eScore
slb.comThe eScore is a comprehensive evaluation of a business's online presence and effectiveness. It analyzes multiple factors including digital presence, brand communication, conversion optimization, and competitive advantage.
SLB demonstrates a sophisticated digital presence with exceptional content authority and topic coverage, reflecting its market leadership. The website's content is strategically aligned with the B2B customer journey, addressing topics from core oil and gas innovation to decarbonization and digital solutions. Its global reach is immense, though it could be enhanced with more localized content for key international markets. The recent launch of the Lumi AI platform and a clear digital-first narrative reinforce its position as a technology leader.
Excellent alignment of content with strategic business goals, effectively covering the entire energy landscape from traditional extraction to cutting-edge decarbonization and digital technologies.
Develop and deploy geo-targeted content and localized microsites to deepen market penetration and support regional sales teams in key international markets like the Middle East and Latin America.
The rebranding to SLB has been masterfully executed, creating a consistent and authoritative brand voice that positions the company as a forward-thinking technology leader. The messaging hierarchy is clear and logical, effectively communicating the core value proposition of balancing energy production with sustainability. While messaging is highly effective for C-suite, investor, and technical audiences, it lacks a human element and features generic calls-to-action that could be more persuasive.
Exceptional message consistency and strategic alignment, successfully shifting the brand narrative from 'oilfield services' to a 'global technology company' focused on the energy transition.
Humanize the brand by incorporating customer and employee stories and testimonials into the website to make the company's innovations more tangible and relatable.
The website provides a clear, logical user experience with a professional design and intuitive navigation for its target B2B audience. However, the conversion paths suffer from some friction, including understated secondary CTAs and generic button copy that dampens user action. The provided analysis also points to potential accessibility gaps, such as a lack of default video captions, which could hinder engagement for some users and poses a compliance risk. The sheer volume of information can also create a high cognitive load for users without a clear, persona-based pathway.
A highly professional and visually cohesive design with a clear information architecture that effectively guides sophisticated B2B users to relevant, high-level information.
Conduct a full WCAG 2.1 AA accessibility audit and remediate all identified issues, particularly ensuring all video content has readily available closed captions to improve inclusivity and mitigate legal risk.
SLB exhibits a very high degree of credibility, built on a foundation of transparency and robust governance. The website features extensive third-party validation through prominent news of major contract awards, strategic acquisitions, and partnerships with industry leaders. The company's commitment to ethics, compliance with industry-specific regulations, and detailed investor relations information all serve as powerful trust signals. The primary risk noted in the analysis is in the technical execution of digital compliance (accessibility) rather than a weakness in corporate policy.
Abundant and prominent third-party validation, including news of major contract awards (Equinor), strategic acquisitions (ChampionX), and joint ventures (Aker Carbon Capture), which powerfully substantiates its market leadership and technical capabilities.
Increase the prominence of the corporate 'Ethics and Compliance' program on the main website to further enhance its public posture on anti-corruption, a critical factor in the high-risk energy sector.
SLB's competitive moat is deep and highly sustainable, anchored by its unparalleled integrated technology portfolio, extensive global footprint, and long-standing relationships with major energy producers. Strategic acquisitions, like that of ChampionX, continually strengthen its offerings, particularly in less cyclical production-focused areas. The company's significant and ongoing investment in its proprietary digital AI platform (Lumi) creates a powerful, defensible ecosystem that is difficult for competitors to replicate.
The broadest integrated technology and service portfolio in the industry, allowing SLB to deliver comprehensive, end-to-end solutions that competitors with niche strengths cannot match.
Aggressively market its integrated digital and new energy solutions to counter the strong 'energy technology' narrative successfully built by competitor Baker Hughes, ensuring market perception aligns with SLB's advanced capabilities.
The company is exceptionally well-positioned for scalable growth, driven by its high-margin Digital & Integration segment and its strategic expansion into new energy markets. The business model demonstrates high operational leverage, particularly as software and digital solutions are deployed globally. Significant expansion potential exists in adjacent markets, such as decarbonizing heavy industry and sustainable mineral extraction, leveraging core subsurface expertise.
A clear and well-funded strategy to expand into high-growth 'New Energy' markets like Carbon Capture (CCUS), geothermal, and sustainable lithium, leveraging its core competencies to build new, multi-billion dollar business lines.
Address the identified talent gaps in agile software development and new energy fields by launching aggressive internal reskilling programs and strategic academic partnerships to build the workforce needed to execute its growth strategy.
SLB's business model is highly coherent and demonstrates a masterful strategic pivot in response to market dynamics. The structure is logically organized around its core business, a high-growth digital arm, and a future-focused new energy segment, creating a balanced portfolio. The acquisition of ChampionX is a strategically sound move to bolster recurring, less cyclical revenue streams, enhancing the model's resilience. This clear strategy aligns the interests of customers, investors, and employees toward a unified vision of leading the energy transition.
A well-defined and coherent four-pillar strategy (Innovating in Oil & Gas, Digital at Scale, Decarbonizing Industry, New Energy Systems) that provides a clear roadmap for resource allocation and market communication.
Develop and pilot innovative business models, such as 'Decarbonization-as-a-Service', to monetize outcomes rather than just services and technology, further diversifying revenue streams.
As a market leader in an oligopolistic industry, SLB wields significant market power. Its scale, technological superiority, and integrated offerings grant it considerable pricing power and leverage with suppliers. The company actively shapes market direction through its substantial R&D investments, strategic acquisitions, and by setting new industry standards in digital and decarbonization technologies. This market influence allows SLB to not just compete, but to define the competitive landscape of the future.
Dominant market share and the ability to influence industry trends through technology leadership and large-scale strategic moves, such as the major acquisition of ChampionX to consolidate the production segment.
Launch a dedicated thought leadership platform for C-suite executives, focusing on the financial and strategic aspects of the energy transition to directly influence the capital allocation decisions of key customers.
Business Overview
Business Classification
B2B Energy Technology & Services
Industrial Consulting & Engineering
Energy
Sub Verticals
- •
Oilfield Services & Equipment
- •
Digital Energy Solutions
- •
Decarbonization Technologies
- •
New Energy Systems (Geothermal, CCUS, Hydrogen, Lithium)
Mature
Maturity Indicators
- •
Global operational footprint in over 100 countries.
- •
Century-long history of innovation and market leadership.
- •
Execution of large-scale, multi-billion dollar acquisitions (e.g., ChampionX).
- •
Established brand identity, despite recent rebranding from Schlumberger to SLB.
- •
Significant annual R&D investment and extensive patent portfolio.
- •
Strong, long-term contracts with major national and international energy companies.
Enterprise
Steady
Revenue Model
Primary Revenue Streams
- Stream Name:
Well Construction
Description:Provides products and services for the drilling and positioning of oil and gas wells, representing a core part of the traditional oilfield services business.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:National & International Oil Companies (NOCs/IOCs)
Estimated Margin:Medium
- Stream Name:
Production Systems
Description:Offers technologies and services to manage, monitor, and optimize hydrocarbon production, including artificial lift and production chemicals, significantly bolstered by the ChampionX acquisition. This segment is a key growth driver.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:NOCs, IOCs, Independent E&P Companies
Estimated Margin:High
- Stream Name:
Reservoir Performance
Description:Delivers technologies to characterize, explore, and define hydrocarbon deposits, helping clients understand and access reserves.
Estimated Importance:Secondary
Customer Segment:NOCs, IOCs, Exploration Companies
Estimated Margin:Medium
- Stream Name:
Digital & Integration
Description:Provides digital solutions, software (e.g., Lumi, Delfi platforms), and AI-driven services for data management, interpretation, and operational optimization. This is a high-margin, strategic growth area.
Estimated Importance:Secondary
Customer Segment:All energy and industrial clients
Estimated Margin:High
- Stream Name:
New Energy
Description:Develops and deploys solutions for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS), geothermal, hydrogen, and sustainable lithium production.
Estimated Importance:Tertiary
Customer Segment:Governments, Utilities, Industrial Companies
Estimated Margin:Low-to-Medium
Recurring Revenue Components
- •
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) subscriptions for digital platforms
- •
Long-term service and maintenance contracts.
- •
Performance-based contracts
- •
Consumable production chemical sales
Pricing Strategy
Value-Based & Project-Based
Premium
Opaque
Pricing Psychology
- •
Performance Assurance
- •
Integrated Solution Bundling
- •
Long-Term Partnership Framing
Monetization Assessment
Strengths
- •
Diversified revenue across multiple segments reduces volatility.
- •
High-margin digital business is growing and less tied to commodity cycles.
- •
Strong position in the production phase, which is less cyclical than exploration.
- •
Integrated model allows for significant cross-selling and upselling opportunities.
Weaknesses
- •
Significant portion of revenue is still highly correlated with upstream O&G capital expenditure cycles.
- •
New energy business is still nascent and may require significant investment before becoming a major revenue contributor.
- •
Complex, long sales cycles for large-scale integrated projects.
Opportunities
- •
Monetize decarbonization-as-a-service for heavy industries outside of O&G.
- •
Expand outcome-based pricing models where SLB shares in the value created for the customer.
- •
Grow recurring revenue from the ChampionX production chemicals business.
- •
License proprietary digital and AI technologies to adjacent industries.
Threats
- •
Rapid decline in oil and gas demand could strand core assets and revenue streams.
- •
Intense price pressure from key competitors like Halliburton and Baker Hughes.
- •
Geopolitical instability impacting key operational regions.
- •
Failure to scale new energy solutions profitably could lead to significant financial losses.
Market Positioning
Global Technology Leader for the Energy Transition
Leader
Target Segments
- Segment Name:
National Oil Companies (NOCs)
Description:State-owned enterprises (e.g., ADNOC, Saudi Aramco) managing a country's hydrocarbon resources. They focus on long-term value, national energy security, and increasingly, emissions reduction.
Demographic Factors
Large, state-owned entities
Global operations
Psychographic Factors
Focus on sovereignty and long-term resource management
Risk-averse, seeking proven and reliable technology partners
Behavioral Factors
Engage in long-term, multi-billion dollar contracts
Value integrated project management and local content development
Pain Points
- •
Maximizing recovery from mature fields
- •
Meeting national decarbonization targets
- •
Training and developing a local workforce
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
International Oil Companies (IOCs) & Supermajors
Description:Publicly-traded multinational corporations (e.g., Equinor, TotalEnergies) with globally diversified portfolios, balancing shareholder returns with energy transition commitments.
Demographic Factors
Large, multinational public companies
Operations across multiple continents
Psychographic Factors
Driven by profitability, efficiency, and shareholder value
Increasingly focused on ESG performance and decarbonization
Behavioral Factors
Early adopters of new technology to gain competitive edge
Form strategic technology partnerships.
Pain Points
- •
Reducing operational costs and improving capital efficiency
- •
Lowering the carbon intensity of operations (Scope 1 & 2 emissions)
- •
Accelerating time-to-first-oil on new projects
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:Medium
- Segment Name:
New Energy & Industrial Clients
Description:A growing segment including geothermal developers, utilities, and companies in hard-to-abate sectors (e.g., cement, steel) seeking decarbonization and sustainable energy solutions.
Demographic Factors
Utilities, project developers, heavy industrial manufacturers
Psychographic Factors
Focused on sustainability, regulatory compliance, and pioneering new business models
Behavioral Factors
Seeking partners with technical expertise in geology, subsurface, and large-scale project execution
Pain Points
- •
High upfront capital costs for new energy projects
- •
Subsurface risk and uncertainty (e.g., for CCUS and geothermal)
- •
Lack of integrated solutions for industrial decarbonization
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:High
Market Differentiation
- Factor:
Integrated Portfolio Breadth
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Proprietary Technology & Digital Ecosystem
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Global Operational Scale & Expertise
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Commitment to New Energy Transition
Strength:Moderate
Sustainability:Sustainable
Value Proposition
We are a global technology company providing leading digital solutions and innovative technologies that enable our customers to access energy, enhance performance, and decarbonize operations for a balanced planet.
Good
Key Benefits
- Benefit:
Improved Operational Performance & Efficiency
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
Case studies demonstrating production gains
Performance-based contracts
- Benefit:
Reduced Emissions & Environmental Impact
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
Methane and flaring elimination solutions
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCUS) projects
- Benefit:
Accelerated Project Timelines
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Common
Proof Elements
Integrated project management services
Digital planning and simulation tools
- Benefit:
Data-Driven Decision Making through Advanced Digital Platforms
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Unique
Proof Elements
Lumi and Delfi AI platforms
Case studies on AI-driven subsurface insights
Unique Selling Points
- Usp:
Unmatched integration of subsurface science, wellbore engineering, production systems, and digital technology.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
Pioneering end-to-end solutions for the energy transition, from CCUS to geothermal, built on a century of subsurface expertise.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Moderate
- Usp:
Proprietary AI and data platforms (Lumi/Delfi) that create a defensible digital ecosystem for the energy industry.
Sustainability:Medium-term
Defensibility:Strong
Customer Problems Solved
- Problem:
Unlocking complex and hard-to-reach hydrocarbon reserves efficiently.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Meeting stringent regulatory and investor pressure to decarbonize operations.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
- Problem:
Managing and interpreting vast amounts of subsurface and operational data to make profitable decisions.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Maximizing production and recovery from aging assets while minimizing operational expenditure.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
Value Alignment Assessment
High
SLB's strategic pivot to a dual mandate of optimizing oil and gas while scaling new energy systems directly aligns with the global energy trilemma: security, affordability, and sustainability.
High
The value proposition directly addresses the core pain points of its enterprise clients, focusing on capital efficiency, performance optimization, and meeting decarbonization targets.
Strategic Assessment
Business Model Canvas
Key Partners
- •
National Oil Companies (NOCs)
- •
International Oil Companies (IOCs)
- •
Technology companies (e.g., AIQ, a JV with ADNOC)
- •
Governments and regulatory bodies
- •
Academic and research institutions.
Key Activities
- •
Research & Development of new technologies.
- •
Integrated project management and execution
- •
Software development and data analytics
- •
Manufacturing of specialized equipment
- •
Strategic acquisitions and joint ventures.
Key Resources
- •
Extensive portfolio of patents and proprietary technology
- •
Global operational infrastructure and supply chain.
- •
Deep domain expertise of engineers, geoscientists, and data scientists
- •
Proprietary industry data sets
- •
Strong brand reputation and long-standing customer relationships
Cost Structure
- •
High Research & Development expenditures
- •
Significant capital investment in equipment and facilities
- •
Global workforce compensation and benefits
- •
Supply chain and raw material costs
- •
Costs associated with mergers and acquisitions
Swot Analysis
Strengths
- •
Market leadership and established global brand.
- •
Unparalleled portfolio of integrated technologies and services.
- •
Strong, long-term relationships with the world's largest energy producers.
- •
Strategic pivot and rebranding to align with the energy transition.
- •
High-margin, growing digital business segment provides resilience.
Weaknesses
- •
Legacy perception as a fossil fuel-centric company.
- •
High fixed costs and operational complexity.
- •
Organizational agility can be a challenge for a company of its size.
- •
Dependence on cyclical capital spending in the oil and gas industry.
Opportunities
- •
Become the dominant technology provider for decarbonization (CCUS, methane elimination).
- •
Leverage subsurface expertise to lead in emerging markets like geothermal and sustainable mineral extraction.
- •
Expand digital platform offerings to adjacent heavy industries.
- •
Utilize strategic acquisitions like ChampionX to capture a larger share of less cyclical operational expenditure budgets.
Threats
- •
Intense competition from established players (Halliburton, Baker Hughes) and agile new entrants in the digital space.
- •
Global energy price volatility impacting client investment decisions.
- •
Geopolitical risks disrupting operations and supply chains.
- •
A faster-than-anticipated decline in fossil fuel demand.
- •
Risk of failing to achieve profitability and scale in new energy ventures.
Recommendations
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Strategic Narrative & Communication
Recommendation:Further simplify and amplify the 'energy technology' narrative to solidify market perception beyond 'oilfield services'. Create clear, outcome-focused value propositions for each new energy vertical.
Expected Impact:Medium
- Area:
Digital Integration
Recommendation:Deepen the integration of digital solutions across all four business segments, ensuring that every project and product sold has a clear data and AI value layer. Position the Lumi/Delfi platform as the central nervous system for client operations.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Talent Management
Recommendation:Aggressively recruit and develop talent in software engineering, data science, and renewable energy to support the strategic pivot, ensuring the corporate culture evolves alongside the business model.
Expected Impact:High
Business Model Innovation
- •
Develop an 'Energy-as-a-Service' (EaaS) model for industrial decarbonization, offering fully-managed CCUS or geothermal solutions with performance-based contracts.
- •
Create a dedicated venture arm or internal accelerator to fast-track the commercialization of new energy technologies with greater autonomy and agility.
- •
Establish a data monetization arm that packages and sells anonymized, aggregated operational insights to financial institutions, insurers, and commodity traders.
Revenue Diversification
- •
Actively market digital twin and AI-powered operational efficiency platforms to adjacent heavy industries like mining, chemicals, and heavy manufacturing.
- •
Expand the production chemicals business acquired via ChampionX into new industrial applications, such as water treatment and processing.
- •
Offer strategic consulting services to governments and industrial clusters on developing decarbonization roadmaps and large-scale 'clean energy hubs'.
SLB is in the midst of a profound and necessary strategic transformation, evolving from Schlumberger, the undisputed leader in oilfield services, to SLB, a diversified global energy technology company. This pivot is a direct response to the global energy transition, positioning the company to capitalize on a dual opportunity: optimizing the efficiency and sustainability of its core oil and gas business while simultaneously building and scaling new growth engines in digital solutions and low-carbon energy systems.
The business model is robust, anchored by a mature, cash-generative core business that funds investment into high-growth areas. The four-pillar strategy—Innovating in Oil and Gas, Delivering Digital at Scale, Decarbonizing Industry, and Scaling New Energy Systems—is coherent and addresses the entire energy value chain. The recent acquisition of ChampionX is a strategically astute move, strengthening SLB's position in the less cyclical production and chemicals market, which provides a more stable revenue base less dependent on volatile exploration spending.
The primary challenge lies in execution. SLB must manage a complex cultural and operational shift, integrating new digital-first and new-energy mindsets into a century-old engineering powerhouse. The success of this evolution will depend on its ability to scale its new energy ventures profitably, defend its leadership in a fiercely competitive core market, and convince investors that it can be a leader in a decarbonized future. The company's unparalleled subsurface expertise, global scale, and deep client relationships provide a formidable, sustainable competitive advantage to build upon during this critical transition.
Competitors
Competitive Landscape
Mature (with Growth segments)
Oligopoly
Barriers To Entry
- Barrier:
High Capital Requirements
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Established Customer Relationships & Global Footprint
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Complex Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Impact:Medium
- Barrier:
Specialized Talent and Expertise
Impact:Medium
Industry Trends
- Trend:
Digital Transformation (AI, IoT, Cloud Computing)
Impact On Business:Critical for operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and creating new service models. SLB is heavily invested in this with its Lumi platform.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Energy Transition and Decarbonization
Impact On Business:Drives demand for new business lines like Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS), geothermal, and hydrogen, requiring significant R&D and strategic shifts away from a pure oil and gas focus.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Increased Focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance)
Impact On Business:Pressure from investors and society to reduce emissions and improve sustainability, impacting brand reputation and access to capital.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
International and Offshore Market Growth
Impact On Business:Represents a significant revenue growth area as North American land markets mature. SLB's global presence is a key advantage here.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Industry Consolidation
Impact On Business:Acquisitions (like SLB's of ChampionX) are key to gaining market share, integrating new technologies, and broadening service portfolios.
Timeline:Near-term
Direct Competitors
- →
Halliburton
Market Share Estimate:Major (Top 3 Player)
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Strong focus on North American market, particularly in hydraulic fracturing and completion services, with a growing emphasis on digital solutions and efficiency.
Strengths
- •
Dominant market position in North American completions and production.
- •
Strong brand recognition and long-standing customer relationships.
- •
Advanced digital platforms (Halliburton 4.0) focused on operational efficiency.
- •
Robust R&D in hydraulic fracturing and drilling technologies.
Weaknesses
- •
Historically more reliant on the North American market compared to SLB, making it more vulnerable to regional downturns.
- •
Perceived as less diversified into new energy solutions compared to SLB and Baker Hughes.
- •
Brand is strongly associated with traditional oil and gas, potentially a challenge in an ESG-focused environment.
Differentiators
- •
Deep expertise and leading technology in unconventional resource extraction (shale).
- •
Focus on delivering lowest cost-per-barrel solutions for customers.
- •
Integrated approach to well construction and completions.
- →
Baker Hughes
Market Share Estimate:Major (Top 3 Player)
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Presents itself as an "energy technology company" with a clear strategic focus on leading the energy transition through technology, including CCUS, hydrogen, and geothermal.
Strengths
- •
Strong, well-defined energy transition strategy and portfolio (CCUS, hydrogen, geothermal).
- •
Significant technology portfolio in turbomachinery, essential for LNG and other industrial processes.
- •
Strategic partnerships with tech companies like Microsoft to advance digital transformation.
- •
First-mover reputation in committing to net-zero goals within the OFS sector.
Weaknesses
- •
Historically has had a smaller market share in certain core oilfield services segments compared to SLB and Halliburton.
- •
Revenue and earnings can be lower than SLB's.
- •
Execution risk associated with scaling new energy ventures to match the profitability of traditional services.
Differentiators
- •
Explicit positioning as an energy technology company, not just an oilfield services provider.
- •
Broad portfolio spanning traditional oilfield services and industrial energy technology.
- •
Strong narrative and branding around decarbonization and sustainability.
- →
Weatherford International
Market Share Estimate:Significant (Tier 2 Player)
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:Positions as a global energy services company focused on integrated solutions across drilling, evaluation, completion, production, and intervention, with a growing emphasis on digital platforms like ForeSite.
Strengths
- •
Specialized product lines with strong market positions, such as managed pressure drilling and artificial lift systems.
- •
Global operational footprint in approximately 75 countries.
- •
Focused on improving profitability and operational efficiency after financial restructuring.
- •
Recent strategic agreement with AWS to enhance digital transformation efforts.
Weaknesses
- •
Significantly smaller market capitalization and revenue base compared to the 'Big 3'.
- •
Less extensive R&D budget and technology portfolio than top-tier competitors.
- •
Brand perception may still be impacted by past financial challenges.
- •
Limited presence in the rapidly growing 'new energy' segments compared to SLB and Baker Hughes.
Differentiators
- •
Offers a more focused portfolio of specialized products and services.
- •
Agility as a smaller player to potentially offer more customized solutions.
- •
Strong focus on production and intervention services.
Indirect Competitors
- →
Major Cloud Providers (AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud)
Description:Provide the foundational cloud infrastructure, data analytics, and AI/ML platforms that power the digital transformation of the energy industry. They partner with but also potentially compete with companies like SLB in the digital solutions space.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Low in physical services, but High in the digital and data analytics layer, potentially commoditizing parts of SLB's digital offerings.
- →
Pure-Play Renewable Energy Companies (e.g., Orsted, NextEra Energy)
Description:These companies are leaders in wind, solar, and other renewables. While they don't compete in oilfield services, they compete for capital, talent, and policy favor within the broader energy landscape, shaping the future of the market SLB operates in.
Threat Level:Low
Potential For Direct Competition:Very Low, but they define the trajectory of the energy transition that SLB must adapt to.
- →
Carbon Capture Specialists (e.g., Carbon Engineering, Climeworks)
Description:Specialized technology companies focused solely on developing and deploying carbon capture technologies. They can be partners or competitors to SLB's own CCUS division.
Threat Level:Low
Potential For Direct Competition:Medium, especially if their technology becomes a market standard, potentially challenging SLB's integrated model.
- →
Industrial Automation Companies (e.g., Siemens, Honeywell)
Description:Provide automation, control systems, and software for industrial processes. Their expertise overlaps with SLB's digital offerings in areas like asset performance management and predictive maintenance for energy facilities.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Medium, particularly in providing digital twin and operational optimization solutions directly to energy clients.
Competitive Advantage Analysis
Sustainable Advantages
- Advantage:
Broadest Integrated Technology and Service Portfolio
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable due to decades of R&D, strategic acquisitions (e.g., Cameron, ChampionX), and deep domain expertise across the entire energy lifecycle.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Extensive Global Footprint and Infrastructure
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. The physical presence in over 120 countries, established supply chains, and local talent are extremely difficult and costly to replicate.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Leading Digital Platform and R&D
Sustainability Assessment:Moderately sustainable. SLB's investment in its Lumi (formerly DELFI) platform provides a strong incumbent advantage, but the pace of digital innovation requires continuous, massive investment to stay ahead of both direct and indirect tech competitors.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
- Advantage:
Long-Standing Relationships with National and International Oil Companies (NOCs/IOCs)
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. These relationships are built on decades of trust, proven performance, and integrated contracts that are difficult for new entrants to penetrate.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
Temporary Advantages
{'advantage': 'First-Mover in a Niche Technology', 'estimated_duration': '1-3 years'}
{'advantage': 'Exclusive Long-Term Integrated Service Contracts', 'estimated_duration': '3-5+ years (contract dependent)'}
Disadvantages
- Disadvantage:
Legacy Perception as a 'Fossil Fuel' Company
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately
- Disadvantage:
High Fixed Costs and Asset Intensity
Impact:Major
Addressability:Difficult
- Disadvantage:
Organizational Complexity and Size
Impact:Minor
Addressability:Moderately
Strategic Recommendations
Quick Wins
- Recommendation:
Launch targeted marketing campaigns showcasing successful geothermal, lithium, and CCUS case studies to accelerate brand perception shift from 'oilfield service' to 'energy technology' leader.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
- Recommendation:
Prominently feature the 'Lumi Data and AI Platform' on the corporate homepage and in investor communications to counter the digital offerings of Halliburton and Baker Hughes.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
Medium Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Expand strategic partnerships with leading AI and cloud computing firms to co-develop next-generation energy solutions, preventing disintermediation by pure-play tech companies.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Continue strategic acquisitions of niche technology companies in high-growth areas like battery storage, hydrogen electrolysis, or advanced geothermal systems.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Develop and market 'Decarbonization-as-a-Service' offerings, bundling consulting, technology (e.g., methane detection, CCUS), and digital tracking into a single performance-based contract.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Long Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Evolve the business model to include direct ownership or operation of new energy assets (e.g., geothermal plants, CCUS hubs), shifting from a pure service provider to an energy producer/operator in select niches.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Lead the industry in creating open data standards for subsurface and operational data to establish the Lumi platform as the indispensable ecosystem for energy application development.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Solidify the position as the premier 'Global Energy Technology Company,' leveraging the unparalleled breadth of the portfolio—from optimizing oil and gas production to pioneering new energy systems—as the core differentiator. The messaging should emphasize integration, scale, and digital intelligence as the key pillars that no competitor can fully match.
Differentiate through 'Integrated Performance'. While competitors offer point solutions or have strengths in specific areas, SLB's unique advantage is its ability to integrate a vast array of technologies (subsurface, drilling, production, digital, new energy) to deliver measurable performance outcomes across the entire energy value chain, from barrels of oil to tons of sequestered CO2.
Whitespace Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Integrated Lithium Extraction Solutions
Competitive Gap:While competitors are focused on traditional energy, SLB can leverage its subsurface characterization and drilling expertise to become the dominant technology provider for direct lithium extraction (DLE), a critical component of the battery supply chain. This is a nascent area with no established leader.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Comprehensive Well Integrity and Abandonment Services for Decarbonization
Competitive Gap:There is a growing, regulated market for plugging and abandoning millions of old oil and gas wells. SLB can package its existing P&A services with advanced methane monitoring and long-term CO2 sequestration verification to create a market-leading, ESG-compliant offering that few can match in scale and technological sophistication.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:Medium
- Opportunity:
Digital Platform for the 'New Energy' Workforce
Competitive Gap:The energy transition requires a massive reskilling of the workforce. SLB could leverage its digital platforms and deep domain expertise to offer advanced training, simulation, and remote operations solutions specifically for geothermal, CCUS, and hydrogen projects, creating a new, high-margin SaaS revenue stream.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:Medium
The competitive landscape for SLB is defined by a mature oligopoly in its core oilfield services business, where it competes primarily with Halliburton and Baker Hughes. In this arena, SLB's key sustainable advantages are its unparalleled portfolio breadth, extensive global footprint, and deep client relationships. Halliburton remains a formidable competitor, especially in the North American market with its strong focus on completions, while Baker Hughes has aggressively and successfully repositioned itself as an 'energy technology' company leading the charge on decarbonization solutions like CCUS and hydrogen. This repositioning by Baker Hughes presents the most direct strategic challenge to SLB's own ambition to lead the energy transition.
The most significant industry trend is the dual challenge of meeting global energy demand while simultaneously decarbonizing the energy system. This has shifted the competitive battleground towards digital solutions and new energy technologies. SLB is well-positioned with its established digital platforms and investments in CCUS, geothermal, and other low-carbon ventures. However, it faces indirect competition from major tech companies in the digital space and specialized startups in new energy niches.
Strategic whitespace exists for SLB to leverage its core competencies in adjacent, high-growth markets like sustainable lithium production and to create comprehensive, technology-driven service offerings for well abandonment and methane elimination. The primary strategic imperative for SLB is to accelerate its brand and business model evolution from the world's largest oilfield services provider to the world's leading, most integrated energy technology company. Success will depend on its ability to out-innovate Baker Hughes in the energy transition narrative and technology, maintain its operational excellence against Halliburton in the core business, and defend its digital turf from encroaching tech giants.
Messaging
Message Architecture
Key Messages
- Message:
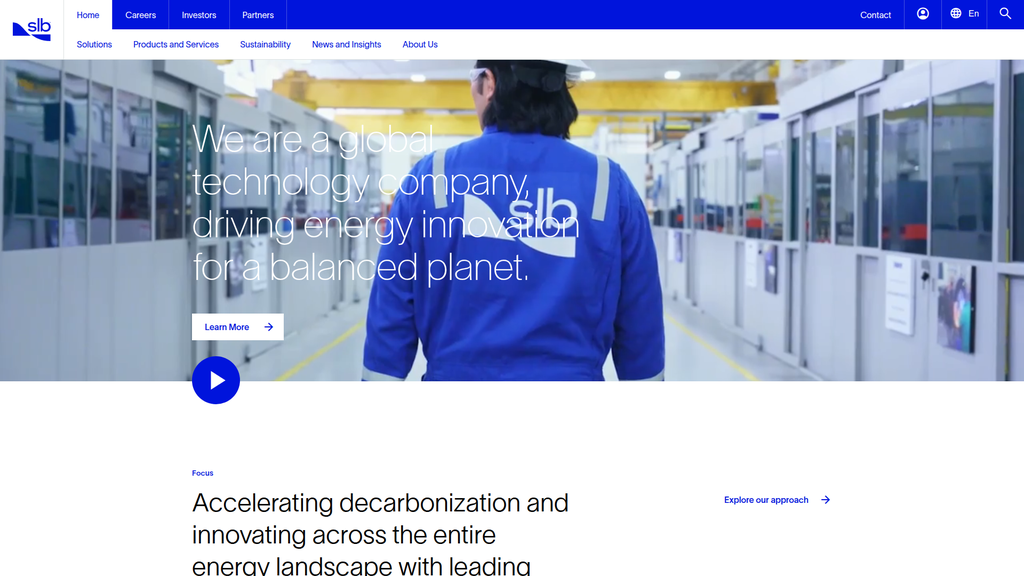
We are a global technology company, driving energy innovation for a balanced planet.
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage Hero Banner
- Message:
Accelerating decarbonization and innovating across the entire energy landscape with leading science, engineering and digital expertise.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage, below the fold
- Message:
Solving industry’s most pressing challenges.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage, Solutions section header
- Message:
Simultaneously reduce emissions while meeting the world’s growing energy demands.
Prominence:Tertiary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage, body copy
The messaging hierarchy is exceptionally well-structured. It begins with a broad, visionary statement ('for a balanced planet') that addresses the core challenge of the energy sector. This is immediately supported by a more concrete strategic message about decarbonization and innovation. The hierarchy then logically flows down into four key strategic pillars (Decarbonizing Industry, Innovating in Oil and Gas, Scaling New Energy Systems, Delivering Digital at Scale) and then to specific, tangible solutions and products. This top-down approach is highly effective for a complex B2B offering.
Messaging is highly consistent across the homepage. The central theme of balancing energy production with sustainability is woven into every section, from the hero banner to the specific solutions like 'Methane and Flaring Elimination' and 'Innovating in Oil and Gas'. This reflects a deliberate and successful rebranding effort from a traditional oilfield services company to a technology leader focused on the energy transition.
Brand Voice
Voice Attributes
- Attribute:
Authoritative
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Solving industry’s most pressing challenges
- •
We create and deploy the technology and systems needed...
- •
SLB’s know-how and technology are helping to overcome industry's greatest challenges...
- Attribute:
Innovative
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
driving energy innovation for a balanced planet
- •
innovating across the entire energy landscape
- •
leading science, engineering and digital expertise
- Attribute:
Responsible
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
...for a balanced planet
- •
Accelerating decarbonization
- •
ensuring progress for people and the planet
- •
Discover how we’re supporting a balanced planet
- Attribute:
Formal
Strength:Moderate
Examples
SLB hosted a conference call to discuss second-quarter 2025 results.
This strategic acquisition strengthens SLB's position...
Tone Analysis
Professional and Confident
Secondary Tones
Forward-looking
Solution-oriented
Tone Shifts
The tone shifts to be more direct and instructional on pages gated for lead generation, such as the 'Access premium content' sections.
Voice Consistency Rating
Excellent
Consistency Issues
No itemsValue Proposition Assessment
SLB is the strategic technology partner that enables the global energy industry to navigate its most significant challenge: simultaneously meeting the world's growing energy demand while aggressively pursuing decarbonization and sustainability.
Value Proposition Components
- Component:
Technology Leadership
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
Evidence:Messaging consistently emphasizes 'global technology company', 'leading science, engineering and digital expertise', and specific high-tech solutions like 'Data and AI Platform'.
- Component:
Comprehensive Energy Portfolio (Oil & Gas and New Energy)
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Unique
Evidence:The website structure clearly balances 'Innovating in Oil and Gas' with 'Scaling New Energy Systems' and 'Decarbonizing Industry', demonstrating a holistic approach.
- Component:
Decarbonization at Scale
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
Evidence:Specific, outcome-focused solutions are highlighted, such as 'Methane and Flaring Elimination', 'Emissions Reduction', and 'Carbon Capture and Storage'.
- Component:
Digital Transformation Enablement
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
Evidence:The 'Delivering Digital at Scale' pillar and products like 'Lumi Data and AI Platform' are prominently featured.
SLB's messaging effectively differentiates it by tackling the energy trilemma (security, sustainability, equity) head-on, rather than positioning itself as solely an oil and gas service provider or a nascent new energy player. The rebranding from Schlumberger to SLB was a strategic move to codify this differentiation. By framing themselves as a 'technology company' solving the entire energy challenge, they position themselves above competitors who may have a narrower focus on either traditional or renewable energy.
The messaging positions SLB as a forward-thinking leader and a partner in the energy transition, not just a contractor. This contrasts with competitors who may still be perceived as more traditional oilfield service companies. The emphasis on 'balanced planet' and decarbonization is a direct appeal to the ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) priorities of their major clients and investors, positioning SLB as a more future-proof investment and partner.
Audience Messaging
Target Personas
- Persona:
C-Suite Energy Executive (e.g., CEO, CSO)
Tailored Messages
- •
driving energy innovation for a balanced planet
- •
Accelerating decarbonization and innovating across the entire energy landscape
- •
SLB completes acquisition of ChampionX
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Operations/Engineering Manager
Tailored Messages
- •
Redefining Production and Recovery
- •
Methane and Flaring Elimination
- •
Case Study: Repsol Sinopec Lidar Camera Trial Advances Methane Emissions Detection
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Investor/Financial Analyst
Tailored Messages
- •
Second-Quarter 2025 Results
- •
SLB OneSubsea Awarded EPC Contract for Equinor’s Fram Sør Project
- •
Investor Relations (Footer Link)
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Potential Employee/Job Seeker
Tailored Messages
Be part of our team
We’re diverse and insightful, pushing the boundaries on a global stage.
Effectiveness:Somewhat
Audience Pain Points Addressed
- •
Pressure to decarbonize operations
- •
Need to improve operational efficiency and reduce costs
- •
Challenge of integrating digital technology and AI
- •
Complexity of scaling new energy systems (Geothermal, CCUS)
- •
Meeting growing energy demand reliably
Audience Aspirations Addressed
- •
Achieving net-zero emissions targets
- •
Becoming a leader in the energy transition
- •
Unlocking new value through data and digitalization
- •
Ensuring long-term business sustainability and profitability
Persuasion Elements
Emotional Appeals
- Appeal Type:
Responsibility/Legacy
Effectiveness:Medium
Examples
...for a balanced planet
...ensuring progress for people and the planet, on the journey to net zero and beyond
- Appeal Type:
Confidence/Security
Effectiveness:High
Examples
Solving industry’s most pressing challenges
SLB’s know-how and technology are helping to overcome industry's greatest challenges
Social Proof Elements
- Proof Type:
Customer Case Studies
Impact:Strong
Evidence:Section featuring case studies with major clients like Repsol Sinopec and Minnkota Power.
- Proof Type:
News & Press Releases
Impact:Strong
Evidence:Announcements of major contract awards (Equinor) and strategic partnerships (AIQ, ADNOC).
- Proof Type:
Acquisitions
Impact:Moderate
Evidence:Highlighting the acquisition of ChampionX and Stimline Digital to signal market leadership and strategic growth.
Trust Indicators
- •
Publicly available financial results ('Second-Quarter 2025 Results')
- •
Detailed sustainability reports
- •
Links to corporate governance information
- •
Prominent display of news and press releases featuring major industry partners
Scarcity Urgency Tactics
None observed; this is appropriate for the industry and brand positioning, which focuses on long-term partnership rather than transactional sales.
Calls To Action
Primary Ctas
- Text:
Explore
Location:Under each of the four main strategic pillars
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Explore our solutions
Location:Solutions Section
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Sign up
Location:Footer / Premium Content Gates
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Start here
Location:Careers Section
Clarity:Clear
The CTAs are appropriate for a B2B audience that engages in a long, research-heavy buying cycle. They are primarily invitational and exploratory ('Learn More', 'Explore'), encouraging deeper engagement without being overly aggressive. The use of 'Sign up' to access premium technical content is a standard and effective B2B lead generation tactic.
Messaging Gaps Analysis
Critical Gaps
The 'human element' is largely absent from the homepage. While the company talks about its diverse global team, there are no stories, testimonials, or faces of the people (employees or customers) driving the innovation. This makes the brand feel very corporate and less relatable.
Contradiction Points
No direct contradictions were found. The messaging manages the potential conflict between its legacy oil and gas business and its new energy focus by consistently framing its role as a technology enabler for both, with a core mission of decarbonization across the board.
Underdeveloped Areas
The 'Careers' section messaging is generic ('Be part of our team'). Given the competition for top engineering and tech talent, this could be significantly strengthened by highlighting specific challenges, career growth opportunities, and the unique impact employees can have on the future of energy.
While case studies are listed, the benefits are not quantified on the homepage. Adding specific metrics (e.g., 'Reduced emissions by X%') directly in the case study teasers would increase their impact.
Messaging Quality
Strengths
- •
Exceptional clarity and strategic alignment of the core message around balancing energy needs and sustainability.
- •
Strong, logical message architecture that guides users from high-level vision to specific solutions.
- •
Effective positioning as a technology leader, successfully shifting perception from its legacy as solely an oilfield services company.
- •
Excellent use of trust indicators like news, case studies, and financial reports to build credibility.
Weaknesses
- •
Overly corporate and impersonal tone that lacks a human element.
- •
Value propositions in some sub-sections could be more benefit-oriented and quantified.
- •
Generic messaging for talent acquisition that may not be competitive enough.
Opportunities
- •
Incorporate customer and employee storytelling to humanize the brand and make the innovations more tangible.
- •
Create persona-specific content journeys that guide different audience segments (e.g., a geothermal plant developer vs. an offshore production manager) to the most relevant information more quickly.
- •
Develop a more compelling employer value proposition message to attract top-tier tech and engineering talent.
Optimization Roadmap
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Brand Storytelling
Recommendation:Develop a 'Faces of Innovation' section or campaign featuring short video interviews with SLB engineers and their customers, telling the story behind a specific project or technology.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Value Proposition Quantification
Recommendation:Update the 'Solutions' and 'Case Studies' sections to include quantifiable results and specific data points (e.g., 'Accelerated time to market by 30%', 'Reduced methane emissions by X tons').
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Talent Acquisition Messaging
Recommendation:Revamp the Careers section messaging to focus on solving the world's biggest challenges, highlighting unique projects and technologies, and articulating a clear employer value proposition.
Expected Impact:Medium
Quick Wins
- •
Add a specific, compelling statistic to the hero message, such as '...helping our partners eliminate X million tons of CO2 annually.'
- •
In the 'Latest news' section, add a brief, benefit-oriented sub-headline to each press release title.
- •
A/B test the 'Sign up' CTA for premium content with more benefit-driven language like 'Get the Technical Paper' or 'Access the Case Study'.
Long Term Recommendations
- •
Build out dedicated content hubs for each key persona, curating relevant solutions, case studies, technical papers, and news to create a more personalized user journey.
- •
Invest in thought leadership content that goes beyond SLB's solutions to discuss broader industry trends and challenges, further cementing their position as an authoritative industry leader.
- •
Develop an interactive tool that allows potential customers to estimate the potential decarbonization or efficiency impact of SLB's solutions on their specific operations.
SLB's strategic messaging is a masterclass in corporate rebranding and repositioning. The company has successfully evolved its narrative from Schlumberger, the world's leading oilfield services provider, to SLB, a global technology company at the forefront of the energy transition. The messaging architecture is clear, logical, and consistently reinforces the core value proposition: enabling energy access while driving decarbonization. This dual focus is not presented as a contradiction but as a unified mission, effectively addressing the primary challenge facing its entire customer base. The brand voice is authoritative and innovative, building confidence and credibility. Persuasion is achieved through strong social proof, such as high-profile partnerships and acquisitions, rather than overt sales tactics, which is appropriate for its sophisticated B2B audience. The primary weakness is the lack of a human element; the messaging is highly corporate and could be significantly enhanced by incorporating authentic stories from the employees and customers behind the technology. By quantifying the impact of its solutions more explicitly and humanizing its brand narrative, SLB can further solidify its position as the indispensable technology partner for a balanced planet.
Growth Readiness
Growth Foundation
Product Market Fit
Strong
Evidence
- •
Established as the world's largest oilfield services company by market share, indicating deep entrenchment with key customers.
- •
Comprehensive portfolio spanning core oil and gas, digital solutions, and new energy systems (e.g., CCUS, Geothermal) addresses the full spectrum of customer needs through the energy transition.
- •
Recent strategic acquisitions like ChampionX and Stimline Digital strengthen core offerings in production and well intervention, demonstrating a commitment to maintaining leadership.
- •
Significant revenue base ($35.48 billion annually) and a market capitalization of over $53 billion underscore a strong, sustained demand for its products and services.
- •
High-margin Digital & Integration segment is growing rapidly, with SaaS revenue up 17% in Q1 2025, showing successful traction for new digital offerings.
Improvement Areas
- •
Accelerate the commercialization and market penetration of 'New Energy' solutions to solidify PMF beyond the traditional oil and gas sector.
- •
Enhance the integration of digital platforms (Lumi, Delfi) with newly acquired technologies to create a seamless, high-lock-in customer ecosystem.
- •
Clearly articulate the value proposition and ROI for sustainability-focused offerings (e.g., Methane Elimination) to customers primarily focused on production cost.
Market Dynamics
Mixed: Traditional Oil & Gas Services (CAGR ~4.5-5.0%). Digital Oilfield Solutions (CAGR ~5.0-6.9%). Carbon Capture (CCUS) (CAGR ~10-28%). Geothermal Power (CAGR ~6.5-7.6%).
Mature/Transforming
Market Trends
- Trend:
Energy Transition & Decarbonization
Business Impact:Creates significant demand for new service lines like CCUS, geothermal, and emissions reduction technologies, representing SLB's primary long-term growth vector.
- Trend:
Digitalization and AI in Energy
Business Impact:Drives adoption of digital platforms (Lumi, Delfi) and AI-powered solutions, shifting revenue towards higher-margin, recurring SaaS models and decoupling growth from drilling activity.
- Trend:
Increased Focus on Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Business Impact:Strengthens the value proposition for SLB's performance-based contracts and digital optimization tools that improve production and lower operational expenditures.
- Trend:
Geopolitical Instability and Supply Chain Pressures
Business Impact:Creates both risks and opportunities. SLB's global diversification provides resilience, but regional conflicts can disrupt operations and capital allocation.
Excellent. SLB is capitalizing on a dual opportunity: a robust traditional energy upcycle demanding efficiency and innovation, and the nascent, high-growth phase of the energy transition requiring new technologies at scale.
Business Model Scalability
High
High fixed costs associated with R&D, global infrastructure, and specialized equipment, but highly scalable as technology and software can be deployed globally with significant operating leverage.
High. Once R&D and platform development costs are covered, deploying digital solutions and proprietary technologies to new customers or projects yields high incremental margins.
Scalability Constraints
- •
Requirement for highly specialized, capital-intensive equipment for field operations.
- •
Need for a large, technically skilled global workforce to deliver services.
- •
Complex global supply chain susceptible to geopolitical and logistical disruptions.
Team Readiness
Very Strong. Experienced leadership team with a clear strategic vision for navigating the energy transition, evidenced by the rebranding to SLB and the defined growth engines of Core, Digital, and New Energy.
Evolving. The company has restructured to align with its three growth engines. Continued focus is needed to ensure agility, especially in the faster-moving Digital and New Energy segments, preventing them from being stifled by the scale of the core business.
Key Capability Gaps
- •
Agile software product development and commercialization at scale.
- •
Talent in emerging energy fields such as geothermal reservoir engineering, lithium extraction, and large-scale carbon sequestration.
- •
Go-to-market and sales expertise for selling complex digital and sustainability solutions to new customer segments outside of traditional E&P operators.
Growth Engine
Acquisition Channels
- Channel:
Enterprise Direct Sales & Key Account Management
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Equip sales teams with dedicated training on digital and new energy portfolios to cross-sell and upsell integrated solutions beyond core services. Focus on value-based selling tied to emissions reduction and production efficiency.
- Channel:
Strategic Partnerships & JVs (e.g., AIQ)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Expand partnerships beyond traditional energy players to include major technology companies (e.g., cloud providers), renewable energy developers, and governments to co-develop and deploy large-scale decarbonization projects.
- Channel:
Thought Leadership & Content Marketing (Technical Papers, Case Studies)
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Increase the volume and accessibility of digital-first content (webinars, interactive reports, ROI calculators) focused on solving decarbonization and digital transformation challenges, using 'premium content' to capture high-intent leads for sales follow-up.
- Channel:
Mergers & Acquisitions
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Continue programmatic M&A to acquire niche technologies and talent in high-growth areas (e.g., advanced AI, new materials for energy storage, specialized CCUS tech) while ensuring a disciplined integration process.
Customer Journey
Dominated by a long, complex B2B enterprise sales cycle involving RFPs, technical validation, and relationship-based selling. The website serves as a critical resource for discovery, validation, and lead generation (via 'Contact Us' and 'Premium Content').
Friction Points
- •
Potential difficulty for prospective 'new energy' clients (e.g., industrial manufacturers) in navigating a website historically oriented towards oil and gas.
- •
Access to key technical specifications and pricing information is gated, which can slow down initial evaluation by technical teams.
- •
Complex portfolio can make it challenging for customers to identify the optimal integrated solution without extensive consultation.
Journey Enhancement Priorities
{'area': 'Website Personalization', 'recommendation': 'Implement industry-based personalization on the website to surface the most relevant solutions and case studies for visitors from different sectors (e.g., Oil & Gas, Power & Utilities, Heavy Industry).'}
{'area': 'Interactive Tools', 'recommendation': 'Develop self-service online assessment tools or calculators that allow potential clients to estimate the potential ROI or emissions reduction from implementing SLB solutions, providing value upfront and capturing qualified leads.'}
Retention Mechanisms
- Mechanism:
Long-Term Service Agreements (LTSAs) & Performance-Based Contracts
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:More aggressively embed digital services and emissions monitoring into all new LTSAs to increase switching costs and demonstrate ongoing value.
- Mechanism:
Technology & Platform Lock-in (e.g., Delfi, Lumi platforms)
Effectiveness:Medium
Improvement Opportunity:Foster a broader third-party developer ecosystem around the Delfi and Lumi platforms to increase their utility and entrench them as the industry-standard operating system.
- Mechanism:
Embedded Customer Relationships & Technical Expertise
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Establish a 'Customer Success' function specifically for digital and new energy clients to ensure they realize the full value of these new solutions, driving adoption and expansion.
Revenue Economics
Strong. As a market leader, SLB commands premium pricing for its differentiated technology and services. The shift towards high-margin digital SaaS revenue is accretive to overall profitability.
High (Not publicly calculable in a standard SaaS model). The LTV of a major energy company client is extremely high, spanning decades and multiple projects, justifying a significant investment in customer acquisition.
Strong. The company has demonstrated improved operating margins and a clear focus on high-return projects and cost optimization.
Optimization Recommendations
- •
Scale the 'Digital & Integration' segment, as its high-margin, recurring revenue model improves overall profit stability and valuation multiples.
- •
Bundle core services with digital and emissions-reduction solutions to increase average contract value.
- •
Pursue performance-based pricing models for new energy projects (e.g., CCUS) to align SLB's revenue with customer success and capture more value.
Scale Barriers
Technical Limitations
- Limitation:
Pace of Commercializing New Energy Technologies
Impact:High
Solution Approach:Utilize a portfolio approach: partner with, invest in, or acquire promising startups to accelerate R&D, while focusing internal efforts on integrating and scaling proven technologies.
- Limitation:
Integrating Disparate Software from Acquisitions
Impact:Medium
Solution Approach:Prioritize integration into the core Lumi and Delfi platforms post-acquisition to maintain a cohesive ecosystem. Dedicate 'platform integration' engineering teams to streamline this process.
Operational Bottlenecks
- Bottleneck:
Global Talent Acquisition and Development in Emerging Fields
Growth Impact:Constrains the speed of expansion in new energy and digital services.
Resolution Strategy:Establish 'Centers of Excellence' for key skills (e.g., AI, Geothermal Science). Create strategic partnerships with leading universities and launch aggressive internal reskilling programs.
- Bottleneck:
Supply Chain for Specialized New Energy Equipment
Growth Impact:Can delay project execution and increase costs for new energy ventures like CCUS and geothermal.
Resolution Strategy:Vertically integrate where strategic. Form long-term partnerships with key suppliers to secure capacity and co-develop next-generation equipment.
Market Penetration Challenges
- Challenge:
Cyclical Nature of Commodity Prices
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Continue diversifying into less cyclical digital and new energy markets. Focus on production and recovery services that are resilient even in lower price environments.
- Challenge:
Intense Competition from Established Peers and Niche Innovators
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Leverage unique ability to deliver integrated solutions at a global scale. Compete on total value (efficiency, safety, decarbonization) rather than on point-solution price. Use M&A to absorb niche innovators.
- Challenge:
Regulatory Uncertainty in New Energy Markets (e.g., CCUS)
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Actively engage in policy advocacy to help shape clear and favorable regulatory frameworks. Develop flexible, modular solutions that can adapt to different policy environments.
Resource Limitations
Talent Gaps
- •
Data Scientists and AI/ML Engineers with deep domain expertise in energy.
- •
Commercial leaders and product managers for SaaS-based business models.
- •
Geoscientists and engineers specializing in geothermal, CCUS, and hydrogen.
Significant and ongoing. Capital is required for large-scale R&D, strategic acquisitions, and potential co-investment in large infrastructure projects (e.g., CCUS hubs).
Infrastructure Needs
- •
Expansion of high-performance computing (HPC) for digital and AI platforms.
- •
Development of manufacturing and service facilities for new energy hardware.
- •
Robust cybersecurity infrastructure to protect critical energy data and platforms.
Growth Opportunities
Market Expansion
- Expansion Vector:
Customer Segment: Heavy Industry Decarbonization
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:High
Recommended Approach:Create a dedicated business unit to adapt and market CCUS, emissions management, and geothermal solutions to non-energy sectors like cement, steel, and power generation. Build partnerships with industrial EPC firms.
- Expansion Vector:
Geographic: Asia-Pacific New Energy Markets
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:Medium
Recommended Approach:Leverage existing operational footprint to aggressively pursue opportunities in fast-growing CCUS and geothermal markets in the region, adapting to local policy incentives.
Product Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Carbon Management as a Service (CMaaS)
Market Demand Evidence:Increasing corporate net-zero commitments and compliance requirements create a need for end-to-end carbon management solutions.
Strategic Fit:Excellent. Combines digital monitoring (Lumi platform), emissions reduction tech, and carbon capture/storage services into a single, recurring-revenue offering.
Development Recommendation:Pilot with a key strategic customer to develop a scalable, replicable service package.
- Opportunity:
Sustainable Lithium Production Solutions
Market Demand Evidence:Explosive growth in EVs and battery storage is creating massive demand for lithium, with a focus on environmentally friendly extraction methods.
Strategic Fit:Strong. Leverages core competencies in subsurface characterization, well construction, and fluid processing.
Development Recommendation:Partner with mining companies or automakers to co-develop and de-risk Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) projects, moving from pilot to commercial scale.
Channel Diversification
- Channel:
Digital Marketplace / Self-Service Platform
Fit Assessment:Good for specific software and data products.
Implementation Strategy:Launch a marketplace on the SLB website for smaller software applications, data sets, or online training modules to capture a longer tail of the market and generate high-margin, low-touch revenue.
Strategic Partnerships
- Partnership Type:
Technology & Cloud Integration
Potential Partners
- •
Microsoft (Azure)
- •
Amazon (AWS)
- •
Google (GCP)
- •
NVIDIA
Expected Benefits:Enhance the scalability and AI capabilities of the Lumi and Delfi platforms, co-develop AI-driven energy solutions, and leverage their sales channels to reach new customer segments.
- Partnership Type:
Project Development & Financing
Potential Partners
- •
Brookfield Asset Management
- •
Macquarie Group
- •
Sovereign Wealth Funds
Expected Benefits:Co-invest in large-scale capital-intensive new energy projects (e.g., CCUS hubs, geothermal plants), reducing SLB's direct capital exposure and accelerating project deployment.
Growth Strategy
North Star Metric
Annualized Recurring Revenue (ARR) from Digital & New Energy
This metric directly tracks the success of SLB's strategic pivot to higher-margin, less cyclical businesses. It aligns the company with a valuation model closer to a technology/industrial-tech firm, reflecting the core growth thesis.
Achieve a 25% year-over-year growth rate in this metric, demonstrating momentum in the strategic growth engines.
Growth Model
Hybrid: Enterprise Sales-Led & Platform Ecosystem
Key Drivers
- •
Cross-selling digital and new energy solutions into the existing core customer base.
- •
New logo acquisition in adjacent industrial markets.
- •
Driving adoption and usage of the Lumi and Delfi platforms, creating a sticky ecosystem.
- •
Strategic M&A to enter new markets or acquire new technologies.
Maintain a world-class enterprise sales force for the core business while building a separate, agile product and business development organization for the platform and new energy ventures.
Prioritized Initiatives
- Initiative:
Launch 'SLB Decarbonize' for Industrial Clients
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:18-24 months
First Steps:Form a dedicated go-to-market team. Identify and sign 3-5 lighthouse customers in the cement or steel industries for pilot projects.
- Initiative:
Scale the Lumi Platform Partner Program
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:12 months
First Steps:Launch a developer portal with robust APIs and SDKs. Onboard the first 20 independent software vendors (ISVs) to build applications on the platform.
- Initiative:
Aggressively pursue CCUS Hub Leadership
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:24-36 months
First Steps:Identify top 5 global locations for CCUS hub development based on geology and policy. Form a consortium with an industrial partner and a financial investor for the first project.
Experimentation Plan
High Leverage Tests
{'experiment': 'Test performance-based pricing models for production optimization contracts where SLB shares in the upside of increased output.', 'hypothesis': 'This will increase contract value and better align SLB with customer outcomes, leading to higher adoption rates.'}
{'experiment': "Pilot a subscription-based 'Digital Twin as a Service' offering for mid-sized operators.", 'hypothesis': 'A lower-cost, subscription model will open up a new market segment currently underserved by high-end digital solutions.'}
Use an A/B testing framework for new commercial models, tracking metrics like sales cycle length, win rate, average contract value (ACV), and customer satisfaction (NPS).
Quarterly review of in-flight experiments and prioritization of new tests by a dedicated Growth Council composed of leaders from each business division.
Growth Team
A centralized Strategy & Corporate Development team to oversee M&A and long-term vision, coupled with decentralized, empowered 'Growth Pods' within each of the three key divisions (Core, Digital, New Energy).
Key Roles
- •
General Manager, Industrial Decarbonization
- •
Head of Platform Ecosystems & Partnerships
- •
Chief Commercial Officer, New Energy
- •
Director of Growth, Digital Products
Acqui-hire small, agile teams in key technology areas. Establish a rotational program for high-potential employees to gain experience across the Core, Digital, and New Energy businesses. Invest heavily in commercial and product management training.
SLB is in a powerful position to lead the global energy industry's transformation. The company has a strong foundation with deeply entrenched product-market fit in its core oil and gas services business, which provides the cash flow and customer relationships necessary to fund and scale its future growth engines. The strategic decision to restructure around 'Core,' 'Digital,' and 'New Energy' is astute, directly addressing the dual challenge of optimizing fossil fuel production while building the low-carbon systems of the future.
The primary growth vectors lie in the Digital and New Energy segments. The Digital business, driven by platforms like Lumi and Delfi, is successfully transitioning SLB's business model towards higher-margin, recurring SaaS revenue, which can decouple profitability from volatile commodity cycles. The New Energy segment, particularly in high-growth markets like Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) and Geothermal, represents the largest long-term expansion opportunity. The market timing is excellent, as both industries are moving past infancy into a rapid scaling phase backed by policy support and corporate demand.
However, significant challenges exist. The primary scale barrier is not technology itself, but the organizational agility and talent required to commercialize these new ventures at a pace that matches market demand. SLB must avoid having its innovative new businesses constrained by the processes and culture of its massive core operations. Competition is fierce, not only from traditional rivals like Halliburton and Baker Hughes but also from a new generation of climate-tech startups and industrial giants entering the energy space.
The recommended growth strategy is to aggressively pursue a dual-track approach: maximize profitability and efficiency in the core business while ring-fencing and accelerating the Digital and New Energy ventures. Key priorities should include expanding into adjacent customer segments (e.g., heavy industry decarbonization), deepening strategic technology partnerships (especially with major cloud and AI players), and using the balance sheet for programmatic M&A to acquire key capabilities and talent. By focusing on 'Annualized Recurring Revenue from Digital & New Energy' as its North Star Metric, SLB can align its entire organization on the strategic pivot that will define its market leadership for the next generation.
Legal Compliance
SLB's 'General Privacy Notice' is comprehensive and prominently accessible from the website footer. It details the types of personal data collected (e.g., Contact Details, Business Contact Details, Account Information, Marketing Data), the methods of collection, and the purposes for processing, which include service provision, marketing personalization, and legal compliance. The policy explicitly states its global applicability, acknowledging its commitment to safeguarding data for business customers, investors, and partners. It covers user rights, data sharing practices with trusted third parties, and security measures. The policy also mentions compliance with legal processes and requests from public authorities, which is crucial for a company in a strategic sector like energy. The inclusion of a mechanism to manage marketing preferences and the clear identification of SLB (Schlumberger Limited and its affiliates) as the data controller are strengths.
SLB provides a 'General Web Site Terms and Conditions of Use' accessible from the footer. The terms clearly state that using the site constitutes agreement to the conditions. Key clauses include disclaimers of liability, particularly regarding financial material and forward-looking statements relevant to its status as a publicly-traded company. The document outlines intellectual property rights for website content and software, specifying that software is licensed for personal, noncommercial use. It defines prohibited uses, such as violating international laws, including those related to data and software export. For its specific digital offerings, SLB has separate 'Online Services Terms and Conditions' which govern data ownership, security obligations, and indemnification, demonstrating a mature approach to B2B service agreements. These terms are reasonably clear and enforceable, though, like most corporate terms, they are heavily weighted to protect the company.
The website uses a cookie consent mechanism, as indicated by the 'Preferences' link in the footer and a cookie banner that appears on first visit (observed via live testing). This banner allows users to accept all cookies or manage their preferences, suggesting a degree of granular control. The subscription form explicitly requires users to agree to the 'General Privacy Notice' before submitting their information, which is a good practice for demonstrating affirmative consent. However, a detailed audit would be required to confirm that non-essential cookies are blocked prior to user consent, which is a key requirement under GDPR and similar regulations.
SLB's data protection framework, detailed in its Privacy Notice, is robust and addresses global standards. It appears to be designed with GDPR and CCPA/CPRA in mind by outlining the legal bases for processing data and providing mechanisms for users to exercise their rights (e.g., access, rectification, erasure). The policy's language about personalizing interactions and using data for targeted advertising is transparent, but it places a significant onus on the user to manage their preferences. Given SLB's operation in over 100 countries, its centralized and comprehensive approach to data protection is a strategic asset, enabling it to navigate the complex web of international privacy laws. The explicit mention of complying with trade control, sanctions, and national security requirements underscores the company's awareness of its obligations in the highly regulated energy sector.
The website shows a basic adherence to accessibility principles. The use of hierarchical headings (H2, H3) provides some structure for screen readers. However, a full compliance audit is necessary. The scraped data for the video players indicates 'captions off, selected,' which could be a significant gap if captions are not readily available or enabled by default for all video content, potentially failing to meet WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) criteria. For a company of SLB's scale and public profile, ensuring the website conforms to WCAG 2.1 AA standards is critical to avoid legal risk under the ADA and other international accessibility mandates and to ensure all stakeholders, including those with disabilities, have equal access to information.
As a global energy technology leader, SLB is subject to a complex matrix of industry-specific regulations. Its website demonstrates awareness of this through dedicated sections on Governance, Investor Relations, and Sustainability. The company explicitly states its commitment to chemical regulations like the EU's REACH, showcasing a proactive stance on product stewardship and environmental compliance. Operating in the oil and gas sector makes SLB subject to stringent anti-corruption laws like the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) and the UK Bribery Act. The 'Ethics and Compliance' section on their corporate site highlights their Code of Conduct and an anonymous reporting hotline, which are critical tools for mitigating bribery and corruption risks. Furthermore, as a provider of digital solutions and AI platforms for critical infrastructure, SLB must navigate cybersecurity regulations and data governance standards specific to the energy sector.
Compliance Gaps
- •
Potential lack of default or easily accessible captions for all video content, which could be an accessibility compliance gap under WCAG/ADA standards.
- •
The effectiveness of the pre-consent cookie-blocking mechanism requires technical verification to ensure full compliance with ePrivacy directives.
- •
While a comprehensive privacy policy exists, the user interface for managing data and marketing preferences could be more proactively presented and simplified for users.
Compliance Strengths
- •
Comprehensive and easily accessible 'General Privacy Notice' and 'Terms and Conditions' that address a global audience and multiple legal frameworks.
- •
Strong evidence of a corporate-level 'Ethics and Compliance' program, including a public Code of Conduct and reporting mechanisms, which is vital for FCPA and UK Bribery Act adherence.
- •
Clear public statements and documentation regarding compliance with complex, industry-specific regulations like chemical safety (REACH).
- •
Separate, detailed terms for 'Online Services' which shows a sophisticated understanding of the legal requirements for B2B digital product delivery.
- •
Inclusion of forward-looking statement disclaimers, demonstrating compliance with securities regulations for a publicly traded company.
Risk Assessment
- Risk Area:
Website Accessibility
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Conduct a full WCAG 2.1 AA audit of the website. Ensure all video content includes closed captions and provide transcripts for audio content to mitigate legal risk under the ADA and improve user experience for all.
- Risk Area:
Cookie Consent
Severity:Low
Recommendation:Perform a technical audit to confirm that no non-essential tracking scripts or cookies are loaded before explicit user consent is obtained via the cookie banner. Ensure the 'Preferences' center is intuitive and allows for easy withdrawal of consent.
- Risk Area:
Anti-Corruption Scrutiny
Severity:High
Recommendation:Continuously promote and ensure the visibility of the 'Ethics and Compliance' program and Code of Conduct on the main corporate website. Given the high-risk nature of the energy sector, this public posture is a critical deterrent and a key element of a defensible compliance program against potential FCPA or UK Bribery Act inquiries.
High Priority Recommendations
Immediately commission a third-party accessibility audit to identify and remediate all WCAG 2.1 AA compliance issues, focusing on multimedia content (video captions) and the accessibility of online forms and technical documents.
Strengthen the public-facing demonstration of the company's anti-corruption and ethics program. While the information exists, making it more prominent can enhance corporate reputation and reinforce its commitment to compliance in a high-risk industry.
SLB has established a strong and mature legal compliance framework for its corporate website, reflecting its status as a major publicly-traded, multinational technology company in the highly regulated energy sector. The legal documentation, including the Privacy Notice and Terms of Service, is comprehensive, well-structured, and tailored to its global operations and diverse stakeholders. This robust legal positioning serves as a significant business asset by building trust with B2B customers, assuring investors of sound governance, and facilitating market access in jurisdictions with stringent data protection and anti-corruption laws. The company's public commitment to ethics and specific regulations like REACH enhances its competitive advantage. The primary areas for improvement are in technical execution rather than policy, specifically in website accessibility (WCAG/ADA) and the verified implementation of its cookie consent mechanism. Addressing these gaps, particularly accessibility, is the most critical next step to align their digital presence fully with their otherwise sophisticated and strategic approach to legal and regulatory risk management.
Visual
Design System
Modern Corporate & Tech-Forward
Excellent
Advanced
User Experience
Navigation
Horizontal Mega Menu (Desktop)
Intuitive
Good
Information Architecture
Logical
Clear
Moderate
Conversion Elements
- Element:
Primary CTA Buttons (e.g., 'Explore our approach', 'Sign in or register')
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:Incorporate more benefit-oriented and urgent language. For example, instead of 'Explore solutions', test 'Unlock Efficiency Now' to create a stronger sense of value.
- Element:
Secondary Text Link CTAs (e.g., 'View more', 'Learn more')
Prominence:Low
Effectiveness:Somewhat effective
Improvement:Increase the tap/click target size and visual weight. Consider adding a subtle icon (like a chevron or arrow) to better signify an interactive link and draw the user's eye.
- Element:
Gated Content Form ('Sign up')
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Somewhat effective
Improvement:The 'Sign up' CTA is clear, but the value proposition could be stronger. Explicitly state the benefits of signing up for premium content, such as 'Gain access to exclusive industry reports, case studies, and technical papers'.
- Element:
Careers CTA ('Be part of our team')
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:To better target top talent, segment the CTA or landing page by role type (e.g., 'Explore Engineering Roles', 'Discover Digital Careers') to guide applicants more efficiently.
Assessment
Strengths
- Aspect:
Cohesive & Professional Brand Identity
Impact:High
Description:The site effectively uses its new SLB branding, featuring a consistent color palette (deep blue, white), clean typography, and high-quality imagery. This projects a strong, modern, and trustworthy image befitting a global technology leader in the energy sector.
- Aspect:
Clear Visual Hierarchy
Impact:High
Description:The use of scale, color, and whitespace creates a clear and scannable hierarchy. Hero sections, headlines, and primary CTAs are immediately distinguishable, guiding users effectively through complex information.
- Aspect:
Structured & Scannable Content Layouts
Impact:Medium
Description:Information is presented in well-organized, card-based layouts and thematic blocks (e.g., 'Latest news,' 'Our solutions in action'). This chunking of content reduces cognitive load and improves readability for busy professional audiences.
- Aspect:
Effective Use of High-Quality Visuals
Impact:Medium
Description:The website utilizes compelling, high-resolution photography and video to showcase its technology and people. This adds visual appeal and helps tell the story of a forward-thinking, innovative company.
Weaknesses
- Aspect:
Understated Secondary CTAs
Impact:Medium
Description:Secondary calls-to-action, such as 'View more' text links, lack visual prominence. They can be easily overlooked, potentially reducing user engagement and exploration into deeper content sections.
- Aspect:
Carousel for Key Information
Impact:Low
Description:The 'Latest news' section uses a carousel. While space-efficient, this pattern can hide important content, as users often don't interact with carousel controls, potentially causing key press releases or reports to be missed.
- Aspect:
Generic CTA Microcopy
Impact:Low
Description:The copy on some CTA buttons is generic (e.g., 'Explore more'). More specific, action-oriented, and benefit-driven language could improve click-through rates by better aligning with user intent.
- Aspect:
Potential for Information Overload
Impact:Medium
Description:As a large multinational, SLB has a vast amount of information. For non-expert users, the sheer volume of solutions and news could be overwhelming without more personalized or persona-based navigation paths.
Priority Recommendations
- Recommendation:
Enhance Visibility of Secondary CTAs
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Improve user flow and content discovery by making secondary links more visually distinct. Simple CSS changes to increase font weight, add an icon, or use a ghost button style can significantly increase click-through rates to deeper pages.
- Recommendation:
A/B Test Action-Oriented CTA Copy
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Optimize conversion points by testing more compelling and specific language on key buttons. This can lead to higher engagement and more qualified leads for gated content and solution explorations.
- Recommendation:
Implement Persona-Based Content Hubs
Effort Level:High
Impact Potential:High
Rationale:To serve diverse audiences (investors, engineers, students, potential clients), create tailored landing pages or content hubs. This would reduce information overload and surface the most relevant content for each user segment, improving their experience and driving them more effectively toward their goals.
- Recommendation:
Replace News Carousel with a Grid Layout
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:Low
Rationale:To ensure key news items are not missed, replace the homepage carousel with a static grid displaying the top 3-4 latest articles. This improves the visibility of all featured content, ensuring critical updates reach a wider audience.
Mobile Responsiveness
Good
Based on the desktop design's component-based structure, the site likely adapts well to tablet and mobile breakpoints. The fluid grid and card-based layouts are inherently flexible.
Mobile Specific Issues
The comprehensive mega-menu navigation would need to be thoughtfully translated into a clear, multi-level mobile menu (e.g., accordion style) to avoid user frustration.
Dense content blocks and data-heavy visuals may require significant vertical scrolling, potentially impacting user engagement on smaller screens.
Desktop Specific Issues
No major desktop-specific issues are apparent from the screenshots. The layout effectively utilizes the available screen real estate.
This visual audit is based on an analysis of the provided screenshots and external research on SLB's business context. SLB, formerly Schlumberger, is a global technology company driving innovation in the energy sector. Its target audience is broad and sophisticated, including corporate clients in the oil & energy industry, investors, engineers, and potential employees. The website's primary goals are to communicate its technological leadership, showcase its commitment to sustainability and decarbonization, generate leads through gated content, and attract top talent.
1. Design System & Brand Identity:
The website successfully executes a recent corporate rebrand from Schlumberger to SLB, projecting a modern, tech-forward, and professional image. The design system is advanced, marked by a highly consistent application of its core brand elements: a dominant deep blue and white color scheme, crisp sans-serif typography, and a clean, structured grid system. The visual language is authoritative and precise, aligning perfectly with a B2B technology leader. It effectively distances the brand from traditional heavy industry stereotypes and repositions it as an innovator focused on a 'balanced planet.'
2. Visual Hierarchy & Information Architecture:
The visual hierarchy is exceptionally clear. The homepage uses large, impactful hero imagery and headlines to establish key themes like 'decarbonization' and 'innovation.' Content is logically segmented into scannable blocks, allowing different user personas—such as an investor looking for 'Latest News' or a potential client exploring 'solutions'—to quickly find relevant entry points. The information architecture appears logical, with top-level navigation categories like 'Products and Services' and 'Sustainability' catering directly to primary user needs.
3. Navigation & User Flow:
The desktop navigation employs a standard and intuitive horizontal mega-menu, which is appropriate for the breadth of SLB's offerings. User flows are generally clear, guiding visitors from broad thematic areas on the homepage to more specific solution or content pages. For instance, a user interested in a specific service can navigate a clear path from the homepage callout to a detailed solution page. The breadcrumb navigation on the inner page is a key strength, providing context and easy backtracking for users exploring deep within the site's structure.
4. Visual Conversion Elements:
Primary calls-to-action are visually prominent, using the brand's solid blue for high contrast. They are effective at drawing user attention to key conversion paths like registering for premium content or exploring solutions. However, their effectiveness could be heightened with more compelling, benefit-driven microcopy. Secondary CTAs are a point of weakness; their low visual weight means they are likely underperforming and represent a missed opportunity for deeper engagement. The gated content strategy on the 'Resource Library' page is a standard B2B lead generation tactic, though the value proposition for signing up could be more explicitly articulated to maximize conversions.
5. Visual Storytelling & Content Presentation:
SLB uses visual storytelling effectively through high-quality photography and videography that depicts both advanced technology and the diverse, skilled people behind it. This humanizes the brand and reinforces its positioning as a hub of innovation. Content on inner pages is presented cleanly, with ample white space and bullet points to enhance readability, which is crucial for communicating complex technical information. The balance between imagery, headlines, and body copy is well-executed, creating a professional and engaging reading experience.
Discoverability
Market Visibility Assessment
SLB holds a dominant, legacy brand authority from its history as Schlumberger, widely recognized as the world's largest oilfield services company. The 2022 rebranding to SLB signals a strategic pivot to position itself as a global technology company focused on 'energy innovation for a balanced planet'. This move aims to expand its authority from traditional oil and gas into high-growth areas like decarbonization, digital solutions, and new energy systems, though shifting market perception from a fossil fuel enabler to a sustainability leader remains a core challenge.
SLB maintains top-tier market share visibility in its core oil and gas segments, consistently competing with Halliburton and Baker Hughes. Its digital presence strongly reflects this leadership. However, its visibility in emerging markets like 'carbon capture and storage (CCS)', 'geothermal energy solutions', and 'energy AI platforms' is contested by both traditional competitors undergoing similar transformations and new, specialized players. Recent acquisitions like ChampionX and Stimline Digital are strategically communicated to reinforce market leadership in production and digital well intervention.
Customer acquisition in this B2B high-value sector is driven by demonstrating technological superiority and project success, not direct online sales. The website's primary role is to validate SLB's capabilities and generate highly qualified leads for a complex sales cycle. The extensive 'Solutions', 'Products & Services', and 'Case Studies' sections are critical assets for influencing procurement decisions by major energy corporations. The use of gated 'Premium Content' is a key mechanism for capturing high-intent leads from technical and strategic decision-makers.
As a global operator in over 120 countries, SLB's digital presence must support its vast international footprint. The current English-centric site serves as a global portal, but the key opportunity lies in creating targeted, localized content that addresses the specific geological, economic, and regulatory challenges of key regional markets (e.g., Middle East, Latin America, Southeast Asia). This would enhance penetration by demonstrating localized expertise and supporting regional sales teams.
The website demonstrates excellent and deliberate coverage of key industry topics. It strategically balances its core business ('Innovating in Oil and Gas') with future-focused growth areas: 'Decarbonizing Industry', 'Scaling New Energy Systems', and 'Delivering Digital at Scale'. Specific solution pages for Methane Elimination, CCS, Geothermal, and AI platforms show a comprehensive grasp of current and future energy trends, aligning perfectly with the industry's pivot toward digitalization and sustainability.
Strategic Content Positioning
Content is well-aligned with a sophisticated B2B customer journey. High-level messaging like 'driving energy innovation' addresses the awareness stage. Detailed 'Solutions' and 'Products' pages cater to the consideration stage. Critically, the 'Case Studies' and gated technical content serve the decision and validation stages, providing the proof points necessary for high-stakes procurement decisions.
SLB is effectively using press releases and case studies but has a significant opportunity to elevate its thought leadership. This includes creating more forward-looking, C-suite-oriented content such as proprietary data-driven industry reports (e.g., 'Annual State of Energy Decarbonization'), executive keynotes on future energy systems, and in-depth analyses on the financial and strategic implications of the energy transition, moving beyond just technological solutions.
While SLB's technical content is robust, competitors like Halliburton and Baker Hughes are also aggressively pushing their digital and energy transition narratives. A potential gap for SLB is content that explicitly quantifies the business impact (ROI, operational efficiency gains, risk reduction) of its sustainability and digital solutions for a CFO or CEO audience. Creating content that translates complex technology into clear financial outcomes would be a powerful differentiator.
The brand messaging is exceptionally consistent. The strategic narrative of being a 'global technology company, driving energy innovation for a balanced planet' is cohesively integrated throughout the site architecture, from the homepage banner to the categorization of solutions and news. The rebranding from Schlumberger to SLB is effectively executed, visually and textually reinforcing this forward-looking identity across all digital touchpoints.
Digital Market Strategy
Market Expansion Opportunities
- •
Develop dedicated content ecosystems for stakeholders beyond engineering, specifically targeting finance, policy, and ESG investors with tailored reports, webinars, and articles.
- •
Create strategic content for nascent energy verticals like clean hydrogen production, sustainable lithium extraction, and direct air capture to establish early thought leadership and capture emerging market share.
- •
Launch geo-targeted campaigns showcasing region-specific case studies and solutions to deepen penetration in key international growth markets.
Customer Acquisition Optimization
- •
Implement an Account-Based Marketing (ABM) strategy that uses engagement with premium content to identify and nurture high-value target accounts.
- •
Create high-intent 'problem/solution' content that answers specific technical and commercial questions posed by project managers and procurement teams at target companies.
- •
Develop interactive tools, like ROI calculators for decarbonization projects, to capture leads and provide immediate value to potential customers.
Brand Authority Initiatives
- •
Launch a flagship annual 'Future of Energy' report combining SLB's proprietary data and expert analysis, positioning it as an indispensable resource for the industry.
- •
Establish a prominent 'SLB Insights' platform featuring regular commentary and long-form articles from company executives and lead scientists on pressing industry challenges.
- •
Systematically pursue speaking opportunities at major industry and technology conferences and amplify this presence through a coordinated digital content strategy.
Competitive Positioning Improvements
- •
Aggressively frame SLB as a 'digital and AI-first' company that leverages technology to solve energy challenges, directly competing with the positioning of major tech firms entering the space.
- •
Shift the narrative on sustainability from a corporate responsibility to a direct driver of client profitability and operational performance.
- •
Position its end-to-end portfolio, strengthened by acquisitions, as the industry's most integrated platform for optimizing asset performance and achieving net-zero goals simultaneously.
Business Impact Assessment
Market share growth in this industry is best indicated by tracking the share of voice in media and analyst reports for strategic growth topics (e.g., 'AI in upstream', 'CCS projects'). Another key indicator is the frequency of contract award announcements that specifically mention SLB's new energy or digital technologies.
Success is measured not by transaction volume but by lead quality and sales pipeline influence. Key metrics include: number of qualified leads from target accounts engaging with gated content, content-influenced pipeline growth, and an increase in inbound inquiries for strategic solutions like decarbonization and digital platforms.
Brand authority can be measured by tracking media mentions, executive quotes in top-tier publications, citations of SLB's reports, organic search rankings for non-branded strategic keywords (e.g., 'geothermal energy drilling technology'), and the volume of speaker invitations for its experts.
Benchmarking should focus on qualitative and quantitative comparisons against key competitors (Halliburton, Baker Hughes, NOV). This includes share of voice on 'energy transition' topics, the nature and frequency of strategic partnership announcements, and how their brand is framed in relation to SLB in financial and industry analysis.
Strategic Recommendations
High Impact Initiatives
- Initiative:
Develop a 'C-Suite Series' of content focused on the financial ROI and strategic value of decarbonization and digital transformation.
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Addresses the need to influence executive decision-makers who approve large-scale projects, moving the conversation from technical features to business value.
Success Metrics
- •
Engagement from Director-level and above at target accounts
- •
Inbound inquiries citing the content series
- •
Sales team feedback on content utility
- Initiative:
Launch Account-Based Marketing (ABM) campaigns targeting companies in emerging new energy sectors (e.g., geothermal, green hydrogen).
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Establishes SLB as the technology partner of choice in new, high-growth energy markets, capturing early market share.
Success Metrics
- •
Pipeline generation from new energy verticals
- •
Number of new accounts engaged
- •
Conversion rate from initial contact to qualified lead
- Initiative:
Create and promote a proprietary 'Digital Energy Index' report, leveraging SLB's vast data to benchmark the industry's digital maturity.
Business Impact:Medium
Market Opportunity:Solidifies SLB's position as the leading authority on digital transformation in energy, creating a unique, data-backed thought leadership asset.
Success Metrics
- •
Report downloads and registrations
- •
Media citations of the index
- •
Organic search visibility for 'digital energy' keywords
Solidify SLB's position as the definitive technology partner for the global energy transition. This requires moving beyond the 'services' narrative to lead the industry discourse on integrating digital innovation, decarbonization technologies, and core oil and gas expertise to achieve a profitable and sustainable energy future.
Competitive Advantage Opportunities
- •
Leverage its unparalleled historical subsurface data as a competitive moat for developing superior AI and predictive analytics solutions.
- •
Market its global operational footprint as a key advantage for deploying and scaling new energy systems (like CCS and geothermal) more rapidly and reliably than smaller competitors.
- •
Build a narrative that frames its acquisitions as a deliberate strategy to create the industry's only fully integrated platform for maximizing energy production while minimizing environmental footprint from reservoir to recovery.
SLB has successfully executed a comprehensive and consistent digital rebranding that aligns with its strategic pivot from a traditional oilfield services giant to a global energy technology company. Its website effectively communicates a forward-looking vision, with robust coverage of both its core oil and gas innovation and high-growth areas like decarbonization, digital transformation, and new energy systems. The digital presence is well-structured to support a high-value, long-cycle B2B sales process by providing the necessary technical validation and case studies to influence major investment decisions.
The primary strategic opportunity is to elevate its digital presence from a validation tool to a powerful market-shaping and demand-generation engine. This involves moving beyond showcasing what they do to authoritatively explaining why it matters to the C-suite. By developing content that translates technological capabilities into quantifiable business outcomes—such as ROI, risk mitigation, and ESG performance—SLB can differentiate itself from competitors who are also vying for the 'energy transition leader' mantle. A concerted focus on data-driven thought leadership, executive-level content, and targeted account-based marketing will be critical to not only defending its market-leading position but also capturing a dominant share of the future energy landscape.
Strategic Priorities
Strategic Priorities
- Title:
Launch 'Industrial Decarbonization' as a Service-Led Business Unit
Business Rationale:The analysis identifies a major growth opportunity in applying SLB's core competencies (CCUS, geothermal, emissions management) to non-energy sectors like cement, steel, and power generation. This diversifies revenue away from cyclical O&G spending and captures a massive, underserved market driven by global net-zero commitments.
Strategic Impact:Transforms SLB from an energy-focused service provider into a broad industrial technology leader, establishing a new, multi-billion dollar revenue pillar. This move directly monetizes the energy transition and builds a significant competitive moat in a nascent market.
Success Metrics
- •
Revenue generated from non-O&G industrial clients
- •
Number of pilot projects converted to long-term 'Decarbonization-as-a-Service' contracts
- •
Total tons of CO2 equivalent contracted for reduction or sequestration
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Revenue Model
- Title:
Establish Market Dominance in Technology-Led Sustainable Minerals Extraction
Business Rationale:The analysis highlights a significant whitespace opportunity in sustainable lithium extraction, leveraging SLB's world-class subsurface characterization and drilling expertise. The soaring demand for battery minerals creates a high-growth, adjacent market where SLB can become the dominant technology partner before a clear leader emerges.
Strategic Impact:Pivots the business model to capture value from the entire energy transition supply chain, from energy production to energy storage (batteries). This positions SLB as an indispensable enabler of electrification, creating a powerful new growth story for investors.
Success Metrics
- •
Number of partnerships with mining companies and automakers for Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) projects
- •
Pipeline value of DLE technology and service contracts
- •
Market share of technology deployed in new sustainable minerals projects
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Market Position
- Title:
Forge a Landmark Alliance with a Hyperscale AI & Cloud Provider
Business Rationale:The competitive analysis shows a medium-to-high threat from tech giants entering the energy data space. A deep, strategic partnership with a leader like Microsoft, AWS, or Google would accelerate the capabilities of SLB's Lumi platform, create a unified and defensible digital ecosystem, and leverage the partner's sales channels to reach new markets.
Strategic Impact:Solidifies SLB's Lumi platform as the undisputed standard for the energy industry, shifting its competitive position from a service provider using tech to a 'digital-first' technology company. This would prevent disintermediation and create a powerful network effect.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) for the 'Digital & Integration' segment
- •
Number of third-party applications developed on the co-branded platform
- •
Volume of customer data and workflows migrated to the Lumi platform
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Partnerships
- Title:
Develop an Asset Co-Investment Model for Large-Scale New Energy Projects
Business Rationale:The long-term analysis suggests evolving the business model from a pure service provider to include direct ownership or operation of new energy assets. Partnering with financial institutions to co-invest in projects like CCUS hubs or geothermal plants would create long-term, stable revenue streams and capture more of the value chain.
Strategic Impact:Fundamentally transforms SLB's revenue model by adding asset-based, recurring revenue, reducing reliance on service contracts. This demonstrates ultimate commitment to the energy transition, aligning the company's financial success directly with the deployment of clean energy infrastructure.
Success Metrics
- •
Value of capital co-deployed into new energy projects
- •
Annualized revenue generated from operated energy assets
- •
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) on co-invested projects
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Long-term Vision (12+ months)
Category:Business Model
- Title:
Launch a 'C-Suite Institute' Focused on the Economics of Energy Transition
Business Rationale:The analysis reveals a strategic content gap in translating SLB's technological superiority into quantifiable C-suite business outcomes (ROI, risk management). This initiative moves beyond technical marketing to establish SLB as the definitive thought leader on the financial strategy of decarbonization, directly influencing the capital allocation decisions of its largest customers.
Strategic Impact:Elevates SLB's brand positioning from a premier technology supplier to an indispensable strategic partner. This builds a powerful competitive moat based on insight and C-suite influence, directly countering the strong energy transition narratives of competitors like Baker Hughes.
Success Metrics
- •
Engagement from C-level executives at target accounts with institute content (reports, forums)
- •
Increase in media citations of SLB as a strategic authority on the energy transition
- •
Growth in sales pipeline for large, integrated decarbonization projects
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Quick Win (0-3 months)
Category:Brand Strategy
SLB must accelerate its transformation from an oilfield services leader into the definitive technology partner for the global energy transition. This requires aggressively commercializing new business models in industrial decarbonization and sustainable minerals, while solidifying its digital platform as the industry's essential operating system through strategic alliances.
The unparalleled ability to integrate a full spectrum of technologies—subsurface science, production systems, digital AI, and new energy solutions—at a global scale to deliver measurable performance outcomes across the entire energy value chain.
Rapidly expanding the high-margin, recurring revenue from the 'Digital & Integration' and 'New Energy' segments, primarily by penetrating adjacent industrial markets and establishing platform leadership.