eScore
gevernova.comThe eScore is a comprehensive evaluation of a business's online presence and effectiveness. It analyzes multiple factors including digital presence, brand communication, conversion optimization, and competitive advantage.
GE Vernova inherits significant domain authority from its GE legacy, providing a strong foundation for its digital presence. The content effectively targets mid-to-late funnel search intent with detailed product and solution information. However, there is a noticeable gap in early-stage, problem-aware content, which limits its ability to capture users at the beginning of their research journey. Furthermore, while the site is globally focused, there's a lack of explicit voice search optimization or highly interactive content, which are becoming standard for industry leaders.
Excellent inherited domain authority and strong content alignment for audiences in the consideration and decision stages of their journey.
Develop a robust thought leadership platform with problem-oriented content (e.g., 'guides to grid modernization') to capture early-stage search intent and build a distinct brand authority separate from GE.
The brand's core message of 'electrifying and decarbonizing' is powerful, consistent, and effectively tailored to different core audiences like utilities and industrial partners. The messaging successfully creates a sense of purpose and optimism, mapping well to the emotional drivers of the energy transition. The primary weakness lies in a lack of quantifiable proof points to back up the aspirational claims, and conversion messaging is often weakened by generic calls-to-action.
A powerful, unified, and memorable core purpose ('electrify and decarbonize') that is consistently applied across all website sections.
Incorporate a 'By the Numbers' section on the homepage and within key solution pages to add quantifiable proof of impact (e.g., 'X GW of renewable energy installed,' '% reduction in emissions enabled by our tech').
The website provides an excellent cross-device experience with a flawless mobile-responsive design. However, the overall conversion experience is hampered by significant friction points, most notably the use of understated, low-prominence 'ghost buttons' for key CTAs like newsletter subscriptions and partnerships. A moderate cognitive load on text-heavy interior pages and a lack of a formal accessibility statement also detract from an otherwise professional user experience, posing both conversion and legal risks.
The cross-device journey is seamless, with an excellently executed mobile-responsive design that ensures a consistent experience on any platform.
Immediately convert all primary and secondary call-to-action buttons from the current 'ghost button' (outline) style to a solid, high-contrast fill to dramatically increase their visual weight and click-through rates.
Credibility is exceptionally high, built upon the GE legacy, strong third-party validation through major partnership announcements, and a mature approach to legal transparency in its privacy and cookie policies. The business model, centered on long-term service agreements for critical infrastructure, is a powerful risk mitigator for customers. The primary gap is a lack of customer-centric proof, such as direct testimonials or detailed, data-rich case studies, which are rated as having only 'moderate' impact.
A comprehensive and transparent legal compliance framework, particularly for data privacy (GDPR) and cookie consent, which builds significant trust for a global B2B audience.
Develop a robust library of detailed, quantifiable case studies and feature prominent customer testimonials on the homepage and relevant solution pages to translate corporate credibility into tangible customer success evidence.
GE Vernova's competitive moat is deep and highly defensible, primarily rooted in its massive global installed base which generates high-margin, recurring service revenue. This, combined with a comprehensive portfolio spanning the entire energy transition (gas, wind, grid), allows for integrated solutions that few competitors can match. High switching costs for its incumbent technology and a significant R&D budget further solidify its market position, making its advantages very sustainable.
The vast global installed base of power generation equipment provides a highly sustainable, high-margin services revenue stream and a captive market for upgrades, creating an extremely difficult moat for competitors to overcome.
More explicitly leverage the GE legacy of innovation in messaging as a unique advantage over competitors like Siemens Energy, while simultaneously highlighting the agility gained from the post-spin-off focus.
The company is exceptionally well-positioned to scale, with a strong balance sheet and a business model directly aligned with the multi-trillion dollar global energy transition. Strong market expansion signals, particularly in the high-demand data center vertical, provide a clear path for growth. The primary constraints are operational, tied to the high fixed costs and physical capacity of heavy manufacturing, and the persistent unprofitability of the crucial Wind segment.
Excellent market timing and positioning, having spun off at the precise moment of a massive global investment cycle in energy transition and grid modernization, particularly for high-demand sectors like AI.
Continue the aggressive operational restructuring of the Wind segment to achieve sustained profitability, which is essential for unlocking the full scaling potential of the integrated business model.
GE Vernova's business model is exceptionally coherent, leveraging the profitable, cash-generative Power segment to fund growth in the Wind and Electrification businesses. The recent spin-off has sharpened the company's strategic focus entirely on the energy transition, aligning its resources, market timing, and stakeholder interests with this singular mission. The model's only significant incoherence is the historical drag from the underperforming Wind segment, which is actively being addressed.
A highly synergistic model where the stable, high-margin service revenues from the massive installed base in the Power segment provide the financial foundation to invest in and capture the high-growth opportunities in Wind and Electrification.
Further break down internal silos between the Power, Wind, and Electrification segments to accelerate the development and sale of integrated, multi-part solutions that competitors cannot easily replicate.
As a technology provider for approximately 30% of the world's electricity, GE Vernova wields immense market power and influence. Its premium pricing strategy is supported by technological leadership and a massive installed base that grants it significant leverage with customers and partners. The company's market share is stable and poised for growth, and its ability to publish policy roadmaps demonstrates its influence in shaping market direction.
Dominant market share and pricing power, derived from technological leadership and an unparalleled installed base that makes it an indispensable partner in the global energy ecosystem.
Develop and market a clearer, more aggressive narrative around its software and digital offerings (e.g., GridOS) to better compete with software-centric rivals and establish market power in the digital layer of the energy transition.
Business Overview
Business Classification
B2B Industrial Technology & Services
Energy Project Development & Management
Energy
Sub Verticals
- •
Power Generation (Gas, Nuclear, Hydro, Steam)
- •
Renewable Energy (Onshore & Offshore Wind)
- •
Grid Solutions & Electrification
- •
Energy Storage Systems
- •
Electrification Software
Mature (in Transformation Phase)
Maturity Indicators
- •
Recent spin-off from General Electric (April 2024), now an independent public company (NYSE: GEV).
- •
Constituent business units possess decades of operational history and technological expertise.
- •
Large global footprint with approximately 80,000 employees and over 100 manufacturing facilities.
- •
Substantial existing installed base, generating approximately 30% of the world's electricity.
- •
Significant capital investments in capacity expansion (e.g., gas turbine and grid equipment factories).
Enterprise
Steady to Rapid
Revenue Model
Primary Revenue Streams
- Stream Name:
Long-Term Service Agreements (LTSA) & Services
Description:High-margin, recurring revenue from servicing, maintaining, and upgrading the vast installed base of power generation equipment (e.g., gas turbines). This is the core profit driver, especially in the Power segment, accounting for ~70% of that segment's revenue.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Utilities & Power Producers
Estimated Margin:High
- Stream Name:
Capital Equipment Sales
Description:Project-based sales of large-scale energy hardware, including gas turbines, wind turbines, grid transformers, and High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) systems.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Utilities, Renewable Developers, Industrial Companies
Estimated Margin:Medium
- Stream Name:
Integrated Solutions & Turnkey Projects
Description:Delivery of complex, end-to-end energy projects, such as power plant construction, grid modernization, and industrial electrification systems.
Estimated Importance:Secondary
Customer Segment:Governments, Utilities, Large Industrials
Estimated Margin:Medium-Low
- Stream Name:
Electrification Software & Digital Services
Description:Software solutions (e.g., GridOS®) for grid management, predictive maintenance, and operational optimization of energy assets.
Estimated Importance:Tertiary
Customer Segment:Utilities, Grid Operators
Estimated Margin:High
Recurring Revenue Components
- •
Long-Term Service Agreements (LTSA)
- •
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) for grid management
- •
Transactional services and spare parts
Pricing Strategy
Value-Based & Project-Based Contracting
Premium
Opaque
Pricing Psychology
- •
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) focus
- •
Long-term partnership value
- •
Reliability and performance guarantees
Monetization Assessment
Strengths
- •
Massive installed base creates a durable, high-margin services revenue stream.
- •
Diversified portfolio across Power, Wind, and Electrification allows for cross-selling and integrated solutions.
- •
Strong order backlog provides excellent revenue visibility.
Weaknesses
- •
Historical unprofitability and operational challenges in the Wind segment, particularly offshore.
- •
Reliance on large, cyclical capital projects which can be affected by economic uncertainty.
- •
Margin pressure from rising raw material costs and supply chain disruptions.
Opportunities
- •
Leverage strong demand from data centers and AI to secure premium pricing and long-term agreements for gas power.
- •
Expand high-margin digital and grid software offerings to increase recurring revenue.
- •
Capitalize on government incentives (e.g., Inflation Reduction Act in the US) to improve project economics.
Threats
- •
Intense competition from major global players like Siemens Energy, Vestas, and ABB.
- •
Rapid technological shifts could make existing product lines obsolete.
- •
Geopolitical risks and trade tariffs impacting global supply chains and project costs.
Market Positioning
A comprehensive, technology-driven partner for the global energy transition, providing solutions to electrify and decarbonize.
Major Player/Leader
Target Segments
- Segment Name:
Electric Utilities & Power Producers
Description:Incumbent and independent power producers, transmission and distribution system operators responsible for generating and delivering electricity.
Demographic Factors
Large-scale enterprises (public, private, or state-owned)
Global presence
Psychographic Factors
Prioritize grid reliability, stability, and long-term asset performance
Risk-averse, focused on proven technology
Behavioral Factors
Engage in long-term procurement cycles
Value established relationships and comprehensive service agreements
Pain Points
- •
Integrating intermittent renewable energy sources into the grid
- •
Modernizing aging infrastructure
- •
Meeting decarbonization mandates while ensuring reliability
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
Industrial & Commercial Heavy Energy Users
Description:Energy-intensive industries seeking to decarbonize operations, ensure power quality, and reduce energy costs. Includes data centers, metals, mining, and oil & gas.
Demographic Factors
Large multinational corporations
High energy consumption as a primary operational cost
Psychographic Factors
Focused on operational efficiency, sustainability goals (ESG), and energy security
Behavioral Factors
Invest in on-site generation, microgrids, and electrification of processes
Pain Points
- •
High and volatile energy costs
- •
Pressure to meet corporate sustainability targets
- •
Need for uninterrupted, high-quality power for critical operations (e.g., data centers)
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
Renewable Energy Developers
Description:Companies specializing in the development, construction, and operation of wind and solar power projects.
Demographic Factors
Varies from specialized firms to large utility-scale developers
Psychographic Factors
Focused on Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE)
Highly sensitive to project financing and policy incentives
Behavioral Factors
Seek technology partners for core equipment (turbines)
Often engage EPC (Engineering, Procurement, Construction) firms
Pain Points
- •
Project profitability challenges due to supply chain costs and competition.
- •
Permitting and grid connection delays
- •
Technology reliability and long-term maintenance costs
Fit Assessment:Fair to Good
Segment Potential:High
Market Differentiation
- Factor:
Installed Base & Service Revenue
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Comprehensive Portfolio (Gas, Wind, Grid)
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
GE Engineering Legacy & Technology IP
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Global Scale and Project Execution Capability
Strength:Moderate
Sustainability:Sustainable
Value Proposition
To continue electrifying the world while simultaneously working to decarbonize it, leveraging a comprehensive portfolio of technologies to accelerate a more reliable, affordable, and sustainable energy future.
Good
Key Benefits
- Benefit:
Grid Stability & Reliability
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
Gas power as a bridge fuel for grid resilience.
Grid solutions like synchronous condensers and STATCOMs.
- Benefit:
Integrated Decarbonization Pathway
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Unique
Proof Elements
Portfolio spanning gas (with hydrogen capability), wind, hydro, and nuclear (SMRs).
Expertise in integrating renewables into the grid.
- Benefit:
Long-Term Asset Performance & Efficiency
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
Extensive service network and digital tools for predictive maintenance.
High-efficiency gas turbines (7HA series).
Unique Selling Points
- Usp:
The ability to pair a world-leading gas power business with a full suite of renewable and grid technologies, offering a pragmatic path to decarbonization.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
Decades of accumulated data and operational expertise from the world's largest power generation installed base.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
Customer Problems Solved
- Problem:
Maintaining grid stability while increasing the share of intermittent renewables.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Meeting ambitious climate goals without compromising energy affordability or reliability.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
- Problem:
Managing the complexity and cost of large-scale energy infrastructure projects.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
Value Alignment Assessment
High
The business model is directly aligned with the 'energy trilemma' (sustainability, reliability, affordability) and the multi-trillion dollar global investment in energy transition.
High
The value proposition directly addresses the primary challenges of utilities, power producers, and industrial customers navigating decarbonization and electrification.
Strategic Assessment
Business Model Canvas
Key Partners
- •
Electric Utilities (e.g., Saudi Electricity Company)
- •
Industrial Companies (e.g., data center operators, Crusoe Energy)
- •
Renewable Energy Developers
- •
EPC (Engineering, Procurement, Construction) Firms
- •
Technology Partners (e.g., PyroGenesis, Rolls-Royce for SMRs)
- •
Governments and Regulators
Key Activities
- •
Research & Development in energy technology ($1B annually)
- •
Advanced Manufacturing of heavy industrial equipment
- •
Global Project Management & Execution
- •
Long-Term Equipment Servicing & Maintenance
- •
Supply Chain Management
Key Resources
- •
Extensive portfolio of Intellectual Property (Patents)
- •
Global manufacturing and service footprint
- •
Large, highly skilled engineering workforce (~80,000 employees)
- •
Massive installed base of equipment
- •
Strong brand reputation inherited from GE
Cost Structure
- •
High R&D investment
- •
Significant capital expenditure for manufacturing facilities
- •
Raw material and component costs
- •
Labor costs for manufacturing and services
- •
Warranty provisions and service costs
Swot Analysis
Strengths
- •
Dominant market position with a vast installed base providing stable, high-margin service revenue.
- •
Unique and comprehensive portfolio covering Power, Wind, and Electrification.
- •
Strong balance sheet with more cash than debt post-spin-off, enabling strategic investments.
- •
Technology leadership and strong brand reputation inherited from GE.
Weaknesses
- •
Historically challenged profitability and execution in the Wind segment, which is a key growth area.
- •
Vulnerability to supply chain disruptions and volatile raw material prices.
- •
Large, complex organization may face agility challenges compared to smaller, specialized competitors.
- •
High warranty costs have impacted profitability in the past, particularly in Wind.
Opportunities
- •
Explosive growth in electricity demand driven by AI, data centers, and vehicle electrification.
- •
Massive global investment cycle in energy transition and grid modernization.
- •
Government policies and subsidies (e.g., IRA) accelerating clean energy deployment.
- •
Emerging markets for nuclear energy, specifically Small Modular Reactors (SMRs).
Threats
- •
Intense competition from established players (Siemens Energy, ABB) and increasingly, Chinese manufacturers.
- •
Geopolitical instability, trade wars, and tariffs impacting global operations and costs.
- •
Rapid, disruptive technological innovation from new entrants.
- •
Economic downturns that could delay or cancel large capital-intensive energy projects.
Recommendations
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Wind Segment Profitability
Recommendation:Continue aggressive operational restructuring of the Wind segment, focusing on product standardization, supply chain discipline, and selective bidding to prioritize margin over market share. Achieve sustained profitability as guided.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Operational Agility
Recommendation:Fully leverage post-spin-off independence to streamline decision-making processes and foster a more agile culture, breaking down silos between the Power, Wind, and Electrification segments to drive integrated solution sales.
Expected Impact:Medium
- Area:
Digital Services Integration
Recommendation:Accelerate the development and integration of the GridOS® software platform across all hardware offerings to create a sticky digital ecosystem, increasing recurring revenue and creating a competitive moat.
Expected Impact:High
Business Model Innovation
- •
Develop 'Energy-as-a-Service' models for industrial clients, bundling hardware, software, and long-term operational management into a single subscription-like contract.
- •
Establish a dedicated financing arm or partnership to offer innovative financing solutions for large-scale projects, helping customers overcome high upfront capital costs.
- •
Create an open innovation platform to partner with startups and academic institutions to accelerate R&D in emerging areas like green hydrogen and long-duration energy storage.
Revenue Diversification
- •
Aggressively pursue the Small Modular Reactor (SMR) market as a key long-term growth driver, securing strategic partnerships with utilities and governments.
- •
Expand into the circular economy by offering services for decommissioning, repowering, and recycling of aging power generation assets (especially wind turbines).
- •
Double down on grid-stabilizing technologies like synchronous condensers and battery storage systems, which are critical for high-renewable grids and represent a fast-growing market.
GE Vernova emerges from its spin-off from General Electric as a purpose-built industrial titan, strategically positioned at the epicenter of the global energy transition. Its business model is fundamentally a tale of two parts: a mature, highly profitable, and cash-generative Power segment, built on the world's largest installed base of gas turbines, which provides a stable foundation through high-margin, long-term service agreements. This foundation is designed to fund and fuel the second part: capturing the immense growth in the Electrification and Wind segments, which are directly aligned with the multi-trillion dollar investment wave in decarbonization and grid modernization. The company's core competitive advantage is its unique, comprehensive portfolio. Unlike more specialized competitors, GE Vernova can offer a pragmatic, integrated pathway to decarbonization—pairing the reliability of gas power (increasingly essential for backing up renewables and powering AI data centers) with its growing wind and grid capabilities. This positions them not just as an equipment supplier, but as a strategic partner to utilities and governments navigating the complex 'energy trilemma' of balancing sustainability, affordability, and reliability. However, the model is not without significant challenges. The primary weakness has been the persistent unprofitability and operational difficulties within the Wind segment, a critical area for future growth. The entire wind industry has faced margin pressure, but GE Vernova's ability to impose discipline and achieve sustained profitability here remains a key test. Furthermore, as a large, complex industrial firm, it must contend with supply chain volatility, geopolitical risks, and intense competition. The strategic evolution for GE Vernova hinges on successful execution. It must leverage its newfound independence to become more agile, continue the operational turnaround in Wind, and deepen the integration between its business units to sell holistic, high-value solutions. The greatest opportunity lies in capitalizing on the explosive demand for electricity from data centers and AI, which perfectly plays to the strengths of its gas power and grid businesses. By innovating its business model towards more service-oriented and digitally-enabled offerings, GE Vernova has the potential to transform from a traditional industrial manufacturer into a comprehensive energy transition solutions provider, driving significant long-term value creation.
Competitors
Competitive Landscape
Mature, but undergoing rapid transformation (Growth phase for renewables, grid modernization, and decarbonization technologies)
Oligopoly
Barriers To Entry
- Barrier:
High Capital Intensity & Manufacturing Complexity
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Deep Technological Expertise and Intellectual Property
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Long-standing Customer Relationships and Installed Base
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Complex Global Supply Chains
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Stringent Regulatory and Grid Code Compliance
Impact:Medium
Industry Trends
- Trend:
Grid Modernization and Expansion
Impact On Business:Massive growth opportunity for GE Vernova's Electrification segment, including grid solutions, power conversion, and software.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Accelerating Renewable Energy Adoption (Solar & Wind)
Impact On Business:Drives demand for wind turbines and grid integration hardware/software, but also increases competition and margin pressure in the Wind segment.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Electrification of Everything (Transportation, Buildings, Industry)
Impact On Business:Increases overall electricity demand, creating a need for both new power generation (gas, renewables) and robust grid infrastructure.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Surging Power Demand from Data Centers and AI
Impact On Business:Creates urgent demand for reliable power generation and grid solutions, playing to GE Vernova's strengths in gas power and grid stability.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Digitalization and AI in Energy Systems
Impact On Business:Opportunity to create high-margin, recurring revenue streams through software like GridOS for grid optimization and predictive maintenance.
Timeline:Near-term
Direct Competitors
- →
Siemens Energy
Market Share Estimate:Major
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:A global energy technology company with a broad portfolio mirroring GE Vernova's, covering gas services, grid technologies, and wind energy (via Siemens Gamesa).
Strengths
- •
Comprehensive portfolio across the energy value chain.
- •
Strong global presence and brand recognition.
- •
Significant order backlog providing revenue visibility.
Weaknesses
- •
Significant financial and technical challenges within its wind division (Siemens Gamesa), impacting overall profitability.
- •
Weaker balance sheet compared to GE Vernova.
- •
Perceived as having a less 'clean' investment story due to the ongoing turnaround in its wind business.
Differentiators
Stronger position in certain niche grid technologies.
Significant focus on hydrogen electrolyzers.
- →
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) / Mitsubishi Power
Market Share Estimate:Significant
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:A technology leader in high-efficiency gas turbines and power systems, with a strong focus on decarbonization solutions like hydrogen and carbon capture.
Strengths
- •
Leading-edge technology in advanced gas turbines (JAC-series).
- •
Strong market presence in Asia and North America.
- •
Heavy investment in next-generation decarbonization technologies (hydrogen, ammonia, CCS).
Weaknesses
- •
Less comprehensive portfolio in grid solutions and wind compared to GE Vernova and Siemens Energy.
- •
Primary focus is on large-scale thermal power, potentially lagging in distributed energy resources.
- •
Brand recognition in electrification software is lower than competitors.
Differentiators
Market-leading efficiency and reliability in their flagship gas turbines.
Deep expertise in integrated power plant solutions.
- →
Vestas Wind Systems
Market Share Estimate:Leading (in Wind)
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:A pure-play global leader in the manufacturing, installation, and servicing of wind turbines, with a strong market share, particularly in the onshore segment.
Strengths
- •
Leading market share in global wind installations (ex-China).
- •
Extensive service network and large installed base.
- •
Strong brand reputation and focus solely on wind energy technology.
Weaknesses
- •
Subject to the volatility and low margins of the wind energy sector.
- •
Lacks a diversified portfolio to offset challenges in the wind market.
- •
Faces intense competition from Chinese manufacturers and other major players.
Differentiators
Singular focus on wind energy innovation.
Deep operational experience and a vast dataset from its global fleet.
- →
Hitachi Energy
Market Share Estimate:Significant (in Grid)
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:A global technology leader focused on advancing the world's energy system to be more sustainable, flexible and secure. A direct competitor in grid solutions, HVDC, transformers, and grid automation software.
Strengths
- •
Comprehensive portfolio of grid automation and power quality solutions.
- •
Strong position in High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) technology, critical for long-distance power transmission and offshore wind integration.
- •
Leverages Hitachi's broader expertise in digital technology and IoT.
Weaknesses
- •
Does not compete in power generation equipment (turbines).
- •
May be perceived as a component/systems provider rather than a full-scope energy partner.
- •
Faces strong competition from GE Vernova, Siemens, and Schneider Electric in the grid space.
Differentiators
Market leadership in specific high-voltage technologies.
Advanced digital offerings like the Grid-eMotion portfolio for fleet electrification and e-mesh for energy storage.
- →
Schneider Electric
Market Share Estimate:Significant (in Electrification)
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:A leader in the digital transformation of energy management and automation, with a strong focus on medium-to-low voltage solutions, software, and industrial automation.
Strengths
- •
Dominant position in energy management software and automation.
- •
Broad portfolio of electrical distribution and control products.
- •
Strong channel partnerships and reach into commercial and industrial sectors.
Weaknesses
- •
Limited presence in heavy-duty power generation (turbines).
- •
Less focused on utility-scale transmission and high-voltage equipment compared to GE Vernova.
- •
Portfolio is more fragmented across different end markets.
Differentiators
Leader in sustainability services and consulting.
EcoStruxure platform provides a strong, integrated software and hardware ecosystem for energy management.
Indirect Competitors
- →
Renewable Energy Developers (e.g., NextEra Energy, Ørsted)
Description:Large-scale developers and operators of renewable energy projects. While they are major customers for turbine manufacturers, their technology choices, supply chain strategies, and potential for vertical integration pose an indirect competitive threat.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Low, but they heavily influence market dynamics and pricing.
- →
Energy Storage Specialists (e.g., Fluence, Tesla Energy)
Description:Companies specializing in battery energy storage systems (BESS) and software, competing directly with GE Vernova's energy storage solutions. They offer standalone and integrated solutions that are critical for grid stability.
Threat Level:High
Potential For Direct Competition:Already direct competitors in the energy storage sub-segment.
- →
Green Hydrogen Technology Providers (e.g., Plug Power, Nel ASA)
Description:Companies developing electrolyzers and fuel cell technology. They offer an alternative pathway for decarbonizing heavy industry and power generation, potentially displacing demand for gas turbines or competing in long-duration storage.
Threat Level:Low
Potential For Direct Competition:Could become direct competitors if hydrogen becomes a mainstream fuel for power generation.
- →
Small Modular Reactor (SMR) Developers (e.g., NuScale Power)
Description:Innovators in nuclear energy developing smaller, factory-built reactors. This competes with GE-Hitachi's traditional large-scale nuclear offerings and could provide an alternative to gas power for firm, carbon-free electricity.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Directly competitive with GE Vernova's own nuclear division in the long term.
Competitive Advantage Analysis
Sustainable Advantages
- Advantage:
Vast Global Installed Base
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. The fleet of ~7,000 gas turbines and ~57,000 wind turbines provides a massive, long-term, and high-margin services and upgrades revenue stream.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Comprehensive and Integrated Portfolio
Sustainability Assessment:Sustainable. The ability to offer solutions across Power, Wind, and Electrification allows for integrated project delivery (e.g., gas plant + grid connection) that few competitors can match.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Technological Leadership and R&D Scale
Sustainability Assessment:Sustainable. A long history of engineering excellence and significant R&D spending allow for continuous innovation in turbine efficiency, grid software, and decarbonization technologies.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
- Advantage:
Strong Brand Heritage and Customer Relationships
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. The GE brand carries a legacy of trust and reliability in the power sector, facilitating access to large, mission-critical infrastructure projects.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
Temporary Advantages
{'advantage': 'Post-Spinoff Financial Flexibility and Focus', 'estimated_duration': "1-3 years. The recent spin-off provides a 'clean slate' with a strong balance sheet and a singular focus on the energy transition, contrasting with competitors like Siemens Energy who are bogged down by internal issues. "}
Disadvantages
- Disadvantage:
Profitability Challenges in the Wind Segment
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately. The entire wind industry faces margin pressure from supply chain issues, competition, and policy uncertainty. While GE is focused on onshore wind, the segment remains a challenge.
- Disadvantage:
Legacy Fossil Fuel Perception
Impact:Minor
Addressability:Easily. Although a leader in gas, the company's strong renewables and decarbonization narrative helps mitigate this. The key is executing on the 'decarbonize while electrifying' mission.
- Disadvantage:
Competition in High-Growth Digital/Software Space
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately. While GridOS is a strong offering, the grid software market is competitive with specialized players and other industrial giants like Schneider and Siemens investing heavily.
Strategic Recommendations
Quick Wins
- Recommendation:
Launch targeted marketing campaigns highlighting integrated project wins that combine Power, Wind, and Electrification solutions.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
- Recommendation:
Aggressively market grid stabilization solutions to regions with high renewable penetration and growing data center loads.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Create bundled service offerings for the existing installed base that include digital upgrades (e.g., predictive maintenance software) with regular hardware maintenance.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Medium Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Expand 'as-a-service' models for industrial clients, offering turnkey electrification and decarbonization solutions.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Form strategic partnerships with green hydrogen producers to co-develop and deploy hydrogen-ready gas turbines, positioning for the fuel's future adoption.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Continue to invest in and promote SF₆-free grid technologies to establish a clear ESG leadership position in the T&D market.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Long Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Position GE Vernova as the primary 'orchestrator' of the energy transition, focusing on the software and systems integration needed to manage a complex, decentralized grid.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Explore strategic acquisitions of specialized grid software, cybersecurity, or advanced energy storage technology companies to accelerate digital capabilities.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Invest in developing circular economy models for wind turbine blades and other energy equipment to create a sustainable end-of-life value chain.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Solidify GE Vernova's position as the indispensable technology partner for the energy transition, emphasizing the unique ability to deliver integrated solutions that provide reliable, affordable, and sustainable power—from generation to grid.
Differentiate through the unparalleled breadth of the portfolio and the massive installed base. Focus on being the pragmatic, reliable leader that can both optimize existing assets (gas, steam) for decarbonization and deploy new technologies (wind, grid software) at scale.
Whitespace Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Turnkey Decarbonization for Heavy Industry
Competitive Gap:While competitors offer components (e.g., variable speed drives, electric furnaces), few provide a fully integrated, financed, and managed solution for decarbonizing complex industrial sites like steel mills or cement plants.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Grid Resilience as a Service
Competitive Gap:Most competitors sell grid hardware and software. There is a gap for offering outcome-based services to municipalities, data center operators, and industrial parks that guarantee power quality and uptime by deploying and managing a portfolio of assets (BESS, STATCOMs, microgrids).
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Specialized Power Solutions for Data Centers
Competitive Gap:Data centers have unique power needs (high reliability, rapid deployment, sustainability). A dedicated business unit or offering that bundles gas turbines, grid connections, energy storage, and management software specifically for this vertical could capture significant market share.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
End-of-Life Asset Management & Repowering
Competitive Gap:As the first generation of wind and solar farms reaches the end of its life, there is a significant opportunity to provide comprehensive repowering, recycling, and grid upgrade services. GE Vernova's service expertise and OEM knowledge provide a distinct advantage.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:Medium
GE Vernova enters the market as a purpose-built energy transition leader, spun off from General Electric with a formidable portfolio and a massive global installed base. The competitive landscape is an oligopoly of established industrial giants, with Siemens Energy representing the most direct competitor, mirroring GE Vernova's business segments almost exactly. However, GE Vernova currently holds a strategic advantage due to its stronger balance sheet and focused narrative, while Siemens Energy is encumbered by significant issues in its wind division.
The primary competitive arena is defined by the global imperative to electrify and decarbonize. Key battlegrounds include: 1) Gas Power, where GE Vernova competes with MHI's leading turbine technology; 2) Wind Power, a challenging market where it vies with pure-play leader Vestas and faces intense margin pressure; and 3) Electrification, a high-growth segment where it contends with grid specialists like Hitachi Energy and automation leaders like Schneider Electric.
GE Vernova's most sustainable competitive advantage is its installed base, which powers approximately 25% of the world's electricity. This base provides a durable, high-margin service revenue stream and a captive audience for technological upgrades—a moat that is nearly impossible for new entrants to replicate. Its integrated portfolio is another key strength, enabling the delivery of complex, end-to-end solutions that few competitors can match.
Key strategic challenges include navigating the low-margin, highly competitive wind market and fending off both industrial incumbents and specialized software firms in the high-growth grid digitalization space. Opportunities abound in servicing the surging electricity demand from data centers and AI, providing turnkey decarbonization solutions for heavy industry, and positioning its software platforms as the central nervous system for the modern grid. To win, GE Vernova must leverage its scale and integrated portfolio to be the pragmatic, reliable partner for utilities and industries navigating the complexities of the energy transition, differentiating itself not just on individual product performance but on its ability to orchestrate entire systems.
Messaging
Message Architecture
Key Messages
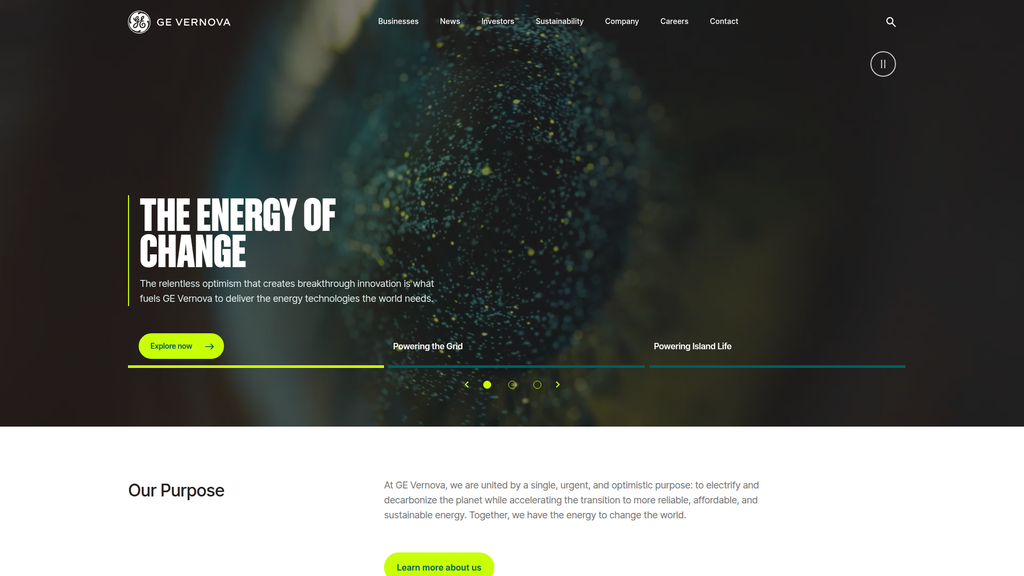
- Message:
the energy of change
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:Medium
Location:Homepage Hero Banner
- Message:
To electrify and decarbonize the planet while accelerating the transition to more reliable, affordable, and sustainable energy.
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Our Purpose section, Homepage
- Message:
Continuing to electrify the world while simultaneously working to help decarbonize it.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Partner with us section, Homepage
- Message:
As innovators in advanced energy conversion and storage systems, we empower our utility and industrial customers by solving their most challenging electrification problems and accelerating their transition to a sustainable, decarbonized future.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Power Conversion Page Header
The messaging hierarchy is generally effective. The primary message, 'the energy of change,' is aspirational and memorable, positioned at the very top of the homepage. It is immediately followed and clarified by a more concrete purpose statement ('electrify and decarbonize'). This structure successfully moves from a high-level, emotional brand concept to a tangible mission. However, the connection between 'the energy of change' and the specific, technical solutions offered could be more direct on the homepage.
Messaging is highly consistent. The core dual theme of 'electrification and decarbonization' is repeated across the homepage and the Power Conversion sub-page, creating a strong, unified narrative. The sub-page effectively translates the high-level corporate purpose into a specific value proposition for its target audience ('empower our utility and industrial customers').
Brand Voice
Voice Attributes
- Attribute:
Optimistic & Aspirational
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
The relentless optimism that creates breakthrough innovation...
- •
Together, we have the energy to change the world.
- •
If you are ready to make a difference and usher in the new era of energy, come join us.
- Attribute:
Purpose-Driven
Strength:Strong
Examples
At GE Vernova, we are united by a single, urgent, and optimistic purpose...
advancing our mission to electrify and decarbonize the world.
- Attribute:
Innovative & Expert
Strength:Moderate
Examples
- •
As innovators in advanced energy conversion and storage systems...
- •
GE Vernova experts are curating vital intelligence on electricity systems worldwide...
- •
bridging energy-intensive computing and renewables for a lower-carbon future.
- Attribute:
Corporate & Formal
Strength:Moderate
Examples
GE Vernova announces new Chief Legal Officer and Corporate Secretary
GE Vernova has signed a supply agreement with Elsewedy Electric Power Systems Projects...
Tone Analysis
Motivational
Secondary Tones
Informative
Corporate
Tone Shifts
The tone shifts from broadly aspirational on the homepage ('the energy of change') to more technical and solution-focused on the 'Power Conversion' page ('integrated electrical systems', 'STATCOMs'). This is an appropriate and effective shift for the target audience of that section.
Voice Consistency Rating
Excellent
Consistency Issues
No itemsValue Proposition Assessment
GE Vernova provides a comprehensive portfolio of technologies and expertise to lead the global energy transition, enabling customers to both electrify and decarbonize their operations reliably and sustainably.
Value Proposition Components
- Component:
Comprehensive Technology Portfolio
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
- Component:
Innovation in Energy Transition
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
- Component:
Global Scale and Experience (130+ years heritage)
Clarity:Somewhat Clear
Uniqueness:Unique
- Component:
Partnership and Problem-Solving for Complex Challenges
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Common
GE Vernova's primary differentiator is its unique combination of a legacy brand (GE), massive global scale, and a purpose-built focus on the energy transition. While competitors like Siemens Energy and Schneider Electric offer similar solutions, the messaging leverages the GE heritage as a badge of quality and ingenuity. The core message of simultaneously electrifying and decarbonizing is a strong position, addressing the central challenge of the energy sector. The differentiation lies less in any single technology and more in the claimed ability to orchestrate the entire transition at scale.
The messaging positions GE Vernova as a pivotal leader in the energy transition, on par with or exceeding major competitors like Siemens Energy. The focus on 'purpose-built' and the new 'Vernova' brand identity aims to frame it as more agile and focused than a traditional conglomerate, while retaining the trust and scale of its GE roots. This positions them to attract large-scale, complex projects with utilities and industrial giants who require a dependable, experienced partner for a multi-decade transition.
Audience Messaging
Target Personas
- Persona:
Utility Executives & Grid Operators
Tailored Messages
- •
Update on GE Vernova expansion of Pennsylvania Factory to manufacture more critical grid technologies
- •
Island Destinations Strengthen Grids for a Renewable Future
- •
Solutions for Power Stability: Synchronous Condensers, STATCOMs, SVCs
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Industrial C-Suite (e.g., in Metals, Mining, Oil & Gas)
Tailored Messages
- •
Power Conversion & Storage business works closely with end users in energy-intense industrial applications.
- •
Solutions for Industrial Electrification: Furnace Electrification, H2 Compressors, Offshore Decarb
- •
Powering Data Growth with Flexible Gas Technology
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Potential Employees / Talent
Tailored Messages
Come bring the energy to change the world
If you are ready to make a difference and usher in the new era of energy, come join us.
Effectiveness:Somewhat Effective
- Persona:
Investors & Partners
Tailored Messages
- •
Latest Announcements (Press Releases)
- •
GE Vernova CEO Scott Strazik to speak at 13th Annual Morgan Stanley Laguna Conference
- •
Partner with us
Effectiveness:Effective
Audience Pain Points Addressed
- •
Grid instability due to renewable integration
- •
Need to decarbonize energy-intensive industrial processes
- •
Aging or inadequate grid infrastructure
- •
Complexity of managing the energy transition
Audience Aspirations Addressed
- •
Achieving corporate sustainability and net-zero goals
- •
Creating a more reliable, affordable, and sustainable energy future
- •
Leading innovation in the new energy era
- •
Driving business growth through sustainable technology
Persuasion Elements
Emotional Appeals
- Appeal Type:
Hope / Optimism
Effectiveness:High
Examples
The relentless optimism that creates breakthrough innovation...
The Energy of Change
- Appeal Type:
Sense of Purpose / Mission
Effectiveness:High
Examples
we are united by a single, urgent, and optimistic purpose...
advancing our mission to electrify and decarbonize the world.
Social Proof Elements
- Proof Type:
News & Media Coverage
Impact:Strong
- Proof Type:
Specific Customer Stories / Case Studies
Impact:Moderate
- Proof Type:
Partnership Announcements
Impact:Strong
Trust Indicators
- •
Explicit mention of company size ('75,000 strong across about 100 countries')
- •
Legacy connection to GE (a well-established industrial brand)
- •
Professional design and corporate tone
- •
Regular press releases and announcements
Scarcity Urgency Tactics
The messaging uses a sense of societal urgency ('urgent...purpose') related to climate change rather than commercial scarcity tactics.
Calls To Action
Primary Ctas
- Text:
Explore more
Location:Homepage Hero
Clarity:Somewhat Clear
- Text:
Learn more
Location:Various sections (Our Purpose, Feature Stories)
Clarity:Somewhat Clear
- Text:
Contact Us
Location:Partner with us section
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Careers with GE Vernova
Location:Careers section
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Subscribe Now
Location:Newsletter section
Clarity:Clear
The CTAs are clear in their direction but lack compelling, benefit-oriented language. 'Learn more' and 'Explore more' are generic and could be improved to create more specific intent (e.g., 'See our Grid Solutions' or 'Discover our Decarbonization Tech'). The primary conversion-focused CTAs, 'Contact Us' and 'Subscribe Now,' are well-placed and direct. Overall effectiveness is moderate; they guide the user journey but don't actively persuade.
Messaging Gaps Analysis
Critical Gaps
Quantifiable Impact: The messaging is strong on purpose but weak on quantifiable results. There are few metrics, data points, or specific KPIs that demonstrate the real-world impact of their solutions (e.g., 'reduced emissions by X%', 'improved grid efficiency by Y%').
Customer-Centric Outcomes: While feature stories exist, the primary messaging doesn't consistently frame value in terms of customer outcomes. It often focuses on what GE Vernova does ('we provide solutions') rather than what the customer achieves ('you gain grid stability').
Contradiction Points
A potential messaging tension exists between the mission to 'decarbonize' and the prominent featuring of solutions for the Oil & Gas industry and 'flexible gas technology'. While this reflects the reality of the energy transition, the website could more proactively address how these activities align with the overall decarbonization goal to prevent perceptions of contradiction.
Underdeveloped Areas
Competitive Differentiation: The site asserts leadership but doesn't explicitly message why GE Vernova is a better choice than a key competitor like Siemens Energy. The GE legacy is implied but not fully leveraged as a unique advantage.
Thought Leadership Content: The 'Feature Stories' are a good start, but there's an opportunity to build a more robust thought leadership platform with in-depth white papers, research reports, and executive insights that would further solidify their expert positioning.
Messaging Quality
Strengths
- •
Strong, unified, and memorable core purpose ('electrify and decarbonize').
- •
Aspirational and optimistic brand theme ('The Energy of Change') that is well-suited for a company tackling global challenges.
- •
Excellent consistency in messaging across different website sections.
- •
Clear, albeit high-level, segmentation of solutions for different industries on the Power Conversion page.
Weaknesses
- •
Over-reliance on corporate jargon and abstract concepts ('relentless optimism', 'breakthrough innovation') without sufficient concrete evidence.
- •
Lack of quantifiable proof points to substantiate claims of impact and effectiveness.
- •
Generic calls-to-action that could be more specific and compelling.
Opportunities
- •
Develop detailed, data-rich case studies for each target industry to move from storytelling to proof of performance.
- •
Create dedicated content journeys for key personas (e.g., a 'Utility Leader's Guide to Grid Modernization') that directly address their pain points.
- •
Integrate more direct 'voice of the customer' elements, such as testimonials or quotes, to build trust and credibility.
Optimization Roadmap
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Value Proposition Communication
Recommendation:Incorporate a 'By the Numbers' section on the homepage highlighting key metrics, such as 'Installed base generates 25% of the world's electricity', GW of renewable energy installed, or total CO2 reduction enabled by technology. This adds immediate credibility.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Calls-to-Action
Recommendation:Replace generic CTAs like 'Learn More' with more specific, action-oriented language. For example, change the CTA under 'Powering the Grid' to 'See Our Grid Solutions' or 'Explore the Case Study'.
Expected Impact:Medium
- Area:
Audience Messaging
Recommendation:Develop dedicated landing pages or content hubs for each key industry (Utilities, Metals, Marine, etc.) that go beyond a list of solutions and feature targeted case studies, insights, and expert contacts for that specific sector.
Expected Impact:High
Quick Wins
- •
Update CTAs with more specific and compelling language.
- •
Add a statistics-based headline to the 'Partner with us' section.
- •
Feature a prominent customer quote or testimonial on the homepage.
Long Term Recommendations
- •
Build out a comprehensive thought leadership library with downloadable assets (white papers, reports) to capture leads and demonstrate deep industry expertise.
- •
Develop a messaging framework to proactively address the role of gas and O&G solutions within the broader decarbonization mission, turning a potential contradiction into a point of pragmatic strength.
- •
Create an interactive 'Solutions Finder' tool to help prospective customers from different industries quickly navigate to the most relevant technologies and case studies.
GE Vernova's strategic messaging is built on a powerful and timely foundation: leading the global energy transition by simultaneously electrifying and decarbonizing the planet. The core brand theme, 'the energy of change,' is aspirational and effectively frames the company's mission with a sense of optimistic urgency. The message architecture is consistent and logical, moving from a high-level purpose to more specific solutions for target B2B audiences. The brand voice is motivational and purpose-driven, which is appropriate for engaging employees, partners, and customers around a shared, monumental goal.
The primary weakness in the current messaging strategy is a significant gap between the aspirational claims and concrete, quantifiable proof. The website effectively communicates what GE Vernova aims to do but falls short in demonstrating how well it does it. The value proposition, while strong, relies heavily on the implied trust of the GE legacy rather than on explicit data, customer testimonials, or competitive differentiators. This creates a risk of the messaging being perceived as high-level corporate branding rather than a compelling business case.
To drive measurable business outcomes, the messaging must evolve from asserting purpose to proving performance. This involves integrating specific metrics of success, framing solutions around customer-centric outcomes, and making a clearer case for why GE Vernova's scale and portfolio offer a distinct advantage over competitors. By enriching the powerful 'why' with a data-driven 'how,' GE Vernova can convert its aspirational brand positioning into a powerful engine for customer acquisition and market leadership.
Growth Readiness
Growth Foundation
Product Market Fit
Strong
Evidence
- •
GE Vernova is a recently spun-off entity from General Electric, inheriting a massive installed base, deep engineering expertise, and long-standing customer relationships in the global energy sector.
- •
The company reported strong Q2 2025 results with revenue of $9.1 billion (up 11% YoY) and a backlog of $128.7 billion, indicating sustained high demand for its core offerings.
- •
Its portfolio directly addresses the global mega-trends of electrification and decarbonization, with specific solutions for grid modernization, renewable energy integration, and industrial efficiency.
- •
Secured major contracts and agreements with global entities like Saudi Electricity Company and partnerships with companies like Crusoe Energy for data center power demonstrate market trust and demand.
Improvement Areas
- •
Further integrate and promote digital and AI-powered solutions, like the GridOS platform, to create higher-margin, recurring revenue streams and enhance the value of core hardware.
- •
Clarify and simplify the value proposition of integrated solutions that span across the Power, Wind, and Electrification segments to solve complex customer problems holistically.
- •
Increase focus on customer-centric service models, potentially moving towards 'Energy-as-a-Service' offerings for specific industrial applications.
Market Dynamics
The global energy transition market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.4% to 15.41%, reaching over $6.4 trillion by 2032. Key sub-segments like grid modernization (~16% CAGR) and battery energy storage (~27% CAGR) are growing even faster.
Mixed: The market for traditional gas power is mature, while segments like grid-scale battery storage, green hydrogen, and advanced grid software are in a high-growth phase.
Market Trends
- Trend:
Accelerating Electrification & Decarbonization
Business Impact:Massive tailwind for GE Vernova's entire portfolio, from power generation to grid solutions, driven by global policy, corporate sustainability goals, and declining renewable energy costs.
- Trend:
Surging Power Demand from AI and Data Centers
Business Impact:Creates urgent demand for stable, reliable power, boosting the market for gas turbines, grid infrastructure, and integrated power solutions.
- Trend:
Grid Modernization Imperative
Business Impact:Aging infrastructure and the need to integrate intermittent renewables are driving multi-trillion dollar investments in grid technologies, a core strength of the Electrification segment.
- Trend:
Digitalization of Energy Systems
Business Impact:Opportunity to layer high-margin software, analytics, and AI-driven optimization services (e.g., GridOS) on top of the existing hardware footprint.
Excellent. GE Vernova's spin-off coincides with a massive global investment cycle in energy transition and grid infrastructure, placing it in a prime position to capture significant market share.
Business Model Scalability
Medium
High fixed costs associated with R&D, manufacturing facilities, and a global sales/service footprint. Scalability depends on maximizing factory throughput and winning large-scale, high-margin projects and service contracts.
Moderate. Operational leverage is achieved through service agreements on the massive installed base and by standardizing product platforms (e.g., gas turbines, inverters) to reduce per-unit costs.
Scalability Constraints
- •
Manufacturing capacity for physical hardware (e.g., transformers, turbines).
- •
Global supply chain dependencies for raw materials and components.
- •
Requirement for highly specialized engineering and project management talent.
- •
Long sales and implementation cycles for large infrastructure projects.
Team Readiness
High. The leadership team comprises seasoned executives from GE with deep domain expertise in the energy and industrial sectors, well-equipped to manage a large, global enterprise.
Appropriate. The structure with three core segments (Power, Wind, Electrification) provides clear focus, but fostering cross-segment collaboration will be critical for delivering integrated solutions.
Key Capability Gaps
- •
Agile software product development and digital marketing talent to accelerate the growth of software-based solutions.
- •
Expertise in new business models like 'Energy-as-a-Service' and complex project financing.
- •
Specialized talent in emerging technologies like green hydrogen and long-duration energy storage.
Growth Engine
Acquisition Channels
- Channel:
Direct Enterprise Sales
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Equip sales teams with digital tools for account-based marketing (ABM) and social selling to target key accounts in high-growth verticals like data centers.
- Channel:
Strategic Partnerships (EPCs, Utilities)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Develop a formal partner program with tiered benefits, co-marketing funds, and technical certifications to expand reach and market penetration.
- Channel:
Industry Events & Thought Leadership
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Amplify presence at key events through targeted digital campaigns and by publishing high-value technical content (whitepapers, case studies) to capture leads.
- Channel:
Content Marketing / PR
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Create dedicated content hubs for key growth areas (e.g., 'Powering AI', 'Grid of the Future') to improve SEO and attract qualified inbound interest from technical decision-makers.
Customer Journey
Long and complex, relationship-based B2B/B2G sales cycle involving awareness, technical evaluation, RFP, negotiation, and procurement. The website serves as a crucial resource for initial research and validation.
Friction Points
- •
Navigating the vast portfolio on the website to find specific, integrated solutions for a complex problem.
- •
Transition from initial web-based inquiry to engagement with the correct technical sales expert.
- •
Long lead times for proposals and project scoping due to complexity.
Journey Enhancement Priorities
{'area': 'Digital Experience', 'recommendation': "Implement an interactive 'Solution Finder' on the website to guide users based on industry and challenge, leading them to relevant case studies and technical experts."}
{'area': 'Sales Enablement', 'recommendation': 'Develop a robust internal knowledge base and digital asset library to help sales teams quickly access technical specifications, pricing models, and competitive intelligence.'}
Retention Mechanisms
- Mechanism:
Long-Term Service Agreements (LTSAs)
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Embed digital twin, predictive maintenance, and performance optimization services into all new LTSAs to increase recurring revenue and demonstrate ongoing value.
- Mechanism:
Technology Upgrades & Modernization
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Proactively market upgrade paths to the installed base, focusing on efficiency improvements, fuel flexibility (e.g., hydrogen readiness), and digital enhancements.
- Mechanism:
Incumbent Technology Provider (High Switching Costs)
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Strengthen relationships through executive business reviews and by becoming a strategic advisor on customers' long-term decarbonization roadmaps.
Revenue Economics
Project-based and highly variable. Profitability depends on accurate bidding, efficient project execution, and attaching high-margin, long-tail service contracts to initial equipment sales.
Unquantifiable publicly, but expected to be very strong. Customer Lifetime Value is extremely high (often decades of service revenue), while Customer Acquisition Cost is also high but spread over massive contracts.
Strong, as evidenced by a growing backlog and positive free cash flow guidance. The Power and Electrification segments show strong margin expansion, though the Wind segment faces profitability challenges.
Optimization Recommendations
- •
Increase the attach rate of service contracts on all new equipment sales.
- •
Leverage lean manufacturing principles and supply chain optimization to improve gross margins on hardware.
- •
Price digital offerings based on value delivered (e.g., efficiency gains, downtime reduction) rather than cost-plus.
Scale Barriers
Technical Limitations
- Limitation:
Supply Chain for Critical Components
Impact:High
Solution Approach:Diversify supplier base, invest in domestic manufacturing capacity (as planned with the $0.6B investment), and form strategic partnerships for key materials like rare earth minerals and electrical steel.
Operational Bottlenecks
- Bottleneck:
Project Management of Complex Global Deployments
Growth Impact:Limits the number of large-scale projects that can be executed simultaneously, impacting revenue growth.
Resolution Strategy:Invest in advanced project management software, standardize deployment methodologies, and create specialized rapid-deployment teams for key solution types.
- Bottleneck:
Navigating Diverse and Complex Regulatory Environments
Growth Impact:Slows market entry and project approval, delaying revenue.
Resolution Strategy:Build dedicated, in-country policy and regulatory affairs teams to proactively manage compliance and build relationships with government agencies.
Market Penetration Challenges
- Challenge:
Intense Competition from Global Players
Severity:Critical
Mitigation Strategy:Compete on technological differentiation (e.g., HA-class turbines, SF₆-free grid tech), integrated solutions, and the strength of the long-term service network. Key competitors include Siemens Energy, Schneider Electric, and ABB.
- Challenge:
Price Competition from Low-Cost Manufacturers
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), highlighting reliability, efficiency, and long-term service value over initial capital cost. Avoid competing solely on price for commoditized hardware.
- Challenge:
Profitability in the Wind Segment
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Continue restructuring and cost-out initiatives, focus on the most profitable geographies and turbine models, and improve service margins to offset equipment pricing pressure.
Resource Limitations
Talent Gaps
- •
Power systems engineers with grid modernization expertise
- •
Software and data scientists for AI/ML applications in energy
- •
Specialists in hydrogen and carbon capture technologies
Significant and ongoing capital required for R&D in next-gen technologies, manufacturing capacity expansion, and potential strategic acquisitions.
Infrastructure Needs
Expanded and modernized manufacturing facilities to meet demand for grid components and turbines.
A unified, cloud-based digital platform to support both internal operations and external customer-facing services (e.g., GridOS).
Growth Opportunities
Market Expansion
- Expansion Vector:
Deeper Penetration into the Data Center Vertical
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:Medium
Recommended Approach:Create a dedicated business unit offering an integrated 'Grid-to-Chip' solution, combining gas power, grid connection, and energy management software, marketed directly to hyperscalers and data center developers.
- Expansion Vector:
Geographic Expansion in Southeast Asia and Africa
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:High
Recommended Approach:Establish regional hubs and form joint ventures with local partners to navigate regulatory landscapes and build infrastructure for rapidly growing electricity demand.
Product Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Integrated Grid Software & Hardware Solutions
Market Demand Evidence:Utilities are increasingly seeking end-to-end solutions for grid modernization, not just components. The Electrification segment's strong performance points to this demand.
Strategic Fit:High
Development Recommendation:Bundle GridOS software with sales of high-voltage equipment and create packaged solutions for specific use cases like microgrids, substation automation, and DERMS (Distributed Energy Resource Management Systems).
- Opportunity:
Energy as a Service (EaaS) for Industrial Clients
Market Demand Evidence:Industrial companies want to decarbonize without large upfront capital expenditure, creating a market for outcome-based service models.
Strategic Fit:Medium
Development Recommendation:Launch pilot projects offering a fully managed, financed solution for onsite power generation and energy storage, targeting energy-intensive industries like manufacturing and mining.
- Opportunity:
Green Hydrogen Production Technology
Market Demand Evidence:Hydrogen is a key vector for decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors. Competitors like Siemens Energy are already investing heavily in electrolyzer production.
Strategic Fit:High
Development Recommendation:Leverage expertise in power electronics and industrial processes to partner with or acquire an electrolyzer technology company, integrating it into a holistic 'Power-to-X' offering.
Channel Diversification
- Channel:
Digital Self-Service Portal for Parts & Components
Fit Assessment:Good for standardized, high-volume products.
Implementation Strategy:Develop an e-commerce platform for service partners and end-customers to purchase spare parts and smaller components, reducing the burden on the direct sales force.
Strategic Partnerships
- Partnership Type:
Technology & AI Integration
Potential Partners
- •
NVIDIA
- •
AWS
- •
Microsoft Azure
- •
Palantir
Expected Benefits:Co-develop AI-driven grid optimization and predictive maintenance algorithms; create joint go-to-market strategies for powering the AI economy.
- Partnership Type:
Project Financing
Potential Partners
- •
Blackstone
- •
Brookfield Asset Management
- •
Macquarie Group
Expected Benefits:Create joint ventures or financing vehicles to offer customers integrated technology and capital solutions, de-risking large projects and accelerating sales cycles.
Growth Strategy
North Star Metric
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) from Services & Digital
This metric shifts focus from volatile, project-based revenue to stable, high-margin, and scalable revenue streams. It directly measures the success of the strategy to layer digital services on the hardware installed base, which is critical for long-term profitable growth.
Increase ARR by 20% year-over-year for the next three years.
Growth Model
Hybrid: Enterprise Sales-Led & Ecosystem-Driven
Key Drivers
- •
Effectiveness of the direct sales force in winning large, multi-year contracts.
- •
Breadth and depth of the certified partner ecosystem (EPCs, system integrators).
- •
Attach rate of long-term service and digital contracts to hardware sales.
- •
Technology leadership demonstrated through R&D and thought leadership.
Focus direct sales on the largest strategic accounts and complex, integrated projects. Simultaneously, build a scalable partner program to address the mid-market and specific geographic territories.
Prioritized Initiatives
- Initiative:
Launch 'AI Data Center Power' Integrated Offering
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:6-9 months
First Steps:Form a cross-functional team from Power and Electrification. Develop a standardized reference architecture and TCO model. Identify and target the top 10 global data center developers.
- Initiative:
Digitize the Long-Term Service Agreement (LTSA) Offering
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:12 months
First Steps:Mandate the inclusion of a baseline digital services package (remote monitoring, basic analytics) in all new LTSAs. Develop premium, paid tiers with advanced AI-powered optimization.
- Initiative:
Establish a Strategic Partnership with a Major Cloud Provider (e.g., AWS, Azure)
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:12-18 months
First Steps:Initiate executive-level discussions to define joint value propositions around grid data management, AI-powered grid optimization, and powering their data center infrastructure.
Experimentation Plan
High Leverage Tests
{'experiment': 'Test outcome-based pricing models for digital services (e.g., charge based on % of fuel savings achieved).', 'hypothesis': 'Value-based pricing will increase adoption and willingness to pay for digital solutions compared to flat-fee SaaS models.'}
{'experiment': "Pilot a 'fast-track' program for standardized grid connection projects.", 'hypothesis': 'A streamlined process for common project types can reduce sales cycle time by 30% and improve customer satisfaction.'}
Use an Impact/Effort matrix to prioritize ideas. For each experiment, define a primary success metric (e.g., conversion rate, sales cycle length), a timeframe, and a clear go/no-go decision point.
Quarterly review of strategic growth experiments by a dedicated growth council.
Growth Team
A centralized 'Strategic Growth Office' that reports to the C-suite. This office will not own execution but will be responsible for identifying, validating, and incubating new growth initiatives before handing them off to the business units.
Key Roles
- •
Head of New Ventures
- •
Director of Strategic Partnerships
- •
Market Intelligence Lead
- •
Business Model Innovation Lead
Establish a cross-functional task force for each prioritized growth initiative, composed of members from product, sales, finance, and engineering, to ensure alignment and rapid execution.
GE Vernova is exceptionally well-positioned for sustained growth, having spun off at the inflection point of the global energy transition. Its foundational strength is its massive installed base and deep engineering credibility, which provides a formidable competitive moat and a fertile ground for high-margin service revenue.
The most significant growth lever is the systematic digitization of its business. The company must transition from being primarily a world-class hardware provider to a hardware-enabled software and services powerhouse. The key to this is embedding digital solutions like GridOS and predictive analytics into its core offerings, particularly through long-term service agreements, thereby creating a more predictable, scalable, and profitable revenue model. The explosive growth in electricity demand from AI and data centers presents an immediate, high-value opportunity to package integrated solutions for a specific, well-funded vertical.
Key barriers are primarily operational and competitive. Scaling the manufacturing and delivery of complex physical infrastructure is capital-intensive and subject to supply chain risks. Competition from established giants like Siemens Energy and Schneider Electric is fierce, requiring continuous technological innovation to maintain an edge. The underperformance of the Wind segment remains a drag on overall profitability and requires decisive strategic action.
To accelerate growth, the strategy should be twofold: 1) Defend and Digitize the Core by maximizing the value of the installed base with digital services and upgrades. 2) Attack New Frontiers by aggressively pursuing integrated solutions for high-growth verticals like data centers and making strategic plays in emerging areas like green hydrogen. Success will be defined by the ability to increase the proportion of high-margin, recurring revenue, transforming GE Vernova into a true leader of the digital and sustainable energy future.
Legal Compliance
GE Vernova provides a comprehensive, multi-layered Privacy Policy accessible via the website footer. The policy, updated as of April 2, 2024, covers key areas such as the types of personal information collected, how it is used, and the legal basis for processing (consent, contract performance, legitimate business interests, legal compliance). It specifically mentions that GE Vernova does not sell personal information but may share it within the GE Vernova Group and with contracted service providers. The policy also addresses international data transfers and children's privacy, stating the site is not directed at children under 13. It provides information on user rights (access, correction, etc.) and gives contact details for privacy-related inquiries. The policy's structure and content demonstrate a strong understanding of global privacy principles, likely covering requirements for GDPR and CCPA.
The 'Terms of Use' are clearly accessible from the website footer and were last updated on July 16, 2024. The terms define the relationship between GE Vernova and the user, disclaiming responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of information on the site and positioning it for 'general information only'. Key clauses include limitations on the use of site materials for personal, non-commercial purposes, prohibitions on unauthorized marketing or data interception, and a clear statement on the ownership of intellectual property. The terms also include a standard disclaimer of warranties and limitation of liability. By referencing the site's Privacy Policy for the handling of personal information, it correctly links the two crucial legal documents. The enforceability appears standard for a corporate B2B website.
The website implements a robust cookie consent mechanism. Upon first visit, a banner appears providing granular control over cookie preferences, which aligns with GDPR requirements. The Privacy Policy clearly explains the use of cookies and similar technologies for personalization and analytics. It categorizes cookies (Essential, Advertising) and directs users to a 'Cookie Consent Tool' accessible via a 'Cookies' link in the footer to manage their preferences at any time. This tool allows users to make choices about both GE Vernova and third-party partner cookies, demonstrating a high level of transparency and user control. This is a best-practice implementation that mitigates risks associated with non-compliant tracking.
GE Vernova's overall data protection framework appears mature and well-documented. The combination of a detailed Privacy Policy and a granular Cookie Consent Tool addresses the core requirements of major data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA. The company explicitly states the legal bases for processing data, acknowledges user rights, and provides mechanisms for users to exercise those rights. Furthermore, they have a 'Commitment to the Protection of Personal Information' that outlines principles of fairness, purpose limitation, proportionality, and security in data processing. The company's global presence across North America, Europe, Asia, and other regions necessitates this robust approach to navigate varying international data protection laws effectively.
The website shows a foundational awareness of accessibility principles. The inclusion of a 'Skip to main content' link at the top of the page is a positive indicator for users of screen readers and keyboard-only navigation. However, a comprehensive analysis would require automated and manual testing against Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 Level AA standards, which is the benchmark for ADA compliance in the U.S. and similar regulations globally. Without a formal accessibility statement or a visible accessibility widget, it is unclear to what extent the site fully conforms to requirements like sufficient color contrast, proper heading structures, and ARIA labels for all interactive elements. This represents a potential compliance gap and a risk area for litigation.
As a publicly traded (NYSE: GEV), global energy technology company, GE Vernova is subject to a complex web of industry-specific regulations. Key areas include:
1. SEC Regulations: As a U.S. public company, GE Vernova must adhere to SEC disclosure rules, including filing Forms 10-K and 10-Q. The website's 'Investors' section is a critical hub for this compliance, but any forward-looking statements made on the general website (e.g., in press releases or blog posts about new technology) should be accompanied by a 'safe harbor' statement to mitigate litigation risk under the PSLRA of 1995. While press releases may contain such language, its absence on general marketing pages could be a gap.
2. Energy Sector Regulations: The company operates in a highly regulated field governed by bodies like the FERC in the U.S. and international equivalents. Compliance involves environmental standards (e.g., emissions), grid modernization, and cybersecurity for critical infrastructure. The website content, which focuses on decarbonization and grid stability, implicitly reflects these regulatory drivers but must be careful not to make unsubstantiated environmental or performance claims that could attract regulatory scrutiny.
3. Anti-Bribery and Corruption: For a company with global operations and large-scale industrial contracts, adherence to laws like the FCPA (U.S.) and the UK Bribery Act is paramount. While not directly a website compliance issue, the site should project a strong ethical posture, often supported by a publicly available code of conduct or ethics policy.
Compliance Gaps
- •
Absence of a visible and dedicated 'Accessibility Statement' detailing the company's commitment and conformance level to WCAG standards.
- •
Lack of consistent 'safe harbor' disclaimers for forward-looking statements on marketing and news pages outside of formal investor relations documents.
- •
The Terms of Use do not specify a governing law or jurisdiction for dispute resolution, creating potential legal ambiguity.
- •
No explicit mention of data protection rights specific to residents of states other than California (e.g., Virginia, Colorado, Utah) which have their own privacy laws.
Compliance Strengths
- •
Comprehensive and clearly written Privacy Policy that addresses key requirements of major global regulations like GDPR.
- •
Implementation of a granular, user-friendly Cookie Consent Tool that provides clear opt-in/opt-out choices.
- •
Clear separation and accessibility of key legal documents (Privacy Policy, Terms, Cookies) in the website footer.
- •
Presence of basic accessibility features like a 'Skip to main content' link.
Risk Assessment
- Risk Area:
Accessibility (ADA/WCAG)
Severity:High
Recommendation:Conduct a full WCAG 2.1 AA audit of the website. Remediate all identified issues and publish an 'Accessibility Statement' to demonstrate commitment and reduce legal risk from demand letters and lawsuits.
- Risk Area:
Forward-Looking Statements (SEC)
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Incorporate a concise 'safe harbor' statement or link to a full disclaimer on all pages containing press releases, news, or technology descriptions that discuss future plans, projections, or performance.
- Risk Area:
Data Privacy (U.S. State Laws)
Severity:Low
Recommendation:Update the Privacy Policy to explicitly mention and address the rights of consumers under other emerging U.S. state privacy laws beyond CCPA/CPRA to ensure comprehensive nationwide compliance.
- Risk Area:
Terms of Use
Severity:Low
Recommendation:Amend the Terms of Use to include a governing law and jurisdiction clause (e.g., State of Delaware or Massachusetts, where the company is headquartered) to provide legal certainty in case of disputes.
High Priority Recommendations
Immediately commission a third-party accessibility audit against WCAG 2.1 Level AA standards and create a remediation plan to address critical findings. Following this, publish a formal Accessibility Statement on the website.
Review all public-facing content, particularly in the 'News' and 'Innovation' sections, and add a standard legal disclaimer for any forward-looking statements to mitigate potential securities litigation risk.
GE Vernova's website demonstrates a sophisticated and mature approach to legal compliance, particularly in the areas of data privacy and cookie consent. The legal infrastructure is robust, reflecting the company's status as a major global, publicly-traded entity. The Privacy Policy and consent mechanisms are well-aligned with the stringent requirements of GDPR, which positions the company strongly for operating in the EU and other regions with similar laws.
However, there are strategic risks and compliance gaps that need attention. The most significant is in web accessibility. The lack of a formal accessibility posture and conformance statement creates a notable legal vulnerability in the U.S. market, where ADA-related digital accessibility lawsuits are common. For a B2B company that contracts with government and public entities, failing to meet accessibility standards could also impact eligibility for certain contracts.
Secondly, while their SEC compliance within the 'Investors' section is likely rigorous, this discipline needs to extend to the broader marketing and news content on the site. The absence of consistent 'safe harbor' disclaimers for forward-looking statements on non-investor pages is a medium-risk gap that could be exploited in shareholder litigation.
Overall, GE Vernova's legal positioning is strong but could be significantly enhanced by proactively addressing accessibility to protect against litigation and reinforce its brand as an inclusive, forward-thinking leader. Bolstering disclaimers around forward-looking statements would further solidify its risk management framework.
Visual
Design System
Modern Corporate
Excellent
Advanced
User Experience
Navigation
Horizontal Top Bar with Mega Menus
Intuitive
Excellent
Information Architecture
Logical
Clear
Moderate
Conversion Elements
- Element:
Homepage Hero 'Reimagining the Grid' CTA
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Somewhat Effective
Improvement:Increase color contrast. The vibrant green call-to-action is a brand accent, but it gets slightly lost against the dark, detailed hero image. Consider a solid color fill on hover or a subtle animated effect to draw more attention.
- Element:
Footer 'Careers with GE Vernova' CTA
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:The prominence and clear, benefit-oriented language ('Come bring the energy to change the world') are strong. No immediate improvement needed, but A/B testing alternative imagery could optimize for different talent pools.
- Element:
Inline 'Subscribe to The Current' CTA
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Somewhat Effective
Improvement:The design is clean but passive. Change the CTA button style from an outline/ghost button to a solid fill of the brand's 'urgency green' to increase its visual weight and encourage clicks.
- Element:
Bottom of Page 'Partner with us' CTA
Prominence:Low
Effectiveness:Ineffective
Improvement:This CTA is visually understated with a small, outlined green button. It should be a more prominent, section-wide banner with a solid, high-contrast button to capture potential B2B partnership leads effectively.
Assessment
Strengths
- Aspect:
Strong Brand Identity & Visual Storytelling
Impact:High
Description:The website effectively communicates the GE Vernova brand, which was intentionally designed to blend GE's legacy with a new focus on sustainability ('Ver' for verde, 'Nova' for new). The use of high-quality, impactful imagery of large-scale energy projects and the diverse workforce creates a powerful narrative of innovation, scale, and human expertise. The 'evergreen' brand color is used consistently and meaningfully.
- Aspect:
Clear Information Architecture
Impact:High
Description:The site structure is logical for its B2B audience, which includes utilities, governments, and industrial customers. It is organized around key business segments like Power, Wind, and Electrification, making it easy for visitors to navigate to their specific areas of interest. The mega menus are well-organized and provide clear pathways to deeper content without overwhelming the user.
- Aspect:
Professional & Trustworthy Aesthetic
Impact:Medium
Description:The overall design aesthetic is clean, modern, and professional. Ample white space, crisp typography, and a structured grid system convey a sense of order, precision, and technological leadership, which is critical for a company in the high-stakes energy sector.
Weaknesses
- Aspect:
Understated Call-to-Action Buttons
Impact:High
Description:Multiple key conversion points, such as the 'Subscribe' and 'Partner with us' CTAs, use ghost buttons (outline only). This significantly reduces their visual prominence, making them easy to overlook. For a B2B site focused on thought leadership and partnerships, these elements should be visually prioritized to drive lead generation and engagement.
- Aspect:
Moderate Cognitive Load on Interior Pages
Impact:Medium
Description:While the homepage is well-balanced, some interior pages, like the 'Power Conversion & Storage' example, present dense blocks of text links under solution categories. This creates a high cognitive load, requiring users to read extensively to find their path. Incorporating icons or brief descriptive text for each solution could improve scannability and user guidance.
- Aspect:
Lack of Interactive Data Visualization
Impact:Low
Description:GE Vernova's business is data-rich, focusing on grid modernization, AI-powered analytics, and efficiency metrics. The site currently relies on static images and text. There is a missed opportunity to engage technical and executive audiences with interactive charts, maps, or data visualizations that demonstrate the impact and scale of their technology.
Priority Recommendations
- Recommendation:
Convert All Primary CTA Buttons to a Solid Fill Style
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:High
Rationale:This is a simple CSS change that will dramatically increase the visibility and click-through rate of key conversion elements like newsletter subscriptions and partnership inquiries. It directly addresses the highest-impact weakness with minimal development effort.
- Recommendation:
Enhance Scannability of Solution Listing Pages
Effort Level:Medium
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:On pages with long lists of solutions (e.g., Power Conversion), introduce iconography and 1-2 sentence descriptions for each category. This will break up text walls, reduce cognitive load, and help diverse users—from engineers to procurement managers—quickly identify relevant information, improving user flow and reducing bounce rates.
- Recommendation:
Develop a Pilot Interactive Content Piece
Effort Level:High
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Create an interactive map or dashboard showcasing GE Vernova's global impact (e.g., number of turbines installed, gigawatts generated). This would serve as a powerful piece of visual storytelling, enhance brand perception as a technology leader, and create highly shareable content for marketing and PR efforts, demonstrating their mission to electrify and decarbonize the world.
Mobile Responsiveness
Excellent
The design adapts seamlessly across major breakpoints (mobile, tablet, desktop). Content reflows logically, navigation collapses into a clear mobile pattern, and font sizes adjust for readability.
Mobile Specific Issues
No itemsDesktop Specific Issues
No itemsThe GE Vernova website is a world-class example of a modern corporate digital presence, successfully launching a new brand identity born from a major corporate restructuring. The design system is mature and executed with excellent consistency, reflecting the brand's core mission to lead the energy transition with innovative, sustainable technology. The visual storytelling is a key strength, utilizing powerful, high-fidelity imagery that communicates the company's global scale and technological prowess.
The user experience is generally strong, with an intuitive navigation system and a logical information architecture tailored to a diverse B2B audience ranging from industrial clients to potential employees. The site effectively segments its vast portfolio of offerings—from gas and wind power to electrification and digital services—into digestible sections. Mobile responsiveness is flawlessly executed, ensuring a consistent and accessible experience across all devices.
The primary area for strategic improvement lies in conversion optimization. Several critical call-to-action (CTA) elements are visually understated, particularly the use of ghost buttons for newsletter subscriptions and partnership inquiries. This represents a significant missed opportunity to capture leads and build engagement. By increasing the visual prominence of these CTAs, GE Vernova can better translate web traffic into tangible business value. Furthermore, while the site is rich in information, some deeper pages would benefit from enhanced scannability and the introduction of interactive elements to reduce cognitive load and more dynamically showcase the company's data-driven capabilities.
Discoverability
Market Visibility Assessment
As a recent spin-off from General Electric, GE Vernova inherits a significant legacy of industrial and engineering authority. The company is positioning itself as a purpose-built leader singularly focused on accelerating the energy transition. Its digital presence communicates a high level of expertise, targeting complex, large-scale energy projects. However, as a new brand, it must actively build its own distinct thought leadership identity separate from GE to avoid being seen as merely a legacy division and instead as an agile, focused innovator in the decarbonization space.
GE Vernova's technology is already integral to generating approximately 30% of the world's electricity, giving it a massive foundational market share. Digitally, its primary competitors include Siemens Energy, Schneider Electric, and ABB. While GE Vernova has strong brand recognition, its visibility in search for specific, solution-oriented keywords (e.g., 'grid modernization software', 'industrial electrification solutions') is contested. Competitors like Siemens and Schneider Electric have established, deep content ecosystems around these topics, presenting a challenge for GE Vernova's organic search visibility and share of voice.
The potential for customer acquisition via digital channels is high but nuanced. The target audience consists of utilities, developers, governments, and large industrial electricity users, who engage in long, research-intensive buying cycles. The website's current content, featuring press releases, project spotlights, and solution pages, is well-suited for the consideration and decision stages. The primary opportunity lies in capturing high-value leads by developing in-depth content that addresses early-stage challenges in grid decarbonization, energy storage, and industrial electrification, thereby intercepting potential customers before they are solution-aware.
GE Vernova operates in over 100 countries with a significant installed base globally. The website reflects this through news of projects in the US, Canada, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey. The digital strategy should leverage this global footprint by creating content that addresses regional energy challenges and regulatory environments. This would enhance search visibility in target markets and demonstrate localized expertise, moving beyond a generic global message to one that resonates with regional decision-makers.
The website demonstrates strong coverage across its three main segments: Power, Wind, and Electrification. The 'Power Conversion' section, for instance, effectively breaks down solutions for specific industries like Marine, Oil & Gas, and Metals. This detailed, industry-specific approach is a strategic asset. The opportunity is to deepen this coverage with technical white papers, case studies, and application notes that showcase expertise and rank for long-tail, high-intent search queries from engineers and project managers within these niche verticals.
Strategic Content Positioning
Content is strongest in the mid-to-late stages of the customer journey, showcasing solutions and corporate announcements. There is a strategic gap in early-stage, problem-aware content. For example, a utility executive first researching the 'challenges of integrating intermittent renewables' or the 'economics of grid modernization' may not find GE Vernova's content. Developing thought leadership that frames these industry problems positions GE Vernova as a strategic advisor, not just a vendor, capturing engagement much earlier in the buying cycle.
A significant opportunity exists to establish a definitive thought leadership platform. Competitors like Siemens and Schneider Electric invest heavily in content that positions them as innovators shaping the future of energy. GE Vernova can claim a unique position by publishing data-driven annual reports on topics like 'The State of Global Electrification' or 'Decarbonization Pathways for Heavy Industry'. This type of cornerstone content would attract high-authority backlinks, media mentions, and mindshare among key decision-makers.
Competitors like Siemens Energy and Schneider Electric heavily promote their digital and software solutions, creating integrated narratives around concepts like 'Digital Enterprise' and 'EcoStruxure'. While GE Vernova has strong individual technology offerings, its digital presence could better articulate a unified, software-enabled vision for the energy transition. Creating a content hub around its own digital ecosystem (e.g., GridOS software ) would close a critical competitive gap and better position it against software-centric competitors.
The core brand message—'to electrify and decarbonize the planet'—is exceptionally strong, consistent, and prominently featured across the website. This purpose-driven message is a powerful strategic asset that unifies its diverse portfolio of gas power, wind, and electrification solutions under a single, compelling mission. This consistency helps build a clear and memorable brand identity in a complex market.
Digital Market Strategy
Market Expansion Opportunities
- •
Develop comprehensive content hubs around emerging energy transition topics such as green hydrogen infrastructure, long-duration energy storage, and the circular economy for wind turbines.
- •
Target the growing power demands of AI and data centers with specific content and solutions demonstrating how GE Vernova's gas power and grid solutions provide the necessary reliability and scale.
- •
Create region-specific content strategies that address local policy incentives (like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act ), grid challenges, and market needs to deepen geographic penetration.
Customer Acquisition Optimization
- •
Shift focus from broad, brand-level marketing to targeted, account-based marketing (ABM) content aimed at specific roles within key accounts (e.g., utility grid planners, industrial plant managers).
- •
Develop high-value, gated content assets (e.g., engineering guides, ROI calculators, technical white papers) to capture qualified leads from high-intent search traffic.
- •
Invest in search visibility for problem-based keywords (e.g., 'how to reduce grid congestion', 'challenges with offshore wind integration') to attract prospects at the beginning of their research journey.
Brand Authority Initiatives
- •
Launch an annual flagship 'State of the Energy Transition' report, combining proprietary data and expert analysis to become a go-to industry resource.
- •
Establish a formal expert speakers bureau, promoting GE Vernova's leaders and engineers for top-tier industry conferences and media opportunities.
- •
Forge strategic content partnerships with leading industry publications, academic institutions, and non-governmental organizations to co-author research and amplify reach.
Competitive Positioning Improvements
- •
Elevate the narrative from being a portfolio of energy technologies to being an end-to-end strategic partner for complex decarbonization projects, showcasing integrated solutions.
- •
Strengthen the digital and software narrative, demonstrating how GE Vernova's intelligent platforms orchestrate the entire energy ecosystem from generation to consumption.
- •
Leverage the GE heritage of innovation and reliability while emphasizing the post-spinoff agility and singular focus on energy, creating a unique 'best of both worlds' positioning.
Business Impact Assessment
Success will be measured by an increase in digital 'Share of Voice' for strategic, non-branded keywords against competitors like Siemens Energy and Schneider Electric. Other key indicators include growth in organic search traffic to solution and industry pages, and an increase in inbound inquiries from target accounts identified through web analytics.
Key metrics include the number of qualified leads generated from gated content downloads, the conversion rate of those leads to sales opportunities, and a reduction in the blended customer acquisition cost (CAC) by improving the efficiency of the digital marketing funnel.
Authority will be measured by the growth in branded search volume, the number and quality of backlinks from authoritative industry and news domains, and the volume of media mentions of GE Vernova's research and thought leadership content.
Benchmarking will involve tracking keyword ranking improvements for high-value terms against a defined list of competitors. Success is also defined by outperforming competitor content on engagement metrics (e.g., time on page, social shares) for key industry topics and achieving top-ranking positions for emerging energy transition themes.
Strategic Recommendations
High Impact Initiatives
- Initiative:
Develop 'Problem/Solution' Content Hubs
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Capture early-stage customer interest and establish GE Vernova as a strategic advisor. Addresses key industry challenges like grid modernization, renewable integration, and industrial electrification.
Success Metrics
- •
Organic rankings for problem-focused keywords
- •
Qualified leads from content downloads
- •
Increase in organic traffic to hub pages
- Initiative:
Launch a Flagship 'State of Decarbonization' Annual Report
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Fill a thought leadership void by providing a definitive, data-driven annual resource for the entire energy industry, positioning GE Vernova as the authoritative voice on the energy transition.
Success Metrics
- •
Media mentions and press coverage
- •
High-authority backlinks
- •
Downloads by C-level executives and policymakers
- Initiative:
Create an 'Integrated Digital Energy' Narrative
Business Impact:Medium
Market Opportunity:Compete more effectively with rivals like Siemens and Schneider Electric who lead with strong software and digitalization stories. This addresses the need for a unified digital vision that connects GE Vernova's hardware prowess with intelligent orchestration.
Success Metrics
- •
Increased traffic to software solution pages
- •
Share of voice for 'digital grid' or 'energy AI' keywords
- •
Analyst and media mentions of GE Vernova's digital strategy
Position GE Vernova as the indispensable, end-to-end partner for navigating the complexity of the energy transition. Leverage the deep engineering heritage of GE while emphasizing the agility and singular focus of an independent company. The core message should be that GE Vernova provides not just the powerful hardware to generate and move electrons, but the critical intelligence and integrated solutions to orchestrate a reliable, affordable, and sustainable energy future.
Competitive Advantage Opportunities
- •
Showcase the unique breadth of the portfolio—from gas turbines that ensure grid stability to advanced wind technology and the grid solutions that connect them—as a key differentiator against more specialized competitors.
- •
Amplify the massive scale of its installed base (generating ~30% of world electricity) as proof of unparalleled experience, reliability, and data intelligence.
- •
Leverage its strong position in gas power as a strategic asset for the energy transition, framing it as the essential technology for ensuring reliability as renewables expand, particularly for high-demand sectors like data centers.
GE Vernova enters the market with a formidable legacy and an immense physical footprint, immediately establishing it as a key player in the global energy sector. Its digital presence effectively communicates its core mission: to electrify and decarbonize. The website is well-structured, catering to a sophisticated B2B audience with detailed information on its vast portfolio of products and services for specific industries.
The primary strategic challenge in the digital realm is not brand awareness, but the translation of its industrial might into market-leading thought leadership and dominant search visibility. Key competitors like Siemens Energy and Schneider Electric have invested heavily in creating deep content ecosystems around the core challenges of the energy transition, particularly from a digital and software perspective. They often lead with a narrative of intelligent systems and integrated software platforms, which can position hardware-focused companies as component suppliers rather than strategic partners.
GE Vernova's most significant opportunity is to seize the narrative of complexity and integration. The energy transition is not a simple switch; it is a complex orchestration of variable renewables, stabilizing baseload power, and intelligent grid management. With its unique portfolio spanning gas, wind, and electrification, GE Vernova is uniquely positioned to own this narrative.
Strategic Recommendations:
-
Frame the Industry's Problems: The immediate priority should be to develop a robust layer of top-of-funnel, problem-oriented content. This means creating definitive guides, reports, and expert commentary on the core challenges its customers face—grid instability, the cost of decarbonization, supply chain constraints for new infrastructure, etc. This will intercept potential customers early in their buying journey and establish GE Vernova's role as a trusted advisor.
-
Elevate the Digital & Software Story: A concerted effort must be made to create a unified and compelling narrative around GE Vernova's digital and software capabilities. This involves moving beyond product-specific pages to create a central content hub that explains how GE Vernova's software orchestrates its powerful hardware to solve systemic problems. This directly counters the competitive positioning of rivals and aligns with the market's need for intelligent, integrated solutions.
-
Weaponize Its Global Scale: The company should leverage its project data and global expertise to produce a flagship annual report on the state of the energy transition. This type of high-value, data-driven content is what builds true brand authority, generates high-quality media attention, and earns invaluable backlinks, cementing its position as a definitive leader.
By focusing its digital strategy on demonstrating strategic expertise rather than just product capabilities, GE Vernova can align its market presence with its physical-world impact, ensuring it is not just seen as a manufacturer of equipment, but as the principal architect of the new energy future.
Strategic Priorities
Strategic Priorities
- Title:
Launch a Dedicated 'AI & Data Center Power' Business Initiative
Business Rationale:The analysis repeatedly highlights the explosive, non-discretionary demand for reliable power from AI and data centers as a primary market tailwind. This vertical requires the exact combination of reliable gas power, grid stability solutions, and rapid deployment capabilities that are GE Vernova's core strengths. Failing to capture this market is a significant missed opportunity.
Strategic Impact:Establishes GE Vernova as the indispensable energy partner for the AI revolution, creating a powerful, high-margin revenue stream. This move positions the company at the center of the most critical infrastructure build-out of the next decade, transforming it from a general utility supplier to a high-growth technology enabler.
Success Metrics
- •
Revenue generated from the data center vertical ($B)
- •
Number of Master Service Agreements (MSAs) signed with hyperscalers
- •
Market share of new data center power generation contracts
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Market Position
- Title:
Mandate 'Digital-First' Transformation of the Service Model
Business Rationale:The analysis identifies the high-margin, recurring revenue from Long-Term Service Agreements (LTSAs) as the core profit driver. However, there is a major opportunity to evolve this by embedding digital services (e.g., GridOS®, predictive analytics) into every agreement, moving from a hardware-centric to a value-based, software-enabled model.
Strategic Impact:Shifts the company's primary revenue driver from cyclical equipment sales and reactive maintenance to stable, high-margin Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR). This increases customer lifetime value, creates a formidable competitive moat through high switching costs, and redefines the company as a technology leader.
Success Metrics
- •
ARR from Digital Services & Software
- •
Attach rate of digital service packages on new equipment sales and LTSAs
- •
Improvement in customer asset efficiency/uptime (value metric)
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Revenue Model
- Title:
Execute a Decisive Turnaround Plan for the Wind Segment
Business Rationale:The analysis consistently flags the historical unprofitability and operational challenges in the Wind segment as a critical weakness that drags down overall company performance and investor confidence. Achieving sustained profitability in this key growth area is non-negotiable for long-term success.
Strategic Impact:Eliminates a major drain on capital and management focus, fundamentally strengthening the company's financial profile and P&L. A profitable Wind business validates the integrated portfolio strategy and positions GE Vernova as a disciplined, bankable leader across all facets of the energy transition.
Success Metrics
- •
Wind segment operating margin reaching sustained profitability
- •
Project-level gross margins meeting or exceeding targets
- •
Reduction in warranty provisions and service-related losses
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Quick Win (0-3 months)
Category:Operations
- Title:
Establish 'Proof of Performance' as the Core Brand Message
Business Rationale:The analysis reveals a critical messaging gap between GE Vernova's aspirational purpose ('electrify and decarbonize') and the lack of quantifiable proof points. To win against technically-focused competitors, the brand must pivot from telling what it does to proving what its customers achieve.
Strategic Impact:Transforms the brand narrative from a generic corporate mission to a compelling, data-driven value proposition. This builds immense credibility with technical buyers, justifies premium pricing, and solidifies GE Vernova's position as an results-oriented market leader, not just a legacy manufacturer.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in qualified inbound leads attributed to case studies/data reports
- •
Inclusion of specific, quantifiable outcome metrics in all major marketing assets
- •
Media & analyst mentions of GE Vernova's data-backed performance claims
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Brand Strategy
- Title:
Forge a Capital & Technology Partnership Ecosystem
Business Rationale:The scale of the energy transition requires trillions in capital and deep technological integration. GE Vernova cannot grow at the required pace alone. The analysis points to the need for partnerships to de-risk projects and accelerate digital capabilities, especially with AI leaders and major infrastructure investors.
Strategic Impact:Creates a powerful force multiplier, enabling the company to pursue larger and more numerous projects than its balance sheet alone would allow. It accelerates the sales cycle by offering integrated financing and technology solutions, effectively locking out competitors who can only offer standalone products.
Success Metrics
- •
Number of formal strategic alliances with top-tier cloud/AI providers and private equity firms
- •
Total value of projects co-financed or influenced through the ecosystem
- •
Revenue from joint go-to-market offerings
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Partnerships
GE Vernova must leverage its profitable Power segment and vast installed base as the foundation to aggressively capture the high-growth electrification market. The strategic imperative is to transform from a hardware provider into an integrated solutions partner, driven by a 'digital-first' service model and a laser focus on high-demand verticals like AI data centers.
The ability to deliver integrated, end-to-end decarbonization solutions at scale, combining a world-leading gas power business for grid reliability with a full suite of renewable and grid technologies.
The surging, non-discretionary global demand for reliable electricity, supercharged by the AI and data center boom, which plays directly to the company's core strengths in gas power and grid modernization.