging grid automation data. J.D. Power studies show this significantly boosts satisfaction. '}
{'area': 'Digital Self-Service', 'recommendation': 'Expand the mobile app and web portal to include features like high-bill alerts, energy usage analytics and comparisons, and scheduling for service appointments.'}
Retention Mechanisms
- Mechanism:
Regulated Monopoly Status
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:This is a structural advantage. The focus should be on improving satisfaction to reduce regulatory pressure and public opposition to rate cases.
- Mechanism:
Customer Satisfaction Programs
Effectiveness:Moderate
Improvement Opportunity:Focus on key drivers of J.D. Power satisfaction scores: price, communication, and corporate citizenship. Proactively communicating infrastructure updates and cost-saving tips can mitigate dissatisfaction from rising bills.
- Mechanism:
Energy Efficiency Programs
Effectiveness:Moderate
Improvement Opportunity:Increase awareness and ease of enrollment for programs like smart thermostat rebates and home energy audits to build customer goodwill and help manage grid load.
Revenue Economics
Driven by the 'Rate Base' model. Profitability is a function of the approved rate of return on capital investments (power plants, grid infrastructure). Growth comes from prudently investing capital into the rate base.
Not Applicable. Customers are acquired through residency or business location in the service territory, not through marketing spend.
High (within regulatory constraints). As a monopoly, revenue is guaranteed on approved investments, but growth and profit margins are capped by regulators.
Optimization Recommendations
- •
Focus capital expenditures on projects with high likelihood of regulatory approval and recovery, such as grid modernization and new generation to meet certified demand.
- •
Aggressively manage operating and maintenance (O&M) costs to maximize the margin allowed under the approved rates.
- •
Develop new, non-regulated or performance-based revenue streams, such as fiber optic leasing on utility poles or EV charging services, where permissible.
Scale Barriers
Technical Limitations
- Limitation:
Aging Grid Infrastructure
Impact:High
Solution Approach:Continue the multi-billion dollar grid modernization program to replace aging components, deploy automation, and improve predictive maintenance, justifying costs through reliability improvements.
- Limitation:
Generation Capacity Shortfall
Impact:High
Solution Approach:Execute the Integrated Resource Plan (IRP) to build new generation (primarily natural gas and renewables) to meet forecasted load growth from data centers and electrification.
- Limitation:
Interconnection Queues for Renewables
Impact:Medium
Solution Approach:Streamline the process for connecting third-party and utility-owned renewable projects to the grid, and invest in transmission upgrades to unlock renewable energy zones.
Operational Bottlenecks
- Bottleneck:
Regulatory Approval Process
Growth Impact:The primary governor on growth speed. Delays in rate case approvals or IRP acceptance can stall multi-billion dollar projects.
Resolution Strategy:Maintain a sophisticated government and regulatory affairs team. Proactively engage with commissioners, staff, and public advocates to build consensus and justify investments.
- Bottleneck:
Supply Chain for Key Components
Growth Impact:Delays in acquiring transformers, switchgear, and renewable energy components can delay projects and increase costs.
Resolution Strategy:Diversify suppliers, explore strategic sourcing agreements, and improve long-range material forecasting tied to the capital investment plan.
- Bottleneck:
Workforce Shortages
Growth Impact:Lack of skilled lineworkers, engineers, and technicians can constrain the pace of infrastructure upgrades and new construction.
Resolution Strategy:Invest in apprenticeship programs, partner with local community colleges and technical schools, and develop robust career progression paths.
Market Penetration Challenges
- Challenge:
Public Opposition to Rate Increases
Severity:Critical
Mitigation Strategy:Justify rate increases with clear benefits to reliability and sustainability. Employ targeted communication campaigns to educate the public on the necessity of grid investments and rising energy costs.
- Challenge:
Competition from On-site Generation (DERs)
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Develop new rate structures that fairly compensate for grid services. Offer utility-owned rooftop solar or battery programs. Position the utility as the orchestrator of a DER-enabled grid rather than an opponent.
- Challenge:
Energy Efficiency Mandates
Severity:Minor
Mitigation Strategy:Frame energy efficiency not as a loss of sales, but as a low-cost 'virtual power plant' that reduces the need for expensive new generation, benefiting all customers. Embrace and lead efficiency programs.
Resource Limitations
Talent Gaps
- •
Data scientists for grid analytics
- •
Cybersecurity experts for grid security
- •
Project managers for large-scale renewable and gas plant construction
Extremely high. The $17.5B 5-year plan requires consistent access to capital markets (debt and equity) and a stable regulatory environment that allows for cost recovery.
Infrastructure Needs
- •
New high-voltage transmission lines to support new generation and improve reliability.
- •
A robust, utility-owned EV fast-charging network along key corridors.
- •
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) and supporting communications networks.
Growth Opportunities
Market Expansion
- Expansion Vector:
Deepen Electrification in Existing Territory
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:Medium
Recommended Approach:Launch a comprehensive 'Electrify Everything' initiative. Offer rebates, financing, and education for EV purchases, heat pump installations, and commercial fleet conversion. This is the core organic growth driver.
Product Opportunities
- Opportunity:
EV Charging as a Service (EVCaaS)
Market Demand Evidence:The Edison Electric Institute projects 26.4 million EVs on US roads by 2030, requiring 12.9 million chargers.
Strategic Fit:High
Development Recommendation:Develop turnkey solutions for businesses, multi-family dwellings, and municipalities. Offer to build, own, and operate charging infrastructure in exchange for a long-term service contract. This creates a new, potentially less-regulated revenue stream.
- Opportunity:
Grid Services for Large Customers
Market Demand Evidence:Increasing need from data centers for 100% reliable, carbon-free energy.
Strategic Fit:High
Development Recommendation:Create a consulting arm to help large customers develop sophisticated energy management strategies, including on-site solar, battery storage, and demand response programs that also benefit the grid.
- Opportunity:
Energy Storage Solutions
Market Demand Evidence:Need for grid stability increases as intermittent renewables like wind and solar are added. US battery storage M&A volume is rapidly increasing.
Strategic Fit:High
Development Recommendation:Invest in utility-scale battery storage projects to be included in the rate base. Pilot residential battery programs (like Green Mountain Power's) that provide backup power to customers while allowing the utility to use them for grid support.
Channel Diversification
- Channel:
Partnerships with Auto Dealerships & HVAC Installers
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Implementation Strategy:Create co-marketing programs and incentive schemes. Offer point-of-sale rebates on EVs and heat pumps, with seamless sign-up for special utility rates (e.g., time-of-use for EV charging).
Strategic Partnerships
- Partnership Type:
Technology & Data Center Co-development
Potential Partners
- •
Google
- •
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- •
Microsoft
Expected Benefits:Secure long-term power purchase agreements to underwrite new renewable energy projects. Co-invest in dedicated infrastructure to serve new data centers, ensuring their load growth is met with clean energy as they demand.
- Partnership Type:
Municipal Infrastructure Integration
Potential Partners
- •
Kansas City, MO
- •
Wichita, KS
- •
Topeka, KS
Expected Benefits:Partner with cities to build out public EV charging networks, electrify public transit fleets, and deploy smart city technologies (e.g., smart street lighting) on the utility's network.
Growth Strategy
North Star Metric
Weather-Normalized Retail MWh Sales
This metric directly measures the core growth driver: increasing electricity consumption within the service territory, independent of weather fluctuations. It captures the net effect of new customer load, electrification, and energy efficiency.
Achieve and sustain 3-4% year-over-year growth, exceeding the baseline 2% forecast.
Growth Model
Capital-Cycle & Electrification-Led Growth
Key Drivers
- •
Successful execution of the 5-year, $17.5B capital investment plan.
- •
Regulatory success in getting timely cost recovery for prudent investments.
- •
Driving the adoption rate of electric vehicles and heat pumps in the service territory.
- •
Securing new large-load customers like data centers.
A dual-track approach: 1) An 'internal' track focused on flawless execution of large capital projects and regulatory strategy. 2) An 'external' track focused on stimulating electricity demand through partnerships, marketing, and new service offerings for electrification.
Prioritized Initiatives
- Initiative:
Launch 'KC Electrifies' Flagship Program
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:12-18 months to full launch
First Steps:Establish partnerships with the top 5 auto dealership groups and top 10 HVAC contractors in the Kansas City metro. Design a unified rebate and marketing program.
- Initiative:
Create a Dedicated 'Data Center & Large Load' Concierge Team
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:3-6 months
First Steps:Appoint a senior leader to build a cross-functional team (engineering, rates, legal) to serve as a single point of contact for prospective large customers.
- Initiative:
File for a Utility-Owned EV Charging Program
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:9-12 months (regulatory filing)
First Steps:Conduct a study to identify optimal locations for a public fast-charging network and develop the economic justification for a rate-based investment.
Experimentation Plan
High Leverage Tests
{'area': 'Time-of-Use (TOU) Rate Adoption', 'experiment': "A/B test different marketing messages (e.g., 'Save Money' vs. 'Help the Environment') and enrollment processes (e.g., opt-in vs. opt-out) for residential TOU rates to increase adoption."}
{'area': 'Demand Response Incentives', 'experiment': 'Pilot a program offering different incentive levels to commercial customers for reducing load during peak hours to determine the elasticity of demand.'}
Track metrics such as program enrollment rates, peak load reduction (kW), and customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores for program participants vs. a control group.
Annual pilots aligned with seasonal peaks (summer and winter) and regulatory filing cycles.
Growth Team
A centralized 'Energy Transition & Growth' team that sits outside the traditional utility operations structure. This team should have P&L responsibility for new growth initiatives.
Key Roles
- •
VP of Electrification Strategy
- •
Director of EV Programs
- •
Business Development Manager, Large Load Customers
- •
Product Manager, Grid Services
Acquire talent from outside the utility industry (e.g., tech, automotive, B2B sales) to bring in new skills and a more commercial mindset. Utilize pilot programs to build internal expertise before scaling.
Evergy is a well-run, regulated utility with a strong foundational business. For years, growth in such a company was a slow, predictable function of population growth and regulatory approvals. However, the industry is at a major inflection point. The twin drivers of massive new load from data centers and the broad-based electrification of transportation and heating have transformed the growth landscape from incremental to exponential. Evergy's primary growth readiness is strong, anchored by a captive market and a clear, capital-intensive path to serving this new demand. The company's future growth will not be driven by traditional marketing or customer acquisition, but by its ability to execute a massive, multi-billion dollar capital investment plan to expand generation and modernize its grid. The core growth model is a cycle: secure large customer demand, get regulatory approval to build the required infrastructure, invest capital into this 'rate base,' and earn a regulated return on it. The main barriers are not competitive but are regulatory, financial, and operational. The greatest risk is failing to get timely and sufficient rate recovery from regulators to fund the necessary investments, a risk amplified by public opposition to rising electricity bills. The most significant growth opportunities lie in moving beyond the role of a simple commodity provider to become an orchestrator of the energy transition. This involves proactively driving the adoption of electric technologies (EVs, heat pumps) through new products and partnerships, and developing sophisticated energy solutions for large industrial customers. To fully capitalize on this, Evergy must cultivate new capabilities in product development, strategic partnerships, and data analytics, potentially by bringing in talent from more dynamic sectors. The recommended strategy is to pursue a dual mandate: operational and regulatory excellence in the core business, combined with the creation of a dedicated growth organization focused on stimulating and capturing the demand from electrification.
Legal Compliance
Evergy provides a comprehensive and easily accessible Privacy Policy linked in the website footer. The policy is well-structured, clearly outlining the types of data collected (personal identifiers, commercial information, internet activity, geolocation data), the purposes for its use (e.g., providing service, billing, analytics), and circumstances under which it is shared. A significant strength is the dedicated section detailing consumer rights under the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), including the right to know, delete, and opt-out, along with clear instructions and contact methods for exercising these rights. The policy is written in plain language, enhancing its readability for the average consumer. However, it could be improved by providing more granular detail on data retention periods for different categories of personal information.
The 'Terms of Use' are present and accessible via the website footer. The document is standard for a corporate website, covering acceptable use, intellectual property rights, disclaimers of warranties, and limitations of liability. The terms are clearly written and establish the legal framework for using the website. They specify that the laws of the State of Kansas govern the terms, providing legal clarity. While comprehensive for website usage, it's important to note that the detailed terms governing the provision of electricity service itself are typically contained in separate, state-regulated tariff documents filed with the Kansas Corporation Commission and the Missouri Public Service Commission.
The website utilizes a cookie consent banner on the first visit. The banner informs users about the use of cookies and links to the Privacy Policy. However, it employs an 'implied consent' model with a single 'I Accept' button. It lacks options to 'Decline' or 'Manage Preferences' directly from the initial banner. This approach, while common in the US, does not align with the best practices emerging from stricter privacy laws like the CPRA or international standards like GDPR. It presents a medium risk as US state privacy laws evolve to require more explicit and granular user consent for non-essential cookies. The privacy policy does explain how to block cookies through browser settings, but this is a less user-friendly approach.
Evergy demonstrates a strong understanding of its obligations under US state privacy laws, particularly the CCPA/CPRA. The privacy policy's dedicated section for California residents, complete with a toll-free number and online portal for requests, is a key strength. This proactive stance is crucial for a company handling sensitive customer data, including energy usage (which can reveal personal habits) and financial information. The lack of GDPR-specific language is appropriate and strategically sound, as the company's service area is confined to Kansas and Missouri, avoiding unnecessary compliance overhead for regulations outside its jurisdiction.
Evergy exhibits a robust commitment to digital accessibility. The website features a dedicated 'Accessibility' page, stating its goal of conforming to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 Level AA standards. This public commitment, combined with providing contact information for users who encounter accessibility barriers, significantly mitigates legal risk under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). As an essential service provider, ensuring the website is accessible to all customers, including those with disabilities, is not only a legal requirement but also a critical component of customer service and public trust.
As a regulated electric utility, Evergy's primary compliance obligations stem from the Kansas Corporation Commission (KCC) and the Missouri Public Service Commission (MPSC). The website effectively serves as a key channel for meeting these obligations. It provides customers with easily accessible information on critical, regulated topics such as:
* Rates and Tariffs: The site includes sections detailing rate information, which is a core requirement.
* Financial Assistance: A dedicated 'Financial Help' section addresses regulatory mandates to inform customers about payment assistance programs.
* Safety Information: The 'Power Line Safety' content fulfills the utility's duty to educate the public on safety around electrical infrastructure.
* Outage Reporting: The prominent 'Report an Outage' feature is a crucial operational and regulatory function.
This demonstrates a strong alignment of the digital strategy with the complex regulatory landscape of the utility industry.
Compliance Gaps
- •
The cookie consent mechanism lacks granular controls ('Decline' or 'Manage Preferences' buttons) on the initial banner, relying on a less robust 'implied consent' model.
- •
The Privacy Policy does not specify data retention periods for different categories of personal data, which is a growing expectation in data privacy best practices.
- •
While Terms of Use exist, the distinction between website use terms and the official, tariff-based terms of utility service could be made clearer to avoid customer confusion.
Compliance Strengths
- •
Strong and specific compliance with CCPA/CPRA, including dedicated policy sections and mechanisms for user rights requests.
- •
A dedicated Accessibility statement and commitment to WCAG 2.1 AA standards, mitigating ADA risk.
- •
Excellent alignment with state utility commission requirements, providing clear and accessible information on rates, financial aid, and safety.
- •
Presence of a comprehensive, well-written Privacy Policy and Terms of Use that are easily accessible from the website footer.
Risk Assessment
- Risk Area:
Cookie Consent
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Implement a more advanced cookie consent management platform that provides users with clear options to 'Accept', 'Decline', and 'Manage Preferences' for non-essential cookies directly on the banner. This will future-proof the site against evolving US state privacy laws.
- Risk Area:
Data Retention Policy
Severity:Low
Recommendation:Update the Privacy Policy to include general data retention periods for key categories of personal information. This enhances transparency and aligns with global data protection principles.
- Risk Area:
ADA Compliance
Severity:Low
Recommendation:Periodically conduct third-party accessibility audits to ensure the website continues to conform to WCAG 2.1 AA standards as it is updated, and maintain a log of remediation actions to demonstrate ongoing diligence.
High Priority Recommendations
Upgrade the cookie consent banner to include explicit 'Decline' and 'Manage Preferences' options to mitigate risks from new and evolving state-level data privacy laws.
Overall, Evergy demonstrates a mature and strategically sound legal compliance posture, particularly for a company in the heavily regulated utility sector. Its strengths in accessibility (ADA) and state-level consumer data privacy (CCPA/CPRA) are significant competitive assets, building customer trust and reducing legal risk. The website is effectively leveraged as a tool to meet the complex disclosure and service requirements of state utility commissions, turning a regulatory burden into an effective customer communication platform. The primary area for improvement lies in adopting more modern, granular cookie consent mechanisms. As a regulated entity whose business model depends on maintaining a positive relationship with regulators and the public, Evergy's proactive approach to compliance is a core component of its risk management framework and its license to operate.
Visual
Design System
Corporate
Good
Developing
User Experience
Navigation
Horizontal Top Bar with Mega Menus and Utility Navigation
Clear
Good
Information Architecture
Logical
Somewhat clear
Moderate
Conversion Elements
- Element:
Homepage 'Find Your Relevant Programs' Modal
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Somewhat effective
Improvement:The modal is immediately intrusive upon landing. Instead of a blocking modal, consider a prominent, persistent banner or section on the homepage that prompts users to select their region. This is less disruptive and allows users to explore before committing to a location.
- Element:
Service Page CTA Buttons ('Start Service', 'Stop Service', 'Move Service')
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:The green buttons are clear, but could have more contrast against the white background. Increasing the color saturation or using a slightly darker shade of green would improve visibility and draw more attention.
- Element:
Footer CTA Buttons ('Call Before You Dig 811', 'Report a Scam')
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Somewhat effective
Improvement:These CTAs are for important, but secondary, user tasks. The blue color is consistent with links, but they could be visually differentiated to better signify their importance. Consider using iconography alongside the text to quickly convey their purpose.
Assessment
Strengths
- Aspect:
Clean and Uncluttered Homepage
Impact:Medium
Description:The homepage presents a clean, professional image. The use of whitespace and clear typography makes initial content blocks easy to scan. This is crucial for a utility company where users often arrive with a specific, and sometimes urgent, task to complete.
- Aspect:
Task-Oriented Design
Impact:High
Description:The site is clearly structured around key user tasks such as 'Bill Payment Help', 'Paperless Benefits', and 'Start/Stop Service'. This task-oriented approach is highly effective for a utility provider, as it directly addresses the primary needs of its diverse customer base.
- Aspect:
Clear Iconography for Service Options
Impact:Medium
Description:On the 'Start, Stop or Move' page, the use of simple, universally understood icons (house with a plus sign, house with a stop sign, etc.) effectively communicates the purpose of each section, reducing cognitive load and aiding quick comprehension.
Weaknesses
- Aspect:
Intrusive Homepage Location Modal
Impact:High
Description:The immediate pop-up modal requiring users to select a service area is a point of friction. It interrupts the user's journey before they have had a chance to orient themselves. This can lead to frustration and a negative first impression, particularly for new users or those just seeking general information.
- Aspect:
Lack of Visual Storytelling
Impact:Medium
Description:While the design is clean, it lacks emotional connection and brand personality. The imagery is generic and fails to tell a compelling story about Evergy's commitment to the community, sustainability, or innovation. This is a missed opportunity to build brand affinity with its 1.7 million customers.
- Aspect:
Inconsistent CTA Styling
Impact:Low
Description:The primary green CTA buttons on the service page are effective, but other interactive elements, such as the text links for 'Recent News', have a very subtle hover state. This creates a slight inconsistency in how users interact with clickable elements across the site.
Priority Recommendations
- Recommendation:
Replace the intrusive homepage modal with a persistent banner.
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:High
Rationale:Removing the initial interaction barrier will significantly improve the initial user experience. A persistent banner below the main navigation would serve the same purpose of location selection without frustrating users, leading to lower bounce rates and higher engagement.
- Recommendation:
Incorporate authentic, localized visual storytelling.
Effort Level:Medium
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Replace generic stock photos with high-quality images and videos of real Evergy employees at work in the communities they serve in Kansas and Missouri. Highlighting local projects and community involvement will build trust and a stronger emotional connection with the customer base, humanizing the corporate brand.
- Recommendation:
Enhance visual hierarchy and CTA prominence on key landing pages.
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Increase the contrast and visual weight of primary CTA buttons. For instance, on the 'Start, Stop, Move' page, making the green buttons more vibrant will draw the user's eye more effectively and guide them towards completing these high-value actions, improving task completion rates.
Mobile Responsiveness
Good
The design adapts well to various screen sizes. Content reflows logically, and navigation collapses into a standard, usable mobile menu.
Mobile Specific Issues
The location selection modal can be particularly disruptive on smaller screens, occupying the entire viewport and obscuring all other content immediately upon arrival.
Desktop Specific Issues
Large hero images on desktop can push key informational content below the fold, requiring users to scroll to find important links and news.
The Evergy website presents a competent, corporate design that prioritizes task completion for its large customer base across Kansas and Missouri. Its structure is logical, catering to the primary needs of a utility user: managing service and paying bills. The navigation is clear, and the information architecture for core tasks like starting or stopping service is straightforward. However, the user experience is immediately hampered by an intrusive location-selection modal that creates unnecessary friction. While the design is clean, it feels impersonal and misses a significant opportunity to build a stronger brand identity through visual storytelling. The imagery is generic and fails to reflect Evergy's role in the community or its commitment to sustainability and renewable energy—key themes for the modern energy sector. The conversion elements, particularly the CTA buttons, are generally effective but could benefit from enhanced visual prominence to guide users more decisively. The mobile experience is solid from a technical standpoint, but the initial modal issue is exacerbated on smaller screens. The priority should be to create a more welcoming and less obstructive initial experience, followed by efforts to infuse the site with a more authentic brand personality that resonates with its local customer base.
Discoverability
Market Visibility Assessment
Evergy's brand authority is primarily functional, centered on its role as a necessary utility provider in its service territories of Kansas and Missouri. Their digital presence establishes foundational authority through transactional content (bill pay, outage reporting) and essential information (safety, financial help). Thought leadership is nascent, with content on sustainability, reliability, and community projects (like monarch butterfly conservation) serving as initial proof points. However, they are not yet positioned as a definitive thought leader in broader energy topics like grid modernization or regional energy policy, which presents a significant opportunity to build deeper trust and authority.
Within its defined geographic monopoly, Evergy's market share is absolute. Therefore, 'market share visibility' translates to how effectively they appear for customer-intent queries within their service area. For core transactional searches like 'start service Kansas City' or 'Evergy power outage', their visibility is strong. However, for informational and educational queries such as 'energy saving tips for Missouri summers' or 'Kansas renewable energy programs,' they face competition from news outlets, government agencies, and energy-focused blogs. Their visibility is tactical for existing customers but less dominant in the broader energy conversation happening within their own market.
Customer acquisition is non-traditional, as customers are acquired when they move into Evergy's service area. The digital potential lies in streamlining the onboarding process to reduce operational costs (call center volume) and improve initial customer satisfaction. The website provides clear paths to 'Start, Stop or Move' service. The key potential is to make this digital-first journey so seamless and informative that it becomes the default for all new residents, thereby creating a positive first impression that sets the tone for the entire customer relationship.
The website demonstrates a clear understanding of its distinct service regions (e.g., Missouri Metro, Kansas Central) by prompting users to select their area for a tailored experience. This is a strategic strength. However, the opportunity for deeper penetration lies in creating highly localized content that addresses specific community concerns, local energy projects, or region-specific efficiency rebates. While the framework for geographic targeting exists, the content itself could be more granular to reinforce their position as a local community partner rather than a large, impersonal utility.
Evergy's website covers the foundational pillars of a modern utility: Affordability, Reliability, and Sustainability. The content provides a good overview of their commitments in these areas. The gap is in the depth and educational value of this content. While they state their commitment, they could better demonstrate it through detailed guides, case studies on grid improvements, transparent data on renewable energy generation, and interactive tools that help customers understand their energy usage in the context of these larger goals.
Strategic Content Positioning
Content is well-aligned with the core, transactional stages of the customer journey: moving in (start service), managing an account (pay bill), and dealing with issues (report outage). This functional alignment is a strength. The opportunity is to build out content for pre-awareness (e.g., resources for realtors and new homebuyers) and post-transactional engagement (e.g., advanced energy efficiency guides, community solar program information) to create a more holistic and supportive customer lifecycle.
Significant thought leadership opportunities exist in positioning Evergy as a forward-looking energy partner. Key topics include: the transition to a cleaner energy grid in the Midwest, the benefits and practicalities of electrification (EV charging, heat pumps) for their customers, and detailed explorations of their grid modernization efforts to improve reliability. By creating definitive content on these subjects, they can shape the public narrative and build trust beyond their basic service provision.
The primary 'competitors' in the content space are news organizations reporting on outages and rates, and third-party sites offering generic energy advice. The key gap Evergy can fill is providing authoritative, specific, and transparent information during critical events. A dedicated 'Storm Center' or 'Rate Information Hub' that provides more than just basic data, but also context and explanation, would fill a major gap and position them as the single source of truth, directly countering potential misinformation or negative public sentiment.
The core messages of 'Affordable, Reliable, Sustainable' are consistently presented on the homepage and reinforced through dedicated content hubs. News items and community highlights generally support these themes. The consistency is good at a high level. The next step is to infuse these brand pillars into more granular content, such as explaining how grid reliability investments keep bills affordable long-term, or how sustainability initiatives are being implemented in specific local communities.
Digital Market Strategy
Market Expansion Opportunities
- •
Deepen market relationship by becoming the primary regional authority on home and business electrification, including EV charger installation, heat pump conversions, and smart appliance integration.
- •
Develop content partnerships with local municipalities, economic development councils, and large employers to provide energy resources for businesses and residents relocating to the area.
- •
Create a dedicated content hub for developers and contractors, providing all necessary resources for new construction projects, thereby streamlining a key B2B interaction.
Customer Acquisition Optimization
- •
Enhance the 'Start Service' digital workflow with integrated address validation and educational tooltips to minimize errors and reduce the need for follow-up calls.
- •
Develop a 'New Customer Welcome Kit' delivered digitally, providing essential information on billing, energy saving, and account management to improve the onboarding experience.
- •
Utilize search data to create targeted FAQ content that preemptively answers the most common questions from new residents, further deflecting call center volume.
Brand Authority Initiatives
- •
Launch a 'Future of Energy in [Kansas/Missouri]' content series featuring interviews with engineers, community leaders, and policy experts to establish thought leadership.
- •
Develop an interactive 'Outage Center' that goes beyond a simple map, providing detailed explanations of restoration efforts, crew status, and proactive communications during major weather events.
- •
Publish an annual, consumer-friendly 'Community Impact & Sustainability Report' in a digital format to transparently showcase progress on key initiatives.
Competitive Positioning Improvements
- •
Position Evergy as the most transparent and communicative utility in the region by creating content that explains the 'why' behind rate changes, infrastructure projects, and policy decisions.
- •
Use the digital platform to proactively manage public perception by being the first and most comprehensive source of information during service disruptions or other newsworthy events.
- •
Highlight local employee stories and community investments to reinforce the 'people-first' mindset and position the company as an integral part of the communities it serves, not just a service provider.
Business Impact Assessment
For a regulated utility, traditional market share metrics are irrelevant. Success is indicated by the rate of digital self-service adoption for key transactions (e.g., start/stop service, bill payment), which directly translates to lower operational costs. A secondary indicator is customer satisfaction scores (e.g., J.D. Power ratings) within the service territory.
Key metrics are the completion rate of the online 'Start Service' form, the reduction in call center inquiries related to moving, and the percentage of new customers who enroll in digital services like paperless billing and online account management within the first 30 days.
Authority can be measured by share of voice in search for key non-branded terms (e.g., 'Kansas City power company'), branded search volume trends over time, and media sentiment analysis. Engagement with thought leadership content (e.g., time on page, downloads of reports) also serves as a key indicator.
Performance should be benchmarked against other investor-owned utilities of a similar size (e.g., Ameren, Entergy) on metrics such as digital tool availability, customer satisfaction ratings, and the quality of online educational resources. Another benchmark is the ratio of online self-service transactions to total customer interactions.
Strategic Recommendations
High Impact Initiatives
- Initiative:
Develop a 'Proactive Outage Communications Hub'
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Build unparalleled brand trust and reduce customer frustration during service disruptions by becoming the single, authoritative source of information.
Success Metrics
- •
Reduction in outage-related call center volume
- •
Increased traffic to the outage hub during weather events
- •
Improved customer satisfaction scores following service interruptions
- Initiative:
Create an 'Electrification & Energy Efficiency Resource Center'
Business Impact:Medium
Market Opportunity:Position Evergy as a vital partner in the energy transition, capturing customer interest in EVs, solar, and efficiency to drive adoption of value-added programs and services.
Success Metrics
- •
Organic search ranking for electrification-related terms
- •
Lead generation for energy efficiency programs
- •
Engagement rates with educational content (guides, calculators)
- Initiative:
Optimize the Digital 'Move-In' Experience
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Substantially reduce operational costs and improve day-one customer satisfaction by making the online start-service process the most efficient and preferred method for new residents.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in percentage of service starts completed online
- •
Decrease in form abandonment rate
- •
Reduction in errors and incomplete digital applications
Transition from a functional utility provider to an essential community and energy partner. This involves shifting the digital focus from purely transactional functions to proactive education, transparent communication, and forward-looking thought leadership. The goal is to be the indispensable resource for all energy-related matters in the service territory, building a brand defined by trust, reliability, and community commitment.
Competitive Advantage Opportunities
- •
Leverage hyper-local content to demonstrate a deep, unmatched understanding of the specific communities served, creating an advantage over generic national energy websites.
- •
Achieve superior transparency by using digital channels to openly explain complex topics like grid maintenance and rate structures, building trust that insulates against public criticism.
- •
Build a best-in-class digital self-service platform that creates a frictionless customer experience, turning a basic utility requirement into a key brand differentiator and cost-saver.
Evergy has established a competent digital presence that effectively serves the core transactional needs of its captive customer base in Kansas and Missouri. The website's focus on essential functions like bill payment, service transfers, and outage reporting provides a solid, functional foundation.
The strategic imperative for Evergy is to evolve its digital presence from that of a functional utility to that of an indispensable community partner and thought leader. Its market position is guaranteed, but its public perception and customer relationship are not. The current digital strategy successfully addresses the immediate needs of the customer journey, but a significant opportunity exists to build a more resilient and trusted brand by investing in proactive, educational, and transparent content.
Key strategic recommendations focus on three areas:
1. Operational Excellence through Digital Self-Service: The most immediate business impact can be realized by optimizing the digital 'move-in' process. This will directly reduce customer service costs and improve the crucial first impression for new customers.
2. Building Brand Trust through Proactive Communication: In the utility sector, brand perception is forged during crises. Developing a best-in-class 'Proactive Outage Communications Hub' will transform a point of potential customer friction into a moment of brand-building trust and reliability.
3. Future-Proofing through Education: The energy landscape is changing rapidly. By establishing an 'Electrification & Energy Efficiency Resource Center,' Evergy can position itself as a forward-thinking guide for its customers, shaping the future of energy use in its communities and creating new value streams through targeted programs.
By executing on these initiatives, Evergy can leverage its digital presence to not only reduce operational costs but also to build significant brand equity, enhance customer satisfaction, and solidify its position as a trusted leader in the region's energy future.
Strategic Priorities
Strategic Priorities
- Title:
Establish a 'Large Load & Electrification Growth' Unit
Business Rationale:The analysis identifies a massive 12.2 GW pipeline of new demand from data centers and a generational opportunity in the electrification of transport and heating. The current business model is not structured to proactively capture this demand. A dedicated unit is needed to serve as a concierge for large-load customers and to drive electrification adoption across the residential and commercial base.
Strategic Impact:This initiative transforms Evergy from a passive electricity provider into an active engine for regional economic growth. It positions the company to capture the largest revenue opportunity in decades, securing long-term growth by becoming the preferred partner for energy-intensive industries and the primary enabler of the clean energy transition for all customers.
Success Metrics
- •
Annual MWh sales growth (weather-normalized)
- •
GW of new large-load customers contracted
- •
Market penetration rate of EVs and electric heat pumps in service territory
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Revenue Model
- Title:
Pioneer the 'Grid Orchestrator' Business Model via a Virtual Power Plant (VPP)
Business Rationale:The rise of distributed energy resources (DERs) like rooftop solar and batteries is identified as a primary threat to the traditional utility model. Resisting this trend is futile; embracing it is a strategic necessity. A VPP allows Evergy to manage and orchestrate customer-owned assets to provide grid stability, turning a potential threat into a valuable, controllable resource.
Strategic Impact:This fundamentally future-proofs Evergy's business model against decentralization. It shifts the company's role from a simple commodity seller to a sophisticated platform orchestrator, creating new revenue streams from grid services and reducing the need for expensive new power plants by leveraging customer-sited assets.
Success Metrics
- •
MW capacity of customer-owned assets under management in the VPP
- •
Reduction in peak load management costs
- •
Revenue generated from ancillary grid services
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Business Model
- Title:
Transform Brand Perception through a Proactive Outage Communication & Reliability Hub
Business Rationale:Brand perception for a utility is forged during crises, primarily power outages. The analysis indicates an opportunity to move beyond basic reporting to proactive, transparent communication. Building trust and improving customer satisfaction directly impacts regulatory outcomes and public support for necessary rate increases.
Strategic Impact:This initiative positions Evergy as the most trusted and communicative utility in the region, turning a major point of customer friction into a brand-building opportunity. Superior customer experience becomes a competitive advantage that de-risks the regulatory process and builds significant brand equity.
Success Metrics
- •
Improvement in J.D. Power Customer Satisfaction scores
- •
Reduction in average call volume per customer during outage events
- •
Increase in digital channel adoption for outage information
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Quick Win (0-3 months)
Category:Brand Strategy
- Title:
Launch 'Energy as a Service' (EaaS) for Commercial & Industrial Customers
Business Rationale:Large commercial and industrial customers have increasingly complex energy needs driven by ESG goals and operational demands (e.g., EV fleet charging, on-site solar, microgrids). The regulated model is ill-equipped to provide these holistic solutions. An EaaS offering, potentially as a non-regulated arm, can capture this high-margin business.
Strategic Impact:This diversifies Evergy's revenue streams beyond the sale of regulated kilowatt-hours, creating a new growth engine with higher margin potential. It deepens relationships with the most valuable customers, preventing encroachment from third-party energy solution providers and positioning Evergy as a comprehensive energy partner.
Success Metrics
- •
Revenue from non-regulated EaaS contracts
- •
Number of C&I customers with multi-service agreements
- •
Profitability of the EaaS business unit
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Long-term Vision (12+ months)
Category:Revenue Model
- Title:
Champion a Regulatory Modernization Initiative for Performance-Based Ratemaking
Business Rationale:The current rate-base regulation model incentivizes capital investment but can be misaligned with modern goals like energy efficiency and DER integration. Proactively partnering with regulators in both Kansas and Missouri to develop performance-based rates (PBR) is crucial for aligning Evergy's financial success with customer and societal outcomes.
Strategic Impact:This is a foundational strategic move that rewrites the company's core operating and financial incentives. It allows Evergy to earn revenue based on performance in key areas like reliability, customer satisfaction, and clean energy integration, ensuring the business model remains viable and profitable through the energy transition.
Success Metrics
- •
Successful filing and approval of a PBR pilot program
- •
Percentage of revenue decoupled from pure kWh sales
- •
Achievement of performance incentive targets
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Long-term Vision (12+ months)
Category:Operations
Evergy must aggressively transition from its role as a traditional, regulated power provider to a proactive, integrated energy platform. This requires simultaneously capturing the generational growth from electrification and large-load customers while re-architecting its business model to orchestrate a decentralized, customer-centric grid.
The key sustainable competitive advantage to build is becoming the indispensable orchestrator of the regional energy ecosystem. While the monopoly on 'poles and wires' is a legacy advantage, future dominance will come from the superior capability to integrate, manage, and optimize a complex network of utility-scale and customer-owned energy assets.
The primary growth catalyst is the unprecedented surge in electricity demand from the mass electrification of transportation and buildings, coupled with the attraction of energy-intensive data centers. Actively driving and capturing this demand is the single most important lever for future revenue and shareholder value creation.