eScore
tesla.comThe eScore is a comprehensive evaluation of a business's online presence and effectiveness. It analyzes multiple factors including digital presence, brand communication, conversion optimization, and competitive advantage.
Tesla's digital presence is dominant, characterized by exceptional domain authority and a website that functions as a high-conversion digital showroom. The brand's immense gravity ensures strong search intent alignment for transactional queries, and its multi-channel presence is unified by a consistent, minimalist aesthetic. Content authority is demonstrated through product leadership rather than traditional articles, though this creates a gap in top-of-funnel, educational content that competitors are exploiting. The site's sophisticated localization for dozens of countries demonstrates a strong global reach strategy.
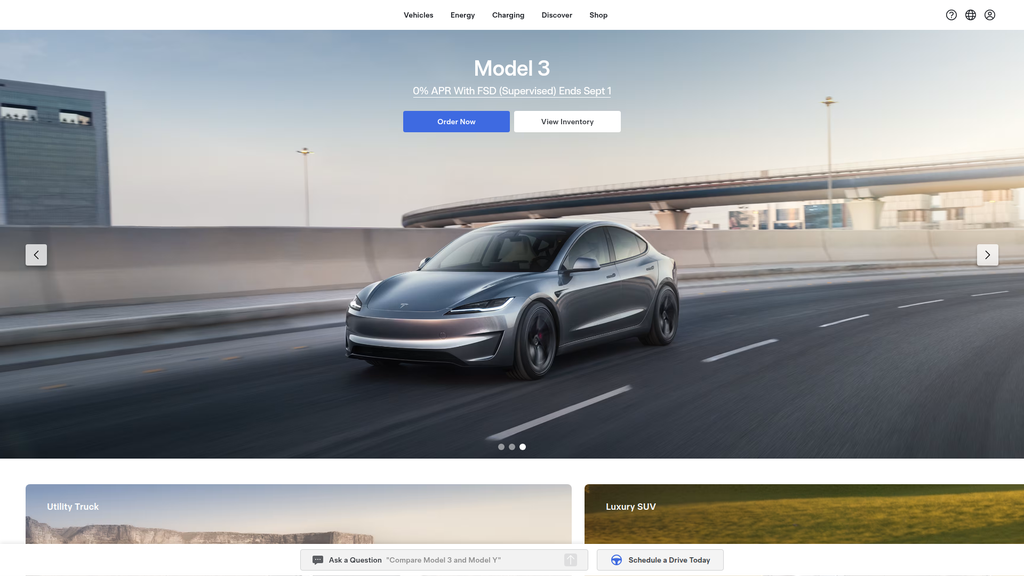
The website is a masterclass in minimalist, product-centric design that functions as a direct-to-consumer sales channel, optimized for high-intent buyers.
Develop a comprehensive 'EV Learning Hub' to capture top-of-funnel search intent from first-time EV buyers, framing the conversation and preventing competitors from owning that initial touchpoint.
Tesla's brand communication is ruthlessly effective at converting high-intent buyers with a clear, minimalist, and confident voice that emphasizes technological superiority and urgent financial incentives. The messaging is highly effective for its target personas (tech-savvy, financially motivated) but lacks a deep emotional connection beyond the product itself, often feeling transactional. While differentiation from competitors is strong, the brand's heavy reliance on the CEO's personal brand creates volatility and has alienated some customers.
Unmatched clarity and simplicity in messaging, with a laser-focus on direct calls-to-action ('Order Now') that streamline the path to purchase for high-intent visitors.
Weave the company's powerful mission—'to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy'—more explicitly into the website narrative to build a stronger emotional connection and brand loyalty beyond product features.
The conversion experience on tesla.com is exceptionally streamlined, representing a core strength of its direct-to-consumer model. Cognitive load is minimized through a clean, visual-first interface and a simple, unambiguous conversion path ('Order' or 'Learn'). Micro-interactions are generally high-quality, and the cross-device journey is seamless due to excellent responsive design. However, the lack of a prominent accessibility statement presents a business risk and a potential friction point for users with disabilities.
An extremely low-friction, digital-native ordering process that removes traditional dealership barriers and guides users from discovery to purchase in minimal steps.
Conduct a third-party accessibility audit against WCAG 2.1 AA standards and publish a formal Accessibility Statement to mitigate legal risk and improve the experience for all users.
Tesla's credibility is a paradox; its powerful brand and innovative products create immense trust, yet it faces significant, high-profile risks. Third-party validation comes more from its market leadership and CEO's influence than from traditional awards. However, ongoing regulatory scrutiny and lawsuits concerning 'Full Self-Driving' claims create substantial legal and reputational risk. Furthermore, inconsistent build quality and well-documented customer service challenges can erode trust and owner satisfaction.
An immensely powerful and globally recognized brand that acts as a primary trust signal, suggesting innovation, leadership, and a high-quality product.
Strengthen internal data handling protocols and employee training to prevent data leaks and unauthorized sharing of customer vehicle data, thereby mitigating a high-severity privacy risk.
Tesla possesses several powerful and sustainable competitive moats that are difficult for rivals to replicate. The proprietary Supercharger network, though now opening up, remains a massive advantage in reliability and integration. Vertical integration and manufacturing innovations like Gigafactories provide significant cost and scaling advantages. Most importantly, its fleet of millions of vehicles provides a vast real-world data advantage for training its FSD AI, a lead that grows with every car sold.
The synergistic combination of a proprietary, reliable Supercharger network and a massive real-world data collection fleet creates a powerful and sustainable ecosystem moat that competitors cannot easily replicate.
Accelerate the development of a lower-cost, mass-market vehicle to build a competitive moat in the high-volume segment currently being targeted by aggressive competitors like BYD.
Tesla has demonstrated phenomenal scalability, with its Gigafactory model enabling rapid global production expansion. Its business model has high operational leverage and extremely low customer acquisition costs, driving strong unit economics. The rapidly growing and high-margin Energy division provides a second pillar of scalable growth. Key constraints remain, including scaling the customer service infrastructure to match the vehicle fleet and navigating complex global supply chains for raw materials.
The modular and highly automated Gigafactory design allows for rapid, repeatable, and cost-effective scaling of manufacturing capacity in strategic global regions.
Invest heavily in scaling the service center and mobile service network to alleviate a critical operational bottleneck that damages customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Tesla's vertically integrated business model is highly coherent, with synergistic divisions across automotive, energy, and software. The model is strategically focused on accelerating the transition to sustainable energy, a mission that aligns stakeholders. Revenue streams are diversifying towards high-margin software (FSD subscriptions) and energy storage. The primary incoherence or risk lies in the massive, long-term bet on achieving full autonomy, a goal whose timeline and commercial viability remain uncertain, creating a disconnect between current financials and a valuation based on future hope.
A synergistic ecosystem where each part reinforces the others: vehicles drive demand for charging and energy products, while the entire fleet serves as a data-gathering network for the high-margin AI/software business.
Clarify the FSD value proposition by better differentiating between current 'supervised' capabilities and the long-term autonomous vision to manage customer expectations and regulatory scrutiny.
Tesla remains a dominant market force, setting industry standards (e.g., NACS charging connector) and wielding significant pricing power. However, its market share trajectory is facing pressure, with its global leadership challenged by BYD and other rivals in key markets like Europe and China. While its brand gives it immense market influence, this is increasingly tied to its CEO's polarizing persona, which has begun to negatively impact brand favorability and create a new competitive risk.
The ability to directly influence industry standards and maintain significant pricing power, allowing it to adjust prices to manage demand, margins, and competitive pressure without relying on a dealership network.
Diversify the brand's public voice beyond the CEO to create a more stable and broadly appealing brand image, mitigating the risks associated with a polarizing personal brand.
Business Overview
Business Classification
Vertically Integrated Technology & Manufacturing
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C)
Automotive & Energy
Sub Verticals
- •
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- •
Battery Technology & Manufacturing
- •
Energy Storage Solutions (Residential & Utility-Scale)
- •
Solar Energy Generation
- •
Autonomous Driving Technology
- •
AI & Robotics
Mature
Maturity Indicators
- •
Global brand recognition as a market leader in EVs.
- •
Established large-scale manufacturing capabilities (Gigafactories).
- •
Sustained profitability and significant market capitalization.
- •
Extensive global sales, service, and charging infrastructure.
- •
Diversification into synergistic, high-growth energy markets.
Enterprise
Steady
Revenue Model
Primary Revenue Streams
- Stream Name:
Automotive Sales & Leasing
Description:Revenue from the sale and leasing of electric vehicles, including Models S, 3, X, Y, and Cybertruck. This is the company's core revenue driver.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Consumers & Commercial Fleets
Estimated Margin:Medium
- Stream Name:
Energy Generation & Storage
Description:Sales of solar energy products (Solar Roof, Solar Panels) and battery energy storage solutions for residential (Powerwall), commercial (Powerpack), and utility-scale (Megapack) applications. This is Tesla's fastest-growing segment.
Estimated Importance:Secondary
Customer Segment:Homeowners, Businesses, & Utility Companies
Estimated Margin:High
- Stream Name:
Services & Other
Description:Includes non-warranty after-sales vehicle services, sales of used vehicles, retail merchandise, vehicle insurance, and revenue from the Supercharger network (including from non-Tesla EVs).
Estimated Importance:Tertiary
Customer Segment:Tesla Owners & Other EV Owners
Estimated Margin:Low-to-Medium
- Stream Name:
Automotive Regulatory Credits
Description:Sale of regulatory credits to other automakers that do not meet emissions standards. While fluctuating, this has historically been a high-margin source of revenue.
Estimated Importance:Tertiary
Customer Segment:Legacy Automotive Manufacturers
Estimated Margin:High
Recurring Revenue Components
- •
Full Self-Driving (FSD) Subscription
- •
Premium Connectivity Subscription
- •
Tesla Insurance Premiums
- •
Supercharger Network Usage Fees
Pricing Strategy
Value-Based & Premium Pricing
Premium
Transparent
Pricing Psychology
- •
Urgency (e.g., 'Federal Tax Credit Ending')
- •
Promotional Pricing (e.g., 'Lease From $299/mo')
- •
Anchoring (Positioning high-value FSD as an add-on)
- •
Price Skimming (Launching high-end models first before more affordable versions)
Monetization Assessment
Strengths
- •
Strong brand loyalty allows for premium pricing.
- •
High-margin, scalable software revenue streams (FSD).
- •
Growing, high-margin energy storage business diversifies revenue from automotive cycles.
- •
Direct-to-consumer model eliminates dealership markups and controls pricing.
Weaknesses
- •
Heavy reliance on automotive sales, which are cyclical and subject to intense competition.
- •
Uncertainty around the take-rate and long-term profitability of FSD subscriptions.
- •
Price cuts to drive volume have compressed automotive gross margins.
Opportunities
- •
Licensing FSD software stack to other automakers.
- •
Expanding the Supercharger network as a universal charging provider.
- •
Scaling the Megapack business to capitalize on grid-scale energy storage demand.
- •
Developing an autonomous ride-hailing network (Robotaxi) to generate recurring service revenue.
Threats
- •
Intensifying competition from legacy automakers and new EV startups (e.g., BYD, Rivian) leading to price wars.
- •
Changes in government subsidies and tax credits for EVs and energy products.
- •
Economic downturns reducing consumer demand for high-priced vehicles.
- •
Regulatory hurdles and public perception challenges for autonomous driving technology.
Market Positioning
Technology and Innovation Leadership
Market Leader (though declining from peak)
Target Segments
- Segment Name:
The Tech-Savvy Professional / Early Adopter
Description:Affluent individuals, often in tech, finance, or entrepreneurial roles, who are drawn to cutting-edge technology, performance, and innovation.
Demographic Factors
- •
Age: 30-55
- •
High household income (>$140,000).
- •
Highly educated (often with graduate degrees).
- •
Predominantly resides in urban or suburban areas.
Psychographic Factors
- •
Values innovation, status, and performance.
- •
Image-conscious and forward-thinking.
- •
Seeks the latest advancements and disruptive products.
Behavioral Factors
- •
Willing to pay a premium for new technology.
- •
Brand loyalist and often an advocate.
- •
Conducts extensive online research before purchasing.
Pain Points
- •
Desire for a vehicle that reflects their identity as an innovator.
- •
Frustration with the outdated technology in traditional cars.
- •
Concern about environmental impact without wanting to sacrifice performance or style.
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:Medium
- Segment Name:
The Eco-Conscious Family
Description:Upper-middle-class families seeking a safe, practical, and sustainable vehicle that aligns with their environmental values without compromising on space or functionality.
Demographic Factors
- •
Age: 35-60
- •
Established families with children.
- •
Solid household income.
- •
Environmentally aware communities.
Psychographic Factors
- •
Prioritizes sustainability and reducing their carbon footprint.
- •
Values safety and long-term cost savings (fuel, maintenance).
- •
Concerned about climate change and air quality.
Behavioral Factors
- •
Makes purchasing decisions based on values and long-term benefits.
- •
Influenced by safety ratings and reviews.
- •
Seeks practical solutions for daily life (e.g., school runs, road trips).
Pain Points
- •
Guilt associated with the environmental impact of traditional SUVs.
- •
High and unpredictable fuel costs.
- •
Worry about the safety of their family in a vehicle.
- •
Range anxiety for longer family trips.
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
Commercial & Utility Clients
Description:Businesses, fleet operators, and utility companies looking to electrify their operations to reduce total cost of ownership, meet ESG goals, and leverage advanced energy management solutions.
Demographic Factors
Fleet managers, energy procurement officers, utility executives.
Psychographic Factors
Focused on ROI, operational efficiency, and long-term cost savings.
Driven by corporate sustainability mandates and regulatory compliance.
Behavioral Factors
- •
B2B sales cycle involving detailed cost-benefit analysis.
- •
Requires scalable and reliable solutions (e.g., Megapacks for grid stability, vehicle fleets).
- •
Values data and analytics for operational optimization (e.g., Tesla's fleet management tools).
Pain Points
- •
Volatile fuel and energy costs impacting profitability.
- •
Pressure to meet corporate and governmental emissions targets.
- •
High maintenance costs and downtime of traditional fleets.
- •
Grid instability and reliance on fossil fuels for power generation.
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:High
Market Differentiation
- Factor:
Vertical Integration
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Proprietary Supercharger Network
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Brand Equity & CEO Influence
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Temporary
- Factor:
Software & Autonomous Driving Leadership (FSD)
Strength:Moderate
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Direct-to-Consumer Sales & Service Model
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Integrated Energy Ecosystem (Car, Solar, Battery)
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
Value Proposition
To accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy through a seamlessly integrated ecosystem of high-performance electric vehicles, battery storage, and clean energy generation.
Excellent
Key Benefits
- Benefit:
Superior Performance & Driving Experience
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
- •
Industry-leading acceleration and handling specifications.
- •
Over-the-air software updates that continuously improve the vehicle.
- •
Minimalist interior with a large touchscreen interface.
- Benefit:
Convenient Long-Range Travel
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Unique
Proof Elements
- •
Extensive and reliable global Supercharger network.
- •
Vehicles with competitive long-range battery capabilities.
- •
Integrated trip planning software that routes through chargers.
- Benefit:
Technological Leadership & Autonomy
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Unique
Proof Elements
- •
Advanced Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (Supervised) features.
- •
Constant software updates introducing new functionalities.
- •
In-house development of AI chips and software.
- Benefit:
Sustainable Energy Ecosystem
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Unique
Proof Elements
- •
Products that work together: charge a Tesla with a Solar Roof and store energy in a Powerwall.
- •
Mission-driven brand focus on sustainability.
- •
Utility-scale Megapacks stabilizing grids with renewable energy.
Unique Selling Points
- Usp:
The integrated hardware and software experience, including Over-the-Air (OTA) updates that improve the car over time.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
The exclusive, reliable, and widespread Supercharger network, which mitigates range anxiety.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
A direct-to-consumer model providing a transparent, no-haggle purchasing and service experience.
Sustainability:Medium-term
Defensibility:Moderate
Customer Problems Solved
- Problem:
Electric vehicles are perceived as slow, unattractive, and having limited range.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Lack of a reliable and ubiquitous charging infrastructure for long-distance travel.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Traditional car ownership experience is complex, with dealership negotiations and infrequent, inconvenient updates.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Desire to reduce personal environmental impact without sacrificing performance or lifestyle.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
Value Alignment Assessment
High
Tesla's value proposition is highly aligned with the growing global market demand for electric mobility, sustainability, and advanced technology. The integrated energy and transport ecosystem is a key differentiator as the world electrifies.
High
The proposition strongly resonates with its core target segments who value technology, performance, sustainability, and brand prestige. The focus on a superior, tech-forward experience directly meets the desires of early adopters and tech-savvy consumers.
Strategic Assessment
Business Model Canvas
Key Partners
- •
Battery cell suppliers (e.g., Panasonic, LG, CATL).
- •
Raw material suppliers (Lithium, Cobalt, Nickel).
- •
Cloud infrastructure providers for AI and data processing (e.g., Alibaba, Tencent in China).
- •
Automakers adopting the NACS charging standard (e.g., Ford, GM).
Key Activities
- •
Research & Development (Battery tech, AI, FSD, Robotics).
- •
Vertically Integrated Manufacturing (Gigafactories, Giga Press).
- •
Software Development (Vehicle OS, FSD, Autobidder).
- •
Direct-to-Consumer Sales & Marketing.
- •
Global Supercharger Network Management & Expansion.
- •
Energy Project Deployment (Megapack).
Key Resources
- •
Brand Reputation & Loyalty.
- •
Intellectual Property (Patents in battery, powertrain, and software).
- •
Global network of Gigafactories and manufacturing expertise.
- •
Proprietary Supercharger Infrastructure.
- •
Vast pool of real-world driving data for FSD training.
Cost Structure
- •
High Capital Expenditures (Factory construction and expansion).
- •
Research & Development Expenses.
- •
Manufacturing Costs (Raw materials, labor, logistics).
- •
Sales, General & Administrative (SG&A) costs for stores, service centers, and personnel.
Swot Analysis
Strengths
- •
Strong global brand recognition and aspirational status.
- •
First-mover advantage and technological lead in EV powertrain and battery technology.
- •
Extensive, proprietary Supercharger network creating a strong competitive moat.
- •
Vertical integration provides greater control over supply chain, innovation, and costs.
- •
Rapidly growing and profitable Energy division providing revenue diversification.
Weaknesses
- •
Dependence on a high-profile, and sometimes controversial, CEO.
- •
Production scalability challenges and past manufacturing delays.
- •
Premium pricing limits market reach compared to lower-cost competitors.
- •
Customer service and vehicle quality control issues have been reported.
Opportunities
- •
Expansion into mass-market, lower-cost vehicle segments.
- •
Growth of the Energy Storage business, particularly with utility-scale Megapacks.
- •
Monetizing the Full Self-Driving software through licensing or a Robotaxi network.
- •
Geographic expansion into untapped markets like India and Southeast Asia.
- •
Leveraging AI and robotics expertise to enter new markets (e.g., Optimus robot).
Threats
- •
Intensifying competition from both legacy auto manufacturers (Ford, GM, VW) and aggressive Chinese EV makers (BYD).
- •
Global supply chain disruptions and volatility in raw material prices (e.g., lithium).
- •
Increased regulatory scrutiny regarding safety, autonomous driving claims, and data privacy.
- •
Global economic slowdown impacting demand for premium vehicles.
- •
Geopolitical tensions, particularly between the US and China, affecting key markets and supply chains.
Recommendations
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Product Lineup Diversification
Recommendation:Accelerate the development and launch of a lower-cost, mass-market vehicle to compete directly with emerging low-price competitors and expand market share globally.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Customer Service & Quality Control
Recommendation:Invest significantly in scaling and improving the consistency of after-sales service and address vehicle quality control issues at the manufacturing stage to enhance brand loyalty and reduce long-term costs.
Expected Impact:Medium
- Area:
FSD Value Proposition Clarity
Recommendation:Simplify the FSD product offering and clearly communicate its current 'supervised' capabilities versus the long-term autonomous vision to manage customer expectations and improve adoption rates.
Expected Impact:Medium
Business Model Innovation
- •
Launch a 'Tesla as a Service' (TaaS) subscription model bundling vehicle, insurance, maintenance, and software (FSD) into a single monthly payment.
- •
Formalize and scale the licensing of the full EV platform (battery, powertrain, OS) to other manufacturers, transitioning from a competitor to a technology supplier.
- •
Create a virtual power plant (VPP) network by integrating Powerwalls, offering grid stabilization services and creating a new revenue stream for both Tesla and its customers.
Revenue Diversification
- •
Aggressively scale the deployment of Megapacks to become a dominant player in the global grid-scale energy storage market, capitalizing on the AI-driven demand for stable power.
- •
Expand Tesla Insurance into all operational markets, leveraging telematics data to offer more competitive pricing and increase service revenue.
- •
Accelerate the development and launch of the Optimus humanoid robot for commercial and industrial applications, creating an entirely new business vertical.
Tesla's business model represents a paradigm shift from traditional automotive manufacturing to a vertically integrated technology ecosystem. Its foundation is built on a direct-to-consumer strategy, controlling everything from design and manufacturing to sales and service, which provides a significant competitive advantage in agility and cost control. The company has successfully cultivated an aspirational brand that commands premium pricing, while its proprietary Supercharger network creates a powerful, defensible moat that competitors struggle to replicate.
The primary business model evolution opportunity lies in transitioning from a company that primarily sells hardware (cars) to one that generates significant recurring revenue from software and services. The success of Full Self-Driving (FSD) as a subscription or a licensed technology, and the potential of an autonomous Robotaxi network, are central to its long-term valuation. However, this is also a key risk, as the timeline for true autonomy remains uncertain.
Simultaneously, Tesla's Energy division is rapidly emerging as a second pillar of growth, with its Megapack and Powerwall products addressing the critical global need for energy storage. This segment is not only diversifying revenue away from the increasingly competitive automotive market but also boasts higher margins and reinforces the company's core mission. The strategic imperative is to scale this business to rival the automotive segment in revenue and profitability.
The most significant threats are intensifying competition, particularly from Chinese manufacturers like BYD who are competing aggressively on price, and the challenge of maintaining growth and innovation at scale. To sustain its leadership, Tesla must accelerate the launch of more affordable vehicles, perfect its autonomous technology, and successfully scale its energy and AI ventures into dominant, profitable business lines. The evolution from a car company to a multifaceted AI, robotics, and energy powerhouse is the core of its future strategic trajectory.
Competitors
Competitive Landscape
Growth
Moderately Concentrated
Barriers To Entry
- Barrier:
High Capital Investment for Manufacturing & R&D
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Battery Technology & Supply Chain Security
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Charging Infrastructure Development
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Software & Autonomous Driving Expertise
Impact:Medium
- Barrier:
Brand Recognition & Customer Loyalty
Impact:Medium
- Barrier:
Regulatory Compliance & Homologation
Impact:Medium
Industry Trends
- Trend:
Intensifying Competition & Price Wars
Impact On Business:Pressure on margins and market share as legacy automakers and new entrants scale EV production.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Diversification of EV Models (Affordable & Niche Segments)
Impact On Business:Requires Tesla to broaden its product portfolio beyond its current premium-focused lineup to capture mass-market growth.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Advancements in Battery Technology (Solid-State, LFP)
Impact On Business:Opportunity to lower costs and increase range, but also a threat if competitors achieve breakthroughs first.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Software-Defined Vehicles & Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Impact On Business:Solidifies a core Tesla strength but requires continuous innovation as competitors develop similar capabilities.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Autonomous Driving Regulation and Development
Impact On Business:A key long-term differentiator for Tesla, but progress is subject to complex regulatory hurdles and technological challenges.
Timeline:Long-term
- Trend:
Geopolitical Influence on Supply Chains and Tariffs
Impact On Business:Poses risks to production costs and market access, particularly regarding Chinese competitors and battery materials.
Timeline:Immediate
Direct Competitors
- →
BYD (Build Your Dreams)
Market Share Estimate:Globally, BYD has surpassed Tesla in total vehicle sales (including hybrids) and is neck-and-neck or has surpassed Tesla in BEV sales in recent quarters.
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Vertically-integrated mass-market EV leader, offering a wide range of affordable to premium vehicles with a strong focus on battery innovation.
Strengths
- •
Complete vertical integration (from battery manufacturing to vehicle assembly).
- •
Broad product portfolio catering to all price points.
- •
Dominant market share in China, the world's largest EV market.
- •
Aggressive international expansion and competitive pricing.
Weaknesses
- •
Lower brand recognition outside of China compared to Tesla.
- •
Software and autonomous driving features are generally perceived as less advanced than Tesla's.
- •
Global expansion faces geopolitical and tariff headwinds.
Differentiators
- •
Proprietary 'Blade Battery' technology (LFP).
- •
Dual-mode (BEV and PHEV) strategy captures a wider market.
- •
Cost leadership enabling aggressive pricing strategies.
- →
Volkswagen Group (VW, Audi, Porsche, Skoda)
Market Share Estimate:A top competitor in Europe, with a significant and growing global EV market share.
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Legacy automotive giant leveraging its scale, brand portfolio, and dealer network to transition to electrification.
Strengths
- •
Massive manufacturing scale and global distribution network.
- •
Diverse portfolio of brands targeting various consumer segments (e.g., Porsche for performance, Audi for luxury, VW for mass-market).
- •
Strong brand loyalty and reputation in key markets like Europe.
- •
Significant investment in dedicated EV platforms (e.g., MEB).
Weaknesses
- •
Software development has been a significant challenge, with delays and performance issues (CARIAD).
- •
Slower to adapt and innovate compared to pure-play EV companies.
- •
Complex corporate structure can hinder agility.
- •
Profitability of EV segment is under pressure.
Differentiators
- •
Established dealership and service network.
- •
Broad range of vehicle types and styles across its brands.
- •
Strong engineering reputation for build quality and driving dynamics.
- →
Ford Motor Company
Market Share Estimate:A leading competitor in the U.S., particularly in the electric truck and SUV segments.
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:Electrifying iconic American nameplates (Mustang, F-150) and leveraging commercial vehicle strength to capture a loyal customer base.
Strengths
- •
Strong brand recognition and loyalty, especially in North America.
- •
Leadership in high-profit segments like pickup trucks (F-150 Lightning).
- •
Extensive dealership network for sales and service.
- •
Strategic shift to more affordable EV platforms and hybrid options to broaden appeal.
Weaknesses
- •
EV division (Model e) has faced significant financial losses.
- •
Slower to achieve cost parity with Tesla.
- •
Reliant on third-party charging networks, though now adopting Tesla's NACS standard.
- •
Pivoting strategy suggests uncertainty in the pace of full electrification.
Differentiators
- •
Focus on electrifying established, iconic models.
- •
Strong position in the commercial EV market (E-Transit).
- •
Combining EV offerings with a renewed focus on hybrids to meet diverse customer needs.
- →
Rivian
Market Share Estimate:A niche but significant player in the premium adventure EV segment (trucks and SUVs).
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:Premium, adventure-focused EV brand for outdoor lifestyle enthusiasts, with a strong B2B partnership with Amazon.
Strengths
- •
Strong brand identity and cult following in the 'adventure vehicle' niche.
- •
Innovative design and features tailored for utility and outdoor use.
- •
Strategic partnership with Amazon for its electric delivery van fleet provides stable demand.
- •
High-performance vehicles with excellent off-road capabilities.
Weaknesses
- •
Struggles with production scaling and achieving profitability.
- •
High vehicle prices limit market size.
- •
Negative gross margins and significant cash burn.
- •
Limited charging infrastructure compared to Tesla.
Differentiators
- •
'Adventure' and outdoor lifestyle branding.
- •
Unique vehicle features like the Gear Tunnel.
- •
Vertically integrated sales and service model, similar to Tesla.
- →
Lucid Motors
Market Share Estimate:Niche player in the ultra-luxury EV sedan market.
Target Audience Overlap:Low
Competitive Positioning:An ultra-luxury EV brand focused on setting new standards for range, efficiency, performance, and interior luxury, directly targeting the high-end of the market.
Strengths
- •
Industry-leading battery efficiency and vehicle range.
- •
Exceptional performance and luxury-focused design.
- •
Proprietary, compact, and powerful electric motor technology.
Weaknesses
- •
Extremely high price point, limiting its addressable market.
- •
Very low production volumes and challenges in scaling.
- •
Low brand awareness compared to established luxury marques and Tesla.
- •
Heavy reliance on funding from Saudi Arabia's Public Investment Fund.
Differentiators
- •
Focus on efficiency (miles per kWh) as a key performance metric.
- •
Ultra-luxurious interior design and materials.
- •
Positioned as a technology leader in EV powertrain engineering.
Indirect Competitors
- →
Toyota & Honda
Description:Legacy automakers with a strong focus on hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles. Their brand reputation for reliability and massive customer base present a significant hurdle to full EV adoption for many consumers.
Threat Level:High
Potential For Direct Competition:High, but their transition to full BEVs has been notably slower and more cautious than competitors.
- →
Waymo (Google) & Cruise (GM)
Description:Technology companies developing and deploying autonomous vehicle technology for ride-hailing services. Their success could disrupt the personal car ownership model that Tesla's business relies on.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:High, as Tesla's long-term vision includes its own 'Robotaxi' network.
- →
Sunrun & SunPower
Description:Specialized residential solar and energy storage companies that compete directly with Tesla's Energy division (Solar Panels, Solar Roof, Powerwall).
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:They are already direct competitors in the energy sector, which is a key part of Tesla's long-term ecosystem strategy.
- →
Uber & Lyft
Description:Ride-sharing services that reduce the necessity of personal vehicle ownership in urban areas. They are also large fleet buyers, but their core model challenges the individual sales model.
Threat Level:Low
Potential For Direct Competition:Low, but they are potential large customers or competitors in a future autonomous ride-hailing market.
Competitive Advantage Analysis
Sustainable Advantages
- Advantage:
Supercharger Network
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. The network's scale, reliability, and integration with the vehicle's navigation is a powerful moat, even with the adoption of the NACS standard by others.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Brand Strength & 'First-Mover' Status
Sustainability Assessment:Sustainable but requires careful management. The brand is synonymous with EVs, but is also increasingly tied to the polarizing persona of its CEO.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Vertical Integration & Manufacturing Innovation
Sustainability Assessment:Sustainable. Innovations like Gigafactories, gigacasting, and in-house battery development provide significant cost and efficiency advantages that are difficult to replicate.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Software and Data Ecosystem
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. The fleet of millions of vehicles collecting real-world driving data creates a powerful feedback loop for developing FSD and other software features, an advantage that grows with every car sold.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
- Advantage:
Direct-to-Consumer Sales Model
Sustainability Assessment:Sustainable. This model provides control over pricing, brand experience, and customer data, and avoids the complexities of a traditional dealership network.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
Temporary Advantages
{'advantage': 'Performance & Range Leadership', 'estimated_duration': '1-3 years. The performance and range gap is closing rapidly as competitors like Lucid, Hyundai/Kia, and others launch vehicles with comparable or superior metrics in specific areas.'}
{'advantage': 'Battery Cost Advantage', 'estimated_duration': '2-4 years. While Tesla maintains a lead, competitors like BYD with their own battery divisions are closing the gap, and industry-wide scaling is reducing costs for all.'}
Disadvantages
- Disadvantage:
CEO-Related Brand Volatility
Impact:Major
Addressability:Difficult
- Disadvantage:
Inconsistent Build Quality & Service Center Issues
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately
- Disadvantage:
Limited Model Lineup and Slower Refresh Cycles
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately
- Disadvantage:
Focus on Premium Segments
Impact:Major
Addressability:Difficult
Strategic Recommendations
Quick Wins
- Recommendation:
Launch aggressive marketing campaigns focused on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) to counter competitor pricing and highlight fuel/maintenance savings.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
- Recommendation:
Improve customer service responsiveness and transparency, particularly around delivery timelines and service appointments.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Medium Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Accelerate development and launch of a lower-cost, mass-market vehicle (e.g., 'Model 2') to compete with offerings from BYD and other legacy automakers.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Diversify the product lineup with additional vehicle types, such as a commercial van, to tap into underserved and high-margin segments.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Expand the service center network and mobile service fleet to alleviate service bottlenecks and improve customer satisfaction.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Long Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Achieve a breakthrough in Full Self-Driving (FSD) to deliver on the Robotaxi concept, creating a new, high-margin revenue stream.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Fully integrate the energy and automotive businesses, offering bundled packages (Car + Solar + Powerwall) with innovative financing to create a sticky home ecosystem.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Diversify battery supply chains and invest in next-generation battery R&D (e.g., reducing reliance on cobalt, scaling 4680 cells) to maintain a long-term cost and technology advantage.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Transition brand positioning from a 'premium EV manufacturer' to a 'leading AI, robotics, and sustainable energy company.' This leverages the full scope of its innovations (FSD, Optimus, Energy) and provides a more durable narrative against the wave of automotive competitors.
Double down on the 'car as a software platform' concept. Focus on unique, delightful, and continuously improving software experiences that legacy automakers struggle to replicate, reinforcing the idea that a Tesla gets better over time while competitors remain static.
Whitespace Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Affordable Compact EV (Sub-$30,000)
Competitive Gap:The global market has a massive unmet demand for affordable, compelling EVs. Most legacy automakers are focused on larger SUVs, and Chinese brands have yet to fully establish trust in Western markets.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Integrated Fleet Management Solutions for Businesses
Competitive Gap:Offer a turnkey solution for commercial fleets including vehicles (Cybertruck, future van), charging infrastructure, energy management (Megapack), and a software platform for optimizing TCO and operations.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Services
Competitive Gap:Leverage the massive distributed battery capacity of the Tesla fleet to offer grid stabilization services, creating a new revenue stream for both Tesla and its vehicle owners. Few competitors have the scale or software capability to deploy this effectively.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Tesla-certified Pre-Owned and Refurbishment Program
Competitive Gap:A robust, manufacturer-backed CPO program could improve resale values, build customer trust, and create a lower-priced entry point for new customers, a market segment that competitors serve through their extensive dealer networks.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:Medium
Emerging Competitive Threats And Market Entry Barriers
Emerging Threats
- Threat:
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities
Description:As vehicles become more connected and software-defined, the risk of large-scale cyberattacks targeting EV fleets increases, posing safety and reputational risks.
Severity:High
- Threat:
Geopolitical Weaponization of Supply Chains
Description:Dependence on specific countries for raw materials (lithium, cobalt) and components creates vulnerability to trade disputes and supply chain disruptions, especially with the rise of Chinese EV giants.
Severity:High
- Threat:
Slowing Mainstream EV Adoption
Description:If consumer adoption in the 'mainstream' phase stalls due to concerns over charging infrastructure, range anxiety, or high purchase prices, the entire market's growth could slow, intensifying competition for a smaller pool of buyers.
Severity:Medium
- Threat:
Disruption from Autonomous Mobility Services
Description:The success of a non-Tesla autonomous ride-hailing network (e.g., Waymo) could fundamentally alter the need for personal car ownership, shrinking Tesla's core market before its own Robotaxi network is viable.
Severity:Medium
Tesla operates within the high-growth, but increasingly competitive, electric vehicle and sustainable energy sectors. The company's historic dominance, built on a powerful brand, superior charging infrastructure, and a significant head start in battery and software technology, is now being challenged on multiple fronts. The primary competitive pressure comes from Chinese automaker BYD, which now rivals or exceeds Tesla in production volume, leveraging complete vertical integration and a broad, affordable product portfolio to dominate its domestic market and expand aggressively abroad. Concurrently, legacy automotive giants like Volkswagen Group and Ford are leveraging their immense scale, brand loyalty, and distribution networks to capture significant market share, albeit with ongoing struggles in software development and EV profitability.
Tesla's most sustainable competitive advantages remain its proprietary Supercharger network, its deeply integrated software and data collection ecosystem for autonomous driving, and its disruptive direct-to-consumer model. These elements are difficult and capital-intensive for competitors to replicate. However, advantages in vehicle range and performance are eroding as new, compelling products from rivals like Hyundai/Kia and Lucid enter the market. The company's key weaknesses—inconsistent build quality, service accessibility, and a narrow model lineup—are becoming more pronounced as consumers have more high-quality alternatives to choose from. Furthermore, the brand's heavy reliance on the polarizing public persona of its CEO presents a unique and significant volatility risk.
The competitive landscape reveals clear strategic imperatives. To sustain growth, Tesla must accelerate the development of a mass-market, lower-cost vehicle to directly counter the offerings from Chinese brands and legacy automakers targeting more price-sensitive consumers. Secondly, the company must aggressively invest in expanding and improving its service infrastructure to address a major source of customer dissatisfaction. Long-term differentiation will hinge on achieving a tangible breakthrough in Full Self-Driving technology, transitioning the business model from one-time hardware sales to recurring software and mobility service revenue. Whitespace opportunities exist in commercial vehicles, integrated home energy solutions, and leveraging its vast fleet for Vehicle-to-Grid services, areas where Tesla's ecosystem approach could create a powerful, defensible moat. The transition from an uncontested leader to one of several major players requires a strategic shift from pure disruption to include operational excellence, product diversification, and disciplined brand stewardship.
Messaging
Message Architecture
Key Messages
- Message:
Urgent Financial Incentives: Take advantage of limited-time offers like tax credits, special lease pricing, and low APR.
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage hero banners, product sections
- Message:
The Future is Electric & Integrated: Tesla offers a complete sustainable energy ecosystem, from vehicles to home energy.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:Medium
Location:Implicit through the grouping of Vehicle, Energy, and Charging products in the navigation and on the homepage.
- Message:
Technological Superiority & Performance: Experience cutting-edge features like Full Self-Driving (Supervised) and industry-leading performance.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Product-specific sections (e.g., 'Cyberbeast Now Includes Luxe Package With FSD')
- Message:
Direct and Simple Ownership: Order directly, find charging easily, and manage your vehicle/energy through a seamless process.
Prominence:Tertiary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Embedded in the user experience and CTAs like 'Order Now' and 'View Inventory'.
The message hierarchy is exceptionally clear and commercially driven. The most prominent messages are time-sensitive financial incentives designed to drive immediate sales conversions. Product categories are next, followed by supporting features and the broader ecosystem. This is a highly effective bottom-of-the-funnel strategy.
Messaging is remarkably consistent. Every product is presented with the same minimalist aesthetic and direct calls-to-action ('Order Now', 'Learn More'). Financial incentives are woven throughout the vehicle pages, reinforcing the primary message of immediate value.
Brand Voice
Voice Attributes
- Attribute:
Minimalist
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Model Y
- •
Luxury SUV
- •
Order Now
- Attribute:
Confident
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Full Self-Driving (Supervised)
- •
Features That Come Standard
- •
The company does not use extensive, persuasive copy, assuming the product's value is self-evident.
- Attribute:
Transactional
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Lease From $299/mo for a Limited Time
- •
Order Now
- •
View Inventory
- Attribute:
Aspirational
Strength:Moderate
Examples
Generate Clean Energy With Your Roof
The overall visual design and product imagery create a sense of a desirable, futuristic lifestyle.
Tone Analysis
Direct and Informative
Secondary Tones
Urgent
Pragmatic
Tone Shifts
The tone shifts slightly from purely transactional on vehicle pages (price, order) to more benefit-oriented on energy pages ('Keep Your Lights On During Outages').
Voice Consistency Rating
Excellent
Consistency Issues
No itemsValue Proposition Assessment
To provide a seamless, technologically advanced, and fully integrated ecosystem of sustainable energy products, from high-performance electric vehicles to energy generation and storage, all accessible through a direct-to-consumer model.
Value Proposition Components
- Component:
Integrated Energy Ecosystem
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Unique
Details:Tesla is uniquely positioned as a single company offering vehicles, solar, and battery storage. This creates a powerful 'one-stop-shop' value proposition that competitors cannot easily replicate.
- Component:
Cutting-Edge Technology & Performance
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
Details:While competitors are catching up, Tesla's brand is synonymous with innovation, particularly in software, autonomous driving features, and performance.
- Component:
Direct-to-Consumer Model
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Unique
Details:The ability to order directly, without dealerships, offers price transparency and a controlled customer experience. This is a significant differentiator in the automotive industry.
- Component:
Extensive Supercharger Network
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Unique
Details:The scale and reliability of the Supercharger network is a massive competitive advantage, directly addressing the core pain point of range anxiety for potential EV buyers.
Tesla’s messaging powerfully differentiates the brand not as a car company, but as a tech and energy company that builds cars. The focus on the entire ecosystem (cars, charging, solar, storage) creates a strategic moat. While competitors message about individual EV models, Tesla messages an entire lifestyle and energy solution, a much stronger long-term position.
The messaging positions Tesla as the undisputed leader and innovator in the EV and sustainable energy space. It doesn't acknowledge competitors. The tone is that of a category creator, setting the standard that others must follow. This confident posture reinforces its premium, market-leading brand identity.
Audience Messaging
Target Personas
- Persona:
The Tech-Savvy Early Adopter
Tailored Messages
Full Self-Driving (Supervised)
Cyberbeast Now Includes Luxe Package With FSD (Supervised) and More
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
The Financially-Motivated Buyer
Tailored Messages
- •
$7,500 Federal Tax Credit Ending
- •
Lease From $299/mo for a Limited Time
- •
0% APR With FSD (Supervised) Ends Sept 1
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
The Eco-Conscious Homeowner
Tailored Messages
Use Solar Energy to Power Your Home and Charge Your Tesla
Keep Your Lights On During Outages
Effectiveness:Effective
Audience Pain Points Addressed
- •
Range Anxiety (via 'Find Your Charge' and Supercharger network map)
- •
High Cost of EVs (via lease deals, tax credits, and financing offers)
- •
Power Outages (via Powerwall messaging: 'Keep Your Lights On')
- •
Complexity of Buying a Car (via simple 'Order Now' CTAs)
Audience Aspirations Addressed
- •
Owning the latest technology and innovation.
- •
Being part of the transition to sustainable energy.
- •
Achieving energy independence.
- •
Projecting a forward-thinking and successful image.
Persuasion Elements
Emotional Appeals
- Appeal Type:
Aspiration & Status
Effectiveness:High
Examples
The sleek, futuristic product photography and minimalist design.
Labeling vehicles as 'Luxury SUV' or 'Luxury Sedan'.
- Appeal Type:
Security & Peace of Mind
Effectiveness:Medium
Examples
Powerwall: 'Keep Your Lights On During Outages'
The visual map showing the vastness of the Supercharger network.
Social Proof Elements
- Proof Type:
Proof in Numbers
Impact:Strong
Details:Displaying '32,739 Superchargers' and '10,398 Destination Chargers' serves as powerful, concrete social proof of the network's scale and viability.
Trust Indicators
- •
The globally recognized and powerful brand name.
- •
Clean, professional, and data-driven website design.
- •
Direct, transparent calls-to-action with clear pricing information.
- •
Clear presentation of product specifications and features.
Scarcity Urgency Tactics
- •
Ending Federal Tax Credit
- •
Limited Time Lease Offers
- •
Financing Offers with Expiration Dates (e.g., 'Ends Sept 1')
Calls To Action
Primary Ctas
- Text:
Order Now
Location:Homepage banners and all product sections
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Learn More
Location:Paired with 'Order Now' on most product sections
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
View Inventory
Location:Homepage banners and product sections
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Demo Drive
Location:Navigation bar and dedicated sections
Clarity:Clear
The CTAs are extremely effective for their intended purpose: driving high-intent visitors to the point of sale. The binary choice of 'Order' or 'Learn' cleanly separates users by their stage in the buying funnel. The language is direct, unambiguous, and consistently applied, which minimizes friction and drives action.
Messaging Gaps Analysis
Critical Gaps
Lack of Top-of-Funnel Content: The site heavily caters to users who are already considering a purchase. There is very little content for someone in the early awareness or consideration phase, such as detailed comparisons with competitors or content that explains the fundamental benefits of EV ownership.
Missing Human Element: The site lacks customer stories, testimonials, or narratives that connect the products to real-world user experiences. This makes the brand feel technologically superior but potentially cold or impersonal.
Contradiction Points
No itemsUnderdeveloped Areas
Mission-Driven Storytelling: The company mission is 'to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy', but the website messaging is almost entirely focused on product features and financial transactions. There's a significant opportunity to create a stronger emotional connection by weaving this mission-driven narrative throughout the site.
Community Building: Tesla has a passionate community of owners, but the website does little to highlight or engage this community. Featuring owner stories or community events could serve as powerful social proof and brand building.
Messaging Quality
Strengths
- •
Unmatched Clarity and Simplicity: The messaging is surgically precise, avoiding jargon and focusing on the core value and action.
- •
Drives Action and Conversion: The entire site is optimized to convert interested visitors into leads or sales, with a heavy and effective use of urgency.
- •
Reinforces Brand Leadership: The confident, minimalist voice and focus on innovation solidify Tesla's position as a premium, forward-thinking brand.
- •
Product-as-Marketing: The website design and messaging let the products' appeal and specifications do most of the persuasive work, which is a sign of a strong product and brand.
Weaknesses
- •
Over-reliance on Pre-existing Brand Knowledge: The site assumes visitors arrive with a high level of awareness and intent, potentially alienating newcomers or those early in their research process.
- •
Lack of Emotional Connection: The transactional focus comes at the cost of storytelling and building a deeper emotional bond with the audience beyond the product itself.
- •
Potentially Intimidating for Non-Tech Users: The emphasis on features like FSD without much context could be overwhelming for less tech-savvy consumers.
Opportunities
- •
Develop a 'Why Tesla?' Section: Create content specifically for users at the top of the funnel that explains the brand's mission, the benefits of its integrated ecosystem, and showcases compelling customer stories.
- •
Integrate Community Content: Leverage user-generated content and stories from the passionate owner base to add a human element and powerful social proof to the website.
- •
Expand 'Learn' Sections: Build out the 'Learn' sections with more narrative content, video guides, and interactive tools that explain the technology and its benefits in simpler, more relatable terms.
Optimization Roadmap
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Homepage Narrative
Recommendation:Introduce a content block below the main product showcase that explicitly states and visualizes Tesla's mission. Connect the vehicles and energy products back to the goal of accelerating the transition to sustainable energy.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Customer Proof
Recommendation:Create a 'Customer Stories' or 'Community' section in the main navigation. Feature high-quality video testimonials and written stories from diverse owners, highlighting how the products have impacted their lives.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Top-of-Funnel Content
Recommendation:Develop a series of articles or guides under the 'Learn' section targeting common questions from new EV buyers (e.g., 'A Guide to Your First EV', 'Tesla vs. Traditional Cars').
Expected Impact:Medium
Quick Wins
- •
Add a single, compelling customer quote to the homepage.
- •
Re-label the 'About' section to 'Our Mission' to better signal its purpose.
- •
Add a small infographic on product pages visualizing the cost savings from gas and incentives.
Long Term Recommendations
- •
Build an integrated content hub that tells the ongoing story of Tesla's innovation and its community's role in the energy transition.
- •
Develop interactive comparison tools that allow users to configure a Tesla against key competitors, highlighting advantages beyond just price.
- •
Invest in documentary-style content that showcases the real-world impact of the company's technology, from individual owners to large-scale Megapack installations.
Tesla's website messaging is a masterclass in direct-to-consumer, conversion-focused communication. It is ruthlessly efficient, leveraging a minimalist design and a confident, transactional voice to guide high-intent buyers toward purchase with minimal friction. The strategic use of urgency through limited-time financial incentives is a powerful driver of immediate action. The site's primary strength lies in its clarity and its ability to let the power of the brand and the products speak for themselves, effectively serving the bottom of the marketing funnel.
However, this singular focus creates a significant strategic gap at the top of the funnel. The messaging assumes a visitor already knows and desires a Tesla, offering little for those in the initial awareness or educational phases of their journey. It lacks the human element of storytelling and community, which could be used to build a deeper emotional connection and justify the premium price point beyond technical specifications. While the current strategy is highly effective for a brand with immense cultural cachet, its long-term sustainability as the EV market becomes more crowded and competitive will depend on its ability to evolve. The key opportunity is to enrich the current transactional framework with mission-driven narratives and authentic customer stories, thereby appealing to a broader audience and building a more resilient, emotionally resonant brand.
Growth Readiness
Growth Foundation
Product Market Fit
Strong
Evidence
- •
Sustained high-volume vehicle sales (Model 3/Y) establishing market leadership in the premium EV segment.
- •
Exceptional growth in the Energy division, with deployments of Megapack and Powerwall more than doubling in 2024 and demand outstripping supply.
- •
Creation of a proprietary, high-demand Supercharger network that is now being adopted as a standard (NACS) by other manufacturers.
- •
High brand recognition and aspirational value, enabling a low/zero traditional advertising spend.
- •
Strong demand for future products like the Cybertruck, Semi, and next-generation vehicles, often indicated by reservation numbers.
Improvement Areas
- •
Address concerns over vehicle build quality and consistency to reduce warranty claims and improve long-term brand perception.
- •
Expand the service center and mobile service network to keep pace with the growing fleet of vehicles, reducing wait times for repairs and maintenance.
- •
Improve customer service responsiveness and resolution times, a frequent point of criticism from owners.
Market Dynamics
High. The global EV market is projected to grow by 19.8% in 2025 to over 21 million units, with forecasts showing the global EV stock reaching 525 million by 2035.
Growing
Market Trends
- Trend:
Intensifying Competition
Business Impact:Increased competition from legacy automakers (VW, GM, Ford) and new entrants (BYD, Rivian, Nio) is leading to price wars and market share erosion in key regions like Europe and China.
- Trend:
Diversification into Energy Storage
Business Impact:The grid-scale energy storage market is expanding rapidly. Tesla's energy division is a significant growth driver, with higher gross margins than the automotive business, providing a crucial hedge against automotive market volatility.
- Trend:
Focus on Autonomous Driving
Business Impact:The race to achieve Level 4/5 autonomy is a key technological frontier. Success in FSD could unlock massive, high-margin revenue from a robotaxi network, fundamentally changing the company's valuation and business model.
- Trend:
Geopolitical and Regulatory Shifts
Business Impact:Trade tariffs, changes in EV subsidies (like the US tax credit), and regional regulations (like the EU's emission standards) directly impact sales volumes and profitability in key markets.
Excellent. Tesla is an established leader in two simultaneously booming markets: electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. While facing increased competition, its first-mover advantage and technological lead provide a strong foundation for continued growth.
Business Model Scalability
High
High fixed costs associated with Gigafactories and R&D, but strong potential for decreasing variable costs per unit through manufacturing innovations (e.g., giga-casting) and economies of scale.
High. The direct-to-consumer sales model and vertically integrated production create significant operational leverage. A small increase in sales volume can lead to a disproportionately large increase in profitability, though this is currently being tested by price competition.
Scalability Constraints
- •
Sourcing and processing of raw materials for batteries (lithium, cobalt, nickel) at scale.
- •
Capital expenditure required to build new Gigafactories to meet global demand.
- •
Scaling the global service, support, and charging infrastructure to match the expanding vehicle fleet.
- •
Ramping production of new, complex products like the Cybertruck and the 4680 battery cells.
Team Readiness
Visionary but concentrated. Leadership is heavily centralized around the CEO, creating both a unique innovation engine and a significant 'key person' risk. Proven ability to execute on large-scale, complex projects.
Agile but strained. The flat, agile structure has enabled rapid innovation but may face challenges in maintaining quality control and operational discipline as the company scales to the size of legacy automakers.
Key Capability Gaps
- •
Global Government and Public Relations: Navigating complex regulatory environments and managing brand perception issues requires a more robust and specialized team.
- •
Mass-Market Manufacturing Consistency: Achieving consistent panel gaps, paint quality, and overall fit-and-finish at the level of established mass-market automakers remains a challenge.
- •
Customer Service at Scale: Building out a world-class customer service organization that can handle millions of customers efficiently.
Growth Engine
Acquisition Channels
- Channel:
Brand & Public Relations (CEO-led)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Diversify the brand's voice beyond the CEO to mitigate volatility and appeal to a broader demographic. Systematize the use of customer stories and technical deep-dives to reinforce product leadership.
- Channel:
Referral Program
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Re-evaluate and potentially re-launch a more compelling referral program, focusing on high-value rewards like exclusive software features or charging credits to stimulate word-of-mouth.
- Channel:
Direct Online Sales Platform
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Enhance the online configurator with more immersive AR/VR experiences and improve the trade-in valuation process to make it more seamless and competitive.
Customer Journey
Highly streamlined and digital-native, moving from 'Learn' to 'Order' on the website with minimal steps. The path is optimized for direct sales.
Friction Points
- •
Uncertainty around delivery timelines and occasional delays.
- •
Difficulty in securing timely service appointments post-purchase.
- •
Navigating complex and changing government incentives and tax credits.
- •
Lack of physical dealerships for some customers who prefer in-person sales experiences.
Journey Enhancement Priorities
{'area': 'Post-Order Communication', 'recommendation': 'Implement a more proactive and detailed communication system for customers awaiting delivery, providing regular updates and a more accurate delivery window.'}
{'area': 'Service Booking', 'recommendation': 'Overhaul the service scheduling section of the Tesla app to improve usability, offer more transparent pricing, and provide better availability of appointments.'}
Retention Mechanisms
- Mechanism:
Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Introduce more personalization options and on-demand features that can be purchased or subscribed to directly from the vehicle's interface.
- Mechanism:
Supercharger Network Ecosystem
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Continue strategic expansion of the network while integrating loyalty programs (e.g., discounted rates for long-term owners) to reinforce the ecosystem's value.
- Mechanism:
Full Self-Driving (FSD) Subscription
Effectiveness:Medium
Improvement Opportunity:Achieve feature-complete, truly autonomous driving to dramatically increase the take rate and value proposition. Experiment with tiered subscription models to lower the entry barrier.
Revenue Economics
Strong but under pressure. Historically best-in-class automotive gross margins are being compressed by increased competition and price cuts. The energy division exhibits strong and improving profitability.
Extremely High (Estimated). Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is famously low due to the lack of traditional advertising. Lifetime Value (LTV) is high and growing, driven by high-margin software sales (FSD), potential for future services (robotaxi network), and energy product cross-sells.
High
Optimization Recommendations
- •
Aggressively scale the high-margin Energy business to diversify revenue and profit pools.
- •
Increase the take-rate of FSD subscriptions to grow recurring revenue.
- •
Leverage manufacturing innovations to further reduce the bill of materials (BOM) and production costs to offset competitive price pressures.
Scale Barriers
Technical Limitations
- Limitation:
Achieving True Level 5 Autonomy
Impact:High
Solution Approach:Continued massive investment in AI, data collection (from the global fleet), and neural net training. Overcoming regulatory hurdles for wide-scale deployment is as critical as solving the technical problem itself.
- Limitation:
Next-Generation Battery Production (4680 cells)
Impact:Medium
Solution Approach:Solving the complex manufacturing challenges of the dry-coating process to ramp up production, lower costs, and increase energy density, which is key for future products like the Semi and Cybertruck.
Operational Bottlenecks
- Bottleneck:
Service Center Capacity
Growth Impact:Limits customer satisfaction and brand loyalty, potentially impacting future sales as the vehicle fleet grows.
Resolution Strategy:Accelerate the build-out of physical service centers and expand the mobile service fleet. Invest in remote diagnostics to reduce the number of physical visits required.
- Bottleneck:
New Product Production Ramps
Growth Impact:Delays in reaching volume production for new models (e.g., Cybertruck, Semi) defer revenue and allow competitors to catch up.
Resolution Strategy:Apply learnings from previous 'production hell' scenarios. Design new products with manufacturing simplicity in mind from the outset (Design for Manufacturing).
- Bottleneck:
Global Supply Chain for Critical Minerals
Growth Impact:Volatility in price and availability of battery materials directly impacts cost of goods sold and production volume.
Resolution Strategy:Continue to secure long-term contracts with diverse global suppliers, invest in battery recycling, and pursue R&D into alternative battery chemistries with more abundant materials.
Market Penetration Challenges
- Challenge:
Intensifying Competition in China
Severity:Critical
Mitigation Strategy:Accelerate the development of a lower-cost vehicle to compete with local brands like BYD. Differentiate on software, autonomous features, and brand cachet. Deepen local partnerships.
- Challenge:
Market Share Decline in Europe
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Refresh existing models (Model 3/Y) to maintain competitiveness against new offerings from VW, BMW, and others. Expand the Supercharger network's accessibility to all EV drivers to generate new revenue and reinforce Tesla's infrastructure leadership.
- Challenge:
Reaching Lower-Priced Market Segments
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Prioritize and expedite the launch of the next-generation, lower-cost vehicle platform to unlock the mass market and drive the next major wave of volume growth.
Resource Limitations
Talent Gaps
- •
AI and Robotics Engineers: Intense competition for top-tier talent from other major tech companies.
- •
Manufacturing Process Engineers: Experts in high-volume, high-quality production are needed to resolve consistency issues.
- •
Global Policy and Regulatory Experts: Crucial for navigating the complex and varied legal landscapes for autonomous driving and new market entry.
Extremely high and ongoing. Billions are required for the construction of new Gigafactories, R&D for FSD and Optimus, and securing raw material supply chains.
Infrastructure Needs
- •
Expansion of Gigafactories in new strategic regions.
- •
Significant build-out of the service and collision repair network globally.
- •
Continued densification of the Supercharger network to support a larger fleet and third-party customers.
Growth Opportunities
Market Expansion
- Expansion Vector:
Geographic Expansion into India & Southeast Asia
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:High
Recommended Approach:Develop a localized, lower-cost vehicle variant. Establish local manufacturing to navigate tariffs and reduce costs. Build out a foundational charging infrastructure before a major vehicle launch.
- Expansion Vector:
Demographic Expansion with a lower-cost vehicle ('Model 2')
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:High
Recommended Approach:Leverage next-gen manufacturing techniques and 4680 cells to achieve a target price point (e.g., ~$25,000) that unlocks the global mass market.
- Expansion Vector:
Commercial Fleets (Semi, Cybertruck, Vans)
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:Medium
Recommended Approach:Establish dedicated sales and support teams for commercial clients. Offer bundled solutions including vehicles, charging infrastructure (Megachargers), and fleet management software.
Product Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Commercialize the Optimus Humanoid Robot
Market Demand Evidence:Significant long-term demand for automation in manufacturing, logistics, and eventually household tasks. Musk projects a massive potential market.
Strategic Fit:High. Leverages Tesla's core competencies in AI, batteries, and advanced manufacturing. Initial use in Tesla's own factories provides a perfect testbed.
Development Recommendation:Focus on deploying thousands of units within Tesla's own factories first to prove utility and refine capabilities before offering it for external sale.
- Opportunity:
Launch a fully autonomous Robotaxi Network
Market Demand Evidence:The global ride-hailing market is enormous. A lower-cost autonomous service could massively expand the total addressable market.
Strategic Fit:High. The ultimate monetization of FSD technology, transforming Tesla from a manufacturer into a high-margin mobility service provider.
Development Recommendation:Continue limited service rollouts in select cities for data gathering and regulatory engagement. Develop the consumer-facing app and fleet management tools in parallel with perfecting the core FSD technology.
- Opportunity:
Expand Energy Division with Virtual Power Plants (VPPs)
Market Demand Evidence:Growing need for grid stability and management of intermittent renewable energy sources. VPPs offer a software-based solution.
Strategic Fit:High. Combines Powerwall, Megapack, and software (AutoBidder) into a synergistic, high-margin energy services business.
Development Recommendation:Partner with more utility companies globally to expand VPP programs. Simplify the enrollment process for residential Powerwall owners to increase participation.
Channel Diversification
- Channel:
Dedicated Fleet & Commercial Sales Division
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Implementation Strategy:Create a separate B2B sales organization with expertise in commercial vehicle financing, fleet management solutions, and corporate ESG goals.
- Channel:
Partnerships with Real Estate Developers
Fit Assessment:Good
Implementation Strategy:Develop a 'Tesla Home' package for new construction, bundling Solar Roof, Powerwall, and a Wall Connector. Offer volume discounts to large developers to make this a standard feature.
Strategic Partnerships
- Partnership Type:
Utility & Grid Operators
Potential Partners
- •
Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E)
- •
National Grid
- •
E.ON
Expected Benefits:Accelerate deployment of Megapack projects for grid stabilization and facilitate the growth of Virtual Power Plants, creating new, high-margin revenue streams.
- Partnership Type:
Insurance Companies
Potential Partners
- •
Allianz
- •
Progressive
- •
State Farm
Expected Benefits:Expand the reach of Tesla Insurance by underwriting policies through established carriers in regions where Tesla is not a licensed insurer. Use real-time driving data to offer more competitive rates.
Growth Strategy
North Star Metric
Weekly Autonomous Miles Driven
This metric shifts the company's core focus from simply selling hardware (cars) to deploying its AI and software capabilities. It's a leading indicator for the readiness of the Robotaxi network, which represents the largest potential value unlock for the company. It directly measures the progress and real-world performance of the core FSD technology.
Achieve a 10x increase in weekly autonomous miles driven by the customer fleet within the next 18 months.
Growth Model
Ecosystem-Led Growth
Key Drivers
- •
Hardware as a Gateway: Vehicles and energy products serve as the entry point into the ecosystem.
- •
High-Margin Software Monetization: FSD subscriptions and future autonomous services generate recurring revenue.
- •
Network Effects: The value of the Supercharger network and the future Robotaxi network increases with each new user.
- •
Vertical Integration: Control over core technologies (AI, batteries, manufacturing) allows for rapid innovation and cost control.
Focus marketing and product development on the synergistic benefits of the ecosystem (e.g., 'Power your Tesla with your own solar energy'). Continue to develop services that lock customers into the ecosystem and increase switching costs.
Prioritized Initiatives
- Initiative:
Launch Next-Generation Low-Cost Vehicle Platform
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:Very High
Timeframe:24-36 Months
First Steps:Finalize vehicle design with a focus on breakthrough manufacturing cost reduction. Secure supply chains for the required volume of 4680 cells.
- Initiative:
Scale Megapack Production and Deployment
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:12-18 Months
First Steps:Ramp up the new Megapack factory in Shanghai to full capacity. Build a dedicated global sales team focused on utility-scale projects.
- Initiative:
Achieve Widespread FSD (Supervised) Rollout in Europe & China
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:12-24 Months
First Steps:Work closely with regulators in key European markets and China to gain approval for FSD. Continue to gather region-specific data to train and validate the driving models.
- Initiative:
Pilot Internal Deployment of Optimus Robots
Expected Impact:Medium (Short-term), Very High (Long-term)
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:18-24 Months
First Steps:Identify 2-3 repetitive, high-value tasks within Gigafactories. Deploy a fleet of 100+ Optimus units to perform these tasks, focusing on reliability and learning rate.
Experimentation Plan
High Leverage Tests
{'test_name': 'Tiered FSD Subscription Pricing', 'hypothesis': 'Offering a lower-priced FSD tier with a subset of features (e.g., advanced Autopilot on highways) will increase the overall number of subscribers and recurring revenue.'}
{'test_name': 'Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Pilot Program', 'hypothesis': 'Partnering with a utility to allow Powerwall and vehicle owners to sell energy back to the grid during peak demand will create a new revenue stream and increase the value proposition of the energy ecosystem.'}
Utilize A/B testing methodology for software features. For pilot programs, track metrics such as adoption rate, customer satisfaction (NPS), revenue generated per participant, and system reliability.
Monthly cycle for software-based experiments. Quarterly review and iteration for larger hardware or partnership-based pilot programs.
Growth Team
Decentralized Growth Pods aligned to key business units (Automotive, Energy, AI/Robotaxi, Optimus) with a central Growth Council for strategy and resource allocation.
Key Roles
- •
Head of Robotaxi Go-to-Market
- •
Director of Energy Services & VPP
- •
Lead AI Product Manager (FSD & Optimus)
- •
Head of International Market Entry
Develop deep internal expertise in AI ethics, regulatory affairs for autonomous systems, and utility-scale energy project finance. Foster a culture of rapid, data-driven experimentation within each business unit.
Tesla stands at a critical juncture, transitioning from an EV market disruptor to a diversified technology conglomerate. Its growth foundation is exceptionally strong, rooted in a powerful brand, clear product-market fit in both automotive and energy sectors, and a scalable, vertically integrated business model. However, the company's first-mover advantage is eroding as the EV market matures, leading to significant scale barriers. Intensifying competition, particularly from Chinese manufacturers like BYD, is compressing margins and challenging market share in key regions like Europe and China.
The primary growth engine, while historically potent due to its brand-driven, low-CAC model, must now evolve. The key to future growth lies not in selling more cars, but in monetizing the existing and future fleet through high-margin, software-defined services. The most significant growth opportunities—and simultaneously the largest risks—are the ambitious bets on full autonomy (Robotaxi network) and humanoid robotics (Optimus). Success in either of these areas would render current automotive competition secondary and unlock a valuation an order of magnitude greater than today.
The recommended growth strategy, therefore, is to pivot the company's core identity and North Star Metric towards becoming an AI and robotics company that happens to make cars. This involves a dual focus: 1) Defending and expanding the core automotive business by launching a lower-cost vehicle to address the mass market and counter competitors. 2) Aggressively investing in and scaling the true long-term value drivers: the Energy division, FSD commercialization, and Optimus development. The primary challenge will be executing on these capital-intensive, technologically complex initiatives while navigating increasing operational strains (service capacity, quality control) and market pressures in the core automotive business.
Legal Compliance
Tesla's Privacy Notice is prominently accessible and articulates a strong 'privacy from day one' stance, stating they do not sell or rent personal data for any purpose. The policy differentiates between data types (vehicle, diagnostic, infotainment, Autopilot) and claims that vehicle data is not associated with a user's identity by default. It addresses key rights under GDPR and CCPA, such as knowledge, access, and deletion. However, the sheer volume of data collected by vehicles (including camera recordings) creates significant regulatory risk. Despite claims of anonymization, Tesla has faced scrutiny and data leak incidents, particularly in Europe, prompting reassessments of its data handling to better align with GDPR's strict standards. The policy's language around data sharing with law enforcement is broad, which could be a point of contention for privacy advocates. Recent actions, spurred by probes like the one from the Dutch DPA, show Tesla is adapting its products (e.g., Sentry Mode) to be more privacy-by-design, shifting some data processing to be in-vehicle by default.
Tesla's website links to a general 'Legal' page which contains multiple agreements, including 'Terms of Use', 'Payment Terms', and product-specific terms. The terms are comprehensive but fragmented across different documents, which could impact clarity for the average user. Key clauses include significant limitations of liability, especially concerning indirect or consequential damages related to their services. A critical aspect is the mandatory arbitration agreement for disputes, which limits users' ability to pursue class-action lawsuits, although some customers have successfully opted out and pursued such actions. Given the ongoing litigation around Full Self-Driving capabilities, the enforceability and scope of liability waivers and disclaimers within these terms are under intense legal scrutiny and represent a major business risk.
The website uses a cookie consent banner that, in some regions, allows for accepting or declining non-essential cookies, which aligns with GDPR principles. Tesla's cookie policy outlines the use of cookies for website functionality and traffic analysis. However, the implementation across different global regions may vary. A key compliance aspect is whether the 'Decline' option is as easily accessible as the 'Accept' option, and whether consent is granular enough to satisfy strict interpretations of ePrivacy regulations. Without a region-by-region audit, it is difficult to confirm universal compliance, but public-facing documents indicate an awareness of the need for consent-based cookie management.
Tesla's data protection framework is built around the principle that users control their data sharing, with opt-in consent required for features like Autopilot data sharing. The company has established a data center in China to comply with data localization requirements, demonstrating a strategic approach to managing regional regulations. It explicitly addresses CCPA, stating it does not sell personal data. However, the company is under review by the California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) due to the vast amount of data collected by its vehicles, which are described as 'connected computers on wheels'. Past incidents involving employee sharing of sensitive customer camera footage have damaged trust and highlighted potential gaps between policy and practice, creating significant legal and reputational risk.
The website content provided shows evidence of considering accessibility, such as a 'Keyboard shortcuts' map legend. However, a dedicated and easily discoverable accessibility statement for 'tesla.com' is not apparent from the provided content or initial search, though unrelated entities with 'Tesla' in their name do have such statements. Achieving compliance with standards like WCAG 2.1 AA is a continuous process. While the site appears largely functional, a lack of a formal statement and commitment could expose Tesla to litigation under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and similar international laws. Given past ADA lawsuits against Tesla's physical locations, ensuring digital accessibility is a critical risk mitigation measure.
Tesla operates in highly regulated automotive, energy, and financial sectors.
1. Automotive Advertising: The marketing of 'Full Self-Driving (Supervised)' is a significant legal risk area. The use of the qualifier 'Supervised' is a deliberate legal strategy to mitigate claims of misleading advertising, but the company still faces numerous class-action lawsuits and regulatory actions from bodies like the California DMV, alleging that historical and current marketing overstates the system's capabilities.
2. Financial Disclosures: Disclaimers for the '$7,500 Federal Tax Credit' are present, but their clarity regarding complex eligibility rules (MSRP caps, income limits, delivery deadlines) is crucial for avoiding deceptive practice claims under consumer protection laws. The IRS provides specific guidance that sellers must follow.
3. Online Vehicle Sales: Tesla's direct-to-consumer model is subject to a patchwork of state-level franchise and online sales laws. While many jurisdictions are adapting to allow online sales, compliance with specific requirements for electronic signatures and documentation remains complex.
4. Solar & Energy: The sale of solar panels and Powerwalls is subject to consumer protection laws that mandate clear disclosures on performance, costs, and financing. States like Washington and California have specific 'Solar Consumer Protection' acts that impose strict rules on contracts and advertising.
Compliance Gaps
- •
Ambiguous FSD Capabilities Advertising: Ongoing lawsuits and regulatory scrutiny indicate that despite adding '(Supervised)', marketing language may still create a misleading impression of autonomy, posing a high risk of consumer protection violations.
- •
Lack of a Clear, Centralized Accessibility Statement: The absence of a prominent WCAG/ADA compliance statement on the main corporate website creates a tangible legal risk for accessibility-related lawsuits.
- •
Fragmented Terms of Service: Legal terms are spread across multiple documents, potentially reducing clarity and enforceability.
- •
Clarity of Financial Offer Disclosures: Disclosures for lease promotions and tax credits may not be sufficiently prominent or detailed to meet the standards of regulations like the Truth in Lending Act (TILA) in all instances.
- •
Inconsistent Regional Cookie Consent: Potential for non-compliant cookie consent mechanisms in jurisdictions with strict opt-in requirements (like the EU), if 'Decline' is not as easy as 'Accept'.
Compliance Strengths
- •
Strong Stated Privacy Position: The public-facing Privacy Notice is clear in its stance against selling personal data and emphasizes user control over data sharing, which is a strong starting point for building trust.
- •
Regional Data Law Compliance Infrastructure: Proactively establishing data centers in regions like China shows a sophisticated understanding of and commitment to complying with complex data localization laws.
- •
Use of Specific Legal Qualifiers: The consistent use of the term 'FSD (Supervised)' is a clear, albeit contested, legal strategy to manage risk and set user expectations.
- •
Clear Data Control Mechanisms: Providing in-vehicle controls for data sharing gives users tangible control, which is a key principle of modern data protection laws like GDPR.
Risk Assessment
- Risk Area:
Automotive Advertising & FSD Claims
Severity:High
Recommendation:Conduct a full audit of all marketing materials (website, videos, social media) to ensure claims about FSD and Autopilot are consistently and prominently qualified with clear disclaimers about driver responsibility. Settle or vigorously defend ongoing class-action lawsuits to establish a clear legal precedent.
- Risk Area:
Data Privacy & Security (Vehicle Data)
Severity:High
Recommendation:Strengthen internal data handling protocols and employee training to prevent unauthorized access or sharing of customer vehicle data. Proactively engage with the California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) to demonstrate robust compliance and mitigate potential enforcement actions.
- Risk Area:
Website Accessibility (ADA/WCAG)
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Engage a third-party auditor to assess tesla.com against WCAG 2.1 AA standards. Publish a formal Accessibility Statement outlining the company's commitment and providing a channel for users to report issues. Implement remediation plan for identified gaps.
- Risk Area:
Financial & Tax Credit Disclosures
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Ensure all advertised lease prices and federal tax credit information are accompanied by clear, conspicuous, and complete disclosures that comply with TILA/Regulation Z and IRS guidelines. Disclaimers should be immediately adjacent to the offer, not just in footnotes.
- Risk Area:
Global E-commerce Compliance
Severity:Low
Recommendation:Implement a geo-targeted compliance framework to ensure that cookie banners, privacy policies, and terms of sale automatically adapt to meet the specific legal requirements of the user's jurisdiction (e.g., GDPR 'Reject All' button for EU users).
High Priority Recommendations
- •
Immediately audit and revise all 'Full Self-Driving' marketing language to further mitigate misleading advertising claims and reduce exposure in ongoing and future litigation.
- •
Publish a comprehensive Website Accessibility Statement conforming to WCAG 2.1 AA standards and create a roadmap for remediation to defend against potential ADA lawsuits.
- •
Strengthen and centralize the Terms of Service for better user clarity and ensure financial offer disclaimers are more prominently displayed to meet regulatory standards.
Tesla's legal positioning is a complex duality. On one hand, the company demonstrates a sophisticated and proactive approach to navigating complex international data privacy laws, such as GDPR and Chinese data localization, by building specific infrastructure and articulating a strong, consumer-friendly privacy stance. This builds customer trust and facilitates market access in heavily regulated regions. On the other hand, its aggressive marketing, particularly around its autonomous driving technology, creates substantial and persistent legal risk. The core tension lies between the marketing promises of 'Full Self-Driving' and the legal reality, stated in disclaimers, that the driver remains fully responsible. This has resulted in a continuous stream of high-stakes class-action lawsuits and intense regulatory scrutiny, which threaten both sales and brand reputation. While the use of the term '(Supervised)' is a clear defensive legal strategy, its effectiveness is still being tested in courts. The company's compliance strengths in data privacy are a strategic asset, but they are partially undermined by the high-profile risks associated with its product advertising. To improve its strategic legal positioning, Tesla must work to close the gap between its marketing narrative and its legal disclaimers, enhance its digital accessibility, and ensure its financial disclosures are impeccably clear.
Visual
Design System
Minimalist
Excellent
Advanced
User Experience
Navigation
Horizontal Top Bar with Mega Menus
Intuitive
Excellent
Information Architecture
Logical
Clear
Light
Conversion Elements
- Element:
Primary CTA ('Order Now', 'Demo Drive')
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:A/B test microcopy to explore urgency or benefit-driven language (e.g., 'Order for Next Month Delivery' vs. 'Order Now').
- Element:
Secondary CTA ('Learn More', 'View Inventory')
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:Ensure the destination pages for 'Learn More' are highly focused and immediately answer top user questions to reduce bounce rate.
- Element:
Vehicle Configurator
Prominence:High (Post-CTA)
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:Incorporate more dynamic cost updates (e.g., estimated monthly payment) that adjust in real-time as a user selects different options to improve transparency.
Assessment
Strengths
- Aspect:
Immersive Visual Storytelling
Impact:High
Description:The site uses full-screen, high-resolution video and imagery to create an emotionally resonant and premium experience. This approach doesn't just display products; it sells a futuristic, sustainable lifestyle, which is central to Tesla's brand identity.
- Aspect:
Minimalist Design & Focus
Impact:High
Description:The clean, uncluttered interface with ample white space directs user attention squarely onto the products and key calls-to-action. This minimalist aesthetic reflects the brand's 'Apple-like' design philosophy of simplicity and technological elegance, reducing cognitive load and streamlining the user journey.
- Aspect:
Clear Conversion Pathways
Impact:High
Description:The site architecture and visual hierarchy are laser-focused on guiding users toward conversion. Prominent, consistently styled primary and secondary CTAs on every major product panel create a clear, frictionless path from discovery to purchase or test drive.
Weaknesses
- Aspect:
Limited 'At-a-Glance' Information
Impact:Medium
Description:The heavy reliance on visual storytelling means that detailed specifications and comparative data are not immediately available on the homepage. Users seeking quick, technical comparisons must click deeper into the site, which could be a point of friction for analytical buyers.
- Aspect:
Potential for High Page Load Times
Impact:Low
Description:The use of full-screen video and high-resolution images can lead to longer load times on slower internet connections, potentially impacting user experience. However, this is a calculated trade-off for the immersive brand experience, and performance is generally well-optimized for their target demographic's typical bandwidth.
- Aspect:
Ambiguous Micro-Interactions
Impact:Low
Description:Certain secondary interactions, like the 'Ask a Question' feature that opens a simple text field pre-filled with a comparison query, can be unintuitive. It sets the expectation of a chat or search function but provides a rigid, less helpful interaction.
Priority Recommendations
- Recommendation:
Introduce an Interactive Comparison Module
Effort Level:Medium
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Add a subtle, expandable module on the homepage or at the top of the 'Vehicles' page that allows users to select two models for a quick, side-by-side comparison of key specs (Range, 0-60, Price). This caters to analytical buyers without cluttering the primary visual-first experience.
- Recommendation:
A/B Test CTA Language
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Systematically test alternative copy for primary and secondary CTAs. Explore language that creates urgency, highlights benefits (e.g., 'Reserve Your Cybertruck'), or clarifies the next step (e.g., 'Build Your Model 3') to optimize click-through rates based on data-driven insights.
- Recommendation:
Enhance the 'Find Your Charge' Module
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:Low
Rationale:Make the supercharger map more interactive directly on the homepage. Allow users to input a zip code or city to see local chargers instantly, which would more effectively address the common customer pain point of 'range anxiety' earlier in the journey.
Mobile Responsiveness
Excellent
The design seamlessly transitions between breakpoints. The single-column, full-width block structure is perfectly suited for vertical stacking on mobile devices. Font sizes, touch targets, and image crops are all appropriately adjusted.
Mobile Specific Issues
No itemsDesktop Specific Issues
No itemsComprehensive Visual & UX Audit: Tesla.com
Tesla.com serves as a masterclass in minimalist, product-centric design that perfectly embodies its brand identity of innovation, luxury, and sustainability. The website eschews traditional automotive marketing in favor of a direct-to-consumer digital experience that feels more akin to a high-end technology company like Apple.
1. Design System and Brand Identity
The website's design system is mature and rigorously consistent. It is built on a foundation of:
* Minimalism: An extremely clean aesthetic with a limited color palette (black, white, grays, and a single blue accent for primary actions) ensures the focus remains on the product.
* Typographic Hierarchy: A simple, modern sans-serif font is used with clear size and weight distinctions to guide the user's eye from headline to sub-text to CTA.
* Immersive Imagery: The entire experience is driven by stunning, full-screen product photography and videography. This isn't just decoration; it's the core of the site's storytelling, conveying performance, luxury, and a vision of the future.
This cohesive system flawlessly expresses Tesla's brand identity—cutting-edge, premium, and relentlessly focused on the product.
2. Visual Hierarchy and User Flow
The visual hierarchy on each page section is unambiguous. The sequence is always:
- Dominant Visual (Car, Solar Roof, etc.)
- Bold Headline (e.g., 'Model 3')
- Concise Sub-headline (Key feature or offer)
- Primary & Secondary CTAs ('Order Now' & 'Learn More')
This creates an effortless, scannable experience that guides users intuitively. The information architecture is flat and product-focused, with a simple top navigation bar leading to the main business verticals (Vehicles, Energy, etc.). The primary user flow is exceptionally streamlined, designed to move a visitor from initial interest to the configuration and ordering process with minimal friction.
3. Conversion Elements and Effectiveness
Conversion is the clear goal of the design. The dual-CTA pattern is used consistently and effectively:
* Primary CTAs (Order Now, Demo Drive) use a high-contrast blue, making them the most prominent interactive element in any view.
* Secondary CTAs (Learn More, View Inventory) are styled with a more subdued white/gray, visually signaling a lower-commitment, information-gathering action.
This clear visual distinction helps users self-segment based on their stage in the buying journey and makes the desired actions obvious.
4. Visual Storytelling
Tesla's website excels at selling an idea, not just a product. The homepage functions like a vertical slideshow, where each scroll reveals a new chapter of the Tesla ecosystem—from a silent, powerful car gliding down a highway to a home powered by solar and Powerwall. This immersive, narrative-driven approach connects with users on an emotional level, aligning with the brand's mission to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy.
Conclusion
Tesla.com is a powerful example of a highly-optimized digital flagship store. Its strengths—immersive visuals, minimalist focus, and clear conversion paths—are deeply integrated and serve the brand's business objectives directly. While minor opportunities exist to cater more to data-driven users with easier access to comparative specs, the overall strategy is exceptionally effective. The site successfully translates a complex, high-consideration purchase into a simple, desirable, and digitally native experience.
Discoverability
Market Visibility Assessment
Tesla's brand authority is unparalleled in the electric vehicle (EV) and sustainable energy sectors. Its digital presence reflects a company that doesn't need to introduce itself; it assumes the user is already aware of its products. The brand is synonymous with the EV category itself, making it the benchmark against which all competitors are measured. This authority is primarily driven by product innovation, first-mover advantage, and the significant public profile of its CEO, rather than a conventional content marketing strategy. Its thought leadership is demonstrated through product launches and technological milestones (like Full Self-Driving updates), not explained through typical blog posts or whitepapers.
Digitally, Tesla commands a dominant share of visibility for branded search terms. Its domain authority is so high that it also ranks prominently for many high-volume, non-branded EV terms. However, as the market matures, competitors like Ford, Hyundai, Rivian, and VW are increasingly targeting these non-branded keywords with dedicated content, chipping away at Tesla's organic visibility for top-of-funnel search queries. Tesla's visibility is a direct proxy for its historical market leadership, but this is the area with the highest risk of competitive encroachment.
The customer acquisition potential through its digital presence is extremely high and functions as a direct-to-consumer sales channel. The website is optimized for conversion, guiding users with existing interest towards a 'Demo Drive' or 'Order'. The primary function of the digital presence is to capture and convert demand generated off-site (e.g., through media coverage, social buzz, word-of-mouth). The potential for growth lies in capturing customers earlier in their research phase, before they are firmly decided on a specific brand.
The website's architecture, with extensive and clearly delineated sections for dozens of countries and languages, indicates a sophisticated and aggressive global market penetration strategy. This digital infrastructure is a core enabler of its global direct sales model, allowing for tailored messaging, pricing, and offers on a regional basis. This represents a significant competitive advantage over newer entrants who are still building out their global presence.
Tesla's topic coverage is deep but strategically narrow. It focuses almost exclusively on its own product ecosystem: vehicles, charging technology, energy storage, and the associated ownership experience. There is a deliberate lack of content on broader, comparative industry topics (e.g., 'Level 2 vs. DC Fast Charging', 'Comparing EV battery types'). This creates a 'walled garden' that educates users on the 'Tesla way,' but leaves a gap for competitors to capture users seeking more general, unbiased industry information.
Strategic Content Positioning
The website content is heavily skewed towards the consideration and decision stages of the customer journey. CTAs like 'Order', 'Compare', 'Trade-in', and 'Lease From...' target users who are actively in the market. The 'Learn' sections and 'Customer Stories' serve the mid-funnel, but there is a clear gap at the top of the funnel (Awareness stage). This awareness is currently outsourced to PR and social media, which is a powerful but potentially volatile strategy.
Tesla's thought leadership is currently demonstrated, not articulated. The opportunity is to translate its technological and mission-driven leadership into accessible, educational content. This could include an 'Engineering Blog' explaining the first-principles thinking behind its innovations, or a data-driven 'Impact Report' section detailing the environmental benefits of its fleet and energy products. Such content would solidify its authority beyond just product specifications.
Competitors are actively filling the educational content gap left by Tesla. They are creating beginner's guides to EV ownership, detailed comparisons (including against Tesla models), and content addressing common EV concerns like range anxiety and battery life. By not competing on these informational keywords, Tesla misses the opportunity to frame the conversation and capture potential buyers at the beginning of their search, ceding that initial touchpoint to rivals.
Brand messaging is exceptionally consistent and disciplined across the entire digital presence. The aesthetic is minimalist, futuristic, and product-focused. The tone is confident and direct. The core messages of performance, safety, technology, and accelerating the transition to sustainable energy are implicitly or explicitly present on every key page, creating a powerful and cohesive brand experience.
Digital Market Strategy
Market Expansion Opportunities
- •
Develop a comprehensive 'EV Ownership' educational hub to attract and educate first-time electric vehicle buyers.
- •
Create in-depth content for B2B segments, including fleet management ROI calculators, case studies for Megapack installations, and guides for businesses hosting commercial chargers.
- •
Target the pre-owned market with content focused on long-term reliability, battery health, and the value of over-the-air updates for used vehicles.
Customer Acquisition Optimization
- •
Create targeted content for specific customer personas and use cases (e.g., 'Best Tesla for Families', 'Road Tripping in a Tesla') to capture long-tail search intent.
- •
Develop robust comparison tools that not only compare Tesla models but also frame the advantages of the Tesla ecosystem against key competitors.
- •
Proactively create content that addresses and debunks common myths or concerns about EV and Tesla ownership, using data from its extensive fleet.
Brand Authority Initiatives
- •
Launch a dedicated 'Tesla Engineering' or 'Data Science' section to publish articles on the technology behind their products, showcasing their expertise.
- •
Systematize the publication of safety and impact reports based on anonymized fleet data, cementing their data-driven leadership in the industry.
- •
Transform 'Customer Stories' into high-quality, in-depth video case studies that highlight the tangible benefits of the Tesla ecosystem (Supercharging network, service, software).
Competitive Positioning Improvements
- •
Develop a content pillar around 'Total Cost of Ownership' to highlight a key competitive advantage over both internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and other EVs.
- •
Create content that explicitly defines and promotes the 'Tesla Ecosystem Advantage' (Superchargers, app, software updates) as a primary differentiator.
- •
Target keywords related to competitor weaknesses, such as public charging unreliability, and position the Supercharger network as the solution.
Business Impact Assessment
The primary indicator of digital market share is the volume of branded search traffic and direct website visits. A key metric to monitor for competitive pressure is the share of non-branded organic traffic for high-intent keywords like 'electric SUV' or '7-seat EV' compared to rivals.
The most important metrics are direct online reservations and completed orders initiated through the website. Leading indicators of acquisition potential include the number of 'Demo Drive' sign-ups, 'Trade-in' value requests, and engagement with finance and leasing calculators.
Brand authority can be measured by share of voice in online media coverage, growth in branded search volume, the number and quality of backlinks from authoritative domains (tech, auto, finance), and overall sentiment analysis on social media platforms.
Success should be benchmarked by tracking organic search ranking and visibility for a basket of high-value, non-branded keywords against a defined set of primary competitors (e.g., Ford, Rivian, Hyundai, Lucid). Another key benchmark is visibility on direct comparison searches, such as 'Model Y vs. Mustang Mach-E'.
Strategic Recommendations
High Impact Initiatives
- Initiative:
Launch the 'Tesla Learning Center': An Educational Hub for New EV Adopters
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Captures the growing mainstream market of first-time EV buyers early in their research journey, allowing Tesla to frame the narrative around EV ownership and counter competitor FUD.
Success Metrics
- •
Organic traffic growth for informational keywords
- •
Top 3 rankings for 'how to' and 'what is' queries related to EVs
- •
Increase in 'Demo Drive' referrals from the Learning Center
- Initiative:
Develop a B2B Content Platform for 'Tesla for Business'
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Targets high-value commercial and enterprise customers for Fleet, Megapack, and Commercial Charging solutions. Establishes Tesla as the premier partner for corporate transition to sustainable energy.
Success Metrics
- •
Number of qualified B2B leads generated (e.g., 'Schedule a Consultation')
- •
Downloads of case studies and ROI calculators
- •
Organic traffic for commercial-intent keywords like 'utility scale battery storage'
- Initiative:
Create an 'Ecosystem Advantage' Content Series
Business Impact:Medium
Market Opportunity:Builds a stronger competitive moat by clearly articulating the value of Tesla's integrated ecosystem (Supercharger network, software, service) which is difficult for competitors to replicate. This helps justify premium pricing and enhances customer loyalty.
Success Metrics
- •
Video views and engagement rates on ecosystem-focused content
- •
Increase in search queries combining brand with ecosystem terms (e.g., 'Tesla supercharger map')
- •
Mentions of the ecosystem in positive third-party reviews
Transition from a purely product-centric digital strategy to a more balanced 'Product and Ecosystem Authority' strategy. While continuing to leverage its dominant brand for direct conversions, Tesla must strategically invest in top-of-funnel educational content to capture and nurture the next wave of mainstream and B2B customers. This involves using its vast data and engineering expertise to create content that not only sells cars but also solidifies its position as the definitive source of knowledge in the electric transition, thereby widening its competitive moat.
Competitive Advantage Opportunities
- •
Leverage real-world fleet data to create unparalleled, authoritative content on EV safety, battery longevity, and real-world range that competitors can only theorize about.
- •
Systematically create content around the reliability and coverage of the Supercharger network, directly contrasting it with the fragmented and often unreliable nature of third-party charging networks used by competitors.
- •
Showcase the value of over-the-air (OTA) software updates through 'feature-focused' content that demonstrates how a Tesla improves over time, a concept foreign to traditional automakers.
Digital Market Presence Analysis: Tesla, Inc.
Executive Summary:
Tesla's digital presence on tesla.com is a masterclass in leveraging dominant brand power for direct-to-consumer conversion. The website functions less as a marketing tool and more as a digital showroom and point-of-sale, reflecting the company's status as the category definer. Its core strength lies in its minimalist, product-focused design and a clear, frictionless path to ordering for high-intent buyers. The brand's authority is so immense that it has historically not needed to engage in traditional content marketing; its products and CEO-driven publicity have been sufficient to generate overwhelming demand.
However, the EV market is rapidly maturing. A wave of credible competitors from both legacy auto and new EV startups is entering the space. These competitors cannot compete with Tesla on brand recognition, so they are strategically competing on information. They are creating comprehensive educational content to intercept potential customers at the very beginning of their buying journey, answering the fundamental questions that first-time EV buyers have. This represents the primary strategic threat to Tesla's long-term digital dominance.
Strategic Imperative:
Tesla's strategic imperative is to evolve its digital presence from a pure conversion engine into an ecosystem and knowledge authority. While maintaining its streamlined purchasing funnel, the company must build a content moat to defend its market leadership and capture the next, more mainstream wave of consumers and B2B clients.
Key Strategic Recommendations:
-
Capture the Top of the Funnel: Tesla must invest in building a comprehensive educational hub for those new to electric vehicles. By creating the definitive resource for topics like home charging, range management, and battery technology, Tesla can frame the conversation on its own terms and ensure potential buyers start their journey within the Tesla ecosystem, rather than on a competitor's blog.
-
Weaponize the Ecosystem Advantage: The Supercharger network, over-the-air software updates, and integrated mobile app are Tesla's most durable competitive advantages. The digital strategy must shift to explicitly and repeatedly articulating the value of this ecosystem. Content should focus on the seamless, reliable, and constantly improving ownership experience that competitors cannot easily replicate.
-
Dominate the B2B Narrative: The commercial and utility sectors represent a massive growth opportunity. Tesla should develop a dedicated content platform for its B2B offerings (Megapack, Fleet, Commercial Charging), using data-rich case studies, ROI analyses, and industry insights to establish itself as the indispensable partner for any organization's transition to sustainable energy.
Conclusion:
Tesla's current digital presence is a reflection of its past and present success. To secure its future market leadership in a more crowded and competitive landscape, it must strategically invest in educational and ecosystem-focused content. By doing so, it can transition from being simply the most popular choice to being the most trusted authority, capturing customers earlier, building deeper loyalty, and creating a competitive moat that extends far beyond vehicle specifications.
Strategic Priorities
Strategic Priorities
- Title:
Accelerate Launch of Next-Generation, Mass-Market Vehicle Platform
Business Rationale:The analysis indicates that the most significant threat to Tesla's market leadership is intensifying competition from low-cost EV manufacturers, particularly BYD. The current premium-focused lineup is vulnerable to price wars and market share erosion. A lower-cost vehicle is essential to enter the high-volume mass market, drive the next wave of adoption, and build a competitive moat against these challengers.
Strategic Impact:This initiative transforms Tesla from a premium/niche player into a true mass-market manufacturer, dramatically increasing its Total Addressable Market (TAM) and vehicle volume. It secures long-term growth by capturing the largest segment of the global automotive market and reinforces the data-gathering flywheel for FSD.
Success Metrics
- •
Target vehicle sale price under $30,000
- •
Automotive gross margin >20% for the new platform
- •
Achieve production run-rate of 2 million units/year within 24 months of launch
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Long-term Vision
Category:Market Position
- Title:
Establish and Scale 'Tesla Energy' as a Standalone Global Utility Partner
Business Rationale:The Energy division (Megapack, Powerwall) is identified as the fastest-growing and potentially highest-margin segment of the business. Aggressively scaling this division diversifies revenue away from the cyclical and increasingly competitive auto market. It positions Tesla as a core infrastructure provider for the global transition to renewable energy, a massive and durable market.
Strategic Impact:This elevates the Energy division to be a co-equal pillar of the company alongside Automotive. It creates a powerful, high-margin revenue stream and positions Tesla at the center of the future energy grid, creating a deep competitive moat in the utility and commercial sectors that car manufacturers cannot easily replicate.
Success Metrics
- •
Annual Megawatt-hours (MWh) deployed (target 100% YoY growth)
- •
Energy division gross margin exceeding 25%
- •
Secure long-term partnership agreements with 5 of the top 20 global utility companies
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative
Category:Revenue Model
- Title:
Overhaul Post-Sale Customer Experience and Service Operations
Business Rationale:The analysis consistently highlights service center capacity, wait times, and inconsistent build quality as major weaknesses and operational bottlenecks. As competition increases, the post-sale experience becomes a critical differentiator and driver of brand loyalty. Failing to address this threatens long-term customer retention and cedes a key advantage to legacy automakers with established service networks.
Strategic Impact:Transforms customer service from a liability into a competitive advantage. This shift improves brand loyalty, increases high-margin service revenue, and reduces a key friction point for potential buyers, thus protecting market share in a mature market.
Success Metrics
- •
Reduce average service wait time by 50%
- •
Increase Net Promoter Score (NPS) for service interactions by 20 points
- •
Decrease warranty claims per vehicle by 25% through improved manufacturing quality control
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative
Category:Operations
- Title:
Launch a Dedicated Commercial and Fleet Division
Business Rationale:The B2B market represents a significant, untapped revenue opportunity identified in the analysis. Commercial clients have different needs (Total Cost of Ownership, uptime, fleet management software) that are not fully served by the current consumer-focused model. A dedicated division can effectively sell and service products like the Semi, Cybertruck, and future vans to high-value fleet customers.
Strategic Impact:Opens up a new, high-volume revenue stream with potentially higher predictability than consumer sales. This move establishes Tesla as a key partner for corporate electrification, bundling vehicles, charging infrastructure, and energy solutions into a comprehensive B2B platform.
Success Metrics
- •
Secure 5 major enterprise fleet contracts for Semi or Cybertruck
- •
Generate $5B in annual revenue from the commercial division within 3 years
- •
Launch a comprehensive 'Tesla for Business' software platform for fleet management
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative
Category:Market Expansion
- Title:
Operationalize a Pilot Autonomous Ride-Hailing Service in a Key Market
Business Rationale:The long-term valuation and core technological promise of Tesla hinge on solving full autonomy. The analysis identifies the Robotaxi network as the ultimate monetization of FSD. Moving from R&D to a live, albeit limited, service is a critical step to navigate regulatory hurdles, validate the business model, and demonstrate a clear path to commercialization, solidifying the company's position as an AI leader, not just a car maker.
Strategic Impact:This initiative provides concrete proof of the viability of the autonomous network, fundamentally shifting Tesla's business model from one-time hardware sales to high-margin, recurring service revenue. It would create an entirely new industry and provide a nearly insurmountable competitive advantage.
Success Metrics
- •
Secure regulatory approval for pilot service in at least one major city
- •
Achieve 1 million paid, fully autonomous miles driven within the pilot program
- •
Develop and release a consumer-facing ride-hailing app with a clear pricing model
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Long-term Vision
Category:Business Model
Tesla must evolve from a product-led, hardware-centric disruptor into a diversified AI, energy, and transportation company focused on operational excellence. The strategic imperative is to defend its core automotive business by entering the mass market while aggressively scaling its high-margin energy and future autonomous software divisions to secure long-term, defensible growth.
The key competitive advantage to build is the seamlessly integrated and intelligent ecosystem. This includes the vehicle, the proprietary charging network, at-home energy solutions (solar and battery), and the overarching AI-driven software platform that continuously improves the entire system.
The primary growth catalyst is the successful commercialization of autonomous technology. Transitioning Full Self-Driving from a feature-sale into a revenue-generating Robotaxi network will unlock exponential growth and shift the company's valuation from manufacturing multiples to high-margin tech and service multiples.