eScore
ti.comThe eScore is a comprehensive evaluation of a business's online presence and effectiveness. It analyzes multiple factors including digital presence, brand communication, conversion optimization, and competitive advantage.
Texas Instruments' digital presence is world-class and expertly tailored to its core audience of engineers. The website's vast library of datasheets, application notes, and reference designs demonstrates exceptional search intent alignment for highly specific, technical queries. Their content authority is immense, built on decades of reliable technical documentation and a dominant brand reputation, resulting in a high domain authority. The platform's global reach is supported by localized content and a direct-to-customer model that strengthens their digital footprint in key markets like automotive and industrial.
Unmatched content authority driven by an exhaustive repository of technical documentation (datasheets, reference designs, E2E forums) that directly aligns with the search intent of design engineers.
Systematically optimize the vast library of PDF-based datasheets and application notes for voice search and featured snippets by creating HTML summary pages that answer common technical questions in a conversational format.
TI's messaging is highly effective due to its precise focus on its primary persona: the design engineer. The brand voice is consistently expert, technical, and direct, which builds credibility and clearly communicates the value proposition of innovation and reliability. The messaging clearly differentiates TI from competitors by emphasizing its broad portfolio, manufacturing scale, and deep application expertise. While the messaging is excellent for its core audience, it is less developed for non-technical stakeholders like procurement executives who may be influenced by different value propositions.
Exceptional messaging alignment with the target audience (design engineers), using a technical and expert brand voice that builds immediate credibility and efficiently communicates product value.
Develop dedicated content streams and messaging for non-engineer personas, such as procurement managers, that explicitly highlight the business benefits of TI's supply chain stability, long product lifecycles, and total cost of ownership.
The website offers a highly optimized conversion experience, where 'conversion' means empowering an engineer to 'design-in' a TI component. The user journey from discovering a product to accessing datasheets, downloading simulation models (PSpice), and ordering samples is streamlined and low-friction. The cognitive load is managed effectively through clear information architecture, despite the complexity of over 80,000 products. The site is well-structured for cross-device use, though complex data tables can be challenging on mobile.
A frictionless conversion path focused on the engineer's workflow, providing immediate access to critical decision-making tools like datasheets, simulation models, and sample requests directly from product pages.
Implement more interactive data visualization tools on product pages, such as comparison charts and parameter filters, to reduce the cognitive load of evaluating dense technical tables and accelerate component selection.
TI has built formidable credibility over decades, which is strongly reflected online through a clear hierarchy of trust signals, including detailed technical specifications and transparent product lifecycle statuses. Third-party validation is evident through its documented market leadership in the analog semiconductor industry. Risk mitigation is a core part of their value proposition, emphasizing supply chain control through in-house manufacturing. Customer success is demonstrated through technical case studies and the highly active E2E support forums where engineers validate solutions.
Deep, intrinsic credibility built on a long history of reliable products, transparent technical documentation, and market leadership, reinforced by a value proposition centered on supply chain control.
Increase the visibility of customer success evidence by featuring more prominent case studies and testimonials on key product and application pages, translating technical wins into tangible business outcomes for prospective customers.
TI's competitive advantages, or 'moat,' are exceptionally strong and sustainable. The primary advantage is its massive investment in vertically integrated 300mm manufacturing, which provides a durable cost and supply chain advantage that is nearly impossible for competitors to replicate. High switching costs are created once an engineer designs a TI component into a long-lifecycle product, especially in the automotive and industrial sectors. The breadth of its 80,000+ product portfolio functions as a significant barrier to entry and encourages customers to consolidate their purchasing with TI.
A highly sustainable competitive moat built on massive, capital-intensive investment in proprietary 300mm wafer fabs, which provides a structural cost and supply chain advantage over competitors.
More aggressively market the supply chain resilience and cost benefits of the in-house manufacturing model as a primary competitive differentiator, especially to procurement and executive-level decision-makers.
The business model is highly scalable, with significant operational leverage derived from its high fixed-cost manufacturing base; once fabs are operational, each additional unit produced has a lower marginal cost. The company shows strong market expansion signals by strategically focusing over 70% of its business on the high-growth industrial and automotive sectors. Unit economics are excellent, as a single 'design-in' win can result in over a decade of high-margin revenue with minimal recurring acquisition cost. The primary constraint on scalability is the immense capital investment and long lead times required for new fab construction.
Exceptional operational leverage from its 300mm manufacturing model, which allows for highly profitable scaling of production volume to meet demand in burgeoning markets like EVs and industrial automation.
Develop and promote more system-level 'solution blueprints' that bundle multiple TI products, accelerating expansion by making it easier for engineering teams to adopt the TI ecosystem for entire subsystems, rather than just single components.
Texas Instruments exhibits a remarkably coherent and focused business model. The company's strategy is transparently centered on leveraging four sustainable competitive advantages: manufacturing/technology, broad portfolio, market reach, and diverse/long-lived positions. Resource allocation is highly disciplined, with massive capital expenditure directed towards 300mm fabs to reinforce its primary manufacturing moat. The strategic focus on the industrial and automotive markets is clear and perfectly timed with secular growth trends in electrification and automation.
Exceptional strategic focus, with a clear, consistent, and publicly articulated business model centered on leveraging manufacturing scale to dominate the industrial and automotive semiconductor markets.
Explore adjacent, high-margin revenue streams by licensing proprietary software and algorithms (e.g., advanced battery gauging, motor control) as standalone products to monetize the intelligence layer that complements its hardware.
As the market share leader in the vast analog semiconductor market, TI exerts significant market power. Its pricing power is demonstrated by consistently high gross margins, supported by its cost advantages from 300mm manufacturing. The company's direct-to-customer sales model and vast customer base (>100,000) mitigate dependency risk on any single client or distributor. TI's market influence is substantial, often setting de facto industry standards through its widely adopted components and extensive technical documentation.
Dominant market share in the analog semiconductor industry, which, combined with a highly diversified customer base, provides significant pricing power and resilience against market fluctuations.
Address market share erosion in certain segments by increasing R&D investment in high-performance niches where competitors like Analog Devices are gaining ground, ensuring TI's portfolio remains competitive at the cutting edge.
Business Overview
Business Classification
Integrated Device Manufacturer (IDM)
B2B Technology & Components Supplier
Semiconductors
Sub Verticals
- •
Analog ICs
- •
Embedded Processors
- •
Power Management
- •
Digital Signal Processors (DSPs)
- •
Wireless Connectivity
- •
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Mature
Maturity Indicators
- •
Long operating history (founded 1930)
- •
Established global brand recognition and reputation
- •
Consistent dividend payments for over two decades.
- •
Large-scale, vertically integrated global manufacturing operations.
- •
Extensive and deep patent portfolio in analog and embedded processing
- •
Serves approximately 100,000 customers worldwide.
Enterprise
Steady (with cyclical market fluctuations)
Revenue Model
Primary Revenue Streams
- Stream Name:
Product Sales: Analog Semiconductors
Description:Sale of a broad range of analog integrated circuits, including power management, signal chain, and high-volume products. These are essential components in virtually all electronic devices. This segment is the largest revenue contributor, accounting for approximately 78% of total revenue.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Industrial, Automotive, Personal Electronics, and others
Estimated Margin:High
- Stream Name:
Product Sales: Embedded Processing
Description:Sale of microcontrollers (MCUs), digital signal processors (DSPs), and applications processors that function as the 'brains' in electronic equipment.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Automotive, Industrial, Communications Equipment
Estimated Margin:High
- Stream Name:
Royalties and Licensing
Description:Revenue generated from licensing Texas Instruments' extensive intellectual property portfolio, including patents related to Digital Light Processing (DLP) technology and other semiconductor innovations.
Estimated Importance:Tertiary
Customer Segment:Consumer Electronics Manufacturers, Enterprise
Estimated Margin:High
Recurring Revenue Components
Long-term supply agreements with major OEMs in automotive and industrial sectors
High customer 'stickiness' due to design-in lock-in effect, where TI components become integral to long-lifecycle products
Pricing Strategy
Volume-Based Pricing
Mid-range to Premium
Semi-transparent
Pricing Psychology
- •
Tiered Pricing (price breaks at higher volumes, e.g., 1ku pricing shown on site)
- •
Bundling (offering a suite of compatible analog and embedded parts for a single system design)
- •
Reference Pricing (engineers compare price against performance specifications)
Monetization Assessment
Strengths
- •
Highly diversified revenue across tens of thousands of customers and products, reducing reliance on any single entity.
- •
Focus on high-margin analog and embedded processing products with long lifecycles.
- •
Increasing direct sales channel (ti.com) enhances margins and customer relationships.
Weaknesses
High sensitivity to the cyclical nature of the semiconductor industry.
Revenue can be impacted by global macroeconomic conditions affecting end markets like automotive and industrial.
Opportunities
- •
Increasing semiconductor content in electric vehicles (EVs) and Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS).
- •
Growth of IoT and factory automation driving demand for analog and embedded chips.
- •
Expansion into next-generation power semiconductors like Gallium Nitride (GaN)
Threats
- •
Intense competition from both broad-based and niche semiconductor suppliers.
- •
Geopolitical tensions impacting global supply chains and access to key markets.
- •
Rapid technological shifts could make certain product lines obsolete
Market Positioning
Technology Leadership, Portfolio Breadth, and Manufacturing Scale
Market Leader (approximately 19-20% share in the analog semiconductor market).
Target Segments
- Segment Name:
Industrial Systems Integrators & OEMs
Description:Engineers and companies designing and manufacturing systems for factory automation, building automation, medical devices, grid infrastructure, and test & measurement equipment.
Demographic Factors
B2B customers
Global distribution
Psychographic Factors
- •
Value reliability and long-term product availability
- •
Risk-averse
- •
Focused on total cost of ownership
Behavioral Factors
- •
Long design cycles
- •
Require extensive technical documentation and support
- •
Purchase through distributors and direct channels
Pain Points
- •
Supply chain instability
- •
Need for robust components that operate in harsh environments
- •
Pressure to improve energy efficiency
- •
Long-term product lifecycle management
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
Automotive Manufacturers & Tier-1 Suppliers
Description:Engineers and companies developing electronics for vehicles, including infotainment, body electronics, powertrain systems (especially for EVs), and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Demographic Factors
Large enterprise B2B customers
Global operations
Psychographic Factors
- •
Prioritize functional safety (ASIL standards) and extreme reliability
- •
Value long-term partnerships with suppliers
- •
Focused on innovation and differentiation
Behavioral Factors
- •
Very long design and qualification cycles (years)
- •
Demand for long-term supply commitments
- •
Deep engineering collaboration with component suppliers
Pain Points
- •
Meeting stringent automotive quality and safety standards
- •
Managing component supply for long vehicle production runs
- •
Increasing electronic complexity in vehicles
- •
Thermal management and power efficiency for EVs
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
Personal & Consumer Electronics Engineers
Description:Design teams at companies creating smartphones, laptops, wearables, home appliances, and other consumer gadgets.
Demographic Factors
Mix of large enterprises and smaller design houses
Primarily located in Asia and North America
Psychographic Factors
- •
Highly sensitive to cost and time-to-market
- •
Value miniaturization and power efficiency
- •
Driven by feature innovation
Behavioral Factors
- •
Fast-paced design cycles
- •
High-volume purchasing
- •
Utilize online design resources and reference designs heavily
Pain Points
- •
Intense cost pressure
- •
Need for smaller components with lower power consumption
- •
Short product lifecycles require rapid innovation
- •
Quickly scaling production volumes
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:Medium
Market Differentiation
- Factor:
Vertically Integrated Manufacturing (IDM Model)
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Unmatched Product Portfolio Breadth
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Extensive Ecosystem of Design Tools & Support
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
Value Proposition
To provide electronics designers with the industry's broadest and most reliable portfolio of analog and embedded processing semiconductors, supported by scalable in-house manufacturing and accessible design tools, to accelerate innovation and reduce time-to-market.
Excellent
Key Benefits
- Benefit:
One-Stop Shop for Analog & Embedded Components
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Unique
Proof Elements
Catalog of over 80,000 products.
Website features like cross-reference search and extensive product categories
- Benefit:
Supply Chain Control and Reliability
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Unique
Proof Elements
Heavy investment in company-owned 300mm wafer fabs.
Vertically integrated manufacturing model provides more control over production.
- Benefit:
Simplified and Accelerated Design Process
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
- •
Extensive library of reference designs
- •
Active engineer-to-engineer support forums (E2E)
- •
Detailed datasheets and application notes for every product
Unique Selling Points
- Usp:
Industry-leading, cost-effective 300mm wafer manufacturing for analog chips.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
A direct-to-customer sales and support model via TI.com, providing engineers direct access to inventory and support.
Sustainability:Medium-term
Defensibility:Moderate
- Usp:
Deep, long-lived product positions in the highly regulated and stable automotive and industrial markets.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
Customer Problems Solved
- Problem:
Sourcing a wide variety of compatible components from multiple vendors is complex and risky.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Supply chain disruptions from outsourced manufacturing partners can halt production.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
- Problem:
Finding reliable, well-documented components for long-lifecycle industrial and automotive products.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
Value Alignment Assessment
High
TI's focus on high-growth, high-value industrial and automotive markets aligns perfectly with secular trends like vehicle electrification, factory automation, and renewable energy.
High
The value proposition of a broad portfolio, extensive design support, and supply chain reliability directly addresses the primary pain points of their core customer base: design engineers.
Strategic Assessment
Business Model Canvas
Key Partners
- •
Global electronic component distributors (e.g., Digi-Key, Mouser)
- •
University research programs for R&D collaboration.
- •
Technology standards bodies
- •
Startup incubators like Silicon Catalyst.
Key Activities
- •
Research & Development (R&D)
- •
Semiconductor design and fabrication (Manufacturing)
- •
Global sales and application support
- •
Supply Chain Management
Key Resources
- •
Proprietary Intellectual Property (IP) and extensive patent portfolio
- •
Company-owned semiconductor fabrication plants (Fabs).
- •
Global distribution network and direct sales platform (TI.com)
- •
Highly skilled engineering talent
Cost Structure
- •
High Capital Expenditures (CapEx) for building and equipping new fabs.
- •
Significant, sustained investment in Research & Development.
- •
Cost of Goods Sold (raw materials, wafer processing)
- •
Sales, General & Administrative (SG&A) expenses
Swot Analysis
Strengths
- •
Vertically integrated manufacturing model provides cost advantages and supply chain control.
- •
Dominant market share and strong brand reputation in the analog market.
- •
Highly diversified revenue streams across numerous products and customers.
- •
Strong financial position with consistent free cash flow generation.
Weaknesses
- •
High capital intensity required for fab construction can impact short-term free cash flow.
- •
Susceptibility to cyclical downturns in the broader semiconductor market.
- •
Massive scale can sometimes lead to slower adaptation compared to smaller, more agile competitors.
Opportunities
- •
Increasing semiconductor content per vehicle, driven by EVs and ADAS.
- •
Rapid growth in Industrial IoT, AI at the edge, and 5G infrastructure.
- •
Government incentives (e.g., CHIPS Act) supporting domestic semiconductor manufacturing.
- •
Expanding direct-to-customer sales via TI.com to improve margins.
Threats
- •
Intense and fragmented competition from numerous global players.
- •
Geopolitical tensions and trade policies impacting global supply chains and market access.
- •
Potential for overcapacity in the industry following large-scale fab investments.
- •
Rapid technological change requiring continuous high levels of R&D investment.
Recommendations
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Digital Customer Experience
Recommendation:Invest in AI-powered tools on TI.com for intelligent component selection, system-level design simulation, and predictive supply chain availability to further embed TI into the engineer's workflow.
Expected Impact:Medium
- Area:
Talent Acquisition & Development
Recommendation:Expand university partnerships and create specialized training programs for analog and power electronics design to secure the next generation of engineering talent in a competitive market.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Supply Chain Transparency
Recommendation:Develop a more sophisticated customer-facing portal that provides real-time visibility into production status and lead times for high-volume orders, enhancing trust and planning for key accounts.
Expected Impact:Medium
Business Model Innovation
Develop system-level platforms that bundle multiple ICs with a software/firmware stack to solve a specific application problem (e.g., a complete EV battery management system), moving from component sales to higher-value solution sales.
Explore subscription models for access to premium design tools, advanced simulation environments, or specialized IP blocks to create a recurring revenue stream from software and services.
Revenue Diversification
Aggressively expand the portfolio of high-power Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) products to capture the high-growth market for efficient power conversion in EVs, data centers, and solar inverters.
License proprietary algorithms and software (e.g., predictive battery gauging, advanced motor control) as standalone products to monetize the software intelligence that complements TI's hardware.
Texas Instruments operates a mature, robust, and highly defensible business model centered on its leadership in analog and embedded processing semiconductors. The company's core strategic differentiator is its commitment to a vertically integrated manufacturing model, specifically its heavy investment in proprietary 300mm wafer fabs. This provides significant, sustainable competitive advantages in cost, supply chain control, and geopolitical resilience, which is a stark contrast to the fabless model prevalent in other parts of the semiconductor industry.
The business model is exceptionally resilient due to its immense diversification. Serving approximately 100,000 customers with over 80,000 products, TI is not overly reliant on any single customer, market, or product line. Its strategic focus on the industrial and automotive markets, which are characterized by long product lifecycles and high qualification barriers, creates a 'sticky' customer base and stable, long-term revenue streams.
Strategic evolution opportunities lie in moving up the value chain. While TI excels at providing essential components, the next phase of growth will involve offering more integrated, system-level solutions. By bundling hardware with proprietary software and algorithms, TI can solve more complex customer problems, command higher margins, and further embed itself in their customers' design processes. The shift toward direct sales via TI.com is a critical step in this evolution, enabling closer customer relationships and better margins.
Future market positioning will be defined by TI's ability to leverage its manufacturing scale to meet the surging demand from the electrification of everything—from vehicles to industrial machinery. The primary challenges are the high capital intensity of its strategy and the inherent cyclicality of the semiconductor industry. However, by focusing on long-term free cash flow per share and disciplined capital allocation, Texas Instruments is well-positioned to navigate these cycles and solidify its market leadership for the long term.
Competitors
Competitive Landscape
Mature
Oligopoly
Barriers To Entry
- Barrier:
High Capital Investment
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Intellectual Property & Patents
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Economies of Scale
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Complex Manufacturing & Supply Chains
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Skilled Talent Shortage
Impact:Medium
Industry Trends
- Trend:
Automotive Electrification & ADAS
Impact On Business:Major growth driver for analog, power management, and embedded processing products.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
AI at the Edge & Data Centers
Impact On Business:Drives demand for high-performance, power-efficient signal chain and power management solutions.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Industrial Automation (Industry 4.0)
Impact On Business:Sustained demand for sensors, controllers, and connectivity solutions.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Supply Chain Resilience & Onshoring
Impact On Business:Favors TI's strategy of investing in domestic manufacturing (e.g., US-based fabs), providing a competitive advantage in supply stability.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Adoption of Wide-Bandgap Materials (GaN, SiC)
Impact On Business:Opportunity to lead in next-generation power electronics, but also a threat if competitors innovate faster.
Timeline:Near-term
Direct Competitors
- →
Analog Devices (ADI)
Market Share Estimate:Approx. 9-11% of analog market
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Leader in high-performance data converters, signal processing, and power management, often targeting premium performance segments.
Strengths
- •
Strong brand reputation for high-performance and precision.
- •
Deep expertise in data converters (ADCs/DACs) and RF technology.
- •
Successful strategic acquisitions (e.g., Linear Technology, Maxim Integrated) expanding portfolio.
- •
Strong position in industrial, automotive, and communications markets.
Weaknesses
- •
Less in-house manufacturing compared to TI, leading to more reliance on foundries like TSMC.
- •
Product portfolio is less broad than TI's, particularly in lower-cost, general-purpose components.
- •
Higher mix of custom chips could pose inventory risks in downturns.
Differentiators
- •
Focus on high-performance, specialized solutions commanding higher margins.
- •
Growth-through-acquisition strategy.
- •
Deep system-level knowledge in their target applications.
- →
NXP Semiconductors
Market Share Estimate:Varies by segment, strong in automotive
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Leader in secure connectivity solutions for embedded applications, with a dominant position in the automotive and industrial & IoT markets.
Strengths
- •
Market leadership in automotive semiconductors (MCUs, networking, radar).
- •
Strong portfolio in secure identification and NFC technology.
- •
Broad microcontroller and processor portfolio (Arm-based).
- •
Deep, long-standing relationships with top automotive OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers.
Weaknesses
- •
High dependence on the cyclical automotive market.
- •
Less dominant in the broad analog market compared to TI and ADI.
- •
Faces intense competition in the microcontroller space from numerous players.
Differentiators
- •
Automotive-first focus.
- •
Expertise in security and secure connectivity.
- •
Comprehensive system solutions for specific end-applications like vehicle networking and mobile payments.
- →
Infineon Technologies
Market Share Estimate:Leading in power semiconductors
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Global leader in power systems and IoT, with a strong focus on automotive, industrial power control, and security solutions.
Strengths
- •
Dominant market share in power semiconductors (IGBTs, MOSFETs).
- •
Leadership in automotive microcontrollers and sensors.
- •
Strong R&D and product leadership in wide-bandgap materials (SiC and GaN).
- •
Focus on quality, reliability, and long-term customer partnerships, particularly in automotive.
Weaknesses
- •
Revenue is heavily concentrated in the automotive and industrial sectors.
- •
Portfolio is less diversified into consumer electronics compared to TI.
- •
Can be perceived as less of a 'one-stop-shop' than TI for a full bill of materials.
Differentiators
- •
Unmatched expertise in power electronics.
- •
Pioneer in SiC and GaN technologies for efficiency and power density.
- •
System-level solutions combining power, sensors, and microcontrollers ('Product to System' approach).
- →
STMicroelectronics
Market Share Estimate:Strong in MCUs and sensors
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:Broad-line semiconductor supplier with strong positions in microcontrollers (STM32 family), sensors (MEMS), and analog/power products for automotive and industrial markets.
Strengths
- •
Extremely popular and well-supported STM32 microcontroller ecosystem.
- •
Leading position in MEMS sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes).
- •
Broad product portfolio serving a diverse range of applications and customers.
- •
Strong presence in both industrial and consumer electronics markets.
Weaknesses
- •
Faces margin pressure due to competition in the broad-based MCU market.
- •
Not the outright market share leader in any single large segment like TI (analog) or Infineon (power).
- •
Can be slower to market with cutting-edge process technologies.
Differentiators
- •
The extensive and accessible STM32 ecosystem, which has a massive developer following.
- •
Leadership in MEMS technology.
- •
Balanced exposure across personal electronics, industrial, and automotive markets.
- →
Microchip Technology
Market Share Estimate:Strong in MCUs and analog
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:A leading provider of microcontroller, mixed-signal, analog, and Flash-IP solutions, known for its vast product portfolio and 'Total System Solutions' approach.
Strengths
- •
Massive and diverse portfolio of 8, 16, and 32-bit microcontrollers (PIC, AVR).
- •
Strong presence in the long-tail of the industrial and consumer markets.
- •
Customer-centric model with strong support and long product lifecycles.
- •
Successful acquisition strategy (e.g., Atmel, Microsemi) that has significantly broadened its portfolio.
Weaknesses
- •
Less emphasis on cutting-edge, high-performance analog compared to ADI.
- •
Can be perceived as a follower rather than an innovator in some technology areas.
- •
Integration of multiple large acquisitions can present operational challenges.
Differentiators
- •
'One-stop-shop' for embedded controllers and associated analog components.
- •
Commitment to customer longevity and non-obsolescence.
- •
Strong direct sales and support channels catering to a wide customer base.
Indirect Competitors
- →
FPGA Companies (Xilinx/AMD, Altera/Intel)
Description:Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) offer reconfigurable hardware that can perform functions of microcontrollers and DSPs, especially in applications requiring high parallel processing. While more expensive and complex to program, they can be an alternative for high-performance applications.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Low, but FPGAs with integrated Arm cores (SoCs) directly compete with high-end MCUs/MPUs from TI in complex applications like vision systems and advanced motor control.
- →
System-on-Chip (SoC) Providers (Qualcomm, MediaTek)
Description:These companies provide highly integrated chips that combine processors, memory, and multiple peripherals onto a single piece of silicon. For high-volume consumer devices (like smartphones), their solutions can reduce the need for many discrete analog and embedded components that TI sells.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Low in industrial/automotive, but high in the personal electronics space where integration is key. They reduce the total addressable market for individual components.
- →
Open-Source Hardware Platforms (Raspberry Pi, Arduino)
Description:These platforms lower the barrier to entry for electronics prototyping and small-scale production. While they often use microcontrollers from TI's competitors (e.g., Raspberry Pi Pico uses an RP2040), they foster a community that may be less reliant on traditional semiconductor vendor evaluation kits and ecosystems.
Threat Level:Low
Potential For Direct Competition:Very Low. They are more of a market enabler than a competitor, but can influence component choice for the next generation of engineers.
Competitive Advantage Analysis
Sustainable Advantages
- Advantage:
Manufacturing Scale and Cost Leadership
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. TI's massive investment in 300mm wafer fabs provides a significant and durable cost advantage per chip that is extremely difficult and capital-intensive for competitors to replicate.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Broad Product Portfolio
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. Offering over 80,000 products allows TI to be a 'one-stop-shop' for customers, increasing switching costs and enabling cross-selling. Building such a portfolio takes decades.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Direct-to-Customer Sales Channel (TI.com)
Sustainability Assessment:Sustainable. Investing in TI.com provides higher margins, direct customer relationships, and valuable data on demand trends. It is a significant logistics and e-commerce undertaking.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
- Advantage:
Extensive Technical Support and Documentation
Sustainability Assessment:Sustainable. TI provides vast resources (datasheets, reference designs, E2E forums) that make it easier for engineers to design with their parts, creating a loyal customer base.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
Temporary Advantages
{'advantage': 'Leadership in Specific Product Cycles', 'estimated_duration': '1-3 years'}
Disadvantages
- Disadvantage:
Lower R&D Spending as a Percentage of Revenue
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately
- Disadvantage:
Perception as a 'Generalist'
Impact:Minor
Addressability:Easily
Strategic Recommendations
Quick Wins
- Recommendation:
Launch targeted marketing campaigns highlighting supply chain advantages of US-based fabs.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
- Recommendation:
Enhance the TI.com user experience with more intuitive cross-reference tools and AI-powered product recommendations.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Create bundled 'solution packs' on TI.com for high-growth applications like robotics or EV charging, combining MCUs, power management, and connectivity.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Medium Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Aggressively expand the GaN and SiC product portfolio to capture the high-growth power electronics market.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Invest in software and toolchains to simplify the development process, particularly for complex embedded systems, to better compete with the ease-of-use of ecosystems like STMicroelectronics' STM32.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Acquire a smaller, innovative company in a niche high-growth area like advanced sensors or AI acceleration hardware to augment the existing portfolio.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Long Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Continue disciplined investment in next-generation 300mm manufacturing capacity to extend cost leadership and supply chain resilience.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Establish a leadership position in hardware for AI at the edge, developing specialized processors and analog front-ends optimized for low-power AI inference.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Develop strategic partnerships with universities and startups to cultivate the next generation of engineers on the TI platform and to scout emerging technologies.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Solidify TI's position as the most reliable, scalable, and cost-effective partner for industrial and automotive electronics development. Shift messaging from 'a portfolio of parts' to 'the foundation for your entire system,' emphasizing stability, longevity, and ease of procurement.
Differentiate on the axis of manufacturing and supply chain. While competitors focus on performance niches, TI's core differentiator is its ability to reliably deliver a vast range of quality components at scale and at a competitive cost, directly to the customer. This message of stability and partnership is a powerful asset in a geopolitically uncertain world.
Whitespace Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Integrated Software/Hardware Development Platforms for SMEs
Competitive Gap:Many competitors focus on either high-end users (ADI) or have a fragmented software experience. There is a gap for a highly integrated, easy-to-use platform combining hardware, software, and cloud connectivity tools for small and medium-sized enterprises in the industrial IoT space.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Ultra-Robust Components for Harsh Environments
Competitive Gap:While many serve the automotive market, there's a growing need for components in adjacent harsh-environment markets (e.g., aerospace, downhole drilling, advanced robotics) that require higher reliability and temperature ratings than standard automotive-grade parts.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:Medium
- Opportunity:
System-Level Solutions for Battery Management Systems (BMS)
Competitive Gap:The EV and energy storage boom creates immense demand for comprehensive BMS solutions. While competitors offer parts, a full platform solution from TI—combining its analog front-ends, MCUs, power components, and connectivity, along with reference software—could capture significant system-level design wins.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
Texas Instruments operates as a dominant force within the mature, oligopolistic semiconductor industry, particularly in its core markets of analog and embedded processing. Its primary competitive advantages are structural and highly sustainable: unparalleled manufacturing scale via 300mm wafer fabs which provides a formidable cost advantage, and an exceptionally broad product portfolio that establishes high switching costs for customers. These strengths position TI as a 'one-stop-shop' for a diverse range of clients, primarily in the stable and growing industrial and automotive sectors. The company's strategy of vertical integration and investment in US-based manufacturing further insulates it from geopolitical supply chain volatility, a key differentiator in the current climate.
Direct competition is fierce. Analog Devices (ADI) competes aggressively in the high-performance analog segment, often winning on specialized performance at a premium price point. NXP and Infineon are formidable leaders in the automotive space, with deep expertise in power electronics (Infineon) and secure connectivity (NXP). STMicroelectronics poses a significant threat with its wildly popular and accessible STM32 microcontroller ecosystem, which has cultivated a massive and loyal developer community. Microchip similarly competes with a vast portfolio and a strong focus on the long-tail of the market.
TI's primary disadvantage is a lower R&D spend as a percentage of revenue compared to key rivals, which could risk ceding ground in technological innovation over the long term. It can also be perceived as a 'generalist' versus the specialized, high-performance branding of a competitor like ADI. However, TI's strategic focus on the industrial and automotive markets is well-aligned with major secular trends like electrification and automation. Key opportunities lie in leveraging its manufacturing advantage to dominate the transition to wide-bandgap materials (GaN/SiC), simplifying its software development ecosystem to attract more engineers, and offering more complete system-level solutions in high-growth areas like battery management. The strategic imperative for TI is to fortify its positioning as the most reliable and scalable semiconductor partner, leveraging its manufacturing and supply chain supremacy as its most powerful competitive weapon.
Messaging
Message Architecture
Key Messages
- Message:
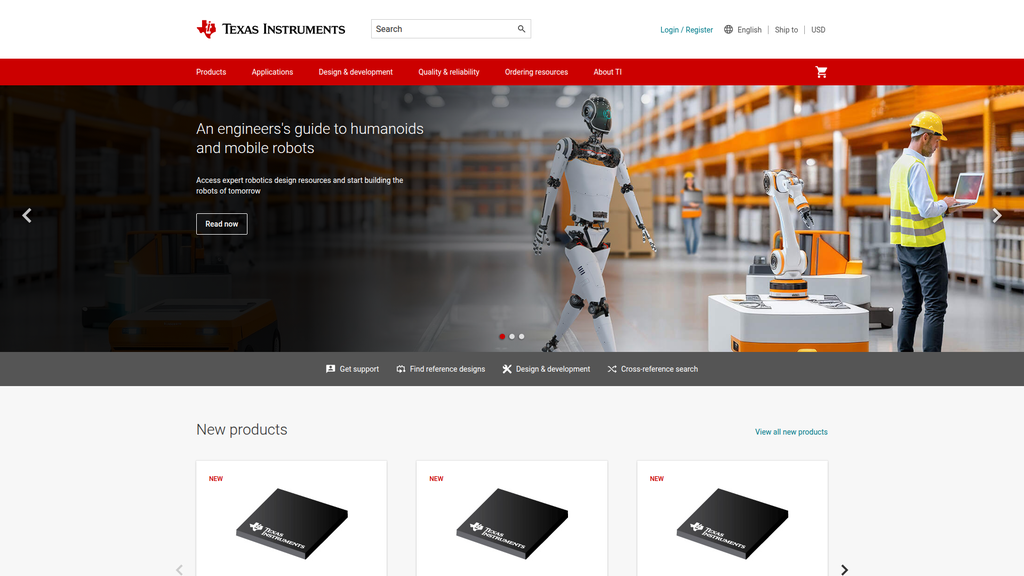
Enabling innovation in future-focused applications like robotics and smart building security.
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage rotating hero banners
- Message:
Delivering cutting-edge, high-performance new products for engineers.
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage 'New products' section
- Message:
Our passion is to create a better world by making electronics more affordable through semiconductors.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Homepage 'Our passion' section (mid-page)
- Message:
TI is committed to corporate citizenship, sustainability, and community impact.
Prominence:Tertiary
Clarity Score:Medium
Location:Homepage 'Our commitment to corporate citizenship' section (lower page)
The messaging hierarchy correctly prioritizes the needs of its core audience: engineers looking for specific solutions and products. Application-specific examples and new product listings are featured at the top, immediately signaling relevance. The broader brand mission and corporate citizenship messages are placed further down, serving as supporting pillars rather than the lead story. This is a logical and effective hierarchy for a deeply technical B2B audience.
Messaging is highly consistent. The focus on technical excellence, innovation, and enabling progress is woven throughout the homepage. The tone remains professional and expert-driven from the hero banners to the product details. The brand's mission, 'Engineering Progress,' is effectively substantiated by the content, which showcases tangible advancements.
Brand Voice
Voice Attributes
- Attribute:
Expert & Technical
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
SMBus 1-4 cell buck battery charge controller with hybrid power boost, battery boost mode and GaN
- •
Automotive 80MHz ARM® Cortex®-M0+ MCU with 256kB flash, 128kB SRAM, 2 CAN, 2 ADC, DAC, COMP
- •
Extend battery run time by up to 30% with the industry’s first predictive battery gauging algorithm
- Attribute:
Innovative
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Technology that predicts the unpredictable
- •
start building the robots of tomorrow
- •
the industry’s first predictive battery gauging algorithm
- Attribute:
Purpose-Driven
Strength:Moderate
Examples
- •
Our passion is to create a better world...
- •
Engineering a better world: our communities, workplace and environmental sustainability impact
- •
Do you want to change the world and love your job? Join us.
- Attribute:
Direct & Efficient
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Get support
- •
Find reference designs
- •
Cross-reference search
- •
View all new products
Tone Analysis
Informative
Secondary Tones
Aspirational
Pragmatic
Tone Shifts
The tone shifts from highly technical and product-focused in the top half of the page to more aspirational and corporate in the 'Our passion' and 'Corporate citizenship' sections.
Voice Consistency Rating
Excellent
Consistency Issues
No itemsValue Proposition Assessment
Texas Instruments provides a vast portfolio of high-quality, innovative, and affordable analog and embedded processing chips, backed by robust design support, enabling engineers to create next-generation electronics that improve the world.
Value Proposition Components
- Component:
Breadth of Portfolio
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
Detail:The homepage immediately showcases a wide range of new products across categories like battery chargers, MCUs, and Wi-Fi modules, reinforcing their extensive catalog.
- Component:
Technological Innovation
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Unique
Detail:Explicitly stated with phrases like 'industry’s first predictive battery gauging algorithm' and 'Technology that predicts the unpredictable.'
- Component:
Engineer Support & Tools
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
Detail:Prominent links to 'Get support', 'Find reference designs', and 'Cross-reference search' demonstrate a commitment to simplifying the design process for their core audience.
- Component:
Affordability
Clarity:Somewhat Clear
Uniqueness:Common
Detail:Mentioned in the mission statement ('making electronics more affordable') but less emphasized on the homepage, where pricing is only shown for bulk orders (1ku).
- Component:
Reliability & Quality
Clarity:Somewhat Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
Detail:Implied through their long-standing brand reputation and technical specificity, but not an explicit headline message on the homepage. The 'ACTIVE' product status is a subtle indicator.
TI differentiates itself through a powerful combination of scale (a massive portfolio of ~80,000 products), deep technical innovation (especially in analog and embedded), and a vertically integrated manufacturing model that provides a cost advantage. The messaging effectively communicates innovation and portfolio breadth but could more strongly emphasize the reliability and supply chain advantages that come from their manufacturing control.
The messaging positions TI as a foundational, indispensable partner for engineers in high-growth sectors like automotive and industrial. Unlike competitors who might focus purely on performance (e.g., Analog Devices) or specific niches, TI's messaging conveys a blend of performance, breadth, accessibility ('affordable'), and reliability. They are positioned not just as a component supplier, but as a core enabler of 'Engineering Progress'.
Audience Messaging
Target Personas
- Persona:
Design Engineer
Tailored Messages
- •
Specific product part numbers (BQ24810, DLP472NP)
- •
Detailed technical specifications ('80MHz ARM® Cortex®-M0+ MCU with 256kB flash')
- •
Direct links to technical resources ('Find reference designs', 'Cross-reference search')
- •
Application-specific content ('guide to humanoids and mobile robots')
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
Procurement Professional / Engineering Manager
Tailored Messages
- •
Approx. price (USD) 1ku
- •
Product lifecycle status ('ACTIVE', 'PREVIEW')
- •
Company stability and values ('Our commitment to corporate citizenship')
- •
Case studies showing successful implementation ('Johnson Controls and TI')
Effectiveness:Somewhat Effective
Audience Pain Points Addressed
- •
Extending battery run time in devices with dynamic loads
- •
Finding the right component quickly and efficiently ('Cross-reference search')
- •
Improving building security systems with modern wireless technology
- •
Accessing design resources to accelerate development ('expert robotics design resources')
Audience Aspirations Addressed
- •
Building the next generation of technology ('robots of tomorrow')
- •
Creating smarter, more efficient, and more reliable electronics
- •
Making a positive impact on the world through engineering ('create a better world')
Persuasion Elements
Emotional Appeals
- Appeal Type:
Appeal to Mastery & Expertise (Logos/Pathos)
Effectiveness:High
Examples
The highly technical product descriptions and application guides appeal to an engineer's desire for competence and solving complex problems.
- Appeal Type:
Appeal to Purpose & Legacy (Pathos)
Effectiveness:Medium
Examples
'Our passion is to create a better world...'
'Do you want to change the world and love your job?'
Social Proof Elements
- Proof Type:
Case Studies / Customer Stories
Impact:Strong
Detail:The Johnson Controls case study provides concrete evidence of TI's technology solving real-world problems for a major company.
- Proof Type:
Data & Statistics
Impact:Moderate
Detail:The corporate citizenship section uses specific data points ('90% Percentage of shipped semiconductor products considered green') to build credibility and demonstrate commitment.
Trust Indicators
- •
Detailed, transparent product specifications
- •
Clear product lifecycle statuses (ACTIVE, PREVIEW)
- •
Publication of corporate citizenship reports
- •
Direct links to support and technical documentation
- •
Long-standing brand reputation (implied)
Scarcity Urgency Tactics
None observed. This is appropriate for the industry, which relies on long-term planning and design cycles rather than impulse purchases.
Calls To Action
Primary Ctas
- Text:
Read now
Location:Hero banners, company blog
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Discover more
Location:Hero banner
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
View all new products
Location:New products section
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Search open jobs
Location:Join our team section
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Download our "2024 Corporate Citizenship Report"
Location:Corporate citizenship section
Clarity:Clear
The CTAs are consistently clear, concise, and action-oriented. They effectively guide the target audience to the next logical step, whether it's learning more about a technology, viewing product details, or accessing corporate information. The language is pragmatic and respects the user's time, which is well-suited for a professional, engineering-focused audience.
Messaging Gaps Analysis
Critical Gaps
The message of 'affordability,' a key part of the corporate mission, is not strongly supported or quantified on the homepage. Pricing is only shown for large quantities, which may not feel 'affordable' to those in R&D or prototyping phases.
There is a lack of explicit competitive comparison. While the value proposition is strong, the messaging doesn't directly address why an engineer should choose TI over a key competitor like Analog Devices or NXP for a specific application.
Contradiction Points
No itemsUnderdeveloped Areas
Storytelling around the impact of their products. While the mission is to 'create a better world,' the connection between a specific MCU or power module and that larger goal is left for the user to infer. More narratives could bridge this gap.
Messaging for non-engineer stakeholders. While the focus on engineers is correct, messaging for executives or procurement leads who may be less technical is not as developed on the homepage.
Messaging Quality
Strengths
- •
Exceptional clarity and relevance for the primary target audience of design engineers.
- •
Strong alignment between high-level brand purpose ('Engineering Progress') and tangible product innovations.
- •
Effective use of technical language to build credibility and convey expertise.
- •
Clear and logical information architecture that allows users to quickly find relevant tools and products.
Weaknesses
- •
The homepage feels slightly fragmented, like a portal of different options, rather than a single, cohesive brand story.
- •
The aspirational messaging ('create a better world') feels disconnected from the very dense, technical product information that dominates the page.
- •
The value proposition of 'affordability' is asserted but not demonstrated effectively to all audience segments.
Opportunities
- •
Create a more unified narrative on the homepage that explicitly links specific product innovations (e.g., the battery gauging algorithm) to the real-world benefits that contribute to a 'better world' (e.g., less waste, more reliable medical devices).
- •
Develop more mid-funnel content that tells customer success stories, moving beyond a single case study to a broader portfolio of examples.
- •
Introduce messaging that speaks more directly to the supply chain and longevity benefits of choosing TI, a key concern for industrial and automotive customers.
Optimization Roadmap
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Homepage Narrative
Recommendation:Revise the hero section to create a stronger bridge between the high-level brand promise and the specific technologies. Instead of leading with one application, lead with the overarching theme. For example: 'Engineering progress for a better world. See how our latest innovations in power, connectivity, and processing are building the robots of tomorrow.'
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Value Proposition Communication
Recommendation:Create a dedicated messaging block that summarily communicates the core value props: 'Why Design with TI? Innovation, Breadth, Reliability, and Support.' This would help solidify the brand's key differentiators upfront.
Expected Impact:Medium
Quick Wins
- •
Elevate the 'Our Passion' section to be more visually prominent, potentially placing it directly below the hero section to frame the rest of the content.
- •
Add a testimonial quote from an engineer or customer near the 'New products' section to add a human element and social proof.
- •
For each hero banner, add a sub-headline that connects the application to a broader human benefit (e.g., 'Transforming building security...' could be '...for safer communities').
Long Term Recommendations
- •
Develop a comprehensive content strategy focused on 'Impact Stories' that trace the journey of a TI component from its datasheet to its role in a life-changing or industry-advancing final product.
- •
Create segmented landing pages or messaging tracks for different key industries (e.g., Automotive, Industrial) that speak more directly to their specific challenges and how TI's portfolio provides a complete solution, not just individual parts.
- •
Invest in interactive tools on the homepage that help visitors quickly identify relevant products based on their end-application needs, visually reinforcing the breadth and applicability of the TI portfolio.
Texas Instruments' website messaging is a masterclass in communicating effectively with a deeply technical core audience. The brand voice is expert and direct, the message architecture is logical, and the content is precisely tailored to the needs of design engineers. Key messages around enabling innovation in future-focused applications and providing cutting-edge new products are communicated with high clarity and prominence. The site successfully builds trust through detailed technical specifications, transparent product lifecycle data, and accessible support resources.
The primary strength lies in its unwavering focus on its target persona; there is no ambiguity about who the site is for or what value it provides them. However, this strength also creates a messaging gap. The connection between the company's aspirational mission to 'create a better world' and its highly specific, technical product offerings is not always clear. The homepage functions more as a highly effective portal for existing customers and knowledgeable engineers than a compelling narrative for a broader audience or a newcomer trying to understand TI's strategic differentiation.
Opportunities for optimization center on bridging this gap. By weaving more storytelling into the user journey—explicitly linking a new power module to longer-lasting medical devices or a new sensor to safer autonomous vehicles—TI can elevate its messaging from simply providing components to being a critical partner in global progress. Strengthening the communication of its unique value propositions, such as the reliability derived from its vertically integrated manufacturing and the often-cited but under-proven claim of 'affordability,' would further sharpen its competitive edge. The foundation is exceptionally strong; the path forward involves building a more powerful narrative on top of it.
Growth Readiness
Growth Foundation
Product Market Fit
Strong
Evidence
- •
Market leader in analog and embedded processing, which constitute over 90% of revenue.
- •
Extensive portfolio of ~80,000 products serving a diverse base of over 100,000 customers.
- •
Deeply entrenched in high-growth, long-lifecycle markets like automotive and industrial, which account for approximately 70% of revenue.
- •
Long history of innovation and market presence, establishing TI as a default choice for many engineers.
- •
Consistently high revenue and profitability, demonstrating sustained market demand.
Improvement Areas
- •
Strengthening the software and development tool ecosystem around embedded processors to increase stickiness.
- •
Expanding offerings in emerging high-power compound semiconductor materials like GaN and SiC to capture new design wins.
- •
Developing more highly integrated system-on-chip (SoC) solutions that combine analog and embedded processing to increase share of bill-of-materials (BOM).
Market Dynamics
Projected global semiconductor market CAGR of 7.5% to 15.4% through 2030, with expectations to reach ~$1 trillion.
Mature
Market Trends
- Trend:
Vehicle Electrification & ADAS
Business Impact:Massive increase in semiconductor content per vehicle, driving substantial growth in TI's core automotive market, which is projected to grow at an 8% CAGR.
- Trend:
Industrial Automation & Electrification (Industry 4.0)
Business Impact:Strong demand for power management, sensors, and embedded processors in factory automation, robotics, and green energy infrastructure.
- Trend:
Edge AI & On-Device Processing
Business Impact:Growing need for low-power microcontrollers and processors with AI capabilities for IoT and smart devices, representing a key growth area for the embedded processing segment.
- Trend:
Geopolitical Reshoring & Supply Chain Resilience
Business Impact:Government incentives like the CHIPS Act support TI's massive investment in domestic manufacturing, providing a competitive advantage in supply assurance.
Excellent. TI is strategically aligned with the most significant secular growth trends in the semiconductor industry, particularly the electrification and intelligence of automotive and industrial applications.
Business Model Scalability
High
High fixed-cost model due to owning wafer fabs, which provides significant operating leverage and cost advantages at scale, particularly with 300mm wafer production.
High. Increased production volume in owned 300mm fabs leads to a lower cost-per-chip, directly improving gross margins.
Scalability Constraints
- •
Extremely high capital expenditure required for building and equipping new 300mm wafer fabs (investing ~$5B annually).
- •
Long lead times (2-3 years) for new fab construction, requiring accurate long-term demand forecasting.
- •
Dependence on a highly specialized global supply chain for raw materials and manufacturing equipment.
Team Readiness
Proven and experienced leadership team with a clear long-term strategy focused on free cash flow per share growth and shareholder returns.
Mature, global organization structured around its core business segments (Analog, Embedded Processing), enabling focused execution.
Key Capability Gaps
Competition for top-tier talent in specialized areas like analog design, systems engineering, and AI/ML hardware/software co-design is intense.
Need for continuous upskilling of the workforce to manage increasingly automated and data-driven 300mm manufacturing facilities.
Growth Engine
Acquisition Channels
- Channel:
Direct Sales & Field Application Engineers (FAEs)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Equip FAEs with AI-driven tools to identify high-potential customer applications and predict component needs, increasing design win rates.
- Channel:
TI.com (Technical Content & E-commerce)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Enhance the on-site experience with AI-powered search, personalized reference designs, and interactive simulation tools to accelerate the engineer's design journey from discovery to sample purchase.
- Channel:
Distribution Partners (e.g., Digi-Key, Mouser)
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:Low
Recommendation:Continue to leverage for reaching the long-tail of the market, but focus strategic growth on increasing direct-to-customer transactions via TI.com, which is now ~80% of revenue.
Customer Journey
The core 'conversion' is an engineer 'designing-in' a TI component. This is a long, research-intensive journey: Problem Identification -> Component Search (TI.com) -> Datasheet/Reference Design Evaluation -> Sample Request/Purchase -> Prototyping -> Volume Production.
Friction Points
- •
Navigating the vast portfolio of 80,000+ products to find the optimal part.
- •
Component availability and lead times can be a concern for procurement during industry shortages.
- •
Complexity of integrating software and hardware for embedded processing applications.
Journey Enhancement Priorities
{'area': 'Component Discovery', 'recommendation': "Develop an AI-based 'System Designer' tool on TI.com where engineers can input system-level requirements (e.g., power budget, processing needs) and receive a recommended bill-of-materials with TI components."}
{'area': 'Prototyping & Development', 'recommendation': 'Invest further in expanding the library of accessible, well-documented reference designs and evaluation modules to reduce development time for customers.'}
Retention Mechanisms
- Mechanism:
Broad Product Portfolio & Long Lifecycles
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Proactively recommend next-generation pin-compatible parts to customers using older components, ensuring they stay within the TI ecosystem for product refreshes.
- Mechanism:
Supply Chain Control (Internal Manufacturing)
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Market the reliability and supply assurance from owned 300mm fabs as a key competitive advantage, especially given recent global shortages. TI aims for over 90% internal manufacturing.
- Mechanism:
Technical Support (E2E Forums, FAEs)
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Utilize AI to analyze E2E forum discussions to identify common customer pain points and inform new product development and documentation improvements.
Revenue Economics
Highly favorable. The analog business is characterized by high margins and long product lifecycles. The shift to 300mm manufacturing further improves cost-per-chip, enhancing profitability.
Not a standard metric. A proxy is 'Design Win Lifetime Value', which is extremely high. A single design win can lead to 10+ years of revenue with minimal ongoing sales cost.
High. The business model is designed for long-term, profitable growth, with a focus on maximizing free cash flow per share.
Optimization Recommendations
- •
Focus R&D on high-margin analog and integrated embedded solutions for automotive and industrial markets.
- •
Continue the strategic shift to 300mm wafer production to drive down costs and expand margins.
- •
Increase the percentage of direct sales through TI.com to improve margin capture by reducing distributor fees.
Scale Barriers
Technical Limitations
- Limitation:
Pace of Innovation in Compound Semiconductors (GaN, SiC)
Impact:Medium
Solution Approach:Increase R&D investment and consider strategic acquisitions of smaller, specialized GaN/SiC technology companies to accelerate product development for high-power EV and industrial applications.
Operational Bottlenecks
- Bottleneck:
Wafer Fab Capacity Planning & Construction
Growth Impact:A miscalculation in long-term demand forecasting can lead to multi-billion dollar fabs being underutilized or, conversely, an inability to meet customer demand.
Resolution Strategy:Employ advanced predictive analytics and modular fab construction strategies to allow for more flexible capacity expansion. Continue building 'shell' fabs that can be equipped as demand materializes.
- Bottleneck:
Global Equipment & Raw Material Sourcing
Growth Impact:Dependence on a concentrated number of global suppliers for critical manufacturing equipment and materials creates supply chain vulnerability.
Resolution Strategy:Diversify the supplier base where possible, establish strategic long-term partnerships, and increase strategic inventory of critical materials and spare parts.
Market Penetration Challenges
- Challenge:
Intense Competition
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Leverage the four key competitive advantages: 1) Manufacturing/Technology (cost & supply), 2) Broad Portfolio, 3) Market Reach (TI.com), and 4) Diverse/Long-Lived Positions.
- Challenge:
Geopolitical Tensions & Trade Restrictions
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Continue diversifying manufacturing footprint globally while capitalizing on domestic incentives (e.g., CHIPS Act) to build a resilient, localized supply chain for key markets.
- Challenge:
Customer In-housing of Chip Design (ASICs)
Severity:Minor
Mitigation Strategy:Focus on providing a broad portfolio of catalog parts that are more cost-effective and faster to implement than custom ASICs for the vast majority of customers who lack the scale of major tech giants.
Resource Limitations
Talent Gaps
Competition for scarce, highly-skilled analog and systems engineers.
Need for data scientists and AI experts to optimize manufacturing and business operations.
Extremely high and ongoing. Requires disciplined capital allocation to fund the multi-billion dollar annual investments in new 300mm fabs.
Infrastructure Needs
Continued investment in global logistics and warehousing to support a growing direct-to-customer business.
Upgrades to IT infrastructure and cybersecurity to support a sophisticated e-commerce platform and protect valuable IP.
Growth Opportunities
Market Expansion
- Expansion Vector:
Deeper Penetration in Automotive Zone Architecture
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:Medium
Recommended Approach:Develop and market specific portfolios of analog, power, and embedded processing solutions tailored for emerging automotive zonal architectures, partnering with Tier 1s and OEMs.
- Expansion Vector:
Grid Infrastructure & Renewable Energy
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:Medium
Recommended Approach:Create a dedicated business initiative focused on the 'electrification of everything,' targeting solar inverters, energy storage systems, and EV charging stations with high-power GaN/SiC and advanced power management ICs.
Product Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Integrated AI-Accelerated MCUs for Edge Devices
Market Demand Evidence:Strong growth in the edge AI market, with demand for on-device intelligence in industrial IoT, robotics, and consumer electronics.
Strategic Fit:High
Development Recommendation:Expand the embedded processing portfolio with a clear roadmap of microcontrollers featuring scalable, low-power AI accelerators and an easy-to-use software development kit (SDK).
- Opportunity:
Expansion of Gallium Nitride (GaN) & Silicon Carbide (SiC) Power Portfolios
Market Demand Evidence:Market for GaN and SiC power devices is growing rapidly (20%+ CAGR), driven by efficiency needs in EVs, data centers, and power supplies.
Strategic Fit:High
Development Recommendation:Accelerate internal R&D and consider acquiring specialized talent or technology to build a comprehensive portfolio of high-voltage GaN and SiC solutions.
Channel Diversification
- Channel:
Enhanced Digital Self-Service & API Integration
Fit Assessment:High
Implementation Strategy:Develop APIs that allow large customers to integrate TI's product catalog, real-time pricing, and inventory data directly into their own procurement and design systems, creating a stickier, more efficient sales process.
Strategic Partnerships
- Partnership Type:
Cloud Service Providers
Potential Partners
- •
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- •
Microsoft Azure
- •
Google Cloud
Expected Benefits:Co-develop integrated IoT solutions that seamlessly connect TI-powered edge devices to cloud platforms, simplifying the development process for customers and driving preference for TI hardware.
- Partnership Type:
University Research & Talent Pipeline
Potential Partners
Top engineering universities (e.g., MIT, Stanford, Georgia Tech, UT Austin)
Expected Benefits:Fund research in next-generation semiconductor technologies and create a dedicated pipeline for recruiting top engineering talent, addressing the industry's talent shortage.
Growth Strategy
North Star Metric
Share of Bill of Materials (BOM) in Target End-Equipment
This metric directly measures market penetration and competitive success within the most valuable customer applications in Automotive and Industrial. It incentivizes the sale of integrated solutions and a broader range of TI products per design.
Increase average dollar content per vehicle and per industrial robot by 15% over the next 3 years.
Growth Model
Engineer-Centric Product-Led Growth (PLG), supported by Enterprise Sales
Key Drivers
- •
Accessibility of high-quality technical content (datasheets, reference designs).
- •
Ease of product discovery and sampling via TI.com.
- •
Robustness of development tools and software.
- •
Responsive technical support.
Treat the entire digital engineering experience as the 'product'. Continuously invest in TI.com, development tools, and support forums to make it frictionless for engineers to find, evaluate, and design-in TI components. Use the data from these digital interactions to arm the direct sales force for high-value enterprise opportunities.
Prioritized Initiatives
- Initiative:
Launch a dedicated 'Grid & Renewables' product portfolio and marketing campaign.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:12-18 months
First Steps:Consolidate existing relevant products (GaN, SiC, power management, MCUs) under a new marketing umbrella and commission market-specific application notes and reference designs.
- Initiative:
Develop an AI-powered 'TI Design Assistant' on TI.com.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:18-24 months
First Steps:Create a cross-functional team of systems engineers, data scientists, and UX designers to build a prototype that recommends a full BOM based on user-inputted system parameters.
- Initiative:
Expand the University Program with a focus on Edge AI.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:9-12 months
First Steps:Develop new curriculum materials and low-cost development kits featuring AI-enabled MCUs and partner with 20 strategic universities to integrate them into their coursework.
Experimentation Plan
High Leverage Tests
{'test': "A/B test different product page layouts on TI.com to optimize for 'Request Sample' and 'Buy Now' click-through rates.", 'metric': 'Conversion rate to sample/buy'}
{'test': 'Pilot a premium, paid support tier for customers needing rapid, dedicated FAE assistance on complex designs.', 'metric': 'Adoption rate and customer satisfaction'}
Utilize a combination of web analytics (for digital interactions), design win tracking (via CRM), and customer satisfaction surveys (CSAT/NPS).
Bi-weekly sprints for digital/web experiments; quarterly reviews for larger strategic pilots.
Growth Team
A centralized 'Growth & Digital Experience' team that supports the core Analog and Embedded Processing business units.
Key Roles
- •
Head of Digital Customer Journey
- •
Growth Data Scientist
- •
Technical Content Strategist
- •
Systems Engineering Lead (focused on cross-portfolio solutions)
Invest in internal training on data analytics and customer journey mapping. Actively recruit talent with experience in building world-class B2B digital platforms and data science.
Texas Instruments exhibits a robust foundation for sustained, long-term growth. Its strong product-market fit in the highly attractive analog and embedded processing markets, particularly with a strategic focus on automotive and industrial sectors, aligns perfectly with major secular trends like electrification and automation. The company's key competitive advantage lies in its integrated device manufacturer (IDM) model, specifically its massive, forward-looking investment in 300mm wafer fabrication. This strategy provides significant cost advantages and, crucially, offers customers supply chain resilience—a powerful differentiator in the post-pandemic era. The primary growth engine is a sophisticated, engineer-centric model where the TI.com digital platform acts as a powerful product-led growth tool, complemented by a strong direct sales force. This engine effectively captures 'design wins' that translate into long-term, high-margin revenue streams. Key growth opportunities lie in deepening penetration into high-growth sub-markets like EVs and grid infrastructure, and expanding the product portfolio into critical technologies like GaN/SiC power stages and AI-accelerated microcontrollers. The main barriers to scale are not market-facing, but rather operational and strategic: the immense capital intensity of fab expansion and the global competition for scarce engineering talent. The recommended growth strategy is to double down on TI's core strengths. The North Star Metric should be 'Share of Bill of Materials' in target applications, driving a focus on providing more complete system solutions. The strategic priority should be to leverage the manufacturing advantage by aggressively pursuing markets undergoing intense electrification and to enhance the digital platform to make it even easier for engineers to design with TI products, thereby building an ever-deeper competitive moat.
Legal Compliance
Texas Instruments demonstrates a mature and robust approach to privacy. The website features a comprehensive 'Privacy Center' with a clear, well-structured global privacy policy. Crucially, it provides jurisdiction-specific information, explicitly addressing the requirements of GDPR for EU users and CCPA/CPRA for California residents. The policy details the types of personal data collected (e.g., contact information, technical data from device access, purchase history), the purposes for collection (e.g., fulfilling orders, providing support, improving services), and the basis for processing, such as user consent and contractual necessity. It clearly outlines user rights, including access, rectification, and erasure, and provides a dedicated Information Request Form for users to exercise these rights. This structured and transparent approach significantly mitigates privacy-related legal risks and builds trust with its global, technically-savvy user base.
The 'Terms of Use' are clearly accessible from the website footer and serve as a binding legal agreement. They are comprehensive, covering critical areas for a technology firm, including the protection of Texas Instruments' extensive intellectual property (copyrights, trademarks on product designs, datasheets, and software), acceptable use of website tools and forums, and restrictions against unauthorized reproduction or resale of content. The terms include robust disclaimers of warranties, stating that all services and information are provided 'AS IS' and with 'ALL FAULTS', and a clear limitation of liability. These clauses are essential for managing legal risk associated with the highly technical and sensitive nature of their products. The terms are enforceable and standard for a major B2B technology corporation.
TI.com has implemented a best-in-class cookie consent mechanism. Upon first visit, users are presented with a clear and non-intrusive banner that does not block content. The consent manager is highly granular, allowing users to individually toggle consent for 'Functional,' 'Analytics,' and 'Advertising' cookies, while correctly classifying 'Strictly Necessary' cookies as non-optional. The availability of an 'Accept all' and a 'Confirm my choices' option (which functions as a 'reject all' for optional cookies if none are selected) respects user autonomy and aligns with the stringent consent requirements of the GDPR and ePrivacy Directive. This implementation is a key strength, demonstrating a sophisticated understanding of data privacy regulations.
Texas Instruments' overall data protection strategy is strong, integrating legal policies with practical security measures. The privacy policy explicitly states that TI does not sell personal data to third parties, a key requirement under CCPA/CPRA. For its registered users ('myTI account'), it employs standard security practices for account management. Disclosures regarding data sharing with third-party service providers (e.g., for shipping or analytics) are present and framed within the context of operational necessity. By appointing joint data controllers in the EU, TI demonstrates a clear understanding of its obligations under GDPR for its European operations, ensuring accountability for data processing activities.
The website shows a strong commitment to digital accessibility, which is a strategic advantage in the B2B sector. A dedicated 'Accessibility' statement is available in the footer, affirming a goal of conforming to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 Level AA. This is the recognized standard for B2B websites. A preliminary manual review indicates good practices are in place, such as clear navigation, logical content structure, and readable text contrast. By providing contact information for accessibility issues, they have established a clear channel for user feedback and remediation. This proactive stance not only mitigates legal risks under laws like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) but also enhances usability for all users, including those with situational or temporary disabilities.
As a global semiconductor leader, TI's legal positioning is heavily influenced by complex, industry-specific regulations. Their website and public filings reflect a robust compliance program in several key areas:
-
Export Controls: Semiconductors are dual-use technologies, subject to stringent U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR), especially concerning shipments to China and other designated countries. TI's public statements and corporate governance materials indicate a long-standing, robust Global Trade Compliance (GTC) program designed to screen customers and orders to prevent misuse and comply with these complex, frequently changing regulations.
-
Environmental Regulations (RoHS/REACH): TI operates in markets, particularly the EU, with strict rules on hazardous substances in electronics like the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) directives. TI provides EU Declarations of Conformity and detailed product information to assure customers of compliance, which is critical for market access.
-
Supply Chain & Conflict Minerals: The company's 'Corporate Citizenship' reports address supply chain responsibility, including policies on conflict minerals, aligning with disclosures required by the Dodd-Frank Act. This transparency is crucial for maintaining relationships with large corporate customers who have their own stringent supplier requirements.
Compliance Gaps
While the Privacy Policy is comprehensive, the specific legal mechanisms for international data transfers (e.g., from the EU to the U.S.) such as Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) or the EU-U.S. Data Privacy Framework are mentioned but could be more prominently detailed for expert users.
The extensive technical documentation (PDF datasheets) may have varying levels of accessibility. Ensuring all new and legacy PDF documents are fully tagged and screen-reader compatible is an ongoing challenge for any company of this scale.
Compliance Strengths
- •
Highly granular and user-friendly cookie consent manager that exemplifies best practices under GDPR.
- •
Comprehensive, multi-jurisdictional Privacy Center that clearly articulates user rights under GDPR and CCPA/CPRA.
- •
Public and explicit commitment to WCAG 2.1 Level AA accessibility standards, enhancing brand reputation and mitigating legal risk.
- •
Transparent and proactive communication regarding complex industry-specific regulations like export controls and environmental compliance (RoHS/REACH).
- •
Strong integration of compliance into business operations, positioning legal adherence as a strategic asset for global market access and customer trust.
Risk Assessment
- Risk Area:
Export Control Violations
Severity:High
Recommendation:Continuously monitor and adapt to the rapidly evolving U.S. export control regulations regarding semiconductors and AI chips. Invest in ongoing, advanced training for the Global Trade Compliance (GTC) team and automate screening processes to mitigate the risk of inadvertent violations, which carry severe financial and reputational penalties.
- Risk Area:
Accessibility Litigation
Severity:Low
Recommendation:Commission regular, third-party accessibility audits of the website and key user pathways, especially for online design tools. Prioritize the remediation of any identified WCAG 2.1 AA conformance issues to maintain a strong defensive position against potential ADA-related lawsuits.
- Risk Area:
Supply Chain & Environmental Non-Compliance
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Maintain rigorous supply chain auditing processes to ensure ongoing compliance with RoHS, REACH, and conflict mineral regulations. A failure in the supply chain could disrupt market access in key jurisdictions like the EU and damage relationships with major customers.
- Risk Area:
Data Breach
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Regularly conduct security penetration testing and data privacy impact assessments, particularly for services collecting engineer and customer data. Given the global nature of its user base, a data breach could trigger significant fines under GDPR and damage the company's reputation with its security-conscious B2B clients.
High Priority Recommendations
- •
Enhance the Global Trade Compliance (GTC) program with advanced AI-powered screening tools and scenario-based training to keep pace with dynamic changes in U.S. export controls targeting the semiconductor industry.
- •
Initiate a comprehensive, programmatic audit of all customer-facing technical documentation (PDFs) to ensure they are fully accessible and conform to WCAG 2.1 AA standards, creating a remediation roadmap for legacy documents.
- •
Prominently feature information on the specific legal mechanisms used for EU-U.S. data transfers within the Privacy Center to provide greater transparency and assurance to European customers and partners.
Overall, Texas Instruments (ti.com) exhibits a highly sophisticated and mature legal compliance posture that is effectively positioned as a strategic business asset. The company's public-facing legal architecture is not merely a defensive measure but a core component of its market access strategy, enabling it to operate effectively within the heavily regulated global semiconductor industry. The granular cookie consent, jurisdiction-specific privacy policies, and clear commitment to accessibility standards demonstrate a proactive approach to building trust with a global, technical audience. Furthermore, their transparent handling of complex, industry-specific regulations—such as export controls and environmental rules—is a significant competitive advantage. This robust compliance framework mitigates substantial legal and financial risks, enhances brand reputation, and solidifies customer loyalty in a B2B environment where regulatory assurance is paramount.
Visual
Design System
Corporate/Technical
Excellent
Advanced
User Experience
Navigation
Horizontal Top Bar with Mega-Menus
Intuitive
Good
Information Architecture
Logical
Clear
Moderate
Conversion Elements
- Element:
Product Card CTA (New Products Section)
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:Incorporate a direct 'View Datasheet' link on the card to accelerate the engineer's primary research workflow.
- Element:
Main Header 'Login / Register'
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:None identified; follows standard best practices.
- Element:
Shopping Cart Icon
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:None identified; placement and design are conventional and clear.
- Element:
Product Page PDF/Email Utility
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Highly Effective
Improvement:These utility icons are well-placed and highly relevant to the target audience's need to save and share technical documentation.
Assessment
Strengths
- Aspect:
Audience-Centric Design
Impact:High
Description:The website's design prioritizes clarity, data accessibility, and functionality, directly addressing the needs of its core audience: design engineers. The focus on technical specifications over marketing messaging builds credibility and streamlines the component selection process.
- Aspect:
Mature & Consistent Design System
Impact:High
Description:A robust design system is evident across all analyzed pages, including different content types (homepage, technical pages) and languages (English, Chinese). This ensures a predictable, professional, and reliable brand experience globally.
- Aspect:
Logical Information Architecture
Impact:High
Description:Content is structured logically around an engineer's workflow: by product, application, or design and development resources. This makes navigating a portfolio of over 80,000 products manageable and intuitive.
Weaknesses
- Aspect:
Over-reliance on Textual Content
Impact:Medium
Description:Technical product pages, while informative, are often dense walls of text. This can increase cognitive load and slow down the process of finding specific data points. Greater use of visual aids could improve scannability.
- Aspect:
Lack of Interactive Data Tools
Impact:Medium
Description:The site presents data effectively in static formats (tables, diagrams) but misses an opportunity to engage users with interactive tools like parameter comparison charts, performance simulators, or cost calculators, which are highly valued by engineers.
- Aspect:
Understated Calls-to-Action (CTAs)
Impact:Low
Description:Some key CTAs, such as 'Read how' in the hero banner or text-based download links, lack visual weight. They could be easily missed, potentially reducing engagement with valuable content marketing assets.
Priority Recommendations
- Recommendation:
Integrate interactive tools on product pages for component evaluation.
Effort Level:High
Impact Potential:High
Rationale:Develop and embed interactive tools like cross-vendor comparison charts, power consumption calculators, or circuit simulators. This would provide immense value, positioning TI.com not just as a catalog but as an essential engineering tool, increasing user engagement and accelerating the design-in process.
- Recommendation:
Improve scannability of technical pages with modular UI components.
Effort Level:Medium
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Break up long-form text on product pages by implementing UI components such as accordions for FAQs, tabs for different sections (Features, Specs, Documentation), and more prominent data tables. This will reduce cognitive load and help engineers find information faster.
- Recommendation:
Standardize and elevate the visual prominence of key CTAs.
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:Convert important text-based CTAs into visually distinct buttons with a clear primary and secondary style. This creates a stronger visual hierarchy and guides users more effectively toward key actions like downloading content, viewing demos, or requesting samples.
Mobile Responsiveness
Good
Based on the clean, component-based structure of the desktop site, the design is likely to adapt well to various breakpoints. The card-based layouts and clear vertical rhythm are foundations of a strong responsive design.
Mobile Specific Issues
Readability of complex data tables and intricate technical diagrams on small screens could be a challenge and should be specifically tested and optimized.
Desktop Specific Issues
No significant desktop-specific usability issues were observed. The layout uses widescreen real estate effectively without feeling cluttered.
This visual audit of Texas Instruments' website (ti.com) reveals a mature, highly effective digital platform that is expertly tailored to its primary audience of design engineers and technical professionals. The company, a global leader in semiconductors, has created a user experience that prioritizes functionality, data accessibility, and brand consistency over superfluous design trends.
Design System and Brand Identity:
The website employs a sophisticated and consistent design system, characterized by a clean, corporate aesthetic. The use of the brand's signature red is strategic and purposeful, providing accents and guiding user attention without overwhelming the technical content. This consistency extends flawlessly across different languages, as seen in the comparison between the English and Chinese product pages, demonstrating a high level of design maturity and a successful global strategy.
Visual Hierarchy and Information Architecture:
The site's greatest strength lies in its clear information architecture and visual hierarchy. Navigation is intuitive, categorized by the logical workflow of an engineer (Products, Applications, Design & development). On content-heavy technical pages, a strong typographical hierarchy and generous use of white space make dense information scannable and digestible. This is critical for users who need to find precise technical data quickly within a massive product portfolio.
User Experience and Conversion:
The user experience is streamlined for technical tasks. Conversion is not about a simple e-commerce transaction but about facilitating an engineer's design process. Key 'conversion' elements are well-implemented, such as providing easy access to datasheets (PDF/Email functions), showcasing new products with key specs upfront, and enabling sample orders through a clear cart and login system. The user flow from discovery on the homepage to deep technical evaluation on a product page is logical and unobstructed.
Opportunities for Enhancement:
Despite its many strengths, there are clear opportunities for strategic improvement. The primary weakness is an over-reliance on static, text-based content on deep product pages. While the information is accurate, its presentation could be enhanced to reduce cognitive load. Introducing more visual and interactive elements—such as modular UI components (tabs, accordions) and dynamic data tools (comparison charts, simulators)—would transform the site from a passive repository of information into an active, indispensable engineering resource. Furthermore, while primary CTAs are clear, secondary CTAs often lack the visual prominence needed to effectively guide users toward valuable content like corporate reports and technical guides, representing a missed opportunity for deeper engagement.
Discoverability
Market Visibility Assessment
Texas Instruments (TI) commands exceptional brand authority within the semiconductor industry, built on a long history of innovation and reliability. Their digital presence reinforces this through a vast library of technical documentation, a well-regarded engineer-to-engineer (E2E) support community, and extensive educational resources. They are perceived as a foundational pillar of the electronics industry, with their brand being synonymous with high-quality analog and embedded processing components. Their thought leadership is demonstrated through in-depth application notes, white papers, and case studies that address complex engineering challenges in high-growth markets like automotive and industrial automation.
TI is the dominant player in the highly fragmented analog semiconductor market, holding a market share of approximately 19% as of recent analyses, significantly ahead of its closest competitors like Analog Devices (ADI). Their digital visibility reflects this leadership. Searches for broad analog product categories frequently lead to TI's website. However, competitors like ADI, STMicroelectronics, and NXP are aggressive in specific niches. TI's strategy of focusing on direct customer engagement via its website enhances data collection and margin, but may reduce visibility in third-party distributor channels where some competitors are stronger.
The customer acquisition potential through digital presence is immense and strategically crucial for TI. Their target audience—design engineers—relies heavily on search engines during the component selection process. TI's website is a powerful acquisition tool, converting visitors through datasheet downloads, sample requests, and access to reference designs and simulation tools. By providing comprehensive technical content that solves specific engineering problems (e.g., 'how to extend battery life'), TI captures engineers early in the design cycle, well before a specific part number is chosen. This solution-oriented digital approach positions them as a partner rather than just a component supplier.
TI has a strong global footprint, with significant revenue from the U.S. and China. Their digital presence supports this with localized website versions and participation in regional online communities and events. A key opportunity lies in deepening penetration in emerging markets, particularly in India's burgeoning electronics and automotive sectors. Digital content tailored to region-specific regulations, applications (like the 48-volt two-wheeler market in India), and engineering challenges can accelerate market share growth in these key geographic areas.
TI demonstrates exceptional breadth and depth in industry topic coverage. Their website is a comprehensive repository covering their core segments of Analog and Embedded Processing. Content spans from high-level application areas like robotics, building security, automotive ADAS, and industrial automation to granular product-level details. Their focus on the industrial and automotive markets, which constitute about 70% of their revenue, is heavily reflected in their digital content strategy. This extensive coverage solidifies their expertise and ensures visibility across a vast range of engineering search queries.
Strategic Content Positioning
TI's content is well-aligned with the highly technical B2B customer journey of a design engineer. It effectively supports all stages: a) Awareness: High-level guides ('An engineers's guide to humanoids') and blogs address broad challenges. b) Consideration: Detailed application notes, reference designs, and whitepapers help engineers evaluate solutions. c) Decision: Product pages with exhaustive datasheets, simulation models, and availability information facilitate component selection. d) Implementation & Support: The E2E forums and extensive technical documentation provide crucial post-selection support.
While TI is a clear technical leader, there is an opportunity to elevate their thought leadership content to be more forward-looking. Currently, much of the content is solution-oriented for existing problems. Opportunities exist to create more content around future-facing topics like the role of analog in edge AI, next-generation power management for sustainable energy, and the future of software-defined vehicles. Highlighting their R&D in areas like Gallium Nitride (GaN) technology can further position them as innovators shaping the future of the industry.
Competitors like Analog Devices are often perceived as stronger in high-performance, specialized converter applications, and their content may reflect a deeper focus in these niches. STMicroelectronics has built a powerful ecosystem around its STM32 microcontrollers, supported by a very strong developer community and content. TI can counter this by creating more content that highlights the integration and system-level benefits of its vast portfolio, showcasing how their components work together to create a complete, optimized solution. They could also increase content showcasing their manufacturing advantages, such as cost benefits and supply chain reliability from their 300mm fabs.
TI's brand messaging of 'Engineering a better world' and making electronics 'more affordable through semiconductors' is consistently applied. This is evident from their homepage content, which features case studies on societal benefits (building security) and technical innovations that improve efficiency (predictive battery gauging). This messaging connects their highly technical products to tangible, real-world benefits, effectively communicating their value proposition beyond just performance specifications.
Digital Market Strategy
Market Expansion Opportunities
- •
Develop dedicated content hubs for emerging high-growth markets like Edge AI, EV charging infrastructure, and next-generation robotics, positioning TI as the foundational technology provider in these nascent fields.
- •
Create comparative content that strategically positions TI's Gallium Nitride (GaN) solutions against competitors' Silicon Carbide (SiC) offerings, educating the market on the benefits of GaN for specific applications like automotive.
- •
Launch a targeted content campaign for academic and student audiences, providing educational kits and resources to build brand loyalty with the next generation of engineers.
Customer Acquisition Optimization
- •
Increase investment in 'problem-first' content that addresses top-of-funnel engineering challenges, capturing potential customers before they begin searching for specific part numbers.
- •
Develop more interactive design and simulation tools directly on the website to increase user engagement and provide a seamless path from research to sample request.
- •
Leverage data from datasheet downloads and sample requests to create targeted email nurturing campaigns that suggest complementary products and relevant application notes, increasing the value of each acquired lead.
Brand Authority Initiatives
- •
Launch a 'TI Distinguished Engineer' video series or podcast, featuring their top technical experts discussing future industry trends and challenges.
- •
Partner with leading research universities on whitepapers and joint studies to solidify TI's position at the forefront of semiconductor innovation.
- •
Create a comprehensive online 'TI University' with certification paths for key technologies (e.g., power management, high-speed data conversion) to become the definitive educational resource for engineers.
Competitive Positioning Improvements
- •
Develop content that emphasizes TI's key competitive advantages: manufacturing scale (300mm fabs), supply chain control, and the breadth of its 80,000+ product portfolio.
- •
Create system-level 'solution blueprints' that showcase how multiple TI components (e.g., MCU, power management, sensors, connectivity) work together, differentiating from competitors who may only offer point solutions.
- •
Launch marketing campaigns that highlight the longevity and reliability of TI products, appealing to industrial and automotive customers who require long product lifecycles.
Business Impact Assessment
Market share growth will be indicated by an increase in organic search visibility for high-volume, non-branded technical keywords (e.g., 'buck boost controller', 'automotive radar sensor') relative to key competitors. Success is also measured by the volume of datasheet downloads and sample requests for new product introductions in strategic growth areas.
Key acquisition metrics are the number of new user registrations on myTI, sample requests originating from content marketing efforts, and qualified leads generated from reference design or whitepaper downloads. A critical, lower-funnel metric is the 'design-in' win rate, which can be tracked through sales team feedback and customer relationship data.
Brand authority is measured by the volume of citations of TI's technical documents (application notes, whitepapers) in external publications and forums, growth in membership and engagement within the E2E support community, and media mentions in reputable industry journals. Another key metric is the 'share of voice' in online technical discussions.
Benchmarking will involve regular analysis of search engine ranking positions for competitive product categories against Analog Devices, STMicroelectronics, and NXP. Success is defined by maintaining or gaining a top-3 position for critical product keywords. Additionally, tracking the sentiment and volume of brand mentions versus competitors on technical forums and social media provides qualitative positioning data.
Strategic Recommendations
High Impact Initiatives
- Initiative:
Launch 'System Solution Hubs'
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Engineers increasingly design complete systems, not just select individual components. Competitors often focus on individual product excellence. This initiative positions TI as a system-level partner, increasing the average number of TI components per design ('design stickiness').
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in cross-product sample requests from a single user session
- •
Downloads of system-level block diagrams and reference designs
- •
Reduction in time-to-market feedback from customers
- Initiative:
Develop a 'Next-Generation Engineer' Educational Program
Business Impact:Medium
Market Opportunity:The competition for engineering talent is fierce. By becoming the preferred educational resource for university students and early-career engineers, TI can build brand loyalty and a talent pipeline long before those engineers have purchasing power, creating a durable competitive advantage.
Success Metrics
- •
Adoption of TI-based curriculum in universities
- •
Engagement with student-focused online content and tutorials
- •
Number of student accounts created on myTI
- Initiative:
Create a 'Manufacturing Advantage' Content Series
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:In a post-pandemic world, supply chain resilience is a primary concern for customers. TI's massive investment in in-house 300mm fabrication is a significant competitive differentiator against more fab-light competitors. Explicitly marketing this advantage can win designs from risk-averse customers in the automotive and industrial sectors.
Success Metrics
- •
Engagement with content highlighting supply chain and cost benefits
- •
Inclusion of 'supply chain stability' as a reason for selection in customer surveys
- •
Increased lead generation from large industrial and automotive accounts
Reposition Texas Instruments from a premier 'component provider' to the essential 'system-level technology partner' for the industrial and automotive sectors. This strategy leverages TI's core strengths—its unparalleled product breadth and manufacturing scale—to offer integrated, reliable, and cost-effective solutions. The digital presence should shift focus from individual product specifications to demonstrating how the entire TI portfolio accelerates customer innovation and de-risks their supply chain.
Competitive Advantage Opportunities
- •
Portfolio Breadth: Create digital experiences that guide engineers through designing an entire subsystem using only TI parts, simplifying their procurement and design process.
- •
Manufacturing Scale & Control: Aggressively market the supply chain security and cost advantages derived from in-house 300mm wafer fabs, a key differentiator against competitors reliant on third-party foundries.
- •
Direct-to-Customer Model: Utilize the rich data from TI.com interactions to personalize content, anticipate customer needs, and proactively suggest solutions, creating a superior customer experience that competitors using traditional distribution models cannot easily replicate.
Texas Instruments (TI) possesses a dominant digital market presence that mirrors its leadership position in the analog and embedded semiconductor markets. The company's website, ti.com, is not merely a product catalog but a comprehensive ecosystem designed to support design engineers through every stage of their complex journey. This digital infrastructure serves as a powerful competitive moat, fostering direct customer relationships and generating invaluable market data.
Market Visibility & Brand Authority:
TI's brand authority is virtually unparalleled. For decades, it has been a foundational resource for the engineering community. Their digital presence is built on a massive repository of high-quality technical content—datasheets, application notes, reference designs, and an active E2E support forum. This content ensures high visibility for a vast array of technical, long-tail search queries that are characteristic of an engineer's research process. They effectively capture users at all funnel stages, from broad problem exploration (e.g., robotics ebooks) to specific component evaluation (e.g., BQ24810 product page).
Strategic Content & Customer Journey:
The website's structure and content are strategically aligned with the engineer's workflow. It successfully addresses the needs of its target audience by providing not just product information, but tangible design aids like simulation tools and reference designs. This reduces friction in the design process and deeply embeds TI into the customer's workflow, making a switch to a competitor more difficult. The primary focus is on empowering the engineer, which builds immense brand loyalty and trust.
Competitive Landscape & Strategic Opportunities:
While TI leads the overall analog market, it faces strong competition in specific niches from players like Analog Devices (high-performance signal chain) and STMicroelectronics (MCU ecosystem). A key strategic imperative is to leverage its digital platform to emphasize its unique competitive advantages:
-
System-Level Solutions: TI's greatest untapped opportunity is to shift its content strategy from promoting individual components to showcasing integrated, system-level solutions. By creating 'solution blueprints' for key applications (e.g., an entire EV battery management system), TI can leverage its portfolio breadth to increase the number of TI parts per design, building a stronger competitive defense.
-
Manufacturing as a Marketable Asset: TI's significant investment in in-house 300mm manufacturing provides cost and supply chain advantages. In today's supply-constrained environment, this is a powerful selling point. A dedicated digital marketing initiative highlighting supply chain reliability, long-term availability, and cost-efficiency can directly influence procurement decisions, especially in the conservative industrial and automotive sectors.
-
Deepening the Direct Relationship: The direct-to-customer model via ti.com is a strategic asset. By further enhancing personalization and leveraging user data, TI can create a highly tailored experience that anticipates engineer needs, proactively recommending relevant content and products, thus optimizing customer acquisition and lifetime value.
Conclusion:
Texas Instruments' digital market presence is a core pillar of its business strategy. It is a world-class example of B2B digital marketing, effectively acquiring and retaining a highly technical audience. To sustain and grow its market leadership, the strategic focus should now evolve from being the best component library to being the most indispensable system design partner. By digitally showcasing the power of its integrated portfolio and the resilience of its manufacturing model, TI can build an even more durable competitive advantage for the decade to come.
Strategic Priorities
Strategic Priorities
- Title:
Weaponize Manufacturing Advantage to Capture Market Share
Business Rationale:In a world of increasing geopolitical tension and supply chain volatility, TI's massive investment in in-house, 300mm manufacturing is its most defensible competitive advantage. Explicitly positioning supply chain reliability as a primary value proposition will attract risk-averse, high-volume customers in the critical automotive and industrial sectors, differentiating TI from fab-light competitors.
Strategic Impact:This strategy shifts TI's market perception from a 'component generalist' to the industry's 'most reliable technology partner,' directly influencing long-term procurement decisions and locking in multi-year, high-volume contracts.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in market share within automotive and industrial segments
- •
"Supply Chain Reliability" cited as a top reason for selection in customer surveys
- •
Growth in number and value of long-term supply agreements
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Market Position
- Title:
Pivot from Component Sales to Integrated System Solutions
Business Rationale:Competitors are strong in niche products or specific ecosystems. TI's unparalleled portfolio breadth is a currently underutilized strategic asset. Bundling multiple components with reference software into complete system-level solutions for high-growth applications (e.g., EV Battery Management, Robotics Motor Control) will increase customer stickiness and average revenue per design.
Strategic Impact:Transforms the revenue model by moving up the value chain, increasing the average 'Share of Bill of Materials' (BOM), and creating a powerful competitive moat against rivals who only offer individual parts.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in average number of TI components per customer design win
- •
Revenue growth from new 'System Solution Packs'
- •
Higher design win rate in head-to-head competitions
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Revenue Model
- Title:
Launch an 'Electrification of Everything' Market Initiative
Business Rationale:The global transition to electrification—spanning electric vehicles, grid infrastructure, and renewable energy—represents the largest secular growth driver for semiconductors. TI must strategically focus its vast resources to become the undisputed foundational technology provider in this space, particularly in high-power GaN and SiC solutions where growth is fastest.
Strategic Impact:This initiative positions TI as the essential partner for the global energy transition, enabling it to capture a disproportionate share of a multi-decade growth market and secure long-term, high-margin revenue streams.
Success Metrics
- •
Year-over-year revenue growth from the Grid & Renewables segment
- •
Market share growth in GaN/SiC power devices
- •
Number of major design wins in EV charging and solar inverter applications
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Long-term Vision (12+ months)
Category:Market Expansion
- Title:
Transform TI.com into an AI-Powered System Design Platform
Business Rationale:TI.com is already a critical direct-sales channel. The next evolution is to transform it from a product catalog into an indispensable engineering partner. By investing in AI-driven tools that help engineers design entire systems—not just find parts—TI can drastically reduce customer time-to-market and embed itself deeper into their daily workflow.
Strategic Impact:Creates an unparalleled digital customer experience that locks in engineers to the TI ecosystem, provides invaluable data on emerging design trends, and accelerates the sales cycle from discovery to high-volume production.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in user engagement and session duration on TI.com design tools
- •
Reduction in the average 'discovery-to-sample' timeline
- •
Positive customer satisfaction (NPS) scores on new AI-based design features
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Long-term Vision (12+ months)
Category:Customer Strategy
- Title:
Establish a 'Next-Generation Engineer' Global Talent Initiative
Business Rationale:The long-term constraint on growth for the entire semiconductor industry is the availability of skilled analog and systems engineering talent. By establishing the definitive educational program in partnership with top universities, TI can build its brand with engineers before they enter the workforce, creating a sustainable talent pipeline and a deep-rooted ecosystem preference.
Strategic Impact:Secures the human capital necessary for future innovation, reduces long-term recruiting costs, and creates a durable competitive advantage by making TI the foundational technology platform for engineering education globally.
Success Metrics
- •
Number of strategic universities adopting TI-based curriculum
- •
Number of student accounts created on myTI
- •
Application rate from partner universities for internships and full-time roles
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Strategic Initiative (3-12 months)
Category:Operations
Texas Instruments must evolve from being the industry's best component library to its most indispensable system design partner. This requires weaponizing its manufacturing and supply chain supremacy as a key market differentiator, while shifting the business model to deliver integrated, system-level solutions for the high-growth electrification market.
The primary competitive advantage to build is unmatched supply chain resilience and reliability, derived from a vertically integrated, 300mm manufacturing scale. This moves the competitive axis from pure performance to stability and strategic partnership.
The primary growth catalyst is increasing the 'Share of Bill of Materials' (BOM) within the fastest-growing applications in the automotive and industrial sectors, driven by the global trend of electrification and automation.