eScore
mastercard.comThe eScore is a comprehensive evaluation of a business's online presence and effectiveness. It analyzes multiple factors including digital presence, brand communication, conversion optimization, and competitive advantage.
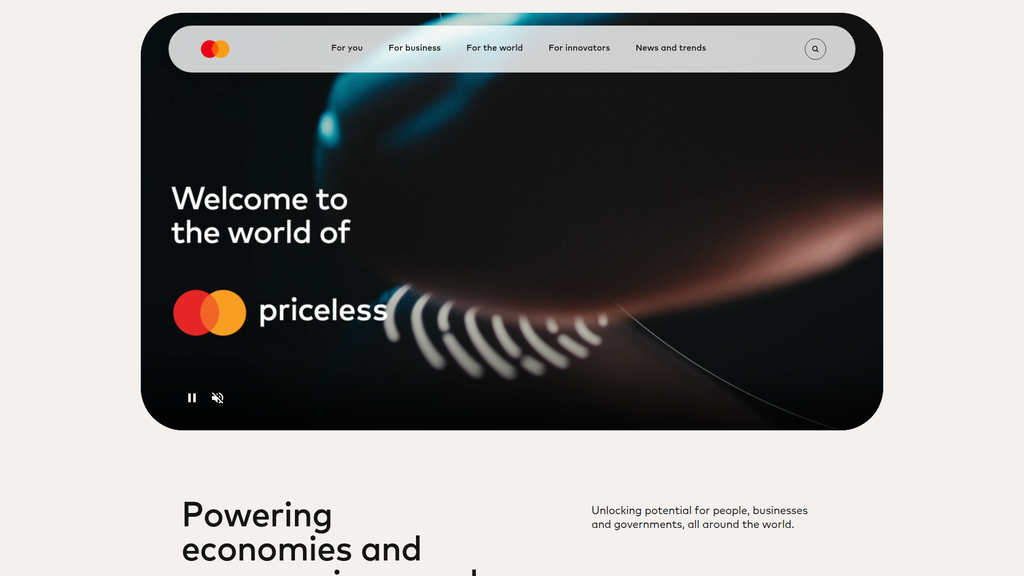
Mastercard exhibits exceptional digital presence, anchored by world-class content authority through its 'Mastercard Economics Institute,' which establishes it as a major thought leader in the global economy. Its multi-channel presence is robust, with a sophisticated website that clearly segments content for diverse audiences and a strong social media strategy that drives engagement. The site architecture demonstrates a mature global-versus-local strategy, with dedicated content for various international regions to maximize market penetration.
The 'Mastercard Economics Institute' is a powerful asset that generates immense content authority, drives brand perception as a data and insights leader, and creates a halo effect over its commercial B2B offerings.
Improve search intent alignment by creating clearer conversion funnels that guide users from high-level thought leadership content (e.g., economic reports) to the specific, relevant B2B products and services that solve the issues discussed.
Mastercard's brand communication is highly effective due to its meticulous audience segmentation, providing tailored messaging for consumers, businesses, innovators, and governments directly from the homepage. The messaging successfully differentiates the brand from competitors by emphasizing its identity as a 'technology company' focused on innovation in AI, data, and security. However, there is a distinct tonal gap between the iconic, emotional 'Priceless' consumer campaign and the more corporate, technical language used in its B2B communications.
Excellent audience segmentation in the website's information architecture ensures that diverse personas are immediately channeled into relevant messaging streams, making a complex B2B2C value proposition clear and navigable.
Create a more integrated brand narrative that weaves the powerful, emotional 'Priceless' concept into B2B and technology messaging to unify the brand voice and differentiate from the purely functional messaging of competitors.
The website provides a high-quality, seamless cross-device experience with a visually appealing and intuitive design that reflects a premium technology brand. It demonstrates a strong commitment to accessibility, a key factor for a global enterprise, which positively impacts market reach. The primary friction point is the moderate cognitive load on the homepage, which serves many distinct audiences, and the repeated use of generic 'Learn more' calls-to-action that could be more specific and benefit-driven.
A highly polished, cohesive, and mobile-responsive design system provides a premium and trustworthy user experience that aligns perfectly with Mastercard's brand positioning as a leading global technology company.
Implement more descriptive, action-oriented call-to-action copy instead of the generic 'Learn more'. A/B testing language like 'Explore B2B Solutions' or 'Discover Card Benefits' would create a stronger information scent and improve click-through rates on key user journeys.
Mastercard has built a fortress of credibility, underpinned by its global brand recognition and a proactive, best-in-class approach to legal and data privacy compliance. The website effectively showcases third-party validation through its thought leadership and media mentions of the Economics Institute, while clearly communicating its commitment to security. The strategic distinction of its role as a technology network, separate from card-issuing banks, is a masterclass in risk mitigation and transparency for all stakeholders.
Proactively adopting top-tier global standards like GDPR for all users and implementing EU-approved Binding Corporate Rules showcases leadership in data protection, turning a compliance necessity into a powerful trust signal and competitive advantage.
Enhance the Accessibility Statement by specifying the exact level of WCAG conformance it targets (e.g., WCAG 2.1 Level AA) to provide a clearer, measurable benchmark that further mitigates legal risk.
Mastercard's competitive advantage is exceptionally strong and sustainable, primarily due to the powerful two-sided network effect of its global acceptance network, which creates a nearly insurmountable barrier to entry. The company is effectively strengthening its moat by heavily investing in value-added services like cybersecurity, data analytics, and AI, which increase switching costs for its partners. This strategic pivot to technology and services provides a crucial differentiation from its main competitor, Visa, and a defensible position against fintech disruptors.
The immense, self-reinforcing network effect, where more consumers attract more merchants and vice-versa, creates a durable and sustainable competitive moat that is extremely difficult for new entrants to replicate.
Accelerate the development of a 'network of networks' strategy to provide value-added services (like security and identity) across alternative payment rails (A2A, RTP), mitigating the long-term risk of disintermediation by fintechs and new payment infrastructures.
The business model is built for massive scalability, with extremely high operating leverage due to a high fixed-cost infrastructure and near-zero marginal cost for each additional transaction. Mastercard is demonstrating strong expansion potential by aggressively targeting new, high-growth payment flows, particularly in the vast B2B and commercial payments sector. Its 'Value-Added Services' are a rapidly growing, high-margin segment that further enhances the economic model and reduces reliance on consumer spending cycles.
The pivot to high-margin, recurring revenue from Value-Added Services (data, security, consulting) is a powerful growth driver that diversifies revenue, deepens client relationships, and improves overall capital efficiency.
Streamline the API access and onboarding experience within the 'Mastercard Developers' platform to reduce friction for fintechs and innovators, encouraging them to build on Mastercard's rails and fostering future ecosystem growth.
Mastercard's business model demonstrates excellent coherence and a clear strategic focus on evolving from a payments network to a diversified technology company. Resource allocation is strategically shifting towards high-impact growth areas like B2B payments, cybersecurity, and open banking services, which aligns perfectly with market trends. This strategic pivot is well-timed to capitalize on the global digitization of commerce and the increasing importance of data and security, ensuring strong stakeholder alignment.
The strategic decision to focus on and grow the 'Value-Added Services' segment demonstrates a coherent and forward-looking business model that leverages core assets (data, trust) to build higher-margin, defensible revenue streams.
Further articulate and promote the value proposition for the public sector. While present, the messaging and solutions for governments could be more prominent and clearly packaged compared to other business segments.
As one half of a global duopoly, Mastercard wields immense market power, including significant pricing power and leverage with partners. Its market share trajectory is stable and growing in key segments, particularly in value-added services where it is gaining ground. The company demonstrates profound market influence, actively shaping industry standards in security and participating in the development of future infrastructure for digital currencies, positioning itself as a central node in the future of the digital economy.
The deeply entrenched relationships with thousands of financial institutions globally provide unparalleled distribution and a formidable barrier to entry, giving Mastercard significant leverage and influence over the entire payments ecosystem.
Address the indirect relationship with end consumers by creating more value-add digital services that build a direct connection, mitigating the risk of disintermediation by digital wallets and 'Super Apps' that control the primary customer interface.
Business Overview
Business Classification
Payments Technology & Global Network
Data Services & Consulting
Financial Services
Sub Verticals
- •
Payment Processing
- •
Cybersecurity & Fraud Prevention
- •
Data Analytics & Insights
- •
Open Banking
- •
Digital Identity
Mature
Maturity Indicators
- •
Global brand recognition and acceptance network
- •
Stable and significant revenue growth
- •
Strong and defensible market position (duopoly with Visa)
- •
Systemically important to the global financial ecosystem
- •
Active in strategic acquisitions to enter new markets and acquire technology
Enterprise
Steady
Revenue Model
Primary Revenue Streams
- Stream Name:
Domestic Assessments
Description:Fees charged to financial institutions (issuers and acquirers) based on the gross dollar volume (GDV) of transactions processed within the same country.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Financial Institutions
Estimated Margin:High
- Stream Name:
Cross-Border Volume Fees
Description:Fees charged on transactions where the card-issuing institution and the merchant's institution are in different countries, often including currency conversion charges.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Financial Institutions
Estimated Margin:High
- Stream Name:
Transaction Processing Fees (Switching)
Description:Fees for authorizing, clearing, and settling transactions. These are charged for both domestic and international transactions and represent the core utility of the network.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Financial Institutions
Estimated Margin:High
- Stream Name:
Value-Added Services & Solutions
Description:A rapidly growing category of revenue from services beyond core transaction processing. This includes cybersecurity and intelligence solutions, data analytics, consulting (Mastercard Advisors), loyalty and rewards programs, and open banking solutions.
Estimated Importance:Secondary
Customer Segment:Financial Institutions, Merchants, Governments, Fintechs
Estimated Margin:High
Recurring Revenue Components
- •
Volume-based assessment fees
- •
Transaction-based processing fees
- •
Subscription/licensing fees for data analytics and cybersecurity products
Pricing Strategy
Transaction-based & Service-based (B2B)
Premium
Opaque
Pricing Psychology
- •
Network Effect Pricing (value increases with more users/merchants)
- •
Value-Based Pricing (for consulting and data services)
- •
Bundling (core processing bundled with security and analytics)
Monetization Assessment
Strengths
- •
Highly scalable model with strong operating leverage.
- •
Diversified revenue across geographies and transaction types.
- •
Growing high-margin 'Value-Added Services' segment reduces reliance on transaction volumes.
- •
The 'network effect' creates a significant barrier to entry and pricing power.
Weaknesses
- •
Revenue is sensitive to macroeconomic conditions affecting consumer and business spending.
- •
Complex and often opaque fee structures can attract regulatory scrutiny.
- •
Dependence on financial institution partners for card issuance and merchant acquisition.
Opportunities
- •
Expansion into new payment flows (B2B, P2P, Government-to-Consumer).
- •
Monetization of Open Banking APIs and data aggregation services.
- •
Developing infrastructure and services for Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and stablecoins.
- •
Further growth in cybersecurity and AI-driven fraud prevention services as digital transactions increase.
Threats
- •
Intense competition from Visa and emerging fintech players (e.g., BNPL, real-time payment networks).
- •
Regulatory pressure on interchange and network fees globally.
- •
Technological disruption from decentralized finance (DeFi) and alternative payment rails.
- •
Geopolitical risks impacting cross-border transaction volumes.
Market Positioning
A global technology company powering a secure, intelligent, and inclusive digital economy for everyone, everywhere.
Second-largest global payments network, in a duopoly with Visa.
Target Segments
- Segment Name:
Financial Institutions (Issuers & Acquirers)
Description:Banks, credit unions, and other financial entities that issue Mastercard-branded cards to consumers and businesses and/or process transactions for merchants. They are Mastercard's primary customers.
Demographic Factors
- •
Global, regional, and local banks
- •
Credit unions
- •
Neobanks and digital-first financial institutions
Psychographic Factors
- •
Risk-averse, focused on security and compliance
- •
Seeking to innovate and compete with fintechs
- •
Value data-driven insights to manage portfolios
Behavioral Factors
- •
Long-term partnership contracts
- •
High integration with Mastercard's network rules and technology
- •
Purchase bundled services (processing, fraud, loyalty)
Pain Points
- •
Fraud and cybersecurity threats
- •
Pressure on fee income
- •
Legacy technology systems
- •
Competition for customer loyalty
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:Medium
- Segment Name:
Merchants
Description:Businesses of all sizes, from small enterprises to large multinational corporations, that accept electronic payments. While not direct customers, their acceptance is critical to the network's value.
Demographic Factors
- •
Retail, eCommerce, Travel, Hospitality
- •
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs)
- •
Large Corporations
Psychographic Factors
- •
Focused on sales growth and customer experience
- •
Concerned about transaction costs (interchange fees)
- •
Seeking to reduce fraud and chargebacks
Behavioral Factors
- •
Reliant on acquirers to process payments
- •
Increasingly adopting digital and contactless payment solutions
- •
Value insights on customer spending patterns
Pain Points
- •
Cost of payment acceptance
- •
Complexity of PCI compliance and data security
- •
Shopping cart abandonment
- •
Managing chargebacks
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
Governments & Public Sector
Description:National, state, and local government entities seeking to digitize payments for services, disbursements, and transit, and to improve financial inclusion.
Demographic Factors
- •
Central banks
- •
Government agencies (tax, social security)
- •
Public transit authorities
Psychographic Factors
Prioritizing efficiency, transparency, and security
Focused on policy goals like financial inclusion and reducing the cash economy
Behavioral Factors
Large-scale contracts and RFPs
Partnerships for social benefit programs and digital currency pilots (CBDCs)
Pain Points
- •
Inefficiency and fraud in cash-based disbursement programs
- •
Need for secure digital identity solutions
- •
Modernizing legacy payment infrastructure
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
Fintechs & Innovators
Description:Startups and technology companies building new financial products and services, leveraging Mastercard's network and APIs via programs like Mastercard Developers and Start Path.
Demographic Factors
- •
Payment startups
- •
Digital wallet providers
- •
Fintech developers
Psychographic Factors
- •
Agile, growth-focused
- •
Seeking speed-to-market and scalability
- •
Value open access to technology and networks
Behavioral Factors
Utilize APIs for building custom solutions
Participate in accelerator and partnership programs
Pain Points
- •
Gaining access to established payment rails
- •
Navigating complex regulatory environments
- •
Achieving scale and trust
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:High
Market Differentiation
- Factor:
Global Acceptance Network & Brand
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Value-Added Services (Cybersecurity, AI, Data Analytics)
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Trust and Security Reputation
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Relationships with Financial Institutions
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
Value Proposition
To connect and power an inclusive, digital economy that benefits everyone, everywhere by making transactions safe, simple, smart and accessible.
Good
Key Benefits
- Benefit:
Secure Transactions
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
- •
AI-powered fraud detection systems
- •
Tokenization technology
- •
Cybersecurity consulting and tools like Cyber Secure
- Benefit:
Global Acceptance & Interoperability
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
Accepted at millions of merchant locations in over 210 countries
Facilitates transactions in over 150 currencies
- Benefit:
Data-Driven Insights & Intelligence
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Unique
Proof Elements
- •
Mastercard Advisors consulting services
- •
Mastercard Economics Institute reports
- •
SpendingPulse™ retail sales data
- Benefit:
Innovation and Future-Proofing
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Unique
Proof Elements
- •
Investments in AI, Open Banking, and Digital Assets
- •
Partnership programs for fintechs (Start Path)
- •
Active development of solutions for CBDCs and stablecoins
Unique Selling Points
- Usp:
Integrated Services Portfolio: A comprehensive suite of solutions combining payments, cybersecurity, data, and consulting under one umbrella.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
Multi-Rail Network Strategy: Actively developing capabilities beyond traditional card payments to include real-time account-to-account (A2A), B2B, and digital currency payment flows.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Moderate
Customer Problems Solved
- Problem:
Lack of a secure and universally trusted method for electronic payments.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Difficulty for businesses and banks to manage the risk of fraud in digital transactions.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Inability for businesses to gain deep insights from transaction data to drive growth.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
- Problem:
Friction and inefficiency in cross-border and B2B payments.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
Value Alignment Assessment
High
Mastercard's strategy is well-aligned with the global shift towards digitization, the increasing importance of data, and the need for enhanced security in all forms of commerce.
High
The value propositions are tailored to the distinct needs of its core B2B/B2G segments, addressing critical pain points around security, innovation, and operational efficiency for financial institutions, governments, and merchants.
Strategic Assessment
Business Model Canvas
Key Partners
- •
Financial Institutions (Issuers & Acquirers)
- •
Merchants & Payment Service Providers (PSPs)
- •
Technology Partners (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay)
- •
Fintech Companies (e.g., Ripple, Consensys for CBDC initiatives)
- •
Governments & Central Banks
Key Activities
- •
Operating and securing the global payments network
- •
Processing transactions (authorization, clearing, settlement)
- •
Developing AI and cybersecurity solutions
- •
Providing data analytics and consulting services
- •
Innovating in new payment flows and digital assets
Key Resources
- •
Global network infrastructure
- •
Mastercard brand and reputation
- •
Vast, anonymized transaction data sets
- •
Patents and proprietary technology
- •
Relationships with the global banking ecosystem
Cost Structure
- •
Technology and infrastructure development & maintenance
- •
General & Administrative expenses
- •
Marketing and sponsorships
- •
Client incentives and rebates
- •
Personnel and data security
Swot Analysis
Strengths
- •
Immense network effect creating a high barrier to entry.
- •
Globally recognized and trusted brand.
- •
Strong, profitable business model with high operating margins.
- •
Diversifying into high-growth, high-margin value-added services.
- •
Deeply entrenched relationships with the global financial system.
Weaknesses
- •
Business performance is highly correlated with global consumer spending.
- •
Complex four-party model can slow down innovation compared to agile fintechs.
- •
Faces continuous regulatory scrutiny over fees and market dominance.
- •
High-value target for sophisticated cyberattacks.
Opportunities
- •
The ongoing global shift from cash to digital payments.
- •
Leading the infrastructure development for CBDCs and regulated stablecoins.
- •
Growth in B2B payments, a market significantly larger than consumer payments.
- •
Expansion of Open Banking services to enable new financial products.
- •
Monetizing AI and data capabilities for new services and insights.
Threats
- •
Antitrust investigations and government regulation targeting network fees.
- •
Competition from national payment schemes (e.g., RuPay in India).
- •
Disruption from account-to-account (A2A) payment technologies and fintechs bypassing card rails.
- •
Geopolitical tensions disrupting cross-border trade and payments.
- •
Emergence of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms offering alternative payment systems.
Recommendations
Priority Improvements
- Area:
B2B & New Payment Flows
Recommendation:Accelerate the development and acquisition of platforms for B2B accounts payable/receivable and cross-border remittances to capture a larger share of non-consumer payment flows.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Open Banking Monetization
Recommendation:Develop a clearer, more aggressive strategy to monetize open banking APIs by offering premium data enrichment, verification, and payment initiation services to FIs and fintechs, especially in markets like the U.S. where competitors have retreated.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Developer & Fintech Ecosystem
Recommendation:Simplify API access and reduce barriers to entry for startups within the Mastercard Developers platform to foster innovation and ensure new financial products are built on Mastercard rails.
Expected Impact:Medium
Business Model Innovation
- •
Transition from a transaction processor to an 'Orchestrator of Value Exchange', providing the secure network layer for any type of value transfer, including digital assets, data, and identity.
- •
Develop a 'Network-as-a-Service' (NaaS) platform, allowing partners (e.g., governments, corporations) to build and operate their own secure, closed-loop payment or value transfer systems on Mastercard's infrastructure.
- •
Pioneer 'Identity-as-a-Service', leveraging its network trust to offer robust, reusable digital identity verification for a wide range of digital interactions beyond payments.
Revenue Diversification
- •
Scale the AI-driven cybersecurity business to offer predictive threat intelligence and cyber risk insurance products to financial institutions and merchants.
- •
Package and sell anonymized, aggregated data insights as a subscription service to new verticals beyond finance, such as urban planning, retail real estate, and CPG brands.
- •
Build a robust service offering around CBDC implementation, providing central banks with a full suite of tools for issuance, security, and ecosystem management on a long-term contract basis.
Mastercard's business model has strategically evolved from a pure-play payments network into a diversified technology company. Its core strength lies in the powerful duopoly it shares with Visa, built upon a vast, global, and highly secure network. This foundation generates substantial, high-margin revenue from transaction-based fees and creates a formidable barrier to entry due to the network effect.
The most significant opportunity and the core of its future strategy lie in the 'Value-Added Services' segment. By leveraging its immense data assets, brand trust, and technological capabilities, Mastercard is building a defensible moat in high-growth areas like cybersecurity, AI-driven analytics, digital identity, and consulting. This strategic pivot serves two critical purposes: it diversifies revenue away from transaction volumes that are susceptible to economic downturns and regulatory pressures, and it further embeds Mastercard within its clients' operations, increasing switching costs. Recent organizational realignments focusing on 'Core Payments', 'New Payment Flows', and 'Services' underscore this strategic intent.
The key challenges are external. Intense regulatory scrutiny over fees is a persistent threat, while technological disruption from real-time A2A payment systems and decentralized finance could challenge the dominance of traditional card rails. Mastercard's proactive engagement with emerging technologies like Open Banking, CBDCs, and stablecoins is a necessary defensive and offensive maneuver, positioning it not as a legacy system to be disrupted, but as the foundational infrastructure for the future of digital value exchange. To sustain its growth trajectory, Mastercard must successfully navigate these threats by continuing to innovate, expand its service offerings, and position its network as the most secure, reliable, and intelligent choice for any digital transaction.
Competitors
Competitive Landscape
Mature
Oligopoly
Barriers To Entry
- Barrier:
Two-Sided Network Effect
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Regulatory Compliance and Licensing
Impact:High
- Barrier:
High Capital Investment for Infrastructure
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Brand Trust and Security Reputation
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Established Relationships with Financial Institutions
Impact:High
Industry Trends
- Trend:
Real-Time Payments (RTP) and A2A Transfers
Impact On Business:Potential disintermediation of card rails for certain transactions, requiring Mastercard to integrate with or build services on top of these new rails.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Rise of Digital Wallets and Super Apps
Impact On Business:Shifts the consumer relationship to the wallet provider (e.g., Apple, Google), though currently still relies on card networks. Opportunity for partnership and 'card-on-file' dominance.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Open Banking (PSD2/3)
Impact On Business:Enables third-party providers to initiate payments directly from bank accounts, creating a competitive threat. Mastercard is addressing this by acquiring open banking platforms like Finicity to participate in the ecosystem.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) proliferation
Impact On Business:Offers an alternative to traditional credit card revolving debt at the point of sale, potentially reducing credit card transaction volumes.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
AI and Machine Learning in Fraud & Cybersecurity
Impact On Business:Creates an arms race for security. Mastercard is investing heavily in AI to differentiate its services and protect its network, as seen in acquisitions like Recorded Future.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Embedded Finance and Vertical SaaS
Impact On Business:Payments are becoming integrated into software platforms, creating new distribution channels and partnership opportunities, but also competition from platform-native solutions.
Timeline:Near-term
Direct Competitors
- →
Visa
Market Share Estimate:Largest global market share by purchase volume and cards in circulation.
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Positions as the world's largest, most reliable, and universally accepted payment network, focusing on scale and security.
Strengths
- •
Largest market share and global acceptance network.
- •
Strong brand recognition and trust.
- •
Superior operating margins and financial scale.
- •
Extensive co-branding partnerships with major financial institutions.
Weaknesses
- •
Business model is nearly identical to Mastercard, making differentiation difficult.
- •
Potentially slower to adopt some newer technologies compared to Mastercard's more aggressive approach.
- •
Faces the same systemic threats from fintech and regulatory changes.
Differentiators
Scale and network size are its primary differentiators.
Historically stronger in the U.S. consumer credit market.
- →
American Express (Amex)
Market Share Estimate:Smaller than Visa/Mastercard by volume, but captures a high-spending, premium segment.
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:A premium, spend-centric brand offering exclusive benefits, rewards, and superior customer service to affluent consumers and businesses.
Strengths
- •
Closed-loop network provides end-to-end control and rich data insights.
- •
Strong brand equity associated with luxury and premium services.
- •
High-spending, loyal customer base.
- •
Direct relationship with cardholders allows for better customer service and marketing.
- •
Diversified revenue streams (interest, fees, merchant discounts).
Weaknesses
- •
Lower merchant acceptance globally compared to Visa/Mastercard due to higher merchant fees.
- •
Smaller overall network size.
- •
More exposed to credit risk as it is both issuer and network.
Differentiators
- •
Closed-loop business model.
- •
Focus on the premium customer segment.
- •
Membership Rewards program is a key loyalty driver.
- →
Discover Financial Services
Market Share Estimate:Significant in the U.S. but with limited international presence.
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:A value-oriented competitor focused on cash-back rewards, no annual fees, and strong customer service, primarily within the U.S. market.
Strengths
- •
Strong reputation for customer satisfaction in the U.S.
- •
Pioneered cash-back rewards programs.
- •
Operates a closed-loop network similar to Amex, providing more control.
- •
Often has lower merchant fees than Amex.
Weaknesses
- •
Limited acceptance and brand recognition outside of North America.
- •
Significantly smaller scale than Visa or Mastercard.
- •
Perceived as less premium than American Express.
Differentiators
- •
Strong focus on U.S.-based customer service.
- •
Emphasis on cash-back rewards and consumer value.
- •
Proposed acquisition by Capital One could significantly alter its competitive position.
- →
China UnionPay
Market Share Estimate:Dominant in China; one of the largest globally by number of cards in circulation, with growing international acceptance.
Target Audience Overlap:Low
Competitive Positioning:The national payment network of China, facilitating domestic payments and expanding internationally to serve Chinese travelers and global partners.
Strengths
- •
Near-monopolistic control of the massive Chinese domestic market.
- •
Strong government backing.
- •
Growing acceptance network along routes popular with Chinese tourists and businesses.
Weaknesses
- •
Limited brand awareness and issuance outside of Asia.
- •
Heavily reliant on the Chinese economy and outbound tourism.
- •
Faces strong competition from Alipay and WeChat Pay within China for digital payments.
Differentiators
Unrivaled access to the Chinese market.
Strategic focus on facilitating international commerce for Chinese citizens and businesses.
Indirect Competitors
- →
PayPal
Description:A digital wallet and online payments platform that allows users to send and receive money and make online purchases. While it often uses card rails, it has its own A2A transfer capabilities and a vast merchant network.
Threat Level:High
Potential For Direct Competition:High, as it builds out its own payment ecosystem and B2B services, potentially bypassing traditional networks.
- →
Block (formerly Square) / Afterpay
Description:Provides merchant payment processing hardware/software (Square) and a leading BNPL service (Afterpay). Its ecosystem connects merchants and consumers, bypassing traditional card interchange fees for some transactions.
Threat Level:High
Potential For Direct Competition:High. The Cash App and Afterpay create a closed-loop ecosystem that directly competes for consumer and merchant transactions.
- →
Stripe
Description:A technology company providing payment processing software and APIs for e-commerce websites and mobile applications. It simplifies payment acceptance for businesses and is expanding into banking-as-a-service.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Medium. While primarily a partner, its growing suite of financial services and direct merchant relationships could reduce reliance on traditional acquirers and networks.
- →
Real-Time Payment Networks (e.g., FedNow, The Clearing House's RTP)
Description:Instant, 24/7 bank-to-bank payment rails that bypass the traditional card networks entirely. These are infrastructure-level competitors that enable A2A payments for P2P, B2B, and C2B use cases.
Threat Level:High
Potential For Direct Competition:N/A (This is a direct alternative infrastructure, not a company that will become a card network).
- →
BNPL Providers (e.g., Klarna, Affirm)
Description:Offer point-of-sale financing, allowing consumers to split purchases into installments, often interest-free. This directly competes with credit cards for financing consumer purchases.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Low, as they are more likely to partner with networks or issue their own cards on existing rails to expand their reach.
Competitive Advantage Analysis
Sustainable Advantages
- Advantage:
Global Acceptance Network & Brand Trust
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable due to the immense difficulty and cost of replicating a trusted, global two-sided network.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Two-Sided Network Effect
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable; more consumers attract more merchants, and vice versa, creating a powerful, self-reinforcing competitive moat.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Relationships with Thousands of Financial Institutions
Sustainability Assessment:Sustainable, built over decades. These partnerships are deeply integrated and represent a significant barrier to entry.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Value-Added Services (Data Analytics, Security, Advisory)
Sustainability Assessment:Moderately sustainable. This is a key battleground. Mastercard's heavy investment in AI and cybersecurity acquisitions (e.g., Recorded Future) aims to make this advantage more durable.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
Temporary Advantages
{'advantage': 'Exclusive Sponsorships (e.g., major sporting events)', 'estimated_duration': 'Contract-dependent (typically 2-5 years)'}
{'advantage': 'First-mover on specific tech innovations (e.g., Agent Pay)', 'estimated_duration': '12-24 months before competitors launch similar offerings'}
Disadvantages
- Disadvantage:
Indirect Relationship with End Consumers
Impact:Major
Addressability:Difficult
- Disadvantage:
Vulnerability to Regulatory Intervention (e.g., interchange fee caps)
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately
- Disadvantage:
Legacy Perception Compared to Fintechs
Impact:Minor
Addressability:Easily
- Disadvantage:
Dependence on the Health of Issuing Bank Partners
Impact:Major
Addressability:Difficult
Strategic Recommendations
Quick Wins
- Recommendation:
Launch targeted marketing campaigns emphasizing the superior security and fraud protection of the Mastercard network versus P2P/A2A payment methods.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
- Recommendation:
Simplify and promote API access for small-to-medium fintechs to encourage innovation on top of Mastercard's rails, solidifying its role as a foundational layer.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Medium Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Aggressively expand 'Mastercard Move' and other B2B payment solutions to capture a larger share of the $145 trillion+ B2B payments market, a key growth area.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Deepen integration of acquired companies (Finicity, Ekata, Recorded Future) to create a holistic 'Trust' platform for partners, bundling identity, open banking, and cybersecurity services.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Develop and scale a white-label BNPL solution for issuing banks to allow them to compete directly with fintech providers, keeping the transaction volume within the Mastercard ecosystem.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Long Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Position Mastercard as a 'network of networks,' creating value-added services (e.g., data analytics, fraud prevention, universal directory) that operate across multiple payment rails, including card, A2A, and potentially blockchain/CBDCs.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Invest in or partner with a leading digital wallet or 'Super App' in a key growth market to gain direct access to consumer data and behavior, mitigating the risk of disintermediation.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Shift positioning from a 'card company' to a 'global multi-rail payment and technology partner.' Emphasize trust, security, and intelligence as key differentiators that enable commerce across any platform or payment method.
Differentiate from Visa on technological agility and innovation in new payment flows (B2B, open banking). Differentiate from fintech disruptors by leveraging the unparalleled scale, trust, and security of the global network. Focus on providing superior value-added services to business and financial institution partners.
Whitespace Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Integrated Small Business Financial OS
Competitive Gap:Small businesses are currently served by a fragmented set of tools for payments, invoicing, cash flow management, and access to capital. Fintechs are attacking this, but a trusted brand like Mastercard could bundle these services for its banking partners to offer.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Cross-Border B2B Payment Optimization
Competitive Gap:International B2B payments remain slow, expensive, and opaque. While fintechs are targeting this, Mastercard can leverage its existing global network and FX capabilities to offer a superior, more integrated solution.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Digital Identity as a Service (IDaaS)
Competitive Gap:There is a growing need for a secure, reusable digital identity for online transactions. Mastercard is uniquely positioned to leverage its trusted network and partnerships with banks to provide a federated identity service that goes beyond payments.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Sustainability & ESG-focused Financial Products
Competitive Gap:Growing consumer and corporate demand for financial products that track and manage carbon footprint (like the Carbon Calculator mentioned on the site) or support sustainable businesses. Mastercard can create a platform for its issuers to build and offer these products at scale.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:Medium
The competitive landscape for Mastercard is that of a mature oligopoly facing unprecedented disruption. For decades, the primary competition was a near-symmetrical battle for market share with Visa, fought through co-branding deals with financial institutions. This core rivalry persists, with Visa maintaining a lead in overall volume, while Mastercard competes effectively through technological innovation and a strong international presence. The key differentiator in this direct competition is shifting from pure network size to the quality and breadth of value-added services.
However, the more significant competitive threat is the multifaceted assault from non-traditional players. The landscape is being fundamentally reshaped by several key trends. First, real-time, account-to-account (A2A) payment infrastructures like FedNow are emerging, threatening to disintermediate the card rails for a growing number of transactions by offering faster, cheaper settlement. Second, fintechs like PayPal and Block are building powerful ecosystems that control both the consumer (digital wallet) and merchant (POS) ends of the transaction, creating the potential for closed-loop systems that bypass card networks. Third, the proliferation of Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services offers consumers alternative financing at the point of sale, directly competing with the core value proposition of credit cards. Finally, Open Banking mandates empower third parties to initiate payments directly from consumer bank accounts, representing another significant channel for A2A payments.
Mastercard's strategy, as evidenced by its website content and recent acquisitions, reflects a clear understanding of this shifting landscape. The company is actively repositioning itself from a mere payment network into a diversified technology company. The heavy emphasis on 'For business' solutions—including cybersecurity, AI, data insights, and open finance—demonstrates a strategy to deepen its moat by becoming an indispensable technology partner to banks and merchants. Strategic acquisitions of companies like Recorded Future (cybersecurity), Finicity (open banking), and Dynamic Yield (personalization) are not ancillary but core to this strategy, designed to build a defensible portfolio of value-added services that competitors cannot easily replicate.
Mastercard's most sustainable competitive advantages remain its global two-sided network, brand trust, and deep integration with the global financial system. The primary challenge is to leverage these core assets to capture value from new payment flows and rails, rather than being bypassed by them. The key strategic opportunity lies in becoming the intelligence and security layer that operates across multiple payment networks—card, A2A, and others—thereby ensuring its relevance and profitability regardless of which rail a transaction travels on. This 'network of networks' strategy is vital for long-term growth and defending against the profound disruption reshaping the payments industry.
Messaging
Message Architecture
Key Messages
- Message:
Powering economies and empowering people
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:Medium
Location:Homepage Hero Section
- Message:
Together the possibilities are priceless
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:Medium
Location:Homepage - Business and Government Solutions Section
- Message:
Innovative solutions for a safer, smarter, digital economy.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage - Business and Government Solutions Section
- Message:
Experiences that ignite your passions
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage - Priceless Experiences Section
- Message:
Mastercard is a technology company in the global payments industry.
Prominence:Tertiary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Implicit throughout business and innovator sections
The message hierarchy is exceptionally well-structured, built around a clear, audience-centric navigation model ('For you', 'For business', 'For the world', 'For innovators'). This immediately channels different user personas into relevant messaging streams. High-level corporate messages like 'Powering economies' sit at the top, while more tactical, solution-oriented messages are nested within their respective audience segments. This structure effectively manages the complexity of Mastercard's B2B2C model.
Messaging is largely consistent within each audience vertical. The themes of innovation (AI, digital assets), security, and global reach are woven throughout both consumer and business sections. However, the emotional, aspirational tone of the 'Priceless' campaign feels somewhat segmented into its own section ('Experience Mastercard'), rather than being a consistent thread that connects the more corporate and technology-focused messaging.
Brand Voice
Voice Attributes
- Attribute:
Innovative
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Mastercard unveils Agent Pay, pioneering agentic payments technology to power commerce in the age of AI
- •
Open finance
- •
Digital assets
- •
Payment passkeys
- Attribute:
Authoritative
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Powering economies and empowering people
- •
Mastercard Economics Institute
- •
Research and insights
- •
Advisory services
- Attribute:
Purpose-Driven
Strength:Moderate
Examples
- •
For the world
- •
Priceless Planet Coalition
- •
Mastercard Center for Inclusive Growth
- •
Doing well by doing good
- Attribute:
Approachable
Strength:Weak
Examples
- •
Pay your way
- •
Find a card that’s right for you
- •
Enjoy Priceless experiences
Tone Analysis
Corporate and Professional
Secondary Tones
- •
Technological
- •
Aspirational
- •
Secure
Tone Shifts
- •
Shifts from a broad, corporate tone on the homepage to a more technical, solution-focused tone in the 'For business' and 'For innovators' sections.
- •
Adopts a consumer-friendly and aspirational tone in the 'For you' and 'Experience Mastercard' sections.
- •
Moves to an earnest and socially conscious tone in the 'For the world' section.
Voice Consistency Rating
Good
Consistency Issues
The primary corporate voice can feel disconnected from the iconic, emotionally resonant 'Priceless' campaign voice, which is presented more as a product ('Priceless Experiences') than an overarching brand ethos.
Value Proposition Assessment
Mastercard is the trusted, innovative, and secure global technology network that connects individuals, businesses, and governments to the digital economy, enabling seamless commerce and unlocking economic potential.
Value Proposition Components
- Component:
Global Payment Network & Technology
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
- Component:
Advanced Security & Fraud Prevention
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Common
- Component:
Data-Driven Insights & Advisory
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Unique
- Component:
Innovation in Payments (AI, Open Finance, Digital Assets)
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
- Component:
Commitment to Social & Environmental Impact
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
Mastercard effectively differentiates itself from competitors like Visa by placing a heavier emphasis on being a 'technology company' and an 'innovator'. While Visa's messaging often centers on universal acceptance ('Everywhere you want to be'), Mastercard's messaging foregrounds its role in pioneering new technologies like AI in payments, open finance, and cybersecurity solutions. The 'Priceless' platform remains a key emotional differentiator, framing the brand around experiences rather than just transactions.
The messaging positions Mastercard not merely as a payment network but as a strategic partner for progress. For businesses and governments, it's positioned as an engine for digital transformation, security, and economic insight. For consumers, it's positioned as the enabler of both everyday transactions and extraordinary experiences. This dual positioning allows it to compete with traditional payment processors like Visa on reliability while also competing with modern fintech players on innovation.
Audience Messaging
Target Personas
- Persona:
Individual Consumers
Tailored Messages
- •
Find a card
- •
Ways to pay
- •
Protecting you
- •
Enjoy Priceless experiences
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Business Leaders (SME to Large Corp)
Tailored Messages
- •
Empowering small business
- •
Commercial payments
- •
Cybersecurity & fraud prevention
- •
Advisory services
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Financial Institutions & Fintechs
Tailored Messages
- •
Open finance
- •
Consumer payments
- •
Acquirers and PSPs
- •
Mastercard Engage
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Developers & Innovators
Tailored Messages
- •
Build with us
- •
Developers
- •
Digital labs
- •
Start Path
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Governments & Public Sector
Tailored Messages
- •
Public sector
- •
Pathways to prosperity
- •
Policy Center for Digital Economy
Effectiveness:Somewhat Effective
Audience Pain Points Addressed
- •
Payment security and fraud concerns
- •
Need for convenient and modern payment methods (contactless, digital)
- •
Business need for efficient commercial payment solutions
- •
Business desire for data insights to drive growth
- •
Developer need for tools and platforms to build new financial products
Audience Aspirations Addressed
- •
Accessing unique and memorable life experiences ('Priceless')
- •
Growing a small business
- •
Driving global economic growth and financial inclusion
- •
Building the future of commerce and finance
- •
Contributing to a sustainable planet
Persuasion Elements
Emotional Appeals
- Appeal Type:
Aspiration
Effectiveness:High
Examples
Experiences that ignite your passions
Priceless Experiences connect you to curated sports, travel, food and entertainment opportunities to cherish forever.
- Appeal Type:
Security / Peace of Mind
Effectiveness:High
Examples
- •
Protecting you
- •
Safety and security benefits
- •
Cybersecurity & fraud prevention
- Appeal Type:
Empowerment
Effectiveness:Medium
Examples
- •
Powering economies and empowering people
- •
Empowering small business
- •
Pay your way
Social Proof Elements
{'proof_type': 'Brand Authority & Scale', 'impact': 'Strong'}
{'proof_type': 'Partnerships (e.g., Priceless Planet Coalition)', 'impact': 'Moderate'}
Trust Indicators
- •
Global brand recognition
- •
Emphasis on 'Safety and security' and 'Cybersecurity'
- •
Dedicated sections on 'Privacy and data responsibility'
- •
Publication of reports and insights from the 'Mastercard Economics Institute'
Scarcity Urgency Tactics
Not applicable; the messaging does not rely on scarcity or urgency tactics, focusing instead on long-term value and trust.
Calls To Action
Primary Ctas
- Text:
Learn more
Location:Multiple sections (e.g., Cards and Benefits)
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Explore priceless.com
Location:Priceless Experiences section
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Find a card
Location:Homepage and 'For you' section
Clarity:Clear
The CTAs are clear and contextually appropriate, primarily designed for navigation and information discovery rather than direct conversion. For a B2B2C company that does not issue cards directly, this exploratory approach is effective. They successfully guide users deeper into the site's vast content architecture based on their initial audience selection.
Messaging Gaps Analysis
Critical Gaps
Lack of a single, powerful, and unifying tagline on the homepage that bridges the corporate/technology messaging with the consumer/emotional messaging.
The value proposition for the 'Public Sector' persona is less clearly articulated on the homepage compared to other business segments.
Contradiction Points
There are no direct contradictions, but there is a tonal dissonance between the highly technical, corporate-speak of 'agentic payments technology' and the simple, human-centric language of the 'Priceless' brand heritage.
Underdeveloped Areas
The integration of the 'Priceless' ethos across the B2B and 'For the world' messaging is underdeveloped. There's an opportunity to connect the idea of 'priceless' moments to business achievements, community impact, or innovation breakthroughs, making the brand's most powerful asset more holistic.
Messaging Quality
Strengths
- •
Excellent audience segmentation that clarifies a complex value proposition for diverse groups.
- •
Strong positioning as a technology and innovation leader in the payments space.
- •
Clear communication of core business solutions and their benefits.
- •
Leverages its corporate responsibility initiatives ('For the world') as a key brand pillar.
Weaknesses
- •
Over-reliance on corporate jargon in some sections can alienate non-expert audiences.
- •
The emotional core of the brand ('Priceless') is not fully leveraged across all communication pillars.
- •
The primary homepage headline, 'Powering economies and empowering people,' is broad and could be more distinctive and benefit-oriented.
Opportunities
- •
Create a more integrated narrative that weaves the 'Priceless' concept into the B2B and innovation stories (e.g., 'the priceless moment a small business gets funded').
- •
Develop more persona-based storytelling content that shows, rather than just tells, how Mastercard's solutions empower different users.
- •
Simplify complex technology concepts (like AI, Open Finance) with clearer, benefit-driven language for a broader business audience.
Optimization Roadmap
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Homepage Headline
Recommendation:A/B test new hero headlines that more directly connect Mastercard's technology to human or business outcomes, potentially incorporating the 'Priceless' ethos. For example: 'Connecting you to what matters. Securely. Innovatively. Pricelessly.'
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
B2B Messaging
Recommendation:Translate technical features into tangible business benefits. Instead of 'Money Movement', lead with a benefit like 'Move money globally, instantly, and securely.' Use case studies and storytelling to illustrate the impact.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Priceless Integration
Recommendation:Develop a messaging framework to infuse the 'Priceless' concept across all verticals. Create content that highlights 'priceless' outcomes for businesses, communities, and innovators, not just consumers.
Expected Impact:Medium
Quick Wins
Refine the sub-headlines in the 'Business and Government Solutions' section to be more active and benefit-focused.
Add more direct links from the 'For business' section to the 'Insights & Intelligence' section to better leverage thought leadership as a persuasion tool.
Long Term Recommendations
Conduct a brand voice harmonization project to create a more unified tone across all audience segments, blending the authoritative, innovative voice with the approachable, aspirational 'Priceless' voice.
Invest in a content marketing strategy focused on persona-based narratives and storytelling that demonstrates the real-world impact of Mastercard's technology.
Mastercard's strategic messaging on its website is highly effective at managing the complexity of its diverse global audiences. The core strength lies in its meticulously segmented information architecture, which provides clear pathways for consumers, businesses, innovators, and social impact stakeholders. This structure allows the brand to speak with authority and relevance to each group. The messaging successfully positions Mastercard as a forward-thinking technology company, moving its brand perception beyond that of a simple credit card network to an essential pillar of the digital economy. The emphasis on innovation—highlighting AI, cybersecurity, and data insights—is a key differentiator against its primary competitor, Visa.
However, the website reveals a significant opportunity to better integrate its most powerful and enduring brand asset: the 'Priceless' concept. Currently, this emotionally resonant idea is largely confined to the consumer-facing 'Experiences' section. This segmentation creates a tonal gap between the innovative but often impersonal corporate messaging and the human-centric legacy of the brand. By failing to weave the 'Priceless' narrative into its B2B, technology, and social impact stories, Mastercard misses a chance to create a more unified and emotionally compelling brand identity. The optimization roadmap should focus on bridging this gap, transforming 'Priceless' from a siloed marketing campaign into the central, unifying theme of the entire corporate narrative, thereby amplifying its differentiation and market positioning.
Growth Readiness
Growth Foundation
Product Market Fit
Strong
Evidence
- •
Global brand recognition and acceptance at millions of merchants worldwide.
- •
Over 2.4 billion Mastercard cards in circulation, demonstrating deep market penetration across consumer credit and debit.
- •
A diversified product portfolio serving consumers, financial institutions, merchants, governments, and fintechs, as detailed on the corporate website.
- •
Strong B2B partnerships with virtually all major financial institutions globally, forming the core of its distribution model.
Improvement Areas
- •
Accelerate adoption and integration with emerging payment form factors like real-time Account-to-Account (A2A) payments and digital wallets to counter disintermediation.
- •
Enhance the value proposition for younger demographics (Gen Z) who are increasingly drawn to alternative financial products like Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL).
- •
Simplify the complex web of card benefits and rewards for end-consumers to improve engagement and loyalty.
Market Dynamics
The global digital payments market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17% to 21% from 2025 to 2030.
Mature/Evolving
Market Trends
- Trend:
Rise of Real-Time Payments & Open Banking
Business Impact:Creates both a threat of disintermediation from card rails and a significant opportunity to provide new network and value-added services for Account-to-Account (A2A) transactions.
- Trend:
AI and Generative AI in Financial Services
Business Impact:Massive potential to enhance fraud detection, offer hyper-personalized services, and create operational efficiencies. Also a key driver of new product offerings in cybersecurity and data analytics.
- Trend:
B2B Payments Digitization
Business Impact:A largely untapped market shifting away from manual processes, representing a major growth vector for commercial card programs, virtual cards, and automated accounts payable/receivable solutions.
- Trend:
Embedded Finance
Business Impact:Banking and payment services are being integrated into non-financial platforms, creating new partnership channels but also increasing competition.
- Trend:
Heightened Regulatory Scrutiny
Business Impact:Increased focus on interchange fees, data privacy, and competition from governments worldwide can constrain revenue and increase compliance costs.
Excellent. While the core card business is mature, the timing is perfect to capitalize on the inflection points in B2B payments, value-added data/AI services, and open banking infrastructure, which are all in high-growth phases.
Business Model Scalability
High
Characterized by high fixed costs for network infrastructure, security, and technology, but extremely low, near-zero variable costs for each additional transaction, leading to significant operating leverage.
Extremely high. Once the network is established, each incremental transaction contributes significantly to profit, making volume growth highly accretive.
Scalability Constraints
- •
Navigating complex and divergent regulatory environments in each new market.
- •
Maintaining network security and fraud prevention capabilities at an ever-increasing scale and against evolving threats.
- •
Intense competition for bank and fintech partnerships, which are essential for distribution.
Team Readiness
Very High. Experienced global leadership team with a clear strategic pivot towards high-growth areas, evidenced by the recent organizational realignment around Core Payments, Commercial & New Payment Flows, and Services.
Recently realigned to focus on key growth areas, indicating adaptability. The structure supports a dual focus on protecting the core business while aggressively pursuing new revenue streams.
Key Capability Gaps
- •
Deep expertise in decentralized finance (DeFi) and Web3 technologies to stay ahead of long-term disruptive threats.
- •
Talent for developing and selling complex, data-intensive enterprise software solutions, which differs from traditional partnership management.
- •
Specialized product management for non-card payment flows and digital identity solutions.
Growth Engine
Acquisition Channels
- Channel:
Partnerships with Financial Institutions (Issuers)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Deepen relationships by co-creating solutions that leverage Mastercard's value-added services (e.g., AI fraud detection, data insights) to help FIs grow their own portfolios.
- Channel:
Partnerships with Acquirers and Payment Service Providers (PSPs)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Equip partners with advanced cybersecurity and data analytics tools to enhance their value proposition to merchants, creating a stickier ecosystem.
- Channel:
Direct Engagement with Fintechs and Digital Players
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Streamline onboarding and API access via programs like 'Mastercard Developers' to become the network of choice for startups building the next generation of financial products.
Customer Journey
For B2B partners (banks, fintechs), the path is a long-cycle, relationship-based sales and integration process. For end consumers, the journey is indirect, via choosing a card issued by a partner bank.
Friction Points
- •
Integration complexity and time-to-market for new partners and fintechs.
- •
Difficulty for merchants in reconciling B2B virtual card payments, a key growth area.
- •
Lack of consumer awareness and understanding of specific Mastercard benefits versus issuer-provided rewards.
Journey Enhancement Priorities
{'area': 'Developer/Fintech Onboarding', 'recommendation': "Invest further in the 'Mastercard Developers' portal with more robust APIs, sandbox environments, and clear documentation to reduce integration friction."}
{'area': 'B2B Supplier Acceptance', 'recommendation': "Aggressively market and expand solutions like 'Mastercard Receivables Manager' to automate and simplify how suppliers accept and reconcile commercial payments. "}
Retention Mechanisms
- Mechanism:
Network Effects
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Strengthen by becoming the primary rail for new payment flows (e.g., B2B, real-time payments), making the network indispensable beyond traditional consumer cards.
- Mechanism:
Value-Added Services (VAS)
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Increase the attach rate of VAS (cybersecurity, data analytics, loyalty programs) to core processing deals, embedding Mastercard deeper into partners' operations and making it harder to switch.
- Mechanism:
Brand Trust and Security
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Publicly lead industry efforts in combating new fraud vectors like AI-powered scams to reinforce the brand's reputation for safety and trust.
Revenue Economics
Extremely strong, driven by the highly scalable network model with minimal variable costs per transaction. Profitability is a function of transaction volume, value, and the mix of higher-margin cross-border and value-added service revenues.
Not directly calculable for a B2B2C model, but the Lifetime Value (LTV) of a major bank partnership is exceptionally high, spanning many years and billions in transaction volume.
High. The company demonstrates consistent strong revenue growth and high profit margins, indicating an efficient revenue engine.
Optimization Recommendations
- •
Focus sales and marketing on increasing the penetration of value-added services, which carry higher margins than core transaction processing.
- •
Drive growth in cross-border and B2B payment volumes, which typically have more favorable economics.
- •
Invest in technology to lower the fixed costs of compliance and fraud monitoring through AI and automation.
Scale Barriers
Technical Limitations
- Limitation:
Interoperability with Emerging Payment Rails
Impact:Medium
Solution Approach:Develop and acquire technology to act as a bridge or value-added layer on top of new rails (e.g., real-time payment networks, CBDCs) rather than competing with them directly.
- Limitation:
Quantum Computing Threat to Cryptography
Impact:Low (Long-term)
Solution Approach:Invest in R&D for post-quantum cryptography standards to future-proof the security of the payment network, as highlighted in their forward-looking strategies.
Operational Bottlenecks
- Bottleneck:
Global Regulatory Compliance
Growth Impact:Acts as a constant drag on the speed of new product rollouts and market entries due to varying rules on data sovereignty, interchange fees, and open banking.
Resolution Strategy:Maintain a robust, in-country government relations and legal presence to anticipate and shape policy. Design products with modularity to adapt to different regulatory requirements.
- Bottleneck:
Managing AI-Driven Fraud at Scale
Growth Impact:Scammers are using AI to create more sophisticated attacks, requiring continuous investment to stay ahead and maintain ecosystem trust.
Resolution Strategy:Continue investing heavily in proprietary AI and machine learning models (e.g., 'Cyber Secure') and industry partnerships to 'fight AI with AI' and create network-level intelligence.
Market Penetration Challenges
- Challenge:
Intense Competition from Visa
Severity:Critical
Mitigation Strategy:Differentiate aggressively on value-added services, particularly in cybersecurity and data analytics, where analysts suggest Mastercard has a competitive edge. Focus on winning in new payment flows like B2B and open banking.
- Challenge:
Disruption from Fintechs and New Payment Rails
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Employ a 'co-opetition' strategy: partner with fintechs to provide them with network access and services, thereby benefiting from their growth rather than only competing with it. Develop solutions that add value to real-time payment systems.
- Challenge:
Geopolitical and Economic Instability
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Leverage a diversified global footprint to mitigate the impact of downturns in any single region. Focus on essential consumer spending and resilient B2B flows during economic uncertainty.
Resource Limitations
Talent Gaps
- •
Top-tier AI and data scientists with experience in financial services.
- •
Cybersecurity experts specializing in emerging threats.
- •
Business development and sales teams skilled in selling complex, high-value data and software solutions to enterprises.
Low. The business generates substantial free cash flow, sufficient to fund organic growth initiatives and strategic acquisitions.
Infrastructure Needs
Continuous investment in next-generation data centers to support AI model training and real-time transaction processing.
Expansion of API infrastructure to support the growth of open banking and developer partnerships.
Growth Opportunities
Market Expansion
- Expansion Vector:
B2B and Commercial Payments
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:Medium
Recommended Approach:Aggressively expand the suite of B2B solutions (e.g., virtual cards, Mastercard Receivables Manager, Commercial Direct Payments) to digitize accounts payable and receivable workflows, a massive and underserved market.
- Expansion Vector:
Geographic Expansion in Emerging Markets
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:High
Recommended Approach:Partner with local governments and fintechs in regions like Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America to drive financial inclusion and the transition from cash to digital payments.
Product Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Expansion of 'Services' Portfolio
Market Demand Evidence:Value-added services are Mastercard's fastest-growing segment, with revenue growth consistently outpacing core payments.
Strategic Fit:Excellent. Leverages existing data, network trust, and partner relationships.
Development Recommendation:Bundle cybersecurity, AI-driven data insights, and consulting into integrated solutions for financial institutions and merchants, creating a strong competitive moat.
- Opportunity:
Open Banking and Digital Identity
Market Demand Evidence:Rapid growth in A2A payments and regulatory mandates are creating a need for trusted third-party providers of identity verification and secure data transfer.
Strategic Fit:High. Extends Mastercard's role as a trusted intermediary in the financial ecosystem.
Development Recommendation:Build or acquire open banking platforms and digital identity solutions that can be offered to partners, positioning Mastercard as the infrastructure layer for the next generation of finance.
- Opportunity:
Digital Asset and Crypto Services
Market Demand Evidence:Growing institutional and consumer interest in digital assets, requiring secure on-ramps, off-ramps, and payment solutions.
Strategic Fit:Medium
Development Recommendation:Focus on providing the underlying infrastructure (e.g., security, payment rails, crypto-linked cards) for the digital asset economy, partnering with regulated crypto players rather than taking direct asset risk.
Channel Diversification
- Channel:
Embedded Finance Partnerships
Fit Assessment:High
Implementation Strategy:Develop turnkey solutions for large e-commerce platforms, marketplaces, and software companies to embed Mastercard payment and financing solutions directly into their ecosystems.
- Channel:
Government Services
Fit Assessment:High
Implementation Strategy:Expand partnerships with public sector entities for Government-to-Person (G2P) disbursements, tax collections, and smart city transit solutions.
Strategic Partnerships
- Partnership Type:
Big Tech Collaboration
Potential Partners
- •
Microsoft
- •
Google
- •
Apple
Expected Benefits:Deep integration into digital wallets, co-development of AI-powered commerce solutions (e.g., Mastercard Agent Pay with Microsoft), and securing a role in next-generation operating systems.
- Partnership Type:
B2B Software/ERP Integration
Potential Partners
- •
SAP
- •
Oracle
- •
NetSuite
Expected Benefits:Embed Mastercard's commercial payment solutions directly into the financial workflows of large corporations, automating B2B payments and increasing transaction volume.
Growth Strategy
North Star Metric
Value-Added Services (VAS) Revenue as a Percentage of Total Revenue
This metric directly tracks the success of Mastercard's strategic shift from a pure payment network to a diversified technology and services company. Growth in this area indicates deeper client relationships, higher margins, and a stronger competitive moat against commoditized transaction processing.
Increase VAS from ~39% of total net revenue to over 50% within the next 3-5 years.
Growth Model
Platform & Service Layer Expansion Model
Key Drivers
- •
Number of active financial institution and fintech partners.
- •
Gross Dollar Volume (GDV) processed on the network.
- •
Attach rate and penetration of high-margin Services (Cyber, Data, Open Banking) per partner.
- •
Volume of B2B and new payment flows processed.
Focus business development on a 'land and expand' strategy: secure core processing deals and then systematically upsell the full suite of cybersecurity, data analytics, and open banking services. Structure the recently realigned 'Services' division with dedicated teams to drive this expansion.
Prioritized Initiatives
- Initiative:
Scale AI-Powered Cybersecurity Suite
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:12-18 months
First Steps:Launch a targeted marketing and sales campaign aimed at existing mid-sized bank partners, bundling the 'Cyber Secure' suite with core processing renewals to accelerate adoption.
- Initiative:
Launch a Turnkey B2B Accounts Payable Automation Platform
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:18-24 months
First Steps:Acquire a smaller B2B payments automation software company to accelerate time-to-market and integrate it with Mastercard's virtual card and cross-border payment capabilities.
- Initiative:
Establish an Open Banking 'Network-as-a-Service'
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:24-36 months
First Steps:Pilot an open banking API platform with a select group of innovative fintech partners in Europe to refine the product offering and business model.
Experimentation Plan
High Leverage Tests
- Test Name:
Bundled Service Pricing Models
Hypothesis:Offering a tiered subscription bundle of Data, Cyber, and Loyalty services will increase the average revenue per partner compared to à la carte pricing.
Metrics To Track:Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) for partners, VAS attach rate, sales cycle length.
- Test Name:
SME Digital Onboarding Funnel
Hypothesis:A fully-digital onboarding process for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) via a partner bank will significantly increase commercial card adoption.
Metrics To Track:Conversion rate, time to first transaction, SME activation rate.
Utilize cohort analysis to track the performance of partners who adopt new initiatives versus a control group. Implement a centralized A/B testing platform for digital channel experiments.
Continuous experimentation within product pods, with a quarterly review of high-impact strategic tests by a dedicated Growth Council.
Growth Team
A centralized 'Strategic Growth' function, aligned with the new organizational structure, with embedded growth teams within each of the three pillars: Core Payments, Commercial & New Payment Flows, and Services.
Key Roles
- •
Head of New Payment Flows
- •
Director of AI Commercialization
- •
Open Banking Product Lead
- •
Strategic Partnerships Manager (Fintech & Big Tech)
Actively acquire talent from enterprise software, AI, and cybersecurity sectors. Develop an internal 'Growth Academy' to train existing product and marketing teams in experimentation, data analysis, and rapid iteration methodologies.
Mastercard's growth foundation is exceptionally strong, built on a globally recognized brand, deep partnerships, and a highly scalable network model. The company is in a mature phase for its core consumer card business but is astutely navigating a major industry evolution. The primary threat is not a direct competitor but the potential for disintermediation from new payment rails like real-time A2A payments and the changing preferences of digital-native consumers.
The most significant opportunity and the clear strategic imperative for Mastercard is to transition from a payment network into a comprehensive technology and services partner for the entire digital economy. The company's fastest-growing and highest-margin opportunities lie in its 'Services' division, particularly in AI-driven cybersecurity, data analytics, and open banking infrastructure. These services leverage Mastercard's core assets—data, trust, and network reach—to build a powerful competitive moat that is difficult for rivals to replicate.
Key growth vectors are clearly identified: 1) Dominating the digitization of B2B payments, a massive, underdeveloped market. 2) Expanding the suite of value-added services to become indispensable to partners. 3) Positioning the Mastercard network as a secure, interoperable layer that adds value to new payment flows, rather than competing against them.
Barriers to this growth are primarily external and regulatory, alongside intense competition from Visa and agile fintechs. Success will depend on execution speed, strategic acquisitions to gain new capabilities, and the ability to attract and retain specialized talent in AI and cybersecurity. The recommended growth strategy is to elevate 'Value-Added Services Revenue' as the North Star Metric, focusing the entire organization on selling deeper into existing partnerships and creating new, high-margin revenue streams that secure Mastercard's central role in global commerce for the next decade.
Legal Compliance
Mastercard maintains a comprehensive and robust Global Privacy Notice, easily accessible from the website's footer. The policy is well-structured, using clear language to detail the types of personal data collected, how it is used, and with whom it is shared. It explicitly addresses the rights of individuals under various global regulations, including GDPR and CCPA/CPRA, demonstrating a mature approach to data protection. The policy details user rights such as access, correction, and erasure, and provides clear mechanisms for users to exercise these rights through an online portal. Mastercard also highlights its adherence to 'Privacy by Design' principles and its EU-approved Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs), which facilitate lawful international data transfers. This showcases a strategic commitment to data protection that exceeds basic compliance.
The website provides 'Terms of Use' that are clearly written and accessible. The terms appropriately define the scope of the website's use as a source of information about Mastercard's products and services. Crucially, they clarify Mastercard's role as a payment technology network, distinguishing it from the financial institutions that issue cards and set terms for cardholders. This distinction is vital for managing legal risk and user expectations. The terms cover standard clauses such as intellectual property rights, limitations of liability, and disclaimers of warranties. From a strategic perspective, the clarity of these terms helps prevent disputes and reinforces Mastercard's brand positioning as a technology provider rather than a direct-to-consumer financial service.
Mastercard's website employs a sophisticated cookie consent banner that appears upon the first visit. It provides clear options to 'Accept all cookies', 'Reject all cookies', or 'Configure my cookies'. This granular control is a best practice under GDPR, allowing users to make informed choices. The 'Configure' option is user-friendly, categorizing cookies by purpose (e.g., Strictly Necessary, Performance, Functional, Targeting) and allowing users to toggle their preferences. The link to the Cookie Notice is prominently displayed within the banner and the site footer. This implementation is strong, demonstrating respect for user privacy choices and aligning with stringent global standards.
Mastercard's overall data protection posture is a significant strategic asset. By publicly committing to high standards like GDPR for all users and implementing EU-approved Binding Corporate Rules, the company builds trust with consumers, partners, and regulators globally. Their privacy policy clearly articulates a 'Privacy by Design' approach, integrating data protection into product development from the outset. This proactive stance not only mitigates the risk of non-compliance fines but also serves as a competitive differentiator in an industry where data security and trust are paramount. The provision of a dedicated online portal for managing data rights further enhances transparency and user empowerment, positioning Mastercard as a responsible data steward.
The website demonstrates a solid commitment to accessibility. Key indicators include the presence of a 'Skip to main content' link, which is a fundamental feature for users of screen readers. A dedicated 'Accessibility' link in the footer leads to a detailed statement affirming their commitment to making their digital properties accessible and referencing the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). While a full technical audit is beyond this analysis, these visible features suggest a proactive and structured approach to meeting standards like the ADA and WCAG. This is crucial not only for legal compliance in key markets like the US and EU but also for aligning with their corporate mission of powering an inclusive economy.
As a central entity in the global payments ecosystem, Mastercard's compliance extends far beyond standard website regulations. The company is a founder and governing member of the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC), which sets the PCI DSS standards mandatory for all entities that process, store, or transmit cardholder data. While the corporate website itself doesn't process transactions, its content and legal framework must reflect the security-first posture that underpins the entire brand. The site provides links to 'Mastercard rules and compliance programs', offering transparency to its partners (financial institutions, merchants). Furthermore, as a financial technology company, it is subject to oversight regarding competition and fair business practices, such as regulations stemming from the Durbin Amendment in the U.S. which mandates network choice for debit transactions. The website's clear disclaimers about not being a card issuer are a key compliance element, managing regulatory risk under consumer financial protection laws.
Compliance Gaps
While the cookie banner is excellent, the user experience for opting out of marketing communications or data analytics programs, although mentioned in the privacy policy, could be more prominently featured on user-facing pages beyond the privacy portal to enhance transparency.
The Accessibility Statement could be enhanced by specifying the exact level of WCAG conformance it targets (e.g., WCAG 2.1 Level AA) to provide greater clarity and a measurable benchmark for users and regulators.
Compliance Strengths
- •
Global Data Protection Leadership: Proactively applying GDPR standards to all users globally and using Binding Corporate Rules for data transfers positions Mastercard as a leader in data privacy.
- •
Granular Cookie Consent: The cookie consent mechanism is a best-in-class example, offering clear, easy-to-use options for granular user control, fully aligning with GDPR's stringent requirements.
- •
Clear Role Distinction: The Terms of Use and other site content effectively and consistently distinguish Mastercard's role as a payment network from that of its card-issuing financial institution partners, which is a critical legal and business distinction.
- •
Accessibility Commitment: The presence of a detailed accessibility statement and functional accessibility features ('Skip to main content') indicates a mature and proactive compliance posture.
- •
Transparency for Partners: Providing direct access to 'Mastercard rules and compliance programs' from the main site enhances transparency and trust within its B2B ecosystem.
Risk Assessment
- Risk Area:
Regulatory Scrutiny
Severity:Low
Recommendation:Continuously monitor evolving global data privacy laws and antitrust regulations in the payments sector. Ensure that marketing language and product descriptions on the website remain precisely aligned with the legal disclaimers about Mastercard's role in the ecosystem to avoid any potential for misinterpretation by regulators.
- Risk Area:
Accessibility Litigation
Severity:Low
Recommendation:To further mitigate the low but persistent risk of accessibility-related lawsuits, specify the target WCAG conformance level (e.g., 2.1 AA) in the Accessibility Statement and conduct periodic third-party audits to validate and document compliance.
- Risk Area:
User Trust Erosion
Severity:Low
Recommendation:While privacy policies are comprehensive, consider adding more concise, user-friendly summaries or FAQs about data use at relevant points of interaction on the site. This would enhance transparency and reinforce the trust established by the detailed legal documents.
High Priority Recommendations
Update the Accessibility Statement to explicitly state the target level of WCAG conformance (e.g., WCAG 2.1 Level AA) to create a clear compliance benchmark and further reduce legal risk.
Conduct a user experience review of the process for opting out of data analytics and marketing programs to ensure it is as simple and accessible as the cookie consent mechanism.
Mastercard's legal positioning, as reflected through its public website, is a strategic fortress. The company demonstrates a world-class understanding of its complex regulatory environment, using its compliance posture not merely as a defense mechanism but as a tool to build market trust and competitive advantage. Their proactive adoption of global best practices in data privacy (GDPR for all), cookie consent, and accessibility showcases a mature and well-resourced legal and compliance function. The meticulous distinction between its role as a technology network versus a financial institution is a cornerstone of its risk management strategy. This clarity permeates the Terms of Use and general site content, effectively managing expectations for consumers, partners, and regulators. By openly providing access to its network rules and compliance program information, Mastercard fosters transparency with its B2B partners, which is essential for maintaining the integrity and stability of its global payment ecosystem. The identified gaps are minor and relate to enhancing user experience rather than correcting fundamental compliance failures. Overall, Mastercard's website projects an image of a legally sophisticated, trustworthy, and responsible market leader, turning complex legal obligations into a strategic asset that underpins its brand and global operations.
Visual
Design System
Modern Corporate Humanism
Excellent
Advanced
User Experience
Navigation
Horizontal Audience-Based Navigation
Intuitive
Excellent
Information Architecture
Logical
Clear
Moderate
Conversion Elements
- Element:
Sectional 'Learn more' CTA Button
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:Replace generic 'Learn more' copy with more specific, benefit-oriented language to better set user expectations and increase intent. For example, 'Explore Security Solutions' or 'Discover Card Benefits'.
- Element:
Clickable Image-led Cards (with arrow icon)
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:Implement subtle hover effects (e.g., slight zoom or shadow lift) to increase affordance and provide clearer visual feedback that the entire element is a clickable target.
- Element:
'Explore priceless.com' CTA Button
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Somewhat effective
Improvement:This CTA leads to a separate brand experience site. Clarifying this with text like 'Visit our Priceless experiences site' could prevent user confusion and better frame the destination.
Assessment
Strengths
- Aspect:
Cohesive Brand & Visual Identity
Impact:High
Description:The website's design is a masterclass in modern corporate branding. It seamlessly integrates Mastercard's iconic red and yellow circles and the 'Priceless' ethos into a sophisticated, clean, and digitally-native aesthetic. The use of generous white space, high-quality diverse imagery, and fluid graphic elements creates a premium and trustworthy feel.
- Aspect:
Effective Visual Storytelling
Impact:High
Description:The homepage tells a compelling story, moving from the high-level brand promise ('Priceless') to the corporate mission ('Powering economies'), then to specific solutions for businesses and tangible benefits for consumers. This narrative structure, supported by human-centric imagery, makes the complex business feel accessible and purpose-driven.
- Aspect:
Clear Information Architecture & Hierarchy
Impact:Medium
Description:The site effectively segments content for its diverse audiences (consumers, businesses, innovators) through both the main navigation and the homepage layout. Large, clear typography and a logical vertical flow guide the user through a large amount of information without feeling overwhelming.
Weaknesses
- Aspect:
Generic Call-to-Action Language
Impact:Low
Description:The repeated use of 'Learn more' across multiple, distinct sections is a missed opportunity. More descriptive and compelling copy could improve the user's information scent and increase qualified click-throughs to deeper pages.
- Aspect:
Moderate Cognitive Load
Impact:Medium
Description:By serving multiple, distinct audiences on a single homepage, there is a risk of choice paralysis or difficulty in finding specific information quickly. While the design is clean, a user must parse many different value propositions to find their own path.
- Aspect:
Static Engagement Elements
Impact:Low
Description:The page relies on a traditional, static scroll-and-click interaction model. There is an opportunity to introduce subtle micro-interactions, animations, or more dynamic modules to enhance engagement and further elevate the premium brand experience.
Priority Recommendations
- Recommendation:
A/B Test Action-Oriented CTA Copy
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Incrementally testing more descriptive CTA copy (e.g., 'Secure your business' vs. 'Learn more') can directly impact conversion rates on key user journeys by providing stronger information scent and aligning with user intent.
- Recommendation:
Introduce an Audience-Selection Tool
Effort Level:High
Impact Potential:High
Rationale:To mitigate cognitive load, implement an interactive module near the top of the page that prompts users to self-identify (e.g., 'I am a cardholder,' 'I run a business,' 'I am a developer'). This would allow for a more personalized and streamlined content experience, increasing relevance and task completion rates for key audiences.
- Recommendation:
Enhance Interactive Feedback
Effort Level:Medium
Impact Potential:Low
Rationale:Incorporate subtle micro-interactions and richer hover states on clickable elements. This would improve the perceived usability and add a layer of polish that reinforces Mastercard's position as a premium, modern technology company.
Mobile Responsiveness
Excellent
The design's modular, card-based structure is inherently flexible, allowing content blocks to stack logically and cleanly across different device viewports. Large fonts and clear touch targets are prioritized.
Mobile Specific Issues
No itemsDesktop Specific Issues
On ultra-wide monitors, the generous white space might cause some thematically-linked content sections to appear visually distant from one another.
The visual design and user experience of Mastercard.com represent a mature and highly effective execution of modern corporate branding. The design system is advanced, consistently applying a clean, human-centric aesthetic that masterfully communicates the brand's evolution from a financial services company to a global technology leader. The brand's core identity, built around the iconic interlocking circles and the emotionally resonant 'Priceless' campaign, is expressed with sophistication and confidence.
The user experience is built on a logical information architecture that successfully caters to a diverse set of audiences, including consumers, B2B clients, and innovators. Navigation is intuitive, and the visual hierarchy effectively guides users through a narrative that connects the company's high-level mission to its tangible products and services. The use of high-quality, diverse imagery and video enhances the storytelling, making the brand feel relatable and purpose-driven.
While the overall experience is excellent, key opportunities for optimization exist. The primary weakness lies in the generic 'Learn more' call-to-action copy, which could be replaced with more specific, action-oriented language to improve user guidance. Furthermore, the high density of information, while well-organized, presents a moderate cognitive load; a personalization feature could significantly streamline the user journey for specific audience segments. Implementing these strategic enhancements would further elevate an already best-in-class digital brand experience.
Discoverability
Market Visibility Assessment
Mastercard exhibits exceptional brand authority, transitioning its digital presence from a payments network to a comprehensive technology and data insights powerhouse. Its primary authority-building asset is the 'Mastercard Economics Institute', which provides global economic analysis and thought leadership, frequently cited in financial media. The website's structure clearly delineates content for diverse, high-value audiences ('For business', 'For innovators', 'For the world'), positioning Mastercard as a central player in global commerce, financial inclusion, and the future of technology like AI and open banking. This strategy elevates the brand beyond transactional services to a strategic partner for businesses and governments.
Digitally, Mastercard competes in a duopoly with Visa, with both having near-universal acceptance among online merchants. While Visa holds a larger market share in the US, Mastercard has a strong presence in Europe and North America and is aggressively competing globally. The more critical digital battleground is in B2B services and emerging fintech solutions. Here, Mastercard competes not only with Visa but also with players like Stripe, PayPal, and Adyen for digital share of voice on topics like 'B2B payment solutions', 'virtual cards', and 'open banking'. Their visibility in these niche B2B search markets is crucial for future growth beyond traditional card transaction fees.
Mastercard's digital presence serves two distinct acquisition functions. For consumers ('For you'), the goal is preference creation, influencing their choice of card from an issuing bank. The website facilitates this indirectly through tools like 'Find a card' and by highlighting 'Priceless' experiences. For B2B audiences ('For business', 'For innovators'), the website is a direct lead generation and customer acquisition engine. Content on cybersecurity, data analytics, open finance, and commercial payments is designed to capture interest from financial institutions, corporations, and fintechs, driving them toward high-value advisory and technology services.
The website demonstrates a strong global-local strategy by featuring dedicated newsrooms for Asia Pacific, Europe, Eastern Europe, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America. This allows for tailored messaging and market-specific insights, enhancing digital penetration in key growth regions. Their content on global travel trends and cross-border payments further solidifies their position as a facilitator of international commerce, appealing to a worldwide audience of both consumers and businesses.
Mastercard's digital content provides comprehensive coverage of the entire payments and financial technology ecosystem. It spans foundational topics (credit/debit cards, payment processing) and strategically invests in forward-looking themes like AI, Digital Assets, Open Banking, and Cybersecurity. This demonstrates a clear strategy to own the conversation around the future of money and data, positioning them not as a legacy payment provider but as an innovator shaping the next generation of commerce and finance.
Strategic Content Positioning
Content is strategically segmented to align with diverse customer journeys. Awareness is driven by high-level thought leadership from the 'Mastercard Economics Institute' and 'News and trends'. The 'For you' section targets consumers in the consideration phase with card comparisons and benefit explanations. The 'For business' and 'For innovators' sections cater to B2B and fintech audiences in the evaluation phase, offering detailed solutions, API documentation for developers, and partnership programs like 'Start Path'. This clear segmentation effectively guides different user personas toward relevant information and conversion points.
Mastercard's primary thought leadership engine, the 'Economics Institute', is world-class. The key opportunity is to create more direct pathways from these high-level insights to their commercial B2B solutions. For example, a report on supply chain disruptions could strategically link to their commercial payment and financing solutions. They can further leverage their data by creating more accessible content formats like executive webinars, podcasts, and data visualizations tailored to specific industries (e.g., retail, travel), transforming broad economic insights into actionable business intelligence.
While Mastercard's content is robust, agile fintech competitors like Stripe and Adyen often lead in creating highly practical, developer-centric content that simplifies complex topics like API integration and embedded finance. Mastercard has a 'Developers' section but could create a more extensive resource hub with tutorials, use cases, and interactive tools to better capture the innovator and developer audience. Furthermore, as competitors like Visa retreat from US open banking, Mastercard has a significant opportunity to become the dominant voice and educator in this space, creating definitive guides and resources for financial institutions and fintechs.
Mastercard achieves excellent brand messaging consistency. The iconic 'Priceless' consumer brand ethos is subtly woven into a broader corporate mission of 'powering economies and empowering people'. This theme of enablement and creating possibilities extends credibly from consumer experiences to empowering small businesses and fostering inclusive growth ('For the world'). This consistency builds a powerful, unified brand narrative that reinforces trust and purpose across all stakeholder groups.
Mastercard's B2B content strategy is highly developed, focusing on sophisticated solutions beyond basic payment processing. They offer extensive resources on cybersecurity, data analytics, AI-driven personalization, and advisory services. Their solutions like 'Mastercard Track' for B2B payments and 'Mastercard Move' for cross-border transactions are supported by content that addresses complex corporate needs, such as accounts payable/receivable automation and treasury management. This positions them as a strategic partner for large corporations and financial institutions.
Digital Market Strategy
Market Expansion Opportunities
- •
Develop a dedicated digital resource center for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) that offers insights on cash flow management, digital transformation, and cybersecurity, positioning Mastercard as an indispensable growth partner against fintechs targeting this segment.
- •
Expand thought leadership in emerging technologies by launching dedicated content hubs for 'AI in Commerce' and 'The Future of Digital Identity', featuring proprietary research, expert interviews, and use cases.
- •
Create industry-specific content verticals (e.g., for Healthcare, Public Sector, Retail) that package their various solutions (payments, data, security) into tailored playbooks addressing the unique challenges of each sector.
Customer Acquisition Optimization
- •
Implement clearer conversion funnels from thought leadership content (e.g., 'Economics Institute' reports) to relevant B2B service pages and lead capture forms, such as 'Request a consultation'.
- •
Develop interactive assessment tools (e.g., 'Cybersecurity Risk Calculator for Businesses') that provide value to potential B2B clients in exchange for lead information.
- •
Create targeted paid media campaigns promoting B2B solutions based on user engagement with specific thought leadership topics, ensuring relevant solutions are presented to interested parties.
Brand Authority Initiatives
- •
Repurpose 'Economics Institute' reports into a recurring video series or podcast featuring their economists discussing key trends, making the content more accessible to a broader business audience.
- •
Launch a global 'State of Fintech' annual report in partnership with their 'Start Path' program, cementing their authority as a central hub of financial innovation.
- •
Actively pursue placements for their executives and data scientists as speakers at major technology and finance conferences to amplify their expertise beyond their own channels.
Competitive Positioning Improvements
- •
Sharpen messaging to differentiate from traditional competitors like Visa by emphasizing technology, data, and value-added services over just the payment network.
- •
Position Mastercard as the trusted, secure, and scalable alternative to fintechs in areas like open banking and B2B payments, highlighting their global infrastructure and compliance expertise.
- •
Launch a content series directly comparing the strategic advantages of their B2B solutions (e.g., data security, global reach) against the more fragmented or niche offerings of newer market entrants.
Business Impact Assessment
Market share will be measured by digital share of voice for strategic B2B keywords (e.g., 'commercial payment solutions,' 'virtual card API') against key competitors. Success is indicated by an increasing share of non-branded organic traffic to B2B solution pages, signifying growing authority and discovery outside their core brand.
For B2B, key metrics include the number of qualified leads generated through the website, such as whitepaper downloads, webinar registrations, and 'Contact Sales' form submissions for high-value services. Tracking the conversion rate from content engagement to lead is critical. For B2C, success is measured by referral traffic to partner bank websites initiated from the 'Find a card' section.
Authority is measured by the volume of citations and media mentions of the 'Mastercard Economics Institute' in reputable financial news outlets, growth in organic search rankings for thought leadership topics (e.g., 'economic outlook 2025'), and engagement rates on social media for insight-led content.
Benchmarking will involve regular analysis of Mastercard's search visibility and content depth on core innovation themes (Open Banking, AI, Cybersecurity) compared to Visa, American Express, and leading fintechs like Stripe and PayPal. Success is defined by achieving and maintaining a top-three search position for these strategic topics.
Strategic Recommendations
High Impact Initiatives
- Initiative:
Launch an 'SME Growth Hub' Content Platform
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Address the underserved SME market by providing value beyond payments, building a competitive moat against fintechs who are aggressively targeting this segment. This fosters loyalty and creates upsell opportunities for Mastercard's B2B services.
Success Metrics
- •
Organic traffic to the SME hub
- •
Downloads of SME-focused guides
- •
Leads generated for small business solutions
- Initiative:
Create a 'From Insight to Action' B2B Conversion Funnel
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Capitalize on the significant authority of the Mastercard Economics Institute by creating a systematic process to convert thought leadership audiences into B2B customers for advisory, data, and cybersecurity services.
Success Metrics
- •
Lead-to-conversion rate from thought leadership content
- •
Number of B2B solution consultations booked from reports
- •
Attributed revenue from content-generated leads
- Initiative:
Establish a Developer & Innovator Center of Excellence
Business Impact:Medium
Market Opportunity:Compete more effectively with developer-first companies like Stripe by creating a best-in-class resource center. This will attract the next generation of fintech innovators to build on Mastercard's platform, ensuring future relevance and partnership opportunities.
Success Metrics
- •
API documentation usage
- •
Engagement in developer forums
- •
Enrollment in the 'Start Path' innovator program
Transition Mastercard's digital market position from a 'global payments network' to a 'trusted digital economy partner.' This strategy leverages its core strengths of security, scale, and data to expand into higher-margin B2B services. The focus should be on demonstrating how Mastercard's technology and insights empower businesses, governments, and innovators to navigate the complexities of modern commerce, thereby justifying its premium position over both traditional and fintech competitors.
Competitive Advantage Opportunities
- •
Leverage proprietary, anonymized transaction data to produce unparalleled economic insights and predictive analytics, a unique asset competitors cannot easily replicate.
- •
Utilize the globally recognized brand trust to be the preferred partner for complex, high-stakes areas like cybersecurity and cross-border B2B payments.
- •
Amplify the 'Priceless' brand halo to create an emotional and purpose-driven connection that transcends the purely functional offerings of many fintech competitors.
Mastercard has successfully evolved its digital presence from a consumer-focused brand platform to a multi-faceted B2B and thought leadership engine. The website architecture, with its clear segmentation for consumers, businesses, innovators, and social impact, reflects a sophisticated understanding of its diverse stakeholders. The brand's primary digital asset is the 'Mastercard Economics Institute', which anchors its authority and provides a powerful halo effect across its commercial offerings.
The core strategic challenge lies in bridging the gap between its world-class thought leadership and its B2B customer acquisition goals. While the content exists, the user journey from consuming an insightful report to exploring a relevant commercial solution is not always clear or compelling. Optimizing this funnel represents the single largest opportunity for digital growth.
Competitively, Mastercard is well-positioned. It can counter the scale of Visa by focusing on its superior technology and data services, and it can counter the agility of fintechs by emphasizing its trust, security, and global infrastructure. The recommended strategy is to double down on this positioning as a 'trusted digital economy partner.' This involves creating dedicated content ecosystems for high-growth segments like SMEs and developers, and systematically converting the authority generated by its economic insights into tangible B2B leads. By focusing on value-added services and leveraging its immense data assets, Mastercard's digital presence can be a primary driver of growth in the next decade, moving beyond transaction fees to become an indispensable partner in global commerce.
Strategic Priorities
Strategic Priorities
- Title:
Accelerate B2B Payment Ecosystem Dominance
Business Rationale:The B2B payments market is significantly larger than consumer payments and remains largely undigitized. Capturing this market is the single greatest opportunity to diversify revenue away from consumer spending and create a new, massive growth engine.
Strategic Impact:Shifts Mastercard's revenue balance from a consumer-cyclical model to a more stable, corporate-focused one. Establishes a competitive moat in the lucrative commercial payments space against both traditional banks and agile fintechs.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in B2B Gross Dollar Volume (GDV) by 40% year-over-year
- •
Revenue from dedicated B2B solutions (e.g., Mastercard Track, virtual cards) as a percentage of total revenue
- •
Market share growth in commercial and cross-border B2B transactions
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Revenue Model
- Title:
Productize 'Trust' into an Integrated Security & Data Services Platform
Business Rationale:Value-Added Services (VAS) are Mastercard's fastest-growing, highest-margin segment. Bundling cybersecurity, AI-driven fraud prevention, data analytics, and digital identity solutions into a single platform moves Mastercard up the value chain from a transaction processor to an indispensable technology partner.
Strategic Impact:Creates a powerful, high-margin recurring revenue stream and significantly increases switching costs for financial institution partners. Solidifies differentiation against Visa (competing on tech) and fintechs (competing on trust and scale).
Success Metrics
- •
VAS revenue growth rate exceeding core payment revenue growth by 2x
- •
Increase in VAS 'attach rate' to core processing deals to over 75%
- •
Launch and adoption rate of the new integrated 'Trust Platform' by key enterprise clients
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Market Position
- Title:
Pioneer a 'Multi-Rail' Strategy to Orchestrate Value Across All Payment Networks
Business Rationale:The rise of real-time Account-to-Account (A2A) payment rails and open banking presents an existential threat of disintermediation. The only viable long-term strategy is to embrace these rails and provide an essential value-added layer (e.g., security, data, identity) on top of them.
Strategic Impact:Future-proofs the business by transforming Mastercard from a 'card network' into a 'network of networks.' This ensures continued relevance and profitability regardless of the underlying payment method, positioning the company as the foundational intelligence and trust layer for all forms of value exchange.
Success Metrics
- •
Volume of A2A transactions secured or enhanced by Mastercard services
- •
Revenue generated from services on non-card payment rails
- •
Number of active partnerships with national real-time payment schemes
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Long-term Vision (12+ months)
Category:Business Model
- Title:
Launch a 'Digital Identity-as-a-Service' (IDaaS) Business Unit
Business Rationale:A secure, reusable digital identity is a critical unmet need in the digital economy, extending far beyond payments. Mastercard's unique position of trust between consumers, merchants, and banks allows it to create a new, defensible business line in this whitespace.
Strategic Impact:Establishes a new, non-transactional revenue stream and embeds Mastercard into a wider range of digital interactions (e.g., age verification, account opening, secure login). This transforms the company into a foundational infrastructure provider for the digital economy.
Success Metrics
- •
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) from the IDaaS business unit
- •
Number of active verified identities on the platform
- •
Number of non-financial service partners using the identity network
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Long-term Vision (12+ months)
Category:Revenue Model
- Title:
Unify the Brand Narrative by Integrating 'Priceless' Across the B2B Portfolio
Business Rationale:The iconic 'Priceless' brand concept is a powerful emotional asset currently siloed in consumer marketing. Infusing this ethos into the B2B and technology story can differentiate Mastercard from the purely functional messaging of fintechs and the corporate tone of competitors.
Strategic Impact:Creates a single, cohesive, and emotionally resonant brand identity that elevates the company's purpose beyond transactions. This strengthens brand preference, enhances employee engagement, and provides a powerful narrative for B2B customer acquisition.
Success Metrics
- •
Improved brand perception scores for 'Innovation' and 'Partnership' among B2B decision-makers
- •
Increase in qualified inbound leads from brand-led B2B content marketing campaigns
- •
Measurable lift in brand value and employer brand attractiveness
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Quick Win (0-3 months)
Category:Brand Strategy
Mastercard must accelerate its evolution from a payment network into a comprehensive digital trust company. This requires aggressively capturing the B2B payments market, productizing its security and data assets into high-margin services, and strategically positioning itself as the essential value layer across all payment rails to ensure long-term relevance and growth.
The key competitive advantage to build is an integrated 'Trust Stack' — a unified platform combining payments, cybersecurity, data intelligence, and digital identity, all underpinned by unparalleled global brand recognition and deep-rooted partnerships within the financial ecosystem.
The primary growth catalyst will be the rapid expansion of the high-margin 'Value-Added Services' portfolio, particularly by embedding these security and data solutions into the massive, underserved B2B digital payments market.