eScore
molinahealthcare.comThe eScore is a comprehensive evaluation of a business's online presence and effectiveness. It analyzes multiple factors including digital presence, brand communication, conversion optimization, and competitive advantage.
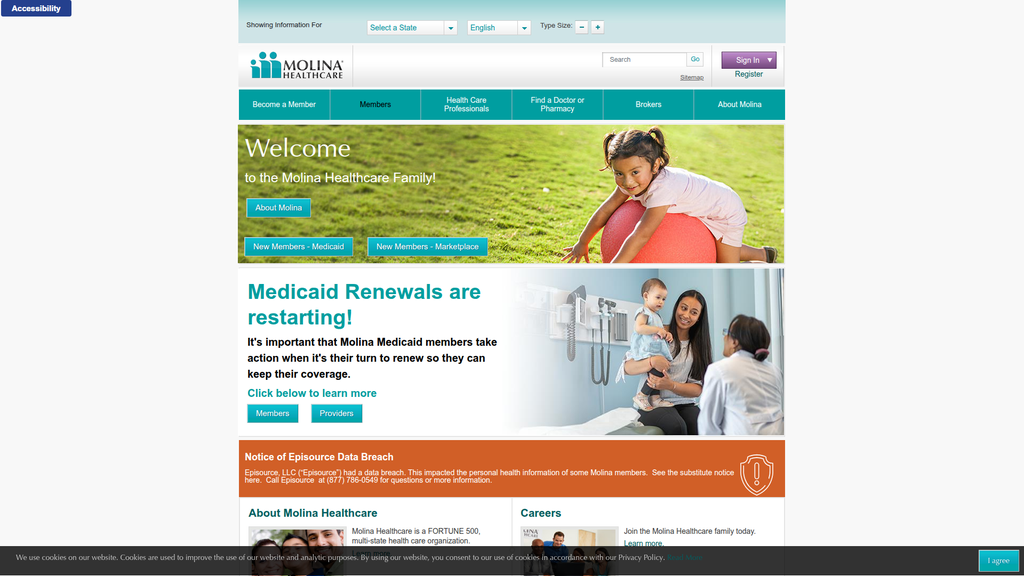
Molina's digital presence is functional for existing members but strategically weak for acquisition and brand building. The website's SEO is underdeveloped, failing to capture users in the crucial awareness and consideration stages of their journey, especially during the critical Medicaid redetermination period. While the site is structured for its core audience with state-specific portals, its content authority is low, lacking thought leadership. The visual design is outdated, which can impact user trust and engagement in a competitive digital landscape.
The website's information architecture is logically segmented by state and primary audience (Members, Providers, Brokers), which is a necessary and effective structure for its business model.
Launch a comprehensive, state-specific content hub focused on 'Medicaid Redetermination & Coverage Transition' to capture high-intent search traffic, reduce member churn, and acquire new Marketplace enrollees.
The brand's messaging is clear, direct, and effectively segmented for its core audiences, which is a strength when communicating urgent tasks like Medicaid renewals. However, it fails to build a deeper emotional connection or strongly differentiate from competitors. The core brand promise, 'Welcome to the Molina Healthcare Family!', is a powerful concept that remains severely underdeveloped and is often contradicted by the site's transactional and institutional tone.
Messaging is highly effective at audience segmentation and communicating timely, relevant information, such as the urgent need for members to complete Medicaid renewals.
Substantiate the 'Family' brand promise by creating a 'Why Molina?' section on the homepage featuring member testimonials, stories of community impact, and tangible proof points about care quality.
The website suffers from significant conversion friction due to a dated visual design and poor visual hierarchy. The homepage presents multiple competing calls-to-action with similar weighting, leading to high cognitive load and decision paralysis for new users. While the inclusion of accessibility features is a critical strength, the overall user journey for a prospective member is unclear and does not effectively guide them toward the primary goal of enrollment.
The prominent display of accessibility and multi-language support tools demonstrates a strong commitment to serving a diverse and vulnerable population, which is a core tenet of the business.
Redesign the homepage 'hero' section to feature a single, compelling headline and one primary call-to-action (e.g., 'Find Your Plan'), demoting secondary links to reduce cognitive load and clarify the user journey.
Molina's credibility is a mix of major strengths and significant weaknesses. As a Fortune 500 company with deep roots in government programs, it has substantial institutional credibility. However, the prominent notice of a massive data breach from a third-party vendor (Episource) severely undermines trust and highlights a critical operational risk. While their transparency is commendable, the event itself exposes the company to significant legal and reputational damage.
Being an established Fortune 500 company with a long history of managing government health contracts provides a strong foundation of institutional credibility and stability.
Overhaul the third-party vendor risk management program with more stringent security audits and contractual obligations to prevent future data breaches and rebuild member and regulator trust.
Molina's primary competitive advantage is its singular focus and deep expertise in the complex government-sponsored healthcare market. This specialization allows it to navigate state-level regulations and cater to the specific needs of low-income populations more effectively than diversified competitors. While it lacks the scale and data capabilities of giants like UnitedHealth Group, its specialized, cost-effective operational model creates a defensible moat.
A deep-rooted, singular focus on government-sponsored healthcare allows for specialized expertise and strong relationships with state partners, which is difficult for more diversified competitors to replicate.
Invest in data analytics capabilities focused on value-based care and population health for the dual-eligible (D-SNP) population to solidify expertise in this high-need, high-revenue niche.
The company has a mature and proven growth model centered on winning state contracts and strategic M&A, demonstrating strong scalability. Recent acquisitions and new contract wins show this engine is effective, with revenue projected to grow. Expansion into the Medicare Advantage and dual-eligible (D-SNP) markets provides a significant runway for future growth, tapping into favorable demographic trends. The primary constraint is the slow, state-by-state nature of regulatory approval and contract procurement.
A disciplined and successful strategy of growth through M&A and winning new state contracts has consistently expanded the company's geographic footprint and membership base.
Establish a formal Integration Management Office (IMO) with a standardized playbook to accelerate the integration of acquired companies, ensuring faster realization of synergies and a consistent member experience.
Molina's business model is exceptionally coherent and tightly aligned with its market. The entire organization is structured to serve the needs of government payers and their beneficiaries, with a revenue model based on predictable, long-term capitation contracts. The strategic focus on a specific market segment (low-income populations) allows for deep expertise and operational efficiency. The model is well-timed to address the ongoing needs of a large, persistent market segment in the US healthcare system.
The business model is highly specialized and perfectly aligned with its target market, creating a virtuous cycle of deep expertise, strong government partner relationships, and a defensible market position.
Accelerate the transition to value-based care partnerships with providers, shifting a greater percentage of revenue to models that share financial risk and reward for improved health outcomes.
Molina is a major player in its niche but is not the market leader in terms of sheer scale; it competes with larger entities like Centene and UnitedHealth Group. Its market power comes from its deep entrenchment in specific state contracts rather than national dominance. The company has limited pricing power, as rates are dictated by government negotiations. However, its specialization gives it significant leverage and influence within the government-sponsored program sector.
Holds a significant market position as one of the top national players focused exclusively on Medicaid and government-sponsored programs, giving it a strong voice and influence in that specific sector.
Develop a robust digital ecosystem for community-based enrollment assisters and brokers, turning them into a powerful, indirect sales channel to gain market share against larger competitors.
Business Overview
Business Classification
Managed Care Organization (MCO)
Healthcare Insurance Provider
Healthcare
Sub Verticals
- •
Government-Sponsored Healthcare
- •
Medicaid Managed Care
- •
Medicare Advantage
- •
Health Insurance Marketplace (ACA)
Mature
Maturity Indicators
- •
FORTUNE 500 company status.
- •
Long-standing public company (IPO in 2003).
- •
Consistent revenue growth over the past decade.
- •
Significant market presence across multiple states (operates in 22 states).
- •
Active and strategic M&A activity to drive expansion.
Enterprise
Steady
Revenue Model
Primary Revenue Streams
- Stream Name:
Medicaid Premiums
Description:Receives fixed per-member, per-month payments (capitation fees) from state governments to manage the healthcare of eligible low-income individuals and families. This is the largest source of revenue.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:State Governments (on behalf of Medicaid beneficiaries)
Estimated Margin:Low to Medium
- Stream Name:
Medicare Premiums
Description:Receives fixed monthly payments from the federal government (CMS) to provide Medicare Advantage (Part C) and Prescription Drug (Part D) plans to eligible seniors and individuals with disabilities.
Estimated Importance:Secondary
Customer Segment:Federal Government (on behalf of Medicare beneficiaries)
Estimated Margin:Medium
- Stream Name:
Marketplace Premiums
Description:Receives premium payments from individuals and families who purchase health insurance plans through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplaces, often supplemented by federal subsidies.
Estimated Importance:Tertiary
Customer Segment:Individuals & Families (ACA Marketplace)
Estimated Margin:Medium
Recurring Revenue Components
- •
Monthly capitation payments from state Medicaid contracts
- •
Monthly payments from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)
- •
Monthly premium payments from Marketplace members
Pricing Strategy
Government-Contracted Capitation and Regulated Premiums
Value-driven
Opaque
Pricing Psychology
Focus on 'low-cost' or 'no-cost' plans for members, with costs covered by government funding
Emphasis on comprehensive benefits for a fixed, predictable cost (to the government payer)
Monetization Assessment
Strengths
- •
Highly predictable and stable revenue from long-term government contracts.
- •
Diversified across Medicaid, Medicare, and Marketplace segments, mitigating risk from any single program.
- •
Growth is directly tied to government healthcare spending and enrollment, which tends to be counter-cyclical.
Weaknesses
- •
High dependency on government contracts and funding, creating significant regulatory and political risk.
- •
Profitability is sensitive to medical cost trends and the Medical Loss Ratio (MLR), which can be volatile.
- •
Thin profit margins are inherent in the government-sponsored healthcare business model.
Opportunities
- •
Expansion into new states through competitive bidding or acquisition of smaller health plans.
- •
Growth in high-need populations, particularly dual-eligibles (Medicaid and Medicare).
- •
Increased adoption of telehealth and digital health platforms to improve efficiency and member engagement.
Threats
- •
Changes in healthcare policy, such as Medicaid funding cuts or alterations to the ACA.
- •
Intense competition from larger national players like Centene and UnitedHealth Group for state contracts.
- •
Rising healthcare costs and unfavorable rate-setting by state governments can compress margins.
Market Positioning
Specialist in Government-Sponsored Healthcare
Major Player (Top 5-10 nationally in Medicaid managed care).
Target Segments
- Segment Name:
Medicaid Beneficiaries
Description:Low-income individuals, families, children, pregnant women, and people with disabilities who qualify for state-run Medicaid programs.
Demographic Factors
- •
Low household income (at or below a percentage of the Federal Poverty Level)
- •
Diverse age groups, from children to seniors
- •
Often from underserved or minority communities
Psychographic Factors
- •
High price sensitivity (often requiring zero-premium plans)
- •
May have limited health literacy or experience navigating the healthcare system
- •
Concerned with basic access to primary and preventative care
Behavioral Factors
Higher utilization of emergency rooms for non-emergency care if primary care is inaccessible
May face social determinants of health (SDoH) challenges like housing or food insecurity
Pain Points
- •
Difficulty finding providers who accept Medicaid
- •
Navigating complex eligibility and enrollment processes
- •
Lack of access to transportation for medical appointments
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
Medicare Beneficiaries (including Dual-Eligibles)
Description:Individuals aged 65 or older, or younger people with specific disabilities, who are eligible for federal Medicare benefits. A key sub-segment is 'dual-eligibles' who qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid.
Demographic Factors
- •
Primarily aged 65+
- •
May have multiple chronic conditions
- •
Dual-eligibles have very low income and complex health needs
Psychographic Factors
- •
Desire for predictable, low out-of-pocket costs
- •
Value for supplemental benefits not covered by original Medicare (dental, vision)
- •
Need for coordinated care to manage complex health issues
Behavioral Factors
- •
High prescription drug utilization
- •
Frequent interaction with the healthcare system
- •
Reliance on care coordinators and case managers
Pain Points
- •
Managing multiple chronic conditions and medications
- •
High out-of-pocket costs for services and prescriptions
- •
Fragmented care between different specialists and providers
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
Marketplace (ACA) Enrollees
Description:Individuals and families who do not have access to employer-sponsored insurance and purchase coverage through the ACA Health Insurance Marketplace, often with income-based subsidies.
Demographic Factors
- •
Variable income levels, often qualifying for subsidies
- •
Gig economy workers, self-employed, or employees of small businesses
- •
Range of ages, typically under 65
Psychographic Factors
Value-conscious, comparing premium costs and deductible levels
Seeking comprehensive coverage that meets ACA essential health benefit requirements
Behavioral Factors
Actively shop for plans during open enrollment periods
Utilize online portals and brokers to compare options
Pain Points
- •
Affordability of premiums and deductibles
- •
Understanding complex insurance terminology and plan differences
- •
Ensuring their preferred doctors and hospitals are in-network
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:Medium
Market Differentiation
- Factor:
Specialized Expertise in Government Programs
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Lean and Cost-Effective Operating Model
Strength:Moderate
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Strategic Acquisitions to Enter New Markets
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
Value Proposition
To provide accessible, high-quality, and cost-effective healthcare coverage to individuals and families qualifying for government-sponsored programs.
Good
Key Benefits
- Benefit:
Affordable Healthcare Access
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Common
Proof Elements
Participation in Medicaid, Medicare, and ACA Marketplace programs
Focus on low-income and underserved populations in their mission statement
- Benefit:
Coordinated Care for Complex Needs
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
Offering of care management and wellness programs.
Strategic focus on dual-eligible populations who require high levels of care coordination.
- Benefit:
Extensive Provider Networks
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Common
Proof Elements
Contracts with hundreds of thousands of healthcare providers and thousands of hospitals nationwide.
Unique Selling Points
- Usp:
Deep-rooted focus and expertise exclusively on government-sponsored healthcare segments, unlike more diversified competitors.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
Proven ability to win state procurement contracts and grow through strategic acquisitions of smaller, regional plans.
Sustainability:Medium-term
Defensibility:Moderate
Customer Problems Solved
- Problem:
Lack of affordable health insurance options for low-income populations.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Difficulty navigating the complex rules and provider networks of government healthcare.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
- Problem:
Managing chronic health conditions without adequate support and care coordination.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
Value Alignment Assessment
High
The business model is directly aligned with the persistent market need for managing government-funded healthcare, a large and growing sector of the U.S. healthcare system.
High
The value proposition directly addresses the primary pain points of its target segments: cost, access, and navigation of a complex system. Its entire operational focus is on serving these specific populations.
Strategic Assessment
Business Model Canvas
Key Partners
- •
State Medicaid Agencies
- •
Federal Government (Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services - CMS)
- •
Healthcare Providers (Hospitals, Physician Groups, Clinics).
- •
Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs)
- •
Technology Vendors (e.g., for EHR integration, data analytics).
- •
Community-Based Organizations.
Key Activities
- •
State Contract Bidding & Management
- •
Provider Network Development & Contracting
- •
Member Enrollment & Services
- •
Claims Processing & Adjudication
- •
Medical Management & Care Coordination.
- •
Regulatory Compliance & Reporting
Key Resources
- •
State and Federal Government Contracts
- •
Extensive Provider Networks
- •
Proprietary Claims and Member Management Systems
- •
Clinical and Administrative Staff
- •
Financial Reserves (to meet statutory requirements)
Cost Structure
- •
Medical Care Costs (Primary driver, measured by Medical Loss Ratio).
- •
General & Administrative Expenses
- •
Provider Network Management Costs
- •
IT and Systems Infrastructure Costs
- •
Marketing and Member Acquisition Costs.
Swot Analysis
Strengths
- •
Strong market leadership and brand recognition in the Medicaid managed care space.
- •
Deep expertise and long-standing relationships with state governments.
- •
Diversified revenue across multiple government programs (Medicaid, Medicare, Marketplace).
- •
Proven track record of successful strategic acquisitions to fuel growth.
Weaknesses
- •
Heavy reliance on government contracts makes revenue susceptible to political and regulatory changes.
- •
Relatively thin profit margins compared to commercial health insurance.
- •
Susceptibility to negative headlines from data breaches or service issues, which can impact contract renewals.
- •
Increasing Medical Care Ratio (MCR) can pressure profitability.
Opportunities
- •
Geographic expansion into new states with Medicaid managed care programs.
- •
Growth in the dual-eligible and Medicare Advantage populations as demographics shift.
- •
Leveraging technology and data analytics for population health management to reduce costs.
- •
Acquiring smaller, struggling single-state health plans.
Threats
- •
Unfavorable changes in government healthcare policy or funding levels.
- •
Intense competition from larger, well-capitalized insurers in state contract bids.
- •
Rising healthcare costs that outpace reimbursement rate increases from government partners.
- •
Medicaid redetermination processes leading to potential membership losses.
Recommendations
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Operational Efficiency
Recommendation:Invest further in automation and AI for claims processing and utilization management to lower administrative costs and improve the Medical Loss Ratio.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Member Engagement
Recommendation:Enhance digital member portals and telehealth services to improve engagement, particularly for chronic disease management, which can lead to better health outcomes and lower long-term costs.
Expected Impact:Medium
- Area:
Data Analytics
Recommendation:Develop more sophisticated predictive analytics capabilities to identify high-risk members for early intervention, focusing on social determinants of health (SDoH) to provide more holistic and cost-effective care.
Expected Impact:High
Business Model Innovation
- •
Develop value-based care partnerships with providers that move beyond fee-for-service, sharing financial risk and reward for improved patient outcomes and reduced costs.
- •
Create a dedicated business unit or subsidiary focused on addressing Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) by partnering with community organizations to provide services like housing support, food security, and transportation, positioning it as a core, value-added service.
- •
Explore modular technology solutions (e.g., population health analytics, member engagement platforms) that could be licensed to smaller, non-competing health plans.
Revenue Diversification
- •
Accelerate the strategic focus on the dual-eligible market, which represents a higher-revenue, high-need population where integrated care can provide significant value.
- •
Continue a disciplined M&A strategy, targeting acquisitions in states with growing Medicaid populations or favorable regulatory environments to expand geographic footprint.
- •
Cautiously expand footprint in the ACA Marketplace, particularly in states where Molina already has a strong Medicaid presence and provider network to leverage operational synergies.
Molina Healthcare operates a mature and highly specialized business model as a Managed Care Organization (MCO) focused exclusively on government-sponsored healthcare programs. Its core strength lies in its deep expertise and established relationships within the complex and regulation-heavy Medicaid, Medicare, and ACA Marketplace sectors. The revenue model, based on capitation payments from government entities, provides a stable and predictable, albeit low-margin, income stream. The company's market positioning is clear and defensible; it is a specialist serving the unique needs of low-income and vulnerable populations, a segment that larger, more diversified commercial insurers may not serve with the same level of focus.
However, this specialization is also its primary vulnerability. The company's fortunes are intrinsically tied to government policy, funding decisions, and the competitive landscape of state-level contract procurement. Threats from regulatory changes, intense competition from giants like Centene and UnitedHealth Group, and the constant pressure of rising medical costs are significant.
For future evolution, Molina's strategic path is well-defined but requires flawless execution. The most promising opportunities for scalable growth and margin improvement lie in three key areas: 1) Deeper penetration into the dual-eligible market, where integrated care models can generate higher value and revenue; 2) Strategic acquisitions to gain market share and achieve economies of scale in new geographies; and 3) Investment in technology and data analytics to drive operational efficiency and transition towards value-based care models. By enhancing its ability to manage population health effectively and prove superior outcomes, Molina can strengthen its value proposition to its government partners, making its contracts more secure and positioning the company for sustainable, long-term growth.
Competitors
Competitive Landscape
Mature
Oligopoly
Barriers To Entry
- Barrier:
Regulatory Licensing and Capital Reserves
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Provider Network Development
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Brand Recognition and Trust
Impact:Medium
- Barrier:
Economies of Scale in Operations
Impact:High
Industry Trends
- Trend:
Growth of Government-Sponsored Plans
Impact On Business:This is Molina's core market, creating both immense opportunity and attracting intense competition from larger, more diversified players.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Focus on Value-Based Care
Impact On Business:Requires significant investment in data analytics and care coordination to shift from fee-for-service models. Success here can be a key differentiator.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Medicaid Redetermination
Impact On Business:Creates significant membership churn. Molina's ability to retain eligible members and recapture others in the Marketplace is critical for stability.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Integration of Telehealth and Digital Health
Impact On Business:Member expectations for digital access are rising. Molina must invest in user-friendly digital tools to improve engagement and manage costs.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Addressing Social Determinants of Health (SDoH)
Impact On Business:Plans are increasingly expected to address non-clinical factors like housing and food insecurity. This requires partnerships and community investment but can improve outcomes and lower long-term costs.
Timeline:Immediate
Direct Competitors
- →
Centene Corporation
Market Share Estimate:Largest Medicaid Managed Care Organization (MCO) in the U.S. with over 23 million members.
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Positions itself as the national leader in government-sponsored healthcare, focusing on under-insured and uninsured individuals through scale and a multi-line portfolio.
Strengths
- •
Unmatched scale in Medicaid, providing significant negotiating leverage.
- •
Diversified specialty services (pharmacy, vision, behavioral health) create multiple revenue streams.
- •
Aggressive growth through acquisition (e.g., WellCare).
- •
Strong presence in the Health Insurance Marketplace (Ambetter).
Weaknesses
- •
Faces scrutiny and legal challenges over business practices, potentially damaging brand reputation.
- •
Integration challenges from large acquisitions can lead to operational inefficiencies.
- •
Customer satisfaction ratings are often average, with complaints about network limitations.
Differentiators
Largest national footprint in Medicaid, operating in the most states.
Focus on providing a comprehensive suite of specialty services in-house or through subsidiaries.
- →
Elevance Health (formerly Anthem)
Market Share Estimate:One of the largest health insurers overall, with significant Medicaid and commercial business.
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Positions as a large, stable, and trusted health partner, leveraging the Blue Cross Blue Shield brand in 14 states and a diversified business model across commercial and government segments.
Strengths
- •
Powerful brand recognition and trust associated with the Blue Cross Blue Shield name.
- •
Large, profitable commercial insurance business provides financial stability and leverage.
- •
Diversified business model across commercial, Medicare, and Medicaid reduces reliance on any single segment.
- •
Strong provider networks and negotiating power due to its large overall membership.
Weaknesses
- •
Less singularly focused on the specific needs of the Medicaid population compared to Molina or Centene.
- •
Can be slower to innovate or adapt due to its federated structure in some markets.
- •
Competition with other independent Blue plans can create complexity.
Differentiators
Strong brand equity and consumer trust from its BCBS affiliation.
Holistic 'whole health' approach, integrating physical, behavioral, and social drivers of health.
- →
UnitedHealth Group (Community & State)
Market Share Estimate:Largest health insurer in the U.S. by revenue, with a massive and growing Medicaid division serving nearly 8.1 million members.
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Leverages the scale and data analytics of the entire UnitedHealth Group, including Optum, to deliver integrated, data-driven care to government program beneficiaries.
Strengths
- •
Unparalleled data and analytics capabilities through its Optum subsidiary.
- •
Vertically integrated model (payer, provider, PBM) offers significant cost control and care coordination advantages.
- •
Vast financial resources for technology investment, innovation, and market expansion.
- •
Strong focus on addressing SDoH through sophisticated data analysis and community partnerships.
Weaknesses
- •
Massive corporate structure can lead to bureaucratic hurdles and a less personalized member experience.
- •
Frequent target of regulatory scrutiny and antitrust concerns due to its market dominance.
- •
Exited some state Medicaid markets, indicating a selective, profit-driven approach.
Differentiators
Synergies with Optum for health services, data, and technology is a unique and powerful competitive advantage.
Ability to offer highly integrated medical, behavioral, pharmacy, and social care models.
- →
Humana
Market Share Estimate:A dominant player in Medicare Advantage, with a growing focus on Medicaid.
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:Positions as a senior-focused health and well-being company, specializing in the needs of the Medicare population while strategically expanding its Medicaid and dual-eligible offerings.
Strengths
- •
Leading brand and market share in the lucrative Medicare Advantage market.
- •
Deep expertise in managing the health needs of seniors and those with chronic conditions.
- •
Strong provider relationships within its established Medicare networks.
- •
Increasing strategic focus on government programs after exiting the employer group business.
Weaknesses
- •
Historically less focused and smaller scale in Medicaid compared to Centene or Molina.
- •
Brand is more associated with seniors than with low-income families.
- •
Less geographic diversity in its Medicaid operations compared to the top MCOs.
Differentiators
Specialized expertise and services tailored to the senior (Medicare) population.
Strong focus on integrated care delivery models for complex and dual-eligible populations.
Indirect Competitors
- →
Kaiser Permanente
Description:An integrated managed care consortium that operates as both the insurer and the provider of care through its own hospitals and medical groups.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:High in its specific geographic markets, especially as it expands its Medicaid contracts, which can lock Molina out of serving those members.
- →
Oscar Health
Description:A technology-first health insurance company focused on the individual (Marketplace) and small group markets, emphasizing user experience and telemedicine.
Threat Level:Low
Potential For Direct Competition:Could become a more direct competitor in the Marketplace segment if it expands its footprint, attracting members with a superior digital experience.
- →
Local & Provider-Sponsored Health Plans
Description:Health plans owned by local hospital systems or non-profits that compete for Medicaid contracts at a state or regional level.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:High at the state-level contract bidding process. These plans often have deep community ties and strong local provider relationships, making them formidable competitors for regional contracts.
Competitive Advantage Analysis
Sustainable Advantages
- Advantage:
Singular Focus on Government-Sponsored Programs
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. This deep expertise allows Molina to navigate complex state-by-state regulations and tailor services to the unique needs of low-income populations more effectively than diversified competitors.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
- Advantage:
Cost-Effective Operational Model
Sustainability Assessment:Moderately sustainable. Molina's business model is built around efficiently managing care for high-need populations, which is difficult to replicate without deep institutional knowledge.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
- Advantage:
Strong State Government Relationships
Sustainability Assessment:Moderately sustainable. Long-standing contracts and experience working with state Medicaid agencies build trust and institutional knowledge, which is a key factor in winning contract renewals and new bids.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
Temporary Advantages
{'advantage': 'Winning Specific State Contracts', 'estimated_duration': '3-5 years (typical contract length). Winning a large state contract like the one in California provides a significant, but time-limited, revenue boost. '}
Disadvantages
- Disadvantage:
Smaller Scale Compared to Giants
Impact:Major
Addressability:Difficult
- Disadvantage:
Lower Brand Recognition
Impact:Minor
Addressability:Moderately
- Disadvantage:
High Dependence on Government Contracts
Impact:Critical
Addressability:Difficult
- Disadvantage:
Data Security Vulnerabilities
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately
Strategic Recommendations
Quick Wins
- Recommendation:
Launch a Targeted Member Retention Campaign
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
- Recommendation:
Enhance Digital Onboarding for New Members
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Proactively Communicate on Data Breach
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
Medium Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Invest in a Unified Digital Member Engagement Platform
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Develop Deeper SDoH Partnerships
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Optimize Provider Network Performance with Data Analytics
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Long Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Become the Leader in Dual-Eligible (Medicare-Medicaid) Care
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Strategic Geographic Expansion
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Position Molina Healthcare as the most specialized and compassionate expert in government-sponsored care, focusing on superior, culturally-sensitive member service and tangible improvements in health outcomes for vulnerable populations.
Differentiate through 'high-touch' member support combined with 'simple-tech' digital tools. Focus on building trust and simplifying the healthcare experience for populations that may have lower digital literacy or face more complex social and health challenges.
Whitespace Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Develop a 'Best-in-Class' Digital Platform for Low-Income Users
Competitive Gap:Many competitors' digital tools are not designed for users with limited digital literacy, older devices, or inconsistent internet access. A simplified, multilingual, and highly accessible platform could be a major differentiator.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Specialized Care Management for Complex Populations
Competitive Gap:While all major players address complex care, there is a gap in providing hyper-specialized programs for niche but high-cost populations, such as those with specific rare diseases or individuals transitioning out of the justice system.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Proactive Management of Medicaid-to-Marketplace Transitions
Competitive Gap:There is a significant gap in providing seamless support for members who lose Medicaid eligibility during redetermination to help them enroll in a Marketplace plan. A proactive, supportive service could retain members within the Molina ecosystem.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:Medium
Molina Healthcare operates in the mature and highly concentrated government-sponsored health insurance market. Its identity is deeply rooted in serving Medicaid and Medicare beneficiaries, a specialization that serves as its primary competitive advantage. This focus allows Molina to develop deep expertise in the complex regulatory and member-specific needs of this population, a feat harder for more diversified competitors to replicate. The market is an oligopoly, dominated by giants like Centene, Elevance Health, and UnitedHealth Group, who compete fiercely on scale, network size, and increasingly, technological capability.
Direct competition is intense. Centene is Molina's most direct analogue, competing on a similar government-first model but at a much larger scale. Elevance Health and UnitedHealth Group, while more diversified, bring immense resources, powerful brand recognition, and vertically integrated assets (like Optum) that Molina cannot match. Molina's key disadvantage is this lack of scale, which limits its negotiating power with providers and ability to invest in technology at the same level as its larger rivals. Furthermore, its heavy reliance on government contracts makes it vulnerable to political and budgetary shifts, a critical risk.
The primary battleground is shifting. While winning state contracts remains paramount, the criteria for winning are evolving. Payers are now judged on their ability to manage population health, integrate digital tools, address social determinants of health (SDoH), and deliver value-based care. This is where Molina can differentiate. By doubling down on its specialized, high-touch care management and developing simple, effective digital tools tailored to its members, it can create a defensible niche. The mention of a data breach on its homepage, however, is a significant self-inflicted wound to member trust that must be managed with extreme transparency and care.
Strategic opportunities lie in underserved, complex niches within the government-sponsored space, such as the dual-eligible population and members with acute behavioral health needs. By becoming the undisputed expert in these areas and creating a seamless, supportive member journey—especially during periods of eligibility change—Molina can build loyalty and prove its value to state partners, securing its position not as the largest player, but as the most effective and dedicated partner in caring for the nation's most vulnerable populations.
Messaging
Molina Healthcare's strategic messaging is highly functional and effective at addressing the immediate, critical needs of its core audience, primarily individuals in government-sponsored health programs. The homepage is dominated by a clear, urgent call-to-action regarding Medicaid renewals, a timely and essential message for member retention in the current healthcare environment. This task-oriented approach demonstrates a practical understanding of its members' primary concerns. However, this functional focus comes at the expense of building a deeper brand narrative and emotional connection. The core brand concept, 'Welcome to the Molina Healthcare Family!', is a powerful emotional hook, but it remains an undeveloped headline rather than an integrated brand promise substantiated by storytelling, member testimonials, or benefit-oriented language. The primary differentiator communicated is corporate scale ('FORTUNE 500'), which signals stability but doesn't translate into a unique member-centric value proposition. Consequently, Molina is positioned as a reliable administrator of health benefits, but not necessarily as a compassionate partner in health, which represents a significant missed opportunity for differentiation and building long-term brand loyalty in a competitive marketplace.
Message Architecture
Key Messages
- Message:
It is critical for Medicaid members to take action to renew and keep their health coverage.
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage - Main Banner
- Message:
Welcome to the Molina Healthcare Family!
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:Medium
Location:Homepage - Main Headline
- Message:
Molina Healthcare is a large, established (FORTUNE 500) healthcare organization.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage - About Molina Section
- Message:
There has been a data breach from a third-party vendor affecting some Molina members.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage - Notice Banner
The message hierarchy is dominated by the urgent and tactical message about Medicaid renewal. While strategically sound for member retention, this prioritization subordinates the core brand message ('Welcome to the Family') to a functional directive. This creates a user experience focused on immediate tasks rather than brand engagement, potentially weakening the brand's appeal to prospective members.
The messaging is highly consistent in its direct, informational, and task-oriented approach across the different sections of the homepage. There is a consistent focus on guiding users to the correct information path based on their status (new member, current member, provider).
Brand Voice
Voice Attributes
- Attribute:
Directive
Strength:Strong
Examples
It's important that Molina Medicaid members take action when it's their turn to renew...
Click below to learn more
- Attribute:
Informational
Strength:Strong
Examples
Molina Healthcare is a FORTUNE 500, multi-state health care organization.
Episource, LLC (“Episource”) had a data breach.
- Attribute:
Welcoming
Strength:Moderate
Examples
Welcome to the Molina Healthcare Family!
Join the Molina Healthcare family today.
- Attribute:
Institutional
Strength:Moderate
Examples
Notice of Nondiscrimination
By using our website, you consent to our use of cookies in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
Tone Analysis
Functional & Urgent
Secondary Tones
- •
Welcoming
- •
Formal
- •
Cautionary
Tone Shifts
A noticeable shift occurs from the warm 'Welcome to the Molina Healthcare Family!' headline to the urgent, instructional tone of the Medicaid renewal banner and the formal, cautionary tone of the data breach notification.
Voice Consistency Rating
Good
Consistency Issues
The warm, relational 'Family' voice is used sparingly and contrasts with the dominant institutional and directive tone, making the 'Family' concept feel more like a tagline than an integrated brand personality.
Value Proposition Assessment
Implied: Molina Healthcare is a large, stable provider that helps you navigate and maintain your government-sponsored health coverage.
Value Proposition Components
- Component:
Access to Government-Sponsored Health Plans
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Common
- Component:
Stability and Scale (FORTUNE 500)
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
- Component:
Guidance on Critical Administrative Tasks (e.g., Renewal)
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Common
- Component:
A Sense of Belonging ('Family')
Clarity:Unclear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
The messaging fails to strongly differentiate Molina from its competitors on the factors that matter most to members: quality of care, ease of access to doctors, or superior member support. The primary differentiator is its 'FORTUNE 500' status, which implies stability but is a corporate-centric value, not a member-centric benefit. The 'Family' concept is a potential differentiator but is not substantiated with any proof points.
Molina is positioned as a large, functional, and reliable administrator of health plans. This positions them as a safe choice but not necessarily the best choice for a superior healthcare experience. The messaging competes on process (maintaining coverage) rather than on outcomes (better health and well-being).
Audience Messaging
Target Personas
- Persona:
Current Medicaid Member
Tailored Messages
It's important that Molina Medicaid members take action when it's their turn to renew so they can keep their coverage.
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Prospective Member (Medicaid or Marketplace)
Tailored Messages
New Members - Medicaid
New Members - Marketplace
Effectiveness:Somewhat Effective
- Persona:
Healthcare Provider
Tailored Messages
Providers [link to learn more about renewals]
Effectiveness:Effective
Audience Pain Points Addressed
The anxiety and confusion surrounding the Medicaid renewal process.
The fear of an unexpected loss of health coverage.
Audience Aspirations Addressed
The messaging does not address audience aspirations, such as achieving better health, living a more secure life, or providing the best care for one's family. The focus is entirely on avoiding a negative outcome (loss of coverage).
Persuasion Elements
Emotional Appeals
- Appeal Type:
Sense of Belonging
Effectiveness:Low
Examples
Welcome to the Molina Healthcare Family!
- Appeal Type:
Urgency / Fear of Loss
Effectiveness:High
Examples
...take action when it's their turn to renew so they can keep their coverage.
Social Proof Elements
- Proof Type:
Authority / Scale
Impact:Moderate
Examples
Molina Healthcare is a FORTUNE 500, multi-state health care organization.
Trust Indicators
- •
FORTUNE 500 status
- •
Notice of Nondiscrimination link
- •
Transparent (though prominent) notice of a data breach
Scarcity Urgency Tactics
The messaging around Medicaid renewal leverages the external, time-sensitive nature of the 'unwinding' process to create urgency for members to take action.
Calls To Action
Primary Ctas
- Text:
New Members - Medicaid
Location:Homepage
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
New Members - Marketplace
Location:Homepage
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
[Link for] Members [to learn about renewals]
Location:Homepage Banner
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
[Link for] Providers [to learn about renewals]
Location:Homepage Banner
Clarity:Clear
The CTAs are functionally effective, clearly labeled, and well-segmented for different audiences. However, they lack persuasive, benefit-driven language. They are navigational instructions ('New Members') rather than compelling invitations ('Find Your Plan' or 'Get Covered Today').
Messaging Gaps Analysis
Critical Gaps
- •
Member Storytelling: There are no member testimonials or stories to give life to the 'Family' concept or demonstrate the positive impact of Molina's services.
- •
Value Proposition Articulation: The core value proposition is not explicitly stated, forcing users to infer it.
- •
Quality of Care Messaging: There is a complete absence of messaging related to health outcomes, quality of the provider network, or the compassion of care.
- •
Brand Promise: Beyond a welcoming headline, there is no clear, memorable promise that encapsulates the Molina brand experience.
Contradiction Points
The warm, relational promise of being a 'Family' is at odds with the transactional, urgent, and institutional tone that dominates the rest of the page.
Underdeveloped Areas
The 'Molina Healthcare Family' concept is a powerful messaging asset that is completely underdeveloped. It appears as a headline but is not supported by any subsequent content, visuals, or proof points.
Messaging Quality
Strengths
- •
Audience Segmentation: The homepage effectively funnels different user types (current members, new members, providers) to relevant information.
- •
Clarity and Directness: The messaging is simple, direct, and easy to understand, which is crucial for an audience that may have varying levels of health literacy.
- •
Timeliness and Relevance: The focus on Medicaid renewal is highly relevant and addresses a pressing, real-world need for its members.
Weaknesses
- •
Lack of Emotional Connection: The messaging is overly functional and fails to build a deeper emotional bond with the audience.
- •
Weak Differentiation: The site does not effectively communicate why a member should choose Molina over a competitor beyond its corporate size.
- •
Absence of Aspiration: The focus is on preventing loss rather than enabling positive gains in health and life.
Opportunities
- •
Substantiate the 'Family' Promise: Weave the 'Family' concept into the user journey with stories, testimonials, and supportive language.
- •
Focus on Member Benefits, Not Just Features: Translate corporate status ('FORTUNE 500') into tangible member benefits like 'the stability and resources to ensure your care is always there.'
- •
Highlight Quality of Care: Develop messaging that showcases the quality of the provider network, unique wellness programs, or member support services.
Optimization Roadmap
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Value Proposition & Brand Story
Recommendation:Develop a dedicated 'Why Molina?' section on the homepage that explicitly states the value proposition and substantiates the 'Family' promise with 2-3 member testimonials (text or video) and key proof points about care quality.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Homepage Messaging Hierarchy
Recommendation:Integrate the 'Welcome' message more effectively with benefit-oriented subheadings before directing users to tactical paths. For example: 'Welcome to the Molina Family, where your health comes first. Let's get you started.'
Expected Impact:Medium
- Area:
Audience Aspiration
Recommendation:Introduce aspirational language that connects having health coverage to achieving life goals, such as 'Worry less, live healthier' or 'The security to focus on what matters most.'
Expected Impact:Medium
Quick Wins
- •
Revise CTA button copy to be more active and benefit-driven (e.g., change 'New Members - Medicaid' to 'Find a Medicaid Plan').
- •
Add a tagline below the 'Welcome' headline that reinforces a key benefit, such as 'Quality healthcare for your family.'
- •
Create a dedicated, reassuring landing page for the data breach notice to remove the negative messaging from the homepage and link to it.
Long Term Recommendations
- •
Conduct a comprehensive brand messaging refresh to define and build a communication strategy around a unique, member-centric brand promise.
- •
Invest in creating a content hub featuring member success stories, health and wellness tips, and resources that demonstrate Molina's role as a partner in health.
- •
Perform A/B testing on key headlines and CTAs to measure the impact of benefit-oriented language versus functional language on member engagement and acquisition.
Growth Readiness
Growth Foundation
Product Market Fit
Strong
Evidence
- •
Established Fortune 500 company specializing in government-sponsored healthcare (Medicaid, Medicare, Marketplace), a large and persistent market segment.
- •
Serves approximately 5.7 million members across multiple states as of mid-2025, indicating significant market adoption and trust from state governments.
- •
Consistent track record of winning state contracts and growing membership, demonstrating a strong value proposition for government partners.
- •
Business model is explicitly designed to serve the needs of financially vulnerable populations, a core objective of government healthcare programs.
Improvement Areas
- •
Enhance the digital member experience to improve engagement, health outcomes, and retention.
- •
Strengthen care management programs for high-acuity members remaining after Medicaid redeterminations.
- •
Improve member communication and onboarding to reduce friction and improve health literacy.
Market Dynamics
Moderate to Strong (Varies by segment: Medicaid stable, Medicare Advantage growing at ~4-7%, Marketplace growing rapidly).
Mature
Market Trends
- Trend:
Medicaid Redetermination: Massive membership churn as pandemic-era continuous enrollment ends, creating both retention challenges and acquisition opportunities.
Business Impact:High risk of losing younger, healthier, more profitable members, leading to a higher-acuity remaining population and potential revenue loss. Also presents an opportunity to capture disenrolled members for Marketplace plans.
- Trend:
Growth in Medicare Advantage (MA) & Dual-Eligible Special Needs Plans (D-SNPs): The MA market continues to grow, although at a slower pace, with a strategic focus on D-SNPs.
Business Impact:Significant growth vector. Molina is actively acquiring MA businesses and expanding its D-SNP footprint to capture this aging demographic.
- Trend:
Shift to Value-Based Care (VBC): Government payers (especially Medicaid) are increasingly pushing Managed Care Organizations (MCOs) toward VBC models that tie reimbursement to quality and outcomes.
Business Impact:Requires significant investment in data analytics, care coordination, and provider network alignment to succeed. A critical long-term competency for profitability and winning state contracts.
- Trend:
Increased Regulatory Scrutiny & Rate Pressure: Government agencies are applying more pressure on MA payment rates and Medicaid rate adequacy.
Business Impact:Potential for margin compression. Requires disciplined medical cost management and sophisticated actuarial capabilities to remain profitable.
Critical. The current market is in flux due to Medicaid redeterminations, creating a limited-time window to capture market share in both Medicaid (retention) and the ACA Marketplace (acquisition). The aging population provides a sustained tailwind for Medicare Advantage growth.
Business Model Scalability
Medium
Primarily variable, driven by medical costs (Medical Loss Ratio - MLR), which scale with membership. SG&A costs have some fixed components but also scale with operational complexity.
Moderate. Leverage is achieved by spreading administrative costs over a larger member base within a state. However, entering a new state requires significant upfront investment in network development and regulatory compliance.
Scalability Constraints
- •
State-by-state regulatory approvals and contract procurement cycles are slow and resource-intensive.
- •
Requirement to build adequate and competitive provider networks in each new market.
- •
Intense competition from larger, well-entrenched national players like Centene and UnitedHealth Group.
- •
Upfront implementation costs for new state contracts can temporarily depress earnings.
Team Readiness
Strong. The executive team has a proven track record of executing a growth-through-acquisition strategy and navigating the complex government programs landscape.
Likely a state-based model with corporate oversight, which is appropriate for the business. The key challenge is integrating new acquisitions and standardizing best practices across disparate state operations.
Key Capability Gaps
- •
Advanced Data Analytics & AI: To optimize risk adjustment, value-based care performance, and medical cost management.
- •
Digital Member Engagement: Expertise in creating seamless digital experiences for member acquisition, onboarding, and retention, especially for the tech-savvier Marketplace segment.
- •
Integration Management: A dedicated team to accelerate and de-risk the integration of acquired companies and their technology platforms.
Growth Engine
Acquisition Channels
- Channel:
State Contract Bidding (RFP Process)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Develop a repeatable 'New State Entry Playbook' that standardizes bid development, network contracting, and implementation to increase win rates and speed-to-market.
- Channel:
Acquisitions (M&A)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Continue the proven M&A strategy, focusing on acquiring plans that provide stable revenue streams in core products (Medicaid, MA) and offer geographic or product line diversification.
- Channel:
ACA Marketplace (Direct-to-Consumer)
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Invest in digital marketing, brand building, and broker channel partnerships to capture individuals disenrolling from Medicaid. Optimize user experience on the enrollment portal to improve conversion.
- Channel:
Community Outreach & Enrollment Brokers
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Utilize data analytics to identify high-potential geographic areas for targeted outreach. Provide brokers with better tools and incentives to drive enrollment for both Medicaid and Marketplace plans.
Customer Journey
Fragmented and complex, dictated by government eligibility and enrollment processes. The journey involves awareness (state directs them or they shop on marketplace), eligibility verification, plan selection, and finally, member onboarding.
Friction Points
- •
Complex government enrollment and renewal paperwork (a major cause of Medicaid churn).
- •
Difficulty understanding plan benefits and finding in-network providers.
- •
Lack of a seamless, digitally-supported onboarding process for new members.
- •
Navigating transitions between coverage types (e.g., Medicaid to Marketplace).
Journey Enhancement Priorities
{'area': 'Medicaid Renewal Process', 'recommendation': "Launch proactive, multi-channel communication campaigns (SMS, email, outbound calls) to guide members through the redetermination process, minimizing procedural disenrollment. The website's 'Keepmyhealthplan' is a good start but needs robust backend support."}
{'area': 'New Member Onboarding', 'recommendation': 'Develop a 30-day digital onboarding journey that welcomes members, helps them find a PCP, explains key benefits, and encourages them to download a mobile app.'}
Retention Mechanisms
- Mechanism:
Medicaid Redetermination Assistance
Effectiveness:Critical/High
Improvement Opportunity:Partner with community organizations and leverage data to target outreach to members most at risk of procedural disenrollment. Offer a 'warm handoff' to Marketplace plans for those who are no longer eligible.
- Mechanism:
Care Management & Wellness Programs
Effectiveness:Medium
Improvement Opportunity:Increase engagement in these programs by using personalized digital outreach. Focus on programs that address Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) to build loyalty and improve outcomes.
- Mechanism:
Member Services & Support
Effectiveness:Moderate
Improvement Opportunity:Invest in AI-powered chatbots and self-service tools to handle simple queries, freeing up human agents to manage more complex member issues. The extensive multi-language support on the website is a key strength to build upon.
Revenue Economics
The model is driven by Per-Member-Per-Month (PMPM) capitated payments from government entities. Profitability hinges on managing the Medical Loss Ratio (MLR), with Medicaid MLR around 90%. This leaves a thin margin for administrative costs and profit, making cost control paramount.
Difficult to calculate precisely but conceptually strong. CAC involves M&A costs and contract implementation, while LTV can be many years of PMPM revenue, especially for long-term Medicaid or Medicare members. The key is minimizing churn.
Medium. Revenue has grown significantly through acquisitions and contract wins. However, recent margin pressure from rising medical costs indicates a potential challenge to efficiency.
Optimization Recommendations
- •
Aggressively manage medical costs through value-based contracts with providers.
- •
Leverage technology to automate administrative tasks and lower the SG&A ratio.
- •
Improve risk adjustment accuracy (especially in Medicare Advantage) to ensure premiums accurately reflect member acuity.
Scale Barriers
Technical Limitations
- Limitation:
Siloed Data Systems
Impact:Medium
Solution Approach:Invest in a unified data platform (e.g., a cloud-based data lakehouse) to create a 360-degree view of the member, enabling better care management, risk stratification, and personalized outreach.
- Limitation:
Legacy Claims & Core Admin Platforms
Impact:High
Solution Approach:Develop a multi-year roadmap for modernizing core administrative systems to improve efficiency, enable faster integration of acquisitions, and support flexible value-based payment models.
Operational Bottlenecks
- Bottleneck:
Provider Network Development & Contracting
Growth Impact:Slows entry into new markets and can limit competitiveness of bids.
Resolution Strategy:Create a dedicated, rapid-response network development team for new market entry. Utilize advanced network analytics to optimize provider contracting and recruitment.
- Bottleneck:
Integrating Acquired Companies
Growth Impact:Delays synergy realization and can lead to inconsistent member experiences.
Resolution Strategy:Establish a formal Integration Management Office (IMO) with a standardized playbook for integrating people, processes, and technology from acquired entities.
Market Penetration Challenges
- Challenge:
Intense Competition from Larger Incumbents
Severity:Critical
Mitigation Strategy:Compete through operational excellence, a focus on underserved niches (like D-SNPs), and strong local relationships with providers and community organizations. Continue opportunistic M&A to gain scale.
- Challenge:
State-Level Political and Regulatory Risk
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Maintain a strong government relations team at both the state and federal levels. Diversify geographically to reduce dependency on any single state's political or regulatory environment.
Resource Limitations
Talent Gaps
- •
Data Scientists and AI/ML Engineers
- •
Digital Product Managers for member-facing tools
- •
Value-Based Care Contract Specialists
Significant and ongoing capital required for acquisitions and to satisfy state-level risk-based capital (RBC) requirements for expansion.
Infrastructure Needs
Modern, scalable data analytics and population health management platforms.
Enhanced cybersecurity infrastructure to protect member data and prevent breaches like the one noted on their homepage.
Growth Opportunities
Market Expansion
- Expansion Vector:
Geographic Expansion into New States
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:High
Recommended Approach:Prioritize entry into states with upcoming large Medicaid RFP cycles or a high concentration of dual-eligible individuals. Use a combination of organic bids and strategic 'tuck-in' acquisitions of smaller, regional plans.
- Expansion Vector:
Deeper Penetration in Dual-Eligible (D-SNP) Market
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:Medium
Recommended Approach:Actively expand D-SNP product offerings in existing and new markets, leveraging expertise to manage this high-need, high-revenue population effectively.
Product Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Enhanced Digital Health & Telehealth Services
Market Demand Evidence:Growing consumer and provider adoption of virtual care, particularly for behavioral health and chronic condition management.
Strategic Fit:High. Improves access to care for vulnerable populations, reduces costs, and can be a key differentiator in state contract bids.
Development Recommendation:Partner with or acquire a leading digital health platform to accelerate time-to-market. Integrate telehealth seamlessly into the member app and provider workflows.
- Opportunity:
Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) Solutions
Market Demand Evidence:Increasing recognition by state Medicaid agencies that addressing SDoH (e.g., food insecurity, housing) is critical to improving outcomes and lowering costs.
Strategic Fit:High. Aligns perfectly with Molina's mission and the needs of its member base. Can improve member retention and performance on value-based contracts.
Development Recommendation:Build a network of community-based organization partners and integrate SDoH screening and referral workflows directly into care management processes.
Channel Diversification
- Channel:
Direct-to-Consumer Digital Marketplace Channel
Fit Assessment:Excellent. Essential for capturing members disenrolling from Medicaid who are now eligible for subsidized ACA plans.
Implementation Strategy:Launch targeted digital advertising campaigns (search, social) aimed at recently disenrolled Medicaid members. Create simplified educational content and tools to help them navigate the Marketplace.
- Channel:
Provider-led Enrollment Partnerships
Fit Assessment:Good. Leverage trusted provider relationships to assist with member retention and acquisition.
Implementation Strategy:Equip key provider partners (especially FQHCs) with tools and resources to help patients with the Medicaid renewal process or enroll in Molina's Marketplace or Medicare plans at the point of care.
Strategic Partnerships
- Partnership Type:
Health Technology (HealthTech) Startups
Potential Partners
- •
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) companies
- •
AI-driven care navigation platforms
- •
Behavioral health virtual clinics
Expected Benefits:Accelerate innovation in care delivery, improve member engagement, and generate data for value-based care initiatives without needing to build all capabilities in-house.
- Partnership Type:
Community-Based Social Service Organizations
Potential Partners
- •
Food banks
- •
Housing assistance programs
- •
Transportation services
Expected Benefits:Address SDoH to improve health outcomes, reduce total cost of care, and fulfill evolving state contractual requirements.
Growth Strategy
North Star Metric
Total Member Months
This metric captures both new member acquisition and the retention of existing members, directly aligning with PMPM revenue streams. It provides a holistic view of the health of the business across all product lines.
Achieve 5-7% year-over-year growth in Total Member Months, balancing Medicaid redetermination losses with growth in Marketplace and Medicare.
Growth Model
Acquisition & State Contract-Led Growth
Key Drivers
- •
Successful state contract RFP bids
- •
Strategic M&A of complementary health plans
- •
High retention rates during Medicaid redetermination
- •
Effective member capture for Marketplace and Medicare Advantage
A dual-pronged approach: 1) A corporate development team focused on M&A and new state bids. 2) State-level growth teams responsible for member acquisition and retention, supported by a centralized marketing and analytics function.
Prioritized Initiatives
- Initiative:
Medicaid Redetermination 'Save & Switch' Campaign
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:6-12 months
First Steps:Segment Medicaid membership by risk of procedural disenrollment. Develop targeted communication workflows and stand up a dedicated support team to assist members with renewal or transition to a Molina Marketplace plan.
- Initiative:
Medicare Advantage D-SNP Expansion Playbook
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:Ongoing
First Steps:Identify top 10 expansion markets based on D-SNP population density and competitive landscape. Develop a standardized product and provider network strategy for rapid deployment.
- Initiative:
Digital Member Onboarding & Engagement Platform
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:12-18 months
First Steps:Map the current new member journey to identify key friction points. Define MVP features for a new digital onboarding experience and select a technology partner or in-house team to build it.
Experimentation Plan
High Leverage Tests
{'test': 'A/B test different outreach messages and channels (SMS vs. Email vs. Call) for Medicaid renewal reminders.', 'hypothesis': 'Proactive SMS alerts will lead to a higher renewal completion rate than email alone.'}
{'test': 'Pilot a new wellness incentive (e.g., gift cards for completing a health risk assessment) for a segment of new Marketplace members.', 'hypothesis': 'A tangible incentive will increase HRA completion rates by 20%, providing valuable data for care management.'}
Use a standard framework tracking Hypothesis, Key Metrics (e.g., conversion rate, engagement rate), Statistical Significance, and Learnings for each experiment.
Run monthly sprints for marketing and digital engagement tests. Run quarterly pilots for larger operational or product initiatives.
Growth Team
A hybrid model with a central 'Center of Excellence' and state-level execution teams. The CoE would house corporate development (M&A, new state bids), digital marketing, and advanced analytics. State Presidents would lead local teams focused on provider relations, community outreach, and member retention.
Key Roles
- •
VP of Market Development (New State Entry & RFPs)
- •
Director of Member Retention
- •
Head of Digital Product (Member Experience)
- •
Chief Data & Analytics Officer
Invest heavily in training for data literacy across the organization. Acquire talent in digital marketing and product management. Develop internal expertise in value-based care by creating cross-functional teams of clinical, network, and finance staff.
Molina Healthcare has a strong foundation for growth, anchored by its deep expertise in the complex and durable government-sponsored healthcare market. Its product-market fit is undeniable, and its growth engine, heavily reliant on winning state contracts and strategic acquisitions, has proven effective. The company's recent M&A activity, particularly in the Medicare Advantage and D-SNP space, is a strategically sound move to diversify revenue and tap into a high-growth demographic.
The most significant and immediate challenge—and opportunity—is navigating the unprecedented churn from Medicaid redeterminations. Success in this environment will be defined by the ability to minimize procedural disenrollment through aggressive, data-driven retention campaigns while simultaneously building a robust digital acquisition funnel to capture those who lose Medicaid but are eligible for ACA Marketplace plans. This represents a critical pivot from a primarily B2G (Business-to-Government) model to one that requires a much stronger B2G2C (Business-to-Government-to-Consumer) muscle.
Key scale barriers are not market demand, but operational and technical readiness. Legacy systems, the complexity of state-by-state operations, and the challenge of integrating numerous acquisitions are significant hurdles. Overcoming these requires sustained investment in a modern, unified technology stack and the creation of standardized playbooks for market entry and M&A integration.
The primary growth opportunities lie in geographic expansion, deeper penetration into the lucrative D-SNP market, and enhancing the product through digital health and SDoH solutions. These initiatives will not only drive top-line growth but also create a more defensible competitive advantage by improving member outcomes and lowering the total cost of care—a key selling point for their government clients. The recommended growth strategy is to double down on the existing contract and M&A model while building a world-class member retention and digital acquisition capability to navigate the current market disruption successfully.
Legal Compliance
The website provides a link to a combined 'Terms & Privacy' policy within its cookie banner. For a healthcare entity of Molina's scale, which handles vast amounts of Protected Health Information (PHI), this combined approach is less than ideal. Best practice under HIPAA is to have a distinct and prominently displayed 'Notice of Privacy Practices' (NPP) that is separate from general website terms. This NPP must clearly detail how PHI is used and disclosed, and outline patient rights regarding their data. While the provided content doesn't allow for a full review of the policy's text, the structure itself suggests a potential gap in meeting the specific, stringent requirements for a HIPAA NPP. Furthermore, with the complexity of state-specific privacy laws like the CCPA/CPRA, a comprehensive and easily navigable privacy center is strategically advantageous for building member trust and ensuring compliance.
The 'Terms & Privacy' document serves as the primary governing agreement for website use. For a healthcare platform, these terms must be exceptionally clear, especially regarding the disclaimers of medical advice, limitations of liability, and user responsibilities. The enforceability of these terms is critical in mitigating legal risk. Given that members may be low-income or have limited English proficiency, the language used must be plain and understandable to be considered equitable and enforceable. Without access to the full text, a key area for strategic review would be ensuring the terms are not overly broad and do not impose unfair obligations on members, which could be challenged under consumer protection laws or state insurance regulations.
The website utilizes a basic cookie banner stating, 'By using our website, you consent to our use of cookies in accordance with our Privacy Policy.' This 'implied consent' or 'browsewrap' model is outdated and legally insufficient under modern privacy regulations like California's CPRA. The CPRA requires clear notice and an easy-to-use mechanism for consumers to opt-out of the sale or sharing of their personal information, which often occurs via tracking cookies. The banner lacks a 'Decline' or 'Manage Settings' option, providing no granular control over cookie categories (e.g., analytics, advertising). This presents a significant compliance gap and a medium-level legal risk, as regulators increasingly expect active, opt-out consent mechanisms.
As a managed care organization dealing with Medicaid and Medicare, Molina is a 'Covered Entity' under HIPAA and must comply with the Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules. The most glaring issue on the homepage is the 'Notice of Episource Data Breach.' Episource, a vendor, experienced a massive breach affecting millions of individuals, including Molina members. While Molina's transparency in posting this notice is commendable, the event itself highlights a critical and high-severity risk area: third-party vendor management. Under HIPAA, Molina is required to have robust Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with all vendors who handle PHI and to ensure they have adequate security measures. This breach indicates a potential failure in the vendor's security posture, which directly impacts Molina's compliance and exposes the company to regulatory investigation, litigation, and significant reputational damage. The breach underscores the absolute necessity of rigorous due diligence and ongoing monitoring of all business associates.
Molina Healthcare demonstrates a strong and commendable commitment to accessibility. The website features an explicit accessibility menu and tools for screen readers. Crucially, it provides links to a 'Notice of Nondiscrimination' and 'Multi-language Interpreter Services.' These elements are direct requirements under Section 1557 of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which prohibits discrimination and mandates language assistance services for entities receiving federal funds, like Molina. This proactive approach is a significant compliance strength. However, full compliance with standards like the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 AA is an ongoing process. While the visible features are excellent, a formal, independent WCAG audit would be the next strategic step to identify and remediate less obvious barriers and solidify their legal positioning as an accessible provider.
Molina operates in one of the most heavily regulated industries in the U.S. Its primary business lines—Medicaid, Medicare, and ACA Marketplace plans—are governed by a complex web of federal and state laws.
- HIPAA/HITECH: This is the bedrock of their data privacy obligations. The Episource breach is a stark reminder of the stringent requirements of the HIPAA Security and Breach Notification Rules.
- Affordable Care Act (ACA): The website's 'Notice of Nondiscrimination' and language assistance information directly address the requirements of ACA Section 1557, a major compliance strength that reduces the risk of civil rights litigation and federal audits.
- CCPA/CPRA: As a large corporation serving California residents, Molina must comply with the CPRA. While PHI covered by HIPAA is largely exempt, other personal information collected via the website (e.g., from marketing activities, job applicants, or website analytics) is not. The current cookie banner and lack of a 'Do Not Sell or Share' link are significant gaps under this regulation.
- State Insurance Regulations: Each state Molina operates in has its own Department of Insurance with specific rules regarding marketing, member communication, and data handling that must be meticulously followed.
The prominent notice of the Episource data breach elevates vendor risk management from a routine operational task to a critical strategic vulnerability for Molina. Episource, a medical coding and risk adjustment vendor, is a classic 'Business Associate' under HIPAA. The breach, which exposed highly sensitive data including Social Security numbers and detailed medical information for over 5.4 million people, represents a systemic failure that directly impacts Molina. This event triggers significant legal and financial risks, including potential HHS Office for Civil Rights (OCR) investigations into Molina's own vendor due diligence processes, class-action lawsuits from affected members, and damage to the trust that is essential in the healthcare relationship. Strategically, this necessitates an immediate and comprehensive review of the security posture and contractual agreements of all vendors with access to PHI.
Compliance Gaps
- •
The cookie consent mechanism is outdated and does not provide an 'opt-out' or 'decline' option, failing to meet CPRA standards.
- •
Absence of a clear, easily accessible 'Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information' link in the website footer, as required by the CPRA.
- •
The use of a combined 'Terms & Privacy' document is not ideal for a healthcare entity; a distinct and comprehensive HIPAA 'Notice of Privacy Practices' should be prominently featured.
- •
The Episource data breach reveals a potential weakness in the due diligence and ongoing security monitoring of third-party vendors (Business Associates).
Compliance Strengths
- •
Excellent adherence to ACA Section 1557 requirements with prominent 'Notice of Nondiscrimination' and 'Multi-language Interpreter Services' links.
- •
Proactive and transparent communication regarding the third-party data breach directly on the homepage.
- •
Visible commitment to web accessibility with dedicated menus and tools for users with disabilities.
- •
Clear focus on the needs of its core member base (Medicaid and Marketplace), indicating a strong understanding of its primary regulatory environment.
Risk Assessment
- Risk Area:
Third-Party Vendor Data Security
Severity:High
Recommendation:Conduct an urgent, comprehensive audit of all Business Associates' security protocols, contractual obligations, and data handling practices. Re-evaluate the vendor selection and monitoring process to include more stringent security requirements.
- Risk Area:
CPRA Compliance
Severity:High
Recommendation:Implement a compliant Consent Management Platform (CMP) for cookies that provides clear opt-out options. Add a 'Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information' link to the website footer and establish a process for handling consumer rights requests under CPRA.
- Risk Area:
HIPAA Privacy Notice
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Develop and prominently display a standalone HIPAA 'Notice of Privacy Practices' that is distinct from the general website Terms of Service. Ensure the language is clear, accessible, and fully compliant with HIPAA requirements.
- Risk Area:
Website Accessibility
Severity:Low
Recommendation:While current efforts are strong, commission a formal WCAG 2.1 AA audit from a qualified third party to identify and remediate any remaining accessibility gaps, thereby further mitigating legal risk under the ADA and ACA.
High Priority Recommendations
- •
Immediately launch a full-scale review of the security and compliance of all third-party vendors with access to PHI, starting with a deep dive into the Episource breach.
- •
Deploy a modern Consent Management Platform to bring cookie handling into compliance with the CPRA, including clear 'opt-out' functionality.
- •
Add a 'Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information' link to the website footer to comply with CPRA requirements.
- •
Separate the HIPAA Notice of Privacy Practices from the general website terms to improve clarity, build member trust, and ensure specific HIPAA disclosure requirements are met.
Molina Healthcare's digital legal positioning reflects a company deeply attuned to its core healthcare regulatory landscape but lagging in the adjacent, fast-evolving area of digital privacy law. The company demonstrates excellence in adhering to the accessibility and non-discrimination mandates of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Section 1557, which is a significant strategic asset that builds trust with its diverse, government-sponsored member base. However, this strength is severely undermined by two critical factors. First, the recent, massive data breach through its vendor, Episource, exposes the company to extreme legal, financial, and reputational risk, highlighting potential systemic issues in its vendor management program. Second, the website's cookie consent and data privacy mechanisms are not compliant with modern standards like the CPRA. This juxtaposition creates a strategic vulnerability: while Molina excels at the 'big picture' healthcare laws, it is exposed to significant risk from gaps in digital operational compliance. The immediate priority must be to overhaul the vendor risk management framework and bring the website's data privacy features into full compliance to protect its members and mitigate the substantial legal and regulatory threats it currently faces.
Visual
Design System
Corporate/Functional
Fair
Basic
User Experience
Navigation
Horizontal Top Bar (Mega Menu)
Clear
Fair
Information Architecture
Somewhat logical
Somewhat clear
Heavy
Conversion Elements
- Element:
Hero Section Primary CTAs ('About Molina', 'New Members - Medicaid', 'New Members - Marketplace')
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Ineffective
Improvement:Consolidate to a single, primary CTA like 'Explore Health Plans' or 'Become a Member'. The current three options create decision paralysis and lack visual priority.
- Element:
Sign In / Register Button
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Somewhat effective
Improvement:Increase the contrast and make the 'Register' link a more prominent secondary button. The purple color feels disconnected from the brand's primary teal palette.
- Element:
'Medicaid Renewals' Section CTA ('Members', 'Providers')
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Ineffective
Improvement:Combine into a single, clearer CTA like 'Learn About Renewals'. Splitting the audience here creates an unnecessary extra step and visual clutter.
- Element:
Main Navigation ('Become a Member')
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:The placement is good, but the visual treatment could be stronger to differentiate it as the primary user acquisition goal.
Assessment
Strengths
- Aspect:
Audience-Centric Navigation
Impact:High
Description:The main navigation clearly segments information for key audiences (Members, Health Care Professionals, Brokers), which is a best practice for insurance websites and helps users self-identify and find relevant information quickly.
- Aspect:
Clear Contact Information and Member Focus
Impact:Medium
Description:The company's mission is member-focused, aiming to provide high-quality care to underserved populations. The site design, while dated, attempts to support this with clear paths for members to find information.
- Aspect:
Accessibility Features
Impact:Medium
Description:The inclusion of an 'Accessibility' button and language/text size selectors at the top is a crucial feature for a healthcare website serving diverse populations, aligning with WCAG best practices.
Weaknesses
- Aspect:
Dated Visual Design
Impact:High
Description:The overall aesthetic, including gradients, drop shadows, and typography, feels outdated (circa Web 2.0). This can erode trust, a critical component for a healthcare provider, making the brand appear less modern and reliable compared to competitors.
- Aspect:
Lack of Visual Hierarchy
Impact:High
Description:The homepage presents multiple competing calls-to-action ('About Molina', 'New Members', 'Medicaid Renewals') with similar visual weight. This creates a high cognitive load and makes it difficult for users to identify the single most important action they should take.
- Aspect:
Inconsistent Brand Expression
Impact:Medium
Description:The use of multiple shades of teal, blue, and a disconnected purple for the 'Sign In' button creates visual dissonance. The brand's official style guide calls for a 'welcoming, open and contemporary' feel with heavy use of white space and the primary PMS 320 (teal), which is not fully realized on the website.
- Aspect:
Poor Visual Storytelling
Impact:Medium
Description:The hero image is generic and doesn't strongly communicate Molina's specific value proposition of serving government-sponsored healthcare members. The imagery throughout the page lacks a cohesive narrative to build an emotional connection with the user.
Priority Recommendations
- Recommendation:
Modernize the UI and Establish a Cohesive Design System
Effort Level:High
Impact Potential:High
Rationale:A full visual refresh is needed to build trust and compete effectively. This includes updating the color palette to align with brand guidelines, adopting modern, clean typography (e.g., a sans-serif font for headings and body), removing gradients and drop shadows, and using high-quality, authentic imagery. This will improve brand perception and user confidence.
- Recommendation:
Redesign the 'Above the Fold' Area to Clarify the Primary User Journey
Effort Level:Medium
Impact Potential:High
Rationale:The hero section should feature a single, compelling headline and one primary call-to-action (e.g., 'Find a Plan' or 'Enroll Now'). Secondary actions, like 'For Current Members', can be given less visual prominence. This will immediately reduce cognitive load and guide new users toward the primary conversion goal.
- Recommendation:
Improve Information Scent and Reduce Clutter
Effort Level:Medium
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Consolidate sections and reduce competing messages. For instance, the 'Medicaid Renewals' and 'Data Breach' notices, while important, detract from the main user journey and could be handled through more subtle banners or integrated into a dedicated member alerts section.
Mobile Responsiveness
Fair
The desktop layout, with its rigid columns and horizontal navigation, is likely to adapt poorly on smaller screens. Elements will probably stack vertically, but without a mobile-first approach, this often leads to excessive scrolling and awkward spacing.
Mobile Specific Issues
- •
The multi-column footer will likely become a very long, single-column list, making it difficult to scan.
- •
The main navigation will probably collapse into a hamburger menu, but its clarity and usability need to be verified on a live device.
- •
The hero section's text overlay on the image may become unreadable on smaller screens if not handled properly with responsive typography and image treatment.
Desktop Specific Issues
The fixed-width layout creates unused space on wider monitors, making the site feel constrained and dated.
Hover states and interactive element feedback are not apparent from the static image but are often underdeveloped in older designs.
This visual audit of Molina Healthcare's website reveals a functional but significantly outdated digital presence that undermines its mission to provide high-quality care. Molina's business model is focused on serving vulnerable populations through government-sponsored programs like Medicaid and Medicare, where establishing trust and ensuring ease of use are paramount.
Design System and Brand Identity:
The current design system is basic and inconsistently applied. The visual style is reminiscent of the early 2010s, characterized by excessive use of gradients, competing colors (teals, blues, purples), and a lack of typographic hierarchy. The brand's stated goal of a 'welcoming, open and contemporary' feel is not achieved. This dated aesthetic can create a subconscious perception of being less credible or technologically adept, which is a significant risk for a healthcare organization handling sensitive information.
Visual Hierarchy and User Experience:
The most critical issue is the lack of a clear visual hierarchy on the homepage. The user is immediately confronted with multiple competing calls-to-action ('About Molina', 'New Members - Medicaid', 'New Members - Marketplace', 'Medicaid Renewals'), which leads to decision fatigue. Best practices for insurance websites recommend simplifying complex processes and guiding users through clear, manageable steps. The current layout presents too much information simultaneously, creating a heavy cognitive load and obscuring the primary user pathways for both prospective and current members.
Navigation and Information Architecture:
The primary navigation is a strength, clearly segmenting content by key user groups ('Members', 'Health Care Professionals', etc.). This is a logical structure for a multi-faceted healthcare provider. However, the user flow is compromised by cluttered page layouts. For instance, critical but transient information like the 'Data Breach Notice' is given significant visual prominence, distracting from core tasks.
Conversion Elements and Actionability:
Call-to-action (CTA) buttons lack consistency in style, color, and prominence. The most important conversion goal for a new visitor—becoming a member—is diluted by multiple, equally weighted buttons in the hero section. The 'Sign In' CTA uses a purple color that is not present elsewhere in the primary palette, making it feel disconnected from the brand identity.
Conclusion and Strategic Direction:
Molina Healthcare is a Fortune 500 company serving millions of members, but its primary digital touchpoint does not reflect this scale or its mission-driven purpose. The website requires a strategic redesign focused on modernization, simplification, and trust-building. The top priority should be to overhaul the visual design to be clean, modern, and accessible, directly followed by a restructuring of the homepage to guide new and existing users through clear, singular conversion paths. By investing in a better user experience, Molina can more effectively serve its members, build brand trust, and create a digital platform that truly supports its vital mission.
Discoverability
Market Visibility Assessment
Molina Healthcare is a recognized FORTUNE 500 company and a significant player in the government-sponsored healthcare sector, focusing on Medicaid, Medicare, and Marketplace plans. Its brand authority is rooted in its mission to serve financially vulnerable populations, a specialization that builds trust with state governments and members. However, its authority as a thought leader is underdeveloped digitally. The website is highly functional and transactional (e.g., member renewals, provider lookups) but lacks substantial content on broader healthcare topics like health equity, navigating public health systems, or policy analysis, which could position them as a leading voice in the industry.
Molina's market share visibility is intrinsically tied to its state-level contracts. Digitally, it competes with national giants like Centene (a direct competitor in the Medicaid/Medicare space), UnitedHealth Group, and Humana, as well as state-specific plans (e.g., L.A. Care Health Plan, Blue Shield of California). Search visibility is critical during open enrollment and for newly eligible individuals. For broad, national terms, Molina is often outranked by larger competitors. Its key opportunity lies in dominating search for hyper-local, state-specific queries like "Medicaid plans in Texas" or "Marketplace insurance in Florida", where it has an established operational presence.
The potential for customer (member) acquisition through digital channels is substantial but appears under-leveraged. The website's homepage prominently features links for new Medicaid and Marketplace members, indicating a focus on direct acquisition. However, the conversion funnel seems to begin at the point of decision rather than awareness or consideration. Major industry events, such as the ongoing Medicaid redeterminations, present a massive opportunity. Millions of individuals are seeking information on retaining coverage or finding alternatives; a strong digital presence with clear, educational content could capture a significant portion of this transitioning population. A recent job posting for a Sr. Digital Marketing Specialist highlights an intent to improve lead journey mapping and use of tools like Salesforce Marketing Cloud, suggesting a move towards more sophisticated digital acquisition.
Molina operates in numerous states, including key markets like California, Florida, Texas, and New York. Its digital strategy must be deeply localized to be effective. The website allows users to select their state, which tailors the information—a necessary first step. However, market penetration requires more than a localized portal. It demands state-specific content hubs that address local health concerns, partner with local community organizations, and provide clear guidance on state-specific enrollment processes. The current structure is a good foundation, but there is a significant opportunity to create richer, geo-targeted content that improves search visibility and community engagement within each state of operation.
The website's current topic coverage is narrow and primarily functional, focusing on member-specific tasks and plan information. It lacks a robust library of educational content covering the complex landscape its members must navigate. Key topics with significant strategic value include:
* Medicaid Redetermination: Guiding users through the process to either maintain Molina coverage or transition to a Molina Marketplace plan.
* Understanding Benefits: Simple, clear explanations of terms like co-pays, deductibles, and networks for a first-time insured audience.
* Preventative Health and Wellness: Content on managing chronic conditions like diabetes or asthma, which are prevalent in their member base.
* Navigating Healthcare: Guides on how to choose a primary care physician, when to use urgent care vs. the ER, and how to prepare for a doctor's visit.
Strategic Content Positioning
Content is misaligned with the full customer (member) journey. It is heavily weighted towards the 'Decision' and 'Retention' stages (e.g., 'New Members' links, renewal notices). The crucial 'Awareness' and 'Consideration' stages are underserved. For someone newly eligible for Medicaid or losing employer coverage, there is a lack of foundational content to help them understand their options, evaluate plans, and see Molina as a trusted advisor before they even begin an application. This gap means Molina is likely missing the opportunity to connect with potential members early in their decision-making process.
Molina is uniquely positioned to be a thought leader on health equity and serving low-income communities. Opportunities include:
* Publishing data-driven reports on health outcomes within their member populations.
* Creating content around Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) and showcasing their community partnerships and initiatives.
* Developing resources for state policymakers on best practices for managed care.
* Establishing a health policy blog or resource center that explains complex legislation (like the ACA) in simple terms. This would build significant brand authority and credibility.
Competitors like Centene and UnitedHealthcare often have more extensive health and wellness libraries and educational resources. The primary competitive gap for Molina is the lack of content that simplifies the complexities of government-sponsored healthcare. While competitors may offer generic wellness tips, Molina can win by creating highly targeted, empathetic content that speaks directly to the challenges and questions of a Medicaid or Marketplace enrollee. This includes multi-lingual video guides, simple infographics comparing plan types, and localized directories of community support services, going beyond just clinical providers.
The stated brand message of being a caring, mission-driven "family" is evident in the website's welcoming tone and accessibility features (multi-language support). However, the user experience is very transactional, which can feel impersonal and bureaucratic, slightly undermining the 'caring' message. The prominent notice about a data breach, while transparent, also impacts brand perception. To improve consistency, the content needs to be more relational and less transactional, offering help and guidance proactively rather than just providing links and forms. Community partnership stories and member testimonials could powerfully reinforce the 'Molina Cares' narrative.
Digital Market Strategy
Market Expansion Opportunities
- •
Develop comprehensive, state-specific resource hubs to deepen penetration in existing markets. These hubs should feature localized health news, provider spotlights, and guides to state-specific programs.
- •
Create a dedicated content pillar around 'Transitioning Coverage' to capture individuals moving off employer plans or aging into Medicare, guiding them towards Molina's Marketplace or Medicare solutions.
- •
Target underserved linguistic communities with dedicated, in-language content hubs beyond simple translations, including culturally relevant health information and videos.
Customer Acquisition Optimization
- •
Launch a major content initiative focused on Medicaid redetermination, with clear, step-by-step guides, checklists, and call-to-action pathways for members to either renew or transition to a Molina Marketplace plan. This is the single largest near-term acquisition and retention opportunity.
- •
Invest in search visibility for 'long-tail' informational keywords related to healthcare eligibility and enrollment to attract potential members earlier in their journey.
- •
Leverage data on Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) to create highly targeted digital outreach campaigns that resonate with the specific life challenges of potential members, positioning Molina as a holistic partner.
Brand Authority Initiatives
- •
Establish a 'Molina Cares' community impact hub on the website, showcasing partnerships, local investments, and success stories to substantiate the brand's mission.
- •
Create an annual public report on health equity, using anonymized data to highlight trends and demonstrate Molina's commitment to improving outcomes in vulnerable populations.
- •
Partner with trusted community-based organizations and state health agencies to co-create content and earn authoritative backlinks and mentions, boosting digital credibility.
Competitive Positioning Improvements
- •
Position Molina as the 'simplifier' of government healthcare. Use clear, jargon-free language, comparison tools, and simple guides to contrast with the often-complex presentation of competitors.
- •
Emphasize the seamless transition pathway for members who move between Molina's Medicaid and Marketplace plans, a key differentiator for retention during income fluctuations.
- •
Develop a robust 'Broker and Navigator Support Center' with dedicated resources, training materials, and tools to become the preferred plan for enrollment assisters, indirectly driving member growth.
Business Impact Assessment
Market share growth will be indicated by increased organic search visibility for enrollment-related terms in key states, leading to a higher volume of traffic to member acquisition landing pages. Success can be measured by tracking rankings for "[State] Medicaid plans" and "[City] Marketplace insurance" against top competitors.
Key metrics include the number of completed plan applications initiated from organic search and a lower blended cost-per-acquisition (CPA) for new members. Tracking the conversion rate from educational content (e.g., a 'How to Renew Medicaid' guide) to an application start is a critical leading indicator of digital marketing effectiveness.
Authority will be measured by an increase in branded search volume (more people searching directly for 'Molina Healthcare'), growth in referral traffic from government and non-profit health sites, and media mentions in discussions about Medicaid and health equity. Share-of-voice analysis on these key topics versus competitors is a core benchmark.
Success will be benchmarked by qualitatively and quantitatively outperforming competitors on member education. This includes having more comprehensive, easier-to-understand content on key topics like redetermination and benefit utilization. Benchmarks include organic ranking superiority for critical non-branded keywords and higher engagement rates (e.g., time on page, lower bounce rate) on educational resource pages.
Strategic Recommendations
High Impact Initiatives
- Initiative:
Launch a 'Medicaid Redetermination & Coverage Transition' Content Hub.
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Address the immediate, large-scale need of millions of Americans navigating Medicaid redeterminations to prevent member loss and capture new Marketplace enrollees.
Success Metrics
- •
Reduction in Medicaid member churn attributable to redetermination.
- •
Increase in new Marketplace plan enrollments.
- •
Top 3 search ranking for state-specific redetermination queries.
- Initiative:
Develop State-Centric Health & Wellness Resource Centers.
Business Impact:Medium
Market Opportunity:Differentiate from national competitors by providing locally relevant health information and community resources, strengthening geographic market penetration and member engagement.
Success Metrics
- •
Increased organic traffic from geo-targeted keywords.
- •
Higher member engagement with localized content.
- •
Improved brand perception in local community surveys.
- Initiative:
Establish a Digital Thought Leadership Platform on Health Equity.
Business Impact:Medium
Market Opportunity:Solidify Molina's brand identity as a mission-driven expert in serving vulnerable populations, building trust with state partners, policymakers, and communities.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in authoritative backlinks from policy and healthcare sites.
- •
Media mentions and citations of Molina's reports/insights.
- •
Growth in branded search volume.
Molina Healthcare should strategically position itself as the most trusted and accessible guide for Americans navigating government-sponsored health insurance. This moves beyond being just a plan administrator to becoming an essential resource and partner. The digital strategy must pivot from being purely transactional to being educational and relational. By simplifying complexity, providing empathetic guidance, and demonstrating community commitment through its content, Molina can build a powerful brand moat that larger, less specialized competitors cannot easily replicate.
Competitive Advantage Opportunities
- •
Become the definitive online resource for the Medicaid-to-Marketplace transition, creating a seamless digital pathway that retains members within the Molina ecosystem.
- •
Leverage deep expertise in specific populations (e.g., dual-eligible, LTSS) to create specialized content that competitors with a broader focus cannot match.
- •
Build the most user-friendly and supportive digital ecosystem for community-based enrollment assisters (navigators, brokers), turning them into a powerful, indirect sales channel.
Digital Market Presence Analysis: Molina Healthcare
Overall Assessment:
Molina Healthcare has established a functional digital presence that serves the basic needs of its existing members. However, its current strategy is fundamentally reactive and transactional, placing it at a competitive disadvantage in member acquisition and brand authority. The website functions as a digital front door but fails to act as a strategic asset for market growth and competitive differentiation. The company's core business—serving government-sponsored health plan members—is undergoing a period of unprecedented disruption due to Medicaid redeterminations, presenting both a significant risk of member attrition and a massive opportunity for acquisition.
Strategic Imperatives:
-
Dominate the Redetermination Narrative: The single most critical strategic imperative is to become the leading digital resource for individuals navigating Medicaid redetermination. This event is reshaping the market in real-time. By creating comprehensive, state-specific guides, tools, and clear pathways, Molina can mitigate membership loss and capture a significant share of those transitioning to Marketplace plans. Failure to do so will result in substantial, avoidable churn.
-
Shift from Transaction to Education: The target audience often has low health literacy and is navigating a complex, intimidating system. A digital presence focused on simple forms and portals fails to build trust. The strategic pivot is to become an educator and guide. By investing in content that simplifies complex topics, explains benefits clearly, and answers questions before they are asked, Molina can build a powerful brand preference early in the member journey, lowering acquisition costs and improving retention.
-
Weaponize Localization: Molina's strength is its contracted presence in specific states. Its digital strategy must mirror this. Competing against national brands on broad terms is inefficient. The opportunity is to win at the local level by creating rich, state-specific content hubs. This means going beyond a translated corporate site to feature local health news, spotlight community partners, and provide guidance tailored to the nuances of each state's programs. This approach will build strong local search visibility and deepen community ties, creating a competitive advantage that is difficult for centralized national players to replicate.
Conclusion:
Molina Healthcare is at a strategic inflection point. Continuing with a passive, transactional digital presence will lead to market share erosion in a volatile environment. By aggressively investing in an educational, empathetic, and highly localized digital strategy focused on the immediate redetermination crisis and long-term brand authority, Molina can transform its website from a simple utility into a powerful engine for member acquisition, retention, and market leadership.
Strategic Priorities
Strategic Priorities
- Title:
Launch 'Project Bridge': A Crisis-Response Initiative for Medicaid Redetermination
Business Rationale:The ongoing Medicaid redetermination is the single largest market event affecting the business, creating a massive risk of member churn and a simultaneous, time-limited opportunity to capture disenrolled individuals for Molina's ACA Marketplace plans. A dedicated, executive-led initiative is required to manage this transition as a unified retention and acquisition strategy, rather than as separate operational tasks.
Strategic Impact:This initiative will transform a significant business threat into a primary growth driver. By providing a seamless pathway for members, Molina can mitigate catastrophic revenue loss in its core Medicaid business, accelerate growth in its higher-margin Marketplace segment, and build lasting member loyalty by being a supportive partner during a critical life event.
Success Metrics
- •
Medicaid Member Retention Rate
- •
Medicaid-to-Marketplace Conversion Rate
- •
Net New Member Growth in ACA Marketplace Plans
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Quick Win (0-3 months)
Category:Customer Strategy
- Title:
Establish Market Dominance in the Dual-Eligible (D-SNP) Segment
Business Rationale:The dual-eligible population is a high-need, high-revenue segment where Molina's specialized care management model can create superior outcomes and a strong competitive moat. While larger competitors focus on broad scale, a concentrated effort to become the national leader in this niche will yield higher margins and create a defensible market position.
Strategic Impact:This strategy shifts Molina from a generalist in government programs to the undisputed specialist in the most complex segment. This builds a powerful brand halo, creates a significant and profitable growth vector, and strengthens the value proposition to state and federal partners by demonstrating expertise in managing the highest-cost populations.
Success Metrics
- •
Year-over-Year D-SNP Membership Growth
- •
D-SNP Revenue as a Percentage of Total Revenue
- •
Improvement in Clinical Outcome Metrics for D-SNP population (e.g., hospital readmission rates)
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Market Position
- Title:
Transform the Member Experience to Substantiate the 'Molina Family' Brand Promise
Business Rationale:The current digital presence is dated and the member experience is transactional, which directly contradicts the 'Molina Family' brand promise. This disconnect erodes trust, a critical asset in healthcare, and makes Molina vulnerable to competitors offering a more modern, supportive member journey. The weak brand messaging fails to differentiate Molina beyond being a functional administrator.
Strategic Impact:This transforms Molina's brand from an empty slogan into a tangible competitive advantage. A superior, relational member experience will significantly improve retention, increase member lifetime value, and create a powerful differentiator that is difficult for larger, more bureaucratic competitors to replicate, thereby reducing reliance on price-based competition.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in Member Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- •
Reduction in Voluntary Member Churn Rate
- •
Increase in Digital Tool Adoption (e.g., Member Portal/App)
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Brand Strategy
- Title:
Overhaul Third-Party Risk Management to Rebuild Trust and Ensure Operational Integrity
Business Rationale:The massive Episource data breach has exposed a critical vulnerability in third-party vendor oversight, creating severe legal, financial, and reputational risks. This is not a routine compliance issue; it is a strategic threat that undermines trust with both members and the state partners who award contracts. A reactive approach is insufficient.
Strategic Impact:This initiative moves vendor management from a back-office compliance function to a core strategic imperative. It will protect the company from catastrophic legal and financial liabilities, proactively rebuild trust with regulators and members, and make robust data security a key part of Molina's value proposition and a competitive advantage in future contract bids.
Success Metrics
- •
Reduction in Critical Third-Party Security Vulnerabilities
- •
Inclusion of 'Security & Oversight' as a strength in state contract reviews
- •
Decrease in Member Complaints Related to Data Privacy
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Operations
- Title:
Accelerate the Transition to Value-Based Care and Risk-Sharing Models
Business Rationale:The government payer market is inexorably shifting from fee-for-service to value-based care (VBC) models that reward health outcomes. Molina's long-term profitability and ability to win state contracts depend on its ability to effectively manage medical costs and demonstrate superior clinical quality. The current operational model and data systems are not fully optimized for this future.
Strategic Impact:This strategy future-proofs Molina's revenue model. By leading in VBC, the company can secure more favorable terms with state partners, build deeper, more collaborative relationships with providers, and achieve sustainable margin improvement by aligning financial incentives with better health outcomes for its members.
Success Metrics
- •
Percentage of Revenue tied to Value-Based Contracts
- •
Improvement in Medical Loss Ratio (MLR)
- •
Achievement of Quality Bonus Payments from State/Federal Partners
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Long-term Vision (12+ months)
Category:Revenue Model
Molina Healthcare must immediately transform the existential threat of Medicaid redetermination into its primary growth engine. This requires pivoting from a functional administrator to a trusted partner by substantiating its 'Family' brand promise with a superior member experience, while aggressively mitigating the systemic risk exposed by its recent third-party data breach.
Molina's defensible competitive advantage lies in becoming the undisputed expert in serving the most complex government-sponsored populations, particularly dual-eligibles. This is achieved through a 'high-touch' care management model that larger, less-focused competitors cannot easily replicate.
The primary growth catalyst is the successful execution of 'Project Bridge'—a unified strategy to minimize member loss during Medicaid redetermination while aggressively capturing those same individuals for its ACA Marketplace plans, effectively converting an industry crisis into a significant market share opportunity.