eScore
uber.comThe eScore is a comprehensive evaluation of a business's online presence and effectiveness. It analyzes multiple factors including digital presence, brand communication, conversion optimization, and competitive advantage.
Uber possesses a dominant digital presence, anchored by unparalleled brand authority and a sophisticated, globally-scaled yet hyper-local web infrastructure. Its content is expertly aligned with high-transactional search intent, capturing users at the point of need for ridesharing or delivery. The multi-channel presence is robust, leveraging social media and digital ads to drive app installs and engagement, effectively making the website a powerful funnel to their core app ecosystem.
Exceptional brand authority and domain presence, making 'Uber' synonymous with its core service and ensuring top rankings for high-intent keywords globally.
Develop a more robust top-of-funnel content strategy by leveraging proprietary data to create thought leadership reports on urban mobility and logistics, capturing organic traffic earlier in the customer journey.
Uber's messaging is a masterclass in functional clarity and audience segmentation, effectively funneling riders, drivers, and business customers into distinct conversion paths. The communication on the website is direct, utilitarian, and highly effective for a user base with immediate transactional needs. However, it underutilizes brand storytelling, missing opportunities to build a deeper emotional connection by highlighting its mission, safety, and sustainability efforts on its primary landing pages.
Crystal-clear audience segmentation that efficiently serves multiple distinct personas from a single, uncluttered homepage, with direct calls-to-action that support core business objectives.
Integrate a dedicated 'Impact' module on the homepage to showcase key safety features, sustainability progress, and positive driver stories, balancing the strong functional messaging with brand-building narrative.
The website offers a best-in-class user experience, characterized by a minimalist design, low cognitive load, and a flawless cross-device journey. The conversion path for booking a ride or signing up is intuitive and streamlined, removing nearly all friction for high-intent users. While digital accessibility is strong with a commitment to WCAG 2.1 AA standards, the primary conversion goal—the app—could be promoted more aggressively on mobile web.
A minimalist, focused design system that creates an uncluttered and low-friction user experience, allowing users to complete primary tasks with maximum efficiency and minimal mental effort.
Implement a persistent, dismissible 'Download App' smart banner for mobile web visitors to more effectively bridge the conversion gap between the web experience and the more strategic native app ecosystem.
Uber projects credibility through its dominant market position, professional web design, and dedicated safety features. The company provides comprehensive privacy documentation and has robust data governance structures. However, this is significantly undermined by massive regulatory risks, including substantial GDPR fines for data transfers and persistent legal battles over worker classification and service accessibility (ADA), which create a disconnect between policy and practice.
Comprehensive and regionally-specific privacy policies, supported by a dedicated privacy center and data protection officer, demonstrating a mature approach to data governance.
Proactively address the physical service accessibility gap by funding and publicly reporting on a time-bound plan to materially increase the availability of wheelchair-accessible vehicles (WAVs) to mitigate legal and reputational risk.
Uber's competitive advantage is deeply entrenched and sustainable, built on powerful two-sided network effects at a global scale that are incredibly difficult for competitors to replicate. This is further fortified by unparalleled brand recognition, proprietary data for operational optimization, and a growing ecosystem of services (Mobility, Delivery, Freight) that increases customer switching costs. The primary challenge is not the strength of the moat itself, but the external regulatory pressures that threaten its foundational business model.
The two-sided network effect, where a massive base of riders and drivers continuously reinforce each other, creates a powerful, self-sustaining competitive moat and a high barrier to entry in its established markets.
Accelerate the integration and cross-promotion of services within the Uber One membership to transform the platform into a true 'super app,' making the combined ecosystem—not just a single service—the primary competitive advantage.
The business model is exceptionally scalable, built on an asset-light framework with high operating leverage, which has been proven by its recent achievement of sustained profitability and massive free cash flow. The company demonstrates strong expansion potential by diversifying into new verticals like grocery and retail delivery, expanding its high-margin advertising business, and pushing deeper into suburban markets. The primary constraint on scalability is not technical or financial, but the operational challenge of acquiring and retaining drivers in a competitive and legally contentious labor market.
A highly scalable, asset-light business model that leverages technology to connect independent providers with consumers, allowing for rapid geographic expansion and new service rollouts with minimal capital expenditure.
Develop more sophisticated, data-driven driver incentive and retention programs to ensure the supply side of the marketplace can scale reliably to meet growing demand in both new and existing markets.
Uber's business model has matured into a coherent and synergistic ecosystem, moving from a single service to a multi-faceted platform for movement. Revenue streams are well-diversified across Mobility, Delivery, Freight, and a rapidly growing, high-margin Advertising business. The strategic focus is clear: leverage the platform to increase customer lifetime value through cross-platform usage, with stakeholder alignment being the most significant weakness due to ongoing tensions with its driver and courier partners.
A well-diversified portfolio of synergistic businesses (Mobility, Delivery, Freight) built on a unified technology platform, which reduces reliance on any single segment and creates a powerful cross-promotional flywheel.
Proactively reshape the gig work model by advocating for and investing in a 'third way' framework that provides drivers with more benefits and earnings stability, improving critical stakeholder alignment and reducing regulatory risk.
Uber wields immense market power, holding a dominant share of the U.S. ridesharing market and a strong secondary position in food delivery. Its ability to implement dynamic 'surge' pricing demonstrates significant pricing power, while its global brand recognition allows it to shape industry trends and influence consumer behavior. The company's strategic shift to a platform for autonomous vehicle companies further solidifies its intent to maintain market leadership through the next technological evolution of transport.
Dominant market share in its core mobility segment and category-defining brand power give Uber significant influence over pricing, industry standards, and the future direction of on-demand transportation.
Form strategic partnerships with public transit agencies to integrate their services into the Uber app, positioning Uber as the central hub for Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) and further cementing its market influence.
Business Overview
Business Classification
Technology Platform
Multi-Sided Marketplace
Transportation & Logistics Technology
Sub Verticals
- •
Ridesharing
- •
Food & Grocery Delivery
- •
Freight Logistics
- •
Business Travel Solutions
- •
Micromobility
Mature
Maturity Indicators
- •
Global brand recognition and operations in over 70 countries and 10,000 cities.
- •
Publicly traded company (NYSE: UBER) with a market capitalization exceeding $190 billion.
- •
Shift in focus from hyper-growth to sustainable profitability and positive free cash flow.
- •
Diversification into multiple, synergistic business segments beyond the core ridesharing product.
- •
Consistent annual revenue growth in the double digits, indicating a strong market position.
Enterprise
Steady
Revenue Model
Primary Revenue Streams
- Stream Name:
Mobility (Ridesharing)
Description:Takes a commission (typically 20-30%) from the total fare paid by riders for various transportation services like UberX, Uber Comfort, and Uber Black. This remains a core revenue driver.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Riders & Drivers
Estimated Margin:Medium
- Stream Name:
Delivery (Uber Eats)
Description:Generates revenue through commission fees from partner restaurants and merchants, as well as delivery and service fees paid by consumers for food, grocery, and other retail delivery. This segment is a major source of earnings growth.
Estimated Importance:Primary
Customer Segment:Eaters, Couriers, Merchants
Estimated Margin:Medium-Low
- Stream Name:
Freight
Description:Connects shippers with carriers through a digital marketplace, earning a fee for facilitating logistics and freight transportation. This B2B service diversifies revenue into the larger logistics industry.
Estimated Importance:Secondary
Customer Segment:Shippers & Carriers
Estimated Margin:Low
- Stream Name:
Advertising
Description:A high-margin, rapidly growing stream involving sponsored listings for restaurants on Uber Eats and in-app advertisements during rides ('Ride Offers'), monetizing its large user base.
Estimated Importance:Tertiary
Customer Segment:Merchants & Advertisers
Estimated Margin:High
Recurring Revenue Components
Uber One Membership: A subscription service offering benefits like free delivery and discounted rides, creating a loyal and high-frequency user base.
Uber for Business: Corporate contracts for managing employee travel and meal programs.
Pricing Strategy
Dynamic & Value-Based Pricing
Mid-range to Premium
Semi-transparent
Pricing Psychology
- •
Surge Pricing: Increases prices based on real-time supply and demand, creating a sense of urgency and balancing the marketplace.
- •
Upfront Pricing: Shows the total cost to the rider before booking, reducing uncertainty and friction.
- •
Tiered Options: Offers a range of services (e.g., UberX, Comfort, Black) at different price points to capture a wider audience.
Monetization Assessment
Strengths
- •
Diversified revenue streams across Mobility, Delivery, and Freight reduce reliance on any single market segment.
- •
Dynamic pricing algorithm effectively maximizes revenue by balancing supply and demand.
- •
High-margin advertising business is scaling rapidly, offering a new path to profitability.
- •
The Uber One subscription model enhances customer loyalty and creates a predictable, recurring revenue stream.
Weaknesses
- •
Heavy reliance on the gig economy workforce, which leads to high driver/courier turnover and dissatisfaction over wages.
- •
Profitability in the Delivery segment is often thin due to intense competition and high operational costs.
- •
Historical record of significant losses has pressured the company to focus on profitability, sometimes at the expense of aggressive growth.
Opportunities
- •
Further expansion of the high-margin advertising platform to monetize the 3.3 billion quarterly trips.
- •
Deeper integration of financial services for drivers and couriers (e.g., instant payouts, financial products).
- •
Expansion into new delivery verticals such as pharmacy, alcohol, and retail to increase the utility of Uber Eats.
- •
Leveraging data analytics for new revenue streams, such as urban mobility planning for cities.
Threats
- •
Intense competition from players like Lyft in ridesharing and DoorDash in food delivery, leading to price wars and pressure on margins.
- •
Regulatory challenges worldwide concerning the classification of drivers as independent contractors vs. employees, which could significantly increase costs.
- •
Economic downturns could reduce discretionary spending on both ridesharing and food delivery.
- •
The long-term development of autonomous vehicle technology by competitors could disrupt Uber's current driver-dependent model.
Market Positioning
Integrated 'Super App' for Movement
Dominant leader in US ridesharing (approx. 71%) and a strong second in US food delivery (approx. 23-30%).
Target Segments
- Segment Name:
Urban & Suburban Commuters
Description:Tech-savvy individuals aged 18-45 living in urban or dense suburban areas who prioritize convenience and efficiency for daily travel.
Demographic Factors
- •
Age: 18-45
- •
Income: Middle to high
- •
Location: Urban and suburban areas
Psychographic Factors
- •
Values convenience and time-saving solutions
- •
Prefers experiences over asset ownership (e.g., car)
- •
Comfortable with mobile technology and cashless transactions.
Behavioral Factors
Frequent use for commuting, social events, and airport travel.
High adoption of on-demand services.
Pain Points
- •
High cost and hassle of car ownership (parking, insurance, maintenance)
- •
Unreliability or inconvenience of public transportation
- •
Difficulty finding transportation after consuming alcohol
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:Medium
- Segment Name:
Convenience-Seeking Eaters
Description:Individuals and families seeking quick, convenient access to a wide variety of local restaurants and grocery stores without leaving home.
Demographic Factors
Age: 18-44 (74.5% of Uber Eats users).
Household: Singles, couples, and busy families
Psychographic Factors
- •
Values time and convenience over cost
- •
Desires variety and choice in food options
- •
Lifestyle often includes busy work schedules
Behavioral Factors
Orders food delivery multiple times per month
Uses app for both meal discovery and routine ordering
Pain Points
- •
Lack of time or desire to cook
- •
Limited dining options within immediate vicinity
- •
Inconvenience of grocery shopping
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Segment Potential:High
- Segment Name:
Gig Economy Workers (Drivers/Couriers)
Description:Individuals seeking flexible, independent work opportunities to supplement their income or as their primary source of earnings.
Demographic Factors
Varied age, with a tendency to be older than riders.
Often seeking part-time or flexible full-time work
Psychographic Factors
- •
Values flexibility and autonomy
- •
Entrepreneurial mindset
- •
Motivated by income potential.
Behavioral Factors
Works during peak demand hours to maximize earnings
May work for multiple gig platforms simultaneously
Pain Points
- •
Income volatility and unpredictability
- •
Vehicle wear and tear and fuel costs
- •
Lack of traditional employment benefits
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:Medium
- Segment Name:
Corporate & Business Travelers
Description:Companies and their employees who require a streamlined and manageable solution for business-related travel, meals, and expense reporting.
Demographic Factors
Professionals of all ages who travel for work
Psychographic Factors
Value efficiency, reliability, and ease of expensing
Organization prioritizes duty of care and cost control
Behavioral Factors
Frequent travel to meetings, airports, and client sites
Use of corporate cards and expense management systems
Pain Points
- •
Complex and time-consuming expense reporting
- •
Difficulty tracking employee travel for safety and budget purposes
- •
Need for reliable, on-demand transport in unfamiliar cities
Fit Assessment:Good
Segment Potential:High
Market Differentiation
- Factor:
Network Effects
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Global Brand Recognition
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Integrated Service Platform ('Super App')
Strength:Moderate
Sustainability:Sustainable
- Factor:
Proprietary Technology & Data Analytics
Strength:Strong
Sustainability:Sustainable
Value Proposition
To provide seamless, on-demand access to transportation, delivery, and logistics, making movement of people and things effortless and accessible for everyone, everywhere.
Excellent
Key Benefits
- Benefit:
On-Demand Convenience
Importance:Critical
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
Ability to request a ride or order delivery in minutes via a mobile app
Real-time tracking of drivers and orders
- Benefit:
Choice & Flexibility
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Somewhat unique
Proof Elements
- •
Multiple ride options (UberX, Comfort, Black, etc.)
- •
Vast selection of restaurants and stores on Uber Eats
- •
Flexible earning opportunities for drivers and couriers
- Benefit:
Integrated Ecosystem
Importance:Important
Differentiation:Unique
Proof Elements
- •
Single app for rides, food, and grocery delivery
- •
Uber One membership benefits apply across services
- •
Higher retention for users of both mobility and delivery services.
Unique Selling Points
- Usp:
The Power of the Platform: Unmatched scale and liquidity in its core markets, driven by powerful hyperlocal network effects.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
Global Operational Footprint: The ability to provide a consistent user experience in thousands of cities worldwide.
Sustainability:Long-term
Defensibility:Strong
- Usp:
Cross-Platform Synergy: A single integrated platform for moving people (Mobility) and things (Delivery), creating a 'super app' flywheel effect.
Sustainability:Medium-term
Defensibility:Moderate
Customer Problems Solved
- Problem:
Immediate need for transportation without owning a vehicle.
Severity:Critical
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Desire for convenient access to a wide variety of prepared foods and groceries.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Complete
- Problem:
Need for flexible, accessible income-earning opportunities.
Severity:Major
Solution Effectiveness:Partial
Value Alignment Assessment
High
Uber's services directly address the growing consumer demand for on-demand convenience, efficiency, and platform-based solutions in transportation and local commerce.
High
The value proposition strongly resonates with its core target segments of urban, tech-savvy consumers and individuals seeking flexible work, by solving their key pain points effectively.
Strategic Assessment
Business Model Canvas
Key Partners
- •
Drivers & Couriers (Gig Workers)
- •
Restaurants & Merchants
- •
Automotive Manufacturers & Rental Companies
- •
Autonomous Vehicle Technology Companies (e.g., Waymo, Momenta).
- •
Payment Processors (e.g., Stripe, PayPal)
- •
Mapping & Navigation Providers (e.g., Google Maps)
- •
Strategic Brand Partners (e.g., Spotify, Chase).
Key Activities
- •
Platform Development & Maintenance
- •
Algorithm & AI Development (pricing, matching, routing).
- •
Marketing & User Acquisition (for all sides of the marketplace)
- •
Driver & Courier Onboarding and Support
- •
Global Operations & Logistics Management
- •
Regulatory Compliance & Government Relations
Key Resources
- •
Proprietary Technology Platform & Mobile Apps
- •
Global Brand & Reputation.
- •
Vast Network of Drivers, Riders, and Merchants.
- •
Rich datasets on mobility and delivery patterns
- •
Engineering & Data Science Talent
Cost Structure
- •
Driver & Courier Payouts and Incentives
- •
Sales & Marketing Expenses
- •
Research & Development (Technology)
- •
Operations & Support Costs
- •
Insurance & Safety Program Costs
Swot Analysis
Strengths
- •
Dominant market leadership and strong global brand recognition.
- •
Powerful, self-reinforcing network effects creating a significant competitive moat.
- •
Diversified business model across Mobility, Delivery, and Freight, reducing risk.
- •
Advanced technology, data analytics, and AI capabilities for operational efficiency.
- •
Asset-light business model allows for high scalability.
Weaknesses
- •
Dependence on a gig worker labor model, facing legal, regulatory, and satisfaction challenges.
- •
History of unprofitability and ongoing pressure to maintain positive cash flow.
- •
Negative brand perception stemming from past controversies related to safety, company culture, and labor practices.
- •
Intense competition in key segments limits pricing power and squeezes margins.
Opportunities
- •
Growth of high-margin revenue streams like advertising.
- •
Expansion into new delivery verticals (e.g., pharmacy, retail, alcohol).
- •
Strategic partnerships with autonomous vehicle companies to reduce long-term operating costs.
- •
Deeper integration of financial technology services for its user base (riders and drivers).
- •
Continued growth in emerging markets and expansion of Uber for Business.
Threats
- •
Intense and well-funded competition from rivals like Lyft, DoorDash, and regional players.
- •
Unfavorable government regulations, particularly regarding driver employment classification.
- •
Potential for economic downturns to reduce consumer discretionary spending on rides and delivery.
- •
Long-term disruption from fully autonomous vehicle networks operated by competitors (e.g., Tesla, Waymo).
- •
Cybersecurity risks and data breaches impacting user trust.
Recommendations
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Driver & Courier Relations
Recommendation:Invest in programs that improve earnings stability, provide access to benefits, and offer clearer communication channels to increase retention and strengthen the supply-side network.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Uber One Subscription
Recommendation:Enhance the value proposition of the Uber One membership by adding more exclusive perks and deeper cross-platform integrations to increase subscriber penetration and create a stickier ecosystem.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Delivery Profitability
Recommendation:Focus on operational efficiencies in the delivery segment, such as order batching and route optimization, and continue to scale the high-margin restaurant advertising business to improve unit economics.
Expected Impact:Medium
Business Model Innovation
- •
Develop a 'Logistics-as-a-Service' (LaaS) platform for small and medium-sized businesses, leveraging the existing courier network for last-mile delivery.
- •
Further integrate third-party services into the Uber app (e.g., public transit ticketing, event bookings, restaurant reservations) to solidify its position as a comprehensive 'super app' for urban mobility.
- •
Leverage anonymized mobility data to create a B2B data insights product for urban planning, retail real estate, and infrastructure development.
Revenue Diversification
- •
Aggressively scale the advertising business by introducing new ad formats and self-service tools for small businesses.
- •
Expand financial product offerings for drivers and couriers, such as micro-loans, insurance, and investment options, creating a fintech arm.
- •
Explore partnerships or acquisitions in adjacent high-frequency service areas, such as home services or personal errand fulfillment.
Uber has successfully evolved from a disruptive ridesharing startup into a mature, multi-faceted technology platform for global movement. Its strategic pivot from a singular focus on 'Mobility' to an integrated ecosystem encompassing 'Delivery' and 'Freight' has been critical in diversifying revenue and building a more resilient business model. The company's core competitive advantages—unmatched brand recognition, powerful network effects, and a scalable, asset-light operational framework—position it as a dominant force.
The current business model is firmly in a phase of optimizing for profitability and sustainable growth, evidenced by positive free cash flow and a focus on high-margin opportunities like advertising. However, its future trajectory is contingent on navigating three key challenges: intense competition in all segments, the persistent regulatory threat to its gig worker model, and the long-term technological disruption of autonomous vehicles.
The most significant strategic opportunity lies in transforming into a true 'super app' for daily life. By deepening the integration between its services, enhancing the Uber One subscription to lock in customers, and leveraging its vast data assets, Uber can increase the lifetime value of its users and create a more defensible ecosystem. Future business model evolution should prioritize strengthening its relationship with the drivers and couriers who form the backbone of its service, while simultaneously pursuing a platform strategy for autonomy, positioning itself as the network on which future self-driving services operate, rather than the developer of the technology itself.
Competitors
Competitive Landscape
Mature
Oligopoly
Barriers To Entry
- Barrier:
Two-Sided Network Effects
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Global Brand Recognition and Trust
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Capital Requirements for Market Penetration (Subsidies)
Impact:High
- Barrier:
Proprietary Technology and Data Analytics
Impact:Medium
- Barrier:
Regulatory Compliance and Lobbying
Impact:Medium
Industry Trends
- Trend:
Platform Integration and 'Super Apps'
Impact On Business:Critical for increasing customer lifetime value and creating a competitive moat beyond single services. Uber is well-positioned with its Mobility and Delivery segments.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
Autonomous Vehicle Integration
Impact On Business:Potential to fundamentally change the cost structure by reducing reliance on drivers, but requires significant R&D investment and navigating regulatory hurdles.
Timeline:Long-term
- Trend:
Electrification and Sustainability
Impact On Business:Growing consumer and regulatory pressure to adopt EVs. Presents an opportunity for brand differentiation but also incurs costs for incentivizing driver transition.
Timeline:Near-term
- Trend:
Regulatory Scrutiny and Labor Law Redefinition
Impact On Business:Ongoing legal battles over driver classification (employee vs. contractor) pose a significant threat to the current business model and profitability.
Timeline:Immediate
- Trend:
AI-Powered Optimization
Impact On Business:AI is crucial for dynamic pricing, route optimization, demand prediction, and personalization, directly impacting efficiency and user experience.
Timeline:Immediate
Direct Competitors
- →
Lyft
Market Share Estimate:Approx. 29% in U.S. Ride-Hailing
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:A more driver-friendly and community-focused ride-hailing alternative, primarily in North America.
Strengths
- •
Strong brand identity in the US and Canada.
- •
Historically perceived as more driver-friendly, aiding driver retention.
- •
Focused business model on mobility allows for specialized improvements.
- •
Strategic partnerships, for example with DoorDash for membership perks.
Weaknesses
- •
Limited geographical presence outside of North America.
- •
Smaller user base and network effect compared to Uber.
- •
Less diversified revenue streams, making it more vulnerable to downturns in the ride-hailing market.
- •
Struggles with achieving consistent profitability.
Differentiators
Primary focus on ride-sharing and mobility services.
Brand positioning that emphasizes a friendly and socially responsible image.
- →
DoorDash
Market Share Estimate:Approx. 67% in U.S. Food Delivery.
Target Audience Overlap:High
Competitive Positioning:The dominant U.S. market leader in food delivery, expanding into grocery, alcohol, and retail.
Strengths
- •
Commanding market share in the lucrative U.S. food delivery market.
- •
Extensive restaurant and retail partnerships.
- •
Successful subscription model (DashPass) driving customer loyalty.
- •
Aggressive expansion into non-food delivery verticals (e.g., groceries, convenience items).
Weaknesses
- •
Lower international presence compared to Uber Eats' global footprint.
- •
Intense competition in a low-margin industry.
- •
Heavy reliance on the North American market.
Differentiators
- •
Market leadership and brand recognition specifically for delivery.
- •
Wide selection of non-restaurant delivery options.
- •
DashPass subscription program is a powerful loyalty driver.
- →
Didi Chuxing
Market Share Estimate:Dominant in China; significant presence in Latin America and other international markets.
Target Audience Overlap:Medium
Competitive Positioning:Global mobility technology platform with a dominant position in the Chinese market and expanding internationally.
Strengths
- •
Market dominance in China after acquiring Uber's local operations.
- •
Strong government relationships in its home market.
- •
Significant investment in autonomous driving and AI.
- •
Broad portfolio of mobility services including ride-sharing, bike-sharing, and financial services.
Weaknesses
- •
Faces significant regulatory scrutiny from the Chinese government.
- •
Brand recognition is lower than Uber's in Western markets.
- •
International expansion efforts have faced intense competition and regulatory hurdles.
Differentiators
Unparalleled scale and network effect within China.
Deep integration with local payment and social media platforms (e.g., WeChat).
- →
Grab
Market Share Estimate:Leading 'Super App' in Southeast Asia.
Target Audience Overlap:Low
Competitive Positioning:The all-in-one 'Super App' for Southeast Asia, offering ride-hailing, food delivery, and financial services.
Strengths
- •
Dominant market position across multiple Southeast Asian countries after acquiring Uber's local business.
- •
Highly successful 'Super App' strategy integrating payments (GrabPay), delivery, and mobility.
- •
Strong localization and understanding of regional market nuances.
- •
Extensive and loyal user base.
Weaknesses
- •
Primarily focused on Southeast Asia, lacking global scale.
- •
Faces intense competition from regional players like Gojek.
- •
Navigates a complex and fragmented regulatory landscape across different countries.
Differentiators
Comprehensive 'Super App' ecosystem is far more integrated than Uber's current offering.
Hyper-local service offerings tailored to specific country needs.
Indirect Competitors
- →
Public Transportation
Description:City-operated buses, subways, trams, and trains provide low-cost alternatives for urban commuting.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:Low, but increasing integration (MaaS - Mobility as a Service) where users can book public transit via the Uber app presents an opportunity for partnership rather than direct competition.
- →
Personal Car Ownership
Description:The traditional model of owning a private vehicle for personal transportation.
Threat Level:High
Potential For Direct Competition:N/A - This is the primary behavior Uber aims to substitute.
- →
Micromobility Services (e.g., Lime, Bird)
Description:App-based rental of electric scooters and bikes for short-distance urban travel.
Threat Level:Medium
Potential For Direct Competition:High. Uber already integrates micromobility options in its app in some cities, turning this from a threat into a service extension.
- →
Traditional Taxi Services
Description:Legacy taxi companies, which are increasingly adopting app-based hailing features (e.g., Curb) to compete.
Threat Level:Low
Potential For Direct Competition:Uber is increasingly partnering with local taxi companies to expand its network, turning competitors into partners.
- →
Autonomous Vehicle Companies (e.g., Waymo)
Description:Companies developing and operating fully autonomous vehicle fleets.
Threat Level:High
Potential For Direct Competition:Very High. These companies could launch their own autonomous ride-hailing networks, becoming direct competitors. Uber's strategy involves partnering with them to integrate their technology onto the Uber network.
Competitive Advantage Analysis
Sustainable Advantages
- Advantage:
Two-Sided Network Effects
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. A large base of riders attracts more drivers, which in turn improves service (lower wait times, wider coverage) and attracts more riders.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Global Brand Recognition
Sustainability Assessment:Highly sustainable. Uber is synonymous with ride-hailing in many parts of the world, creating a high level of trust and automatic user choice, especially for travelers.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Hard
- Advantage:
Proprietary Data and Analytics
Sustainability Assessment:Moderately sustainable. Uber's vast dataset on traffic patterns, demand forecasting, and user behavior is a significant asset for optimizing operations and pricing.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
- Advantage:
Diversified Platform (Mobility, Delivery, Freight)
Sustainability Assessment:Moderately sustainable. The ability to cross-promote services (e.g., Uber One subscription) increases customer stickiness and lifetime value.
Competitor Replication Difficulty:Medium
Temporary Advantages
{'advantage': 'Exclusive Partnerships', 'estimated_duration': '1-3 years'}
{'advantage': 'Promotional Pricing and Subsidies', 'estimated_duration': 'Short-term'}
Disadvantages
- Disadvantage:
Negative Public Perception and Brand Image Issues
Impact:Major
Addressability:Moderately
- Disadvantage:
Driver Dissatisfaction and Labor Disputes
Impact:Critical
Addressability:Difficult
- Disadvantage:
Intense Price Competition
Impact:Major
Addressability:Difficult
- Disadvantage:
Ongoing Regulatory Battles
Impact:Critical
Addressability:Difficult
Strategic Recommendations
Quick Wins
- Recommendation:
Launch targeted driver incentive programs in cities where Lyft has a strong foothold to increase driver supply and reduce rider wait times.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Easy
- Recommendation:
Aggressively market the Uber One subscription bundle, emphasizing cross-platform savings (rides and eats) to counter DoorDash's DashPass.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
Medium Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Deepen the integration of Uber's various services (Rides, Eats, Groceries, Freight) to create a seamless 'Super App' experience, increasing switching costs for users.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Expand the Uber for Business platform with more tailored solutions for corporate clients, creating a high-margin, sticky revenue stream.
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Difficulty:Moderate
- Recommendation:
Form strategic partnerships with public transit agencies to integrate their services into the Uber app, positioning Uber as the central hub for Mobility as a Service (MaaS).
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Long Term Strategies
- Recommendation:
Pursue a flexible strategy for autonomous vehicles, focusing on partnerships with multiple AV technology leaders to avoid dependency and ensure access to the best technology for the Uber network.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
- Recommendation:
Invest in and expand into adjacent high-growth logistics areas, such as last-mile delivery for retail and pharmaceuticals, leveraging the existing driver network.
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Difficulty:Difficult
Position Uber as the indispensable platform for all movement within a city—whether it's people, food, or goods. The brand message should evolve from 'getting a ride' to 'getting anything', emphasizing reliability, convenience, and a unified, seamless user experience.
Differentiate through the power of an integrated platform. While competitors may excel in a single vertical (e.g., DoorDash in food), Uber's strength lies in its ability to offer a bundled, convenient solution for a user's entire mobility and delivery needs, anchored by a compelling subscription program (Uber One).
Whitespace Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Specialized Mobility Services
Competitive Gap:Few competitors offer reliable, scalable solutions for non-emergency medical transportation (NEMT) or specialized transport for children and seniors.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Last-Mile Logistics as a Service for Small/Medium Businesses
Competitive Gap:While DoorDash is entering this space, there is a large, underserved market of SMBs that need on-demand local delivery solutions that Uber's network is perfectly positioned to provide.
Feasibility:High
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Integrated Travel and Commute Planning
Competitive Gap:No single app effectively combines ride-hailing, micromobility, public transit, and even flight/train booking into a single, seamless journey planning and payment experience.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:High
- Opportunity:
Financial Services for Drivers
Competitive Gap:Drivers represent a large, underserved market for financial products like instant pay, micro-loans, and insurance. Deepening these offerings could significantly improve driver loyalty and retention.
Feasibility:Medium
Potential Impact:Medium
Comprehensive Competitive Landscape Analysis: Uber Technologies, Inc.
Uber operates within a mature, oligopolistic market, particularly in its core Mobility and Delivery segments in North America. The industry's defining characteristic is the powerful two-sided network effect : more drivers attract more riders with lower wait times, who in turn provide more business for drivers. This creates a formidable barrier to entry and is Uber's most sustainable competitive advantage. The company has successfully leveraged this, along with its global brand recognition, to become a verb for on-demand transportation.
Direct Competitive Pressures
Uber faces a dual-front war against specialized and formidable competitors:
-
Mobility (Ride-Hailing): In North America, the market is a classic duopoly with Lyft. While Uber maintains a dominant market share, Lyft competes effectively on brand perception, often positioning itself as a more driver- and community-friendly alternative. Globally, Uber faces hyper-local champions like Didi Chuxing in China and Grab in Southeast Asia—both of whom defeated Uber in their home markets, forcing strategic divestitures where Uber retained minority stakes. These competitors demonstrate that a global network effect can be overcome by superior local execution and integration.
-
Delivery (Uber Eats): The food delivery space is even more competitive. In the highly lucrative U.S. market, DoorDash is the undisputed leader, holding a significant market share advantage over Uber Eats. DoorDash's success is driven by a singular focus, a popular subscription service (DashPass), and aggressive expansion into adjacent verticals like grocery and retail delivery. This specialized focus presents a major challenge to Uber Eats, which must fight to maintain and grow its share.
Indirect and Emerging Threats
The long-term competitive landscape is being reshaped by indirect and emerging threats. Public transportation, personal car ownership, and micromobility services remain constant alternatives for consumers. However, the most significant future disruptor is autonomous vehicle (AV) technology. Companies like Waymo could become Uber's biggest competitors by launching their own AV ride-hailing networks. Uber's strategy of partnering with multiple AV companies is a critical, albeit defensive, move to ensure it remains the network of choice, regardless of who—or what—is driving the car.
Strategic Position and Opportunities
Uber's core strategic advantage is its evolution from a single-service app to an integrated platform. The synergy between its Mobility and Delivery segments, tied together by the Uber One subscription, is its key differentiator against specialized players. By increasing the stickiness of its user base across multiple daily use cases, Uber can enhance customer lifetime value and build a competitive moat that is harder for competitors to replicate.
The primary whitespace opportunities lie in leveraging its existing logistics network for new applications. These include expanding last-mile delivery services for businesses, entering specialized mobility verticals like non-emergency medical transport, and becoming the central platform for Mobility as a Service (MaaS) by integrating public transit.
However, Uber's path to sustainable profitability is fraught with challenges. Persistent regulatory battles over driver classification and intense price competition compress margins. Furthermore, driver dissatisfaction remains a critical vulnerability that competitors can exploit. The company's future success hinges on its ability to navigate these regulatory headwinds, deepen its platform integration to fend off specialized competitors, and successfully incorporate transformative technologies like autonomous driving to fundamentally improve its cost structure.
Messaging
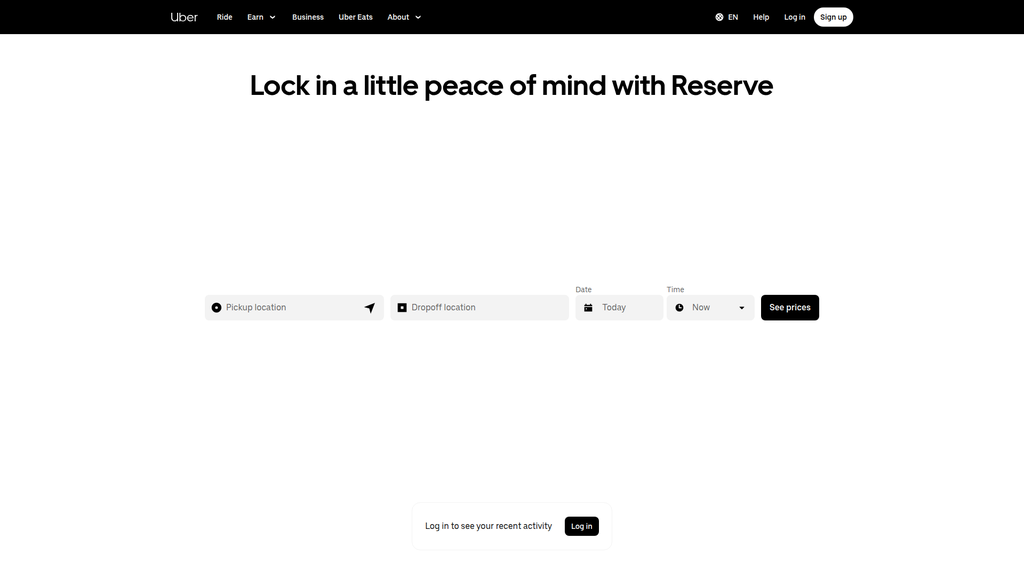
Uber's website messaging is a masterclass in functional clarity and audience segmentation. It operates as a highly efficient digital storefront, immediately segmenting users into its primary funnels: booking a ride, signing up to drive, ordering from Eats, or engaging with Uber for Business. The message architecture is ruthlessly efficient, prioritizing transactional intent above all else. The brand voice is utilitarian and direct, reinforcing the company's role as a facilitator of movement and delivery. While this functional approach is incredibly effective for a user base with high-intent, it comes at the cost of brand storytelling and emotional connection. The messaging successfully communicates the breadth of Uber's platform—its key differentiator against pure-play competitors like Lyft or DoorDash. However, it largely fails to articulate the 'why' behind the brand. Critical messages around safety, sustainability, and community impact, while present in the site's deeper structure, are underdeveloped on the homepage, representing a significant missed opportunity to build brand equity beyond mere utility. The core opportunity for Uber is to infuse its powerful functional messaging with a stronger narrative, connecting its services to the human outcomes they enable and better aligning its homepage communication with its broader corporate mission.
Message Architecture
Key Messages
- Message:
Lock in a little peace of mind with Reserve
Prominence:Primary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Hero Section / Main Banner
- Message:
Go anywhere with Uber. Request a ride, hop in, and go.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Service Suggestions Section (Ride)
- Message:
Drive when you want, make what you need.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Driver Recruitment Section
- Message:
The Uber you know, reimagined for business.
Prominence:Secondary
Clarity Score:High
Location:Uber for Business Section
- Message:
Safety, simplified.
Prominence:Tertiary
Clarity Score:Medium
Location:Safety Feature Section
- Message:
It’s easier in the apps.
Prominence:Tertiary
Clarity Score:High
Location:App Download Section
The message hierarchy is exceptionally clear and directly supports key business objectives. The primary focus is transactional, with the ride-booking widget and 'Reserve' messaging placed at the very top for immediate user action. Secondary messages are effectively segmented to address Uber's distinct audiences (Riders, Drivers, Businesses) in dedicated modules. This structure allows for efficient user navigation and conversion for each target segment.
Messaging is highly consistent within its segmented audiences. Each product line (Ride, Reserve, Food, Grocery) has a clear, concise, and benefit-oriented description that is repeated throughout the user's initial journey. The overarching theme of convenience and on-demand service is a consistent thread connecting all offerings.
Brand Voice
Voice Attributes
- Attribute:
Utilitarian
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Pickup location
- •
Dropoff location
- •
See prices
- Attribute:
Direct
Strength:Strong
Examples
- •
Request a ride, hop in, and go.
- •
Get started
- •
Download the Uber app
- Attribute:
Enabling
Strength:Moderate
Examples
Go anywhere with Uber.
Drive when you want, make what you need.
- Attribute:
Reassuring
Strength:Weak
Examples
Lock in a little peace of mind with Reserve
Safety, simplified
Tone Analysis
Transactional
Secondary Tones
Informational
Action-Oriented
Tone Shifts
The tone shifts from being purely transactional (for riders) to aspirational and empowering when addressing potential drivers ('Make money on your schedule').
A slightly more corporate and solution-oriented tone is adopted for the 'Uber for Business' section.
Voice Consistency Rating
Excellent
Consistency Issues
No itemsValue Proposition Assessment
To provide a single, on-demand platform for moving people and things conveniently and efficiently.
Value Proposition Components
- Component:
Comprehensive Offerings
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Unique
Explanation:The homepage clearly showcases the breadth of services: Ride, Reserve, Rental Cars, Food, and Grocery, establishing a 'one-stop-shop' value prop.
- Component:
Convenience & Immediacy
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Common
Explanation:Phrases like 'Request a ride, hop in, and go' and the prominent booking widget emphasize speed and ease of use, which is a core expectation in the industry.
- Component:
Flexibility & Control
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Somewhat Unique
Explanation:This is communicated for both riders ('Reserve your ride in advance') and drivers ('Drive when you want'), offering a layer of control that addresses key user pain points.
- Component:
Flexible Earning Opportunity
Clarity:Clear
Uniqueness:Common
Explanation:'Drive when you want, make what you need' is a clear and compelling value proposition for the gig economy workforce.
Uber's primary messaging differentiator is its integrated platform. While competitors focus on being the best at ridesharing (Lyft) or food delivery (DoorDash), Uber's messaging positions it as the single solution for a wide range of mobility and delivery needs. The homepage layout, which presents all services side-by-side, is a strategic choice that constantly reinforces this platform advantage.
The messaging positions Uber as the market leader and the most comprehensive platform in the on-demand economy. It doesn't acknowledge competitors, instead focusing on the breadth of its own ecosystem, projecting an image of being the default, all-encompassing choice for consumers, drivers, and businesses.
Audience Messaging
Target Personas
- Persona:
The Rider
Tailored Messages
- •
Go anywhere with Uber.
- •
Reserve your ride in advance so you can relax on the day of your trip.
- •
Safety, simplified.
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
The Driver / Delivery Partner
Tailored Messages
Drive when you want, make what you need.
Make money on your schedule with deliveries or rides—or both.
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
The Business Customer
Tailored Messages
The Uber you know, reimagined for business.
Uber for Business is a platform for managing global rides and meals, and local deliveries, for companies of any size.
Effectiveness:Effective
- Persona:
The Eats Customer
Tailored Messages
Order delivery from local restaurants with Uber Eats.
Get groceries delivered to your door with Uber Eats.
Effectiveness:Somewhat
Audience Pain Points Addressed
- •
Travel uncertainty and scheduling anxiety ('Lock in a little peace of mind with Reserve').
- •
Need for flexible, on-demand income ('Drive when you want, make what you need').
- •
Complexity of corporate travel and meal expensing ('a platform for managing global rides and meals').
- •
The immediate need for transportation ('Request a ride, hop in, and go').
Audience Aspirations Addressed
- •
Seamless and stress-free mobility.
- •
Financial empowerment and autonomy for drivers.
- •
Operational efficiency and cost control for businesses.
Persuasion Elements
Emotional Appeals
- Appeal Type:
Peace of Mind / Reduction of Anxiety
Effectiveness:High
Examples
Lock in a little peace of mind with Reserve
Reserve your ride in advance so you can relax on the day of your trip.
- Appeal Type:
Empowerment / Freedom
Effectiveness:High
Examples
Drive when you want, make what you need.
Social Proof Elements
- Proof Type:
Brand Ubiquity (Implicit)
Impact:Strong
Explanation:The messaging lacks explicit social proof like testimonials or user counts. However, Uber's brand recognition is so high that its very presence serves as powerful, implicit social proof.
Trust Indicators
- •
Dedicated 'Safety, simplified' section.
- •
Professional and clean website design.
- •
Clear contact and help links in the footer.
Scarcity Urgency Tactics
No itemsCalls To Action
Primary Ctas
- Text:
See prices
Location:Hero Section Booking Widget
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Get started
Location:Driver and Business Sections
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Download the Uber app
Location:Dedicated App Section
Clarity:Clear
- Text:
Learn more
Location:Safety Section
Clarity:Clear
The CTAs are highly effective due to their clarity, simplicity, and context-specific placement. They use strong, action-oriented verbs ('Get', 'See', 'Download') and are placed exactly where a user would expect to take the next step for that specific audience segment. The design hierarchy makes the most important CTAs visually prominent.
Messaging Gaps Analysis
Critical Gaps
- •
Lack of explicit social proof: There are no testimonials, case studies, or user statistics to build credibility beyond the brand name itself.
- •
Absence of brand narrative: The homepage does not communicate the company's mission ('We reimagine the way the world moves for the better') or tell a larger story about its impact.
- •
Minimal emotional connection: The messaging is overwhelmingly functional, missing opportunities to connect with users on an emotional level through storytelling.
Contradiction Points
No itemsUnderdeveloped Areas
- •
Safety messaging: The 'Safety, simplified' headline is a good start, but it lacks specific details or proof points on the homepage to be truly reassuring.
- •
Sustainability message: While present in the footer, Uber's significant sustainability goals and initiatives are completely absent from the primary messaging, a major missed opportunity for brand building.
- •
Community and driver stories: The human element is missing. Showcasing stories of drivers who have benefited or communities that have been connected could add a powerful layer to the brand.
Messaging Quality
Strengths
- •
Exceptional clarity and conciseness.
- •
Effective audience segmentation that serves multiple distinct personas from a single page.
- •
Strong, clear calls-to-action that drive conversion.
- •
Successfully communicates the key differentiator of a multi-service platform.
Weaknesses
- •
Overly transactional and functional, lacking emotional resonance.
- •
Relies too heavily on brand recognition, failing to actively build brand affinity.
- •
Absence of social proof and storytelling elements.
- •
Key corporate values like sustainability and community impact are not reflected in the primary messaging.
Opportunities
- •
Integrate user-generated content or testimonials to build trust and add a human element.
- •
Create a dedicated homepage module for 'Our Impact' that touches on safety, sustainability, and economic empowerment.
- •
Develop a stronger narrative around the 'Reserve' feature, focusing on user stories for events like airport travel or special occasions.
- •
Better integrate the Uber Eats value proposition, which currently feels like a secondary add-on rather than a core pillar of the platform.
Optimization Roadmap
Priority Improvements
- Area:
Brand Storytelling
Recommendation:Introduce a homepage module titled 'Moving what matters.' featuring short, rotating stories about a driver achieving a goal, a business streamlining operations, or how Uber is contributing to city sustainability. This directly connects the functional service to a higher-purpose mission.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Trust & Safety
Recommendation:Expand the 'Safety, simplified' section to be an interactive module that visually highlights 3-4 key safety features (e.g., GPS tracking, emergency assistance button, ride-check). Use icons and minimal text to make it easily digestible.
Expected Impact:High
- Area:
Social Proof
Recommendation:Add subtle, data-driven social proof points near relevant CTAs. For example, under the driver 'Get started' button, add a line like 'Join millions of drivers earning on their schedule.'
Expected Impact:Medium
Quick Wins
- •
Update the 'Safety, simplified' CTA from 'Learn more' to a more benefit-driven 'See our safety features'.
- •
Add a single, powerful statistic about Uber's sustainability efforts (e.g., 'X million electric trips taken') to the footer or a relevant section.
- •
Incorporate the word 'trusted' or 'reliable' into the headline messaging for Uber for Business.
Long Term Recommendations
- •
Conduct a full messaging audit to ensure the core brand narrative ('reimagine the way the world moves for the better') is woven more consistently across all digital touchpoints, not just corporate pages.
- •
Develop a content strategy that prioritizes human-centric stories over feature announcements, using the blog and social channels to build a stronger emotional connection with all audience segments.
- •
A/B test different primary headlines on the homepage to see if a more brand-oriented message (e.g., 'Your world, on demand') performs as well for conversion as the current feature-focused message ('Lock in a little peace of mind with Reserve').
Growth Readiness
Growth Foundation
Product Market Fit
Strong
Evidence
- •
Massive global user base with 170 million Monthly Active Platform Consumers (MAPCs) as of Q1 2025.
- •
Exceptional revenue growth, with an 18% YoY increase in Q2 2025 to $12.7 billion.
- •
Deep integration into the daily lives of consumers for both mobility (ride-hailing) and delivery (food, grocery).
- •
High brand recognition and market leadership, holding approximately 76% of the U.S. rideshare market.
- •
Successful cross-platform adoption, where Mobility and Delivery services mutually drive over 20% of customer acquisition for each other.
Improvement Areas
- •
Enhancing driver and courier satisfaction and retention to ensure supply-side stability.
- •
Improving customer support channels to address service issues more effectively.
- •
Addressing the perceived high cost of services, particularly during surge pricing periods.
Market Dynamics
The global ride-hailing market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.97% to 9.64% between 2025 and 2030/2033. The online food delivery market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.7% in 2025.
Mature in core North American and European urban centers, but Growing in suburban/rural areas and emerging markets (Latin America, Asia).
Market Trends
- Trend:
Regulatory Scrutiny of Gig Economy
Business Impact:Increasing regulations regarding driver classification (employee vs. contractor) could significantly raise operational costs and impact the business model.
- Trend:
Platform Diversification and 'Super Apps'
Business Impact:Shift from single-service apps to integrated platforms offering rides, food, grocery, and other services. This increases customer stickiness and LTV.
- Trend:
Sustainability and EV Adoption
Business Impact:Growing consumer and regulatory pressure to transition to electric vehicle fleets, requiring significant investment and partnerships. Uber aims for a zero-emission platform by 2040.
- Trend:
AI and Autonomous Technology
Business Impact:Investment in AI for logistics optimization and partnerships with autonomous vehicle (AV) companies are critical for long-term cost reduction and competitive advantage.
Excellent. As a post-pandemic recovery continues and consumer habits solidify around convenience, Uber is well-positioned to capitalize on both the return of mobility and the sustained growth in delivery services.
Business Model Scalability
High
Primarily variable cost structure (driver payouts, transaction processing) with a significant, but leveraged, fixed cost base (R&D, marketing, platform maintenance). This allows for strong operating leverage as volume increases.
Demonstrated and High. Recent financial reports show profitability scaling faster than revenue, with a 35% YoY growth in Adjusted EBITDA on 14% revenue growth in Q1 2025.
Scalability Constraints
- •
Driver/courier supply acquisition and retention in a competitive labor market.
- •
Navigating complex and fragmented regulatory environments in each new city and country.
- •
Intense price competition from global and regional competitors like Lyft, DoorDash, and Bolt.
Team Readiness
Strong. The executive team has successfully navigated a major strategic pivot from 'growth-at-all-costs' to sustainable, profitable growth, as evidenced by achieving full-year GAAP operating income.
Effective. A divisional structure (Mobility, Delivery, Freight) allows for focused execution, while the platform-centric approach enables cross-functional synergies.
Key Capability Gaps
- •
Deep expertise in navigating international labor regulations and government relations.
- •
Specialized talent in scaling autonomous vehicle partnerships and integration.
- •
Advanced AI and machine learning talent for next-generation logistics and pricing algorithms.
Growth Engine
Acquisition Channels
- Channel:
Digital Marketing (Paid Search/Social)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Focus on optimizing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) by leveraging AI for audience targeting and shifting budget towards higher LTV cross-platform users.
- Channel:
App Store Optimization (ASO)
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Medium
Recommendation:Continuously test and refine app store listings (keywords, visuals) for both Rider and Driver apps to maintain top rankings and drive organic downloads.
- Channel:
Referral Programs
Effectiveness:Medium
Optimization Potential:High
Recommendation:Reinvigorate referral programs with tiered rewards, focusing on activating new users for both Mobility and Delivery to enhance cross-platform growth.
- Channel:
Word of Mouth / Brand Recognition
Effectiveness:High
Optimization Potential:Low
Recommendation:Maintain brand health through consistent service quality, safety initiatives, and public relations efforts.
Customer Journey
Highly optimized and frictionless. The user journey from app download to first ride or order is streamlined and a core competitive advantage.
Friction Points
- •
Price shock from dynamic/surge pricing leading to user drop-off.
- •
Uncertainty in wait times for ride or delivery.
- •
Inconsistent service quality between different drivers/couriers.
- •
Post-service issue resolution (e.g., lost items, incorrect orders).
Journey Enhancement Priorities
{'area': 'Pricing Transparency', 'recommendation': "Experiment with more transparent upfront pricing models or 'surge-free' subscription perks to mitigate negative user perception."}
{'area': 'Cross-Platform Integration', 'recommendation': "Further integrate the Eats and Rides experiences within the app to create a seamless 'one-stop-shop' for mobility and local commerce, encouraging multi-service use."}
Retention Mechanisms
- Mechanism:
Uber One Subscription
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Expand the value proposition by adding exclusive perks, such as partnerships with airlines or entertainment venues, and tiering the membership to offer premium benefits at a higher price point. Uber One members spend 3-4x more and have higher retention.
- Mechanism:
Cross-Platform Promotion
Effectiveness:High
Improvement Opportunity:Utilize AI to deliver highly personalized offers for Eats to frequent Riders (and vice-versa) based on their travel patterns and order history.
- Mechanism:
Personalization and Push Notifications
Effectiveness:Medium
Improvement Opportunity:Move beyond generic promotions to predictive, context-aware notifications (e.g., 'Heading to the airport? Reserve a ride now').
Revenue Economics
Strong and Improving. The company has achieved sustained GAAP profitability and free cash flow, indicating that the core economics per trip/order are sound and benefit from scale.
Assumed Healthy. While exact figures are proprietary, the focus on retaining users via Uber One and driving multi-product adoption suggests a strong LTV that justifies acquisition costs.
High. The ability to grow Adjusted EBITDA (35% YoY) significantly faster than revenue (18% YoY) demonstrates high revenue efficiency and strong operating leverage.
Optimization Recommendations
- •
Continue scaling the high-margin advertising business within Uber Eats, which has surpassed a $1.5B annual run rate.
- •
Drive adoption of higher-margin products like Uber Reserve, Comfort Electric, and premium delivery options.
- •
Optimize driver/courier incentives to ensure supply liquidity without excessively compressing margins.
Scale Barriers
Technical Limitations
- Limitation:
Real-time Geospatial Data Processing
Impact:High
Solution Approach:Continued investment in scalable cloud infrastructure and more efficient algorithms for matching, routing, and ETA prediction at a global scale.
- Limitation:
Platform Uptime and Resilience
Impact:Critical
Solution Approach:Implement advanced SRE (Site Reliability Engineering) practices, multi-region redundancy, and proactive monitoring to ensure near-100% uptime, which is essential for user trust.
Operational Bottlenecks
- Bottleneck:
Driver/Courier Supply Management
Growth Impact:Directly constrains growth in trips and deliveries if supply cannot meet demand, leading to higher prices and longer wait times.
Resolution Strategy:Develop more sophisticated, dynamic incentive programs. Improve the driver onboarding process and provide benefits (like those in Uber Pro) to increase retention.
- Bottleneck:
Regulatory Compliance Overhead
Growth Impact:Slows down market entry and adds significant operational complexity and cost, requiring bespoke solutions for each jurisdiction.
Resolution Strategy:Invest in a dedicated global policy team that works proactively with regulators and develop a flexible platform architecture that can adapt to different local rules.
Market Penetration Challenges
- Challenge:
Intense Competition
Severity:Critical
Mitigation Strategy:Differentiate through the ecosystem strategy (Uber One, cross-platform benefits), superior technology, and brand trust, rather than competing solely on price.
- Challenge:
Public Perception and Safety Concerns
Severity:Major
Mitigation Strategy:Continue to invest in and prominently market safety features within the app. Maintain transparent reporting and proactive communication to build and maintain trust with users and regulators.
- Challenge:
Worker Classification Legislation
Severity:Critical
Mitigation Strategy:Engage in proactive dialogue with governments to advocate for a 'third way' model of portable benefits for gig workers. Simultaneously, model and prepare for potential reclassification scenarios to ensure business continuity.
Resource Limitations
Talent Gaps
- •
AI and Machine Learning PhDs
- •
Autonomous Vehicle Integration Specialists
- •
Senior Public Policy and Government Affairs Experts
Moderate. While now generating significant free cash flow ($2.5B in Q2 2025), capital is still required for strategic M&A (e.g., Trendyol Go), share buybacks ($20B program), and R&D in future tech like AVs.
Infrastructure Needs
Expansion of EV charging partnerships to support the 2040 zero-emission goal.
Enhanced data center capacity to support the growth of AI and machine learning workloads.
Growth Opportunities
Market Expansion
- Expansion Vector:
Deeper Penetration in Suburban/Tier-2 Cities
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:Medium
Recommended Approach:Develop tailored product offerings (e.g., scheduled commuter trips, lower-cost vehicle options) and marketing campaigns that address the unique transportation needs of less dense areas.
- Expansion Vector:
Geographic Expansion in Latin America & Asia
Potential Impact:High
Implementation Complexity:High
Recommended Approach:Pursue a partnership-led approach, working with local companies to navigate regulatory hurdles and adapt the service to local payment methods and consumer behaviors.
Product Opportunities
- Opportunity:
Expansion of Uber for Business (U4B)
Market Demand Evidence:Increasing need for corporate clients to manage employee travel, meals, and local deliveries efficiently.
Strategic Fit:High. Leverages the core platform to serve a high-LTV B2B customer segment.
Development Recommendation:Develop deeper integrations with corporate expense management software (like Brex, Ramp) and enhance the platform's reporting and policy control features.
- Opportunity:
New Delivery Verticals (Pharmacy, Retail, Alcohol)
Market Demand Evidence:Growing consumer expectation for on-demand delivery of all local commerce, not just food.
Strategic Fit:High. Utilizes the existing courier network and logistics technology to enter new, potentially higher-margin markets.
Development Recommendation:Form strategic partnerships with major retail and pharmacy chains to provide a white-label or co-branded last-mile delivery solution.
- Opportunity:
Advertising Platform Growth
Market Demand Evidence:Strong advertiser demand, with the business already surpassing a $1.5B revenue run-rate.
Strategic Fit:Very High. High-margin revenue stream that monetizes existing user traffic without disrupting the core experience.
Development Recommendation:Enhance ad targeting capabilities using platform data and expand ad formats to include video and sponsored recommendations within the ride-hailing experience.
Channel Diversification
- Channel:
B2B Enterprise Sales
Fit Assessment:Excellent
Implementation Strategy:Build out a dedicated enterprise sales team focused on Fortune 1000 companies to sell comprehensive U4B solutions for travel, meals, and commuting programs.
- Channel:
API Integrations (Third-Party Platforms)
Fit Assessment:Good
Implementation Strategy:Allow third-party travel and event platforms (e.g., airlines, hotels, ticketing sites) to integrate Uber's booking functionality directly into their apps/websites for a seamless user experience.
Strategic Partnerships
- Partnership Type:
Autonomous Vehicle Technology
Potential Partners
- •
Waymo
- •
May Mobility
- •
Motional
Expected Benefits:Position Uber as the leading distribution network for autonomous mobility, allowing it to benefit from AVs without bearing the full R&D cost and risk.
- Partnership Type:
Public Transit Integration
Potential Partners
Major city transit authorities (e.g., MTA, TfL)
Expected Benefits:Position Uber as a comprehensive Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platform, handling first/last-mile connections and providing an all-in-one solution for urban transport.
- Partnership Type:
Financial Services
Potential Partners
American Express
Starbucks
Expected Benefits:Enhance the value of Uber One and drive loyalty through co-branded rewards, points programs, and exclusive cardholder benefits.
Growth Strategy
North Star Metric
Cross-Platform Weekly Active Consumers
This metric measures the number of unique users completing at least one trip OR one order per week. It captures frequency (weekly), user base health (active), and, most importantly, the success of the platform ecosystem strategy. Growing this number is a direct indicator of increasing user engagement and dependency on the Uber platform for daily needs.
15-20% Year-over-Year Growth
Growth Model
Platform Ecosystem Growth Model
Key Drivers
- •
Increasing Uber One membership penetration.
- •
Improving the cross-sell conversion rate from Mobility to Delivery (and vice versa).
- •
Expanding the number of services available on the platform (e.g., new delivery verticals).
- •
Increasing order/trip frequency per active user.
Focus product and marketing efforts on creating a seamless, integrated app experience where users are incentivized and naturally discover new ways to use the platform beyond their initial entry point.
Prioritized Initiatives
- Initiative:
Uber One 'Plus' Tier Launch
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:6-9 Months
First Steps:Conduct market research to identify high-value perks (e.g., airport lounge access, guaranteed top drivers) and model subscription pricing elasticity.
- Initiative:
Enterprise Commute Program (U4B)
Expected Impact:High
Implementation Effort:High
Timeframe:12-18 Months
First Steps:Develop a pilot program with 5-10 large corporate partners to refine the product offering for employee commute subsidies and shuttle services.
- Initiative:
AI-Powered Cross-Sell Engine
Expected Impact:Medium
Implementation Effort:Medium
Timeframe:4-6 Months
First Steps:Build and deploy machine learning models that predict and serve the most relevant cross-platform offer to a user at the optimal moment (e.g., offering a discount on a meal from a restaurant near a ride's destination).
Experimentation Plan
High Leverage Tests
{'test': 'A/B test different Uber One benefit bundles to identify the highest drivers of new subscriptions and retention.', 'hypothesis': 'Adding a non-transportation benefit (e.g., streaming service discount) will increase perceived value and conversion more than an additional ride/delivery discount.'}
{'test': 'Experiment with dynamic driver incentives in suburban markets to measure the impact on supply availability and rider wait times.', 'hypothesis': 'Targeted, time-based incentives for drivers in low-density areas will reduce average wait times by over 15% and increase trip completion rates.'}
Utilize a rigorous A/B testing framework measuring statistical significance on key metrics: conversion rate, user retention, LTV, trip/order frequency, and North Star Metric.
Continuous weekly sprints for product teams, with major strategic tests planned on a quarterly basis.
Growth Team
A hybrid model: A central Growth Team responsible for the user lifecycle (Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Referral, Revenue) and embedded 'Growth Pods' within each major business unit (Mobility, Delivery, U4B) to execute on division-specific initiatives.
Key Roles
- •
Head of Growth (oversees central team and pods)
- •
Data Scientist (focused on experimentation and user behavior modeling)
- •
Product Manager, Growth
- •
Lifecycle Marketing Manager
- •
Acquisition Channel Specialist (Paid, SEO/ASO)
Establish a formal 'Experimentation Center of Excellence' to provide training, standardized tools, and best practices to all product and marketing teams, fostering a company-wide culture of data-driven growth.
Uber has successfully transitioned from a hyper-growth, cash-burning startup to a scalable, profitable technology platform. Its growth foundation is exceptionally strong, with dominant product-market fit in both Mobility and Delivery, a highly scalable business model demonstrating significant operating leverage, and a clear path to continued financial outperformance.
The primary growth engine is now the platform ecosystem. The key to future expansion is not just acquiring new users, but deepening engagement with the existing 170 million MAPCs. This will be achieved by driving adoption of the Uber One subscription program—a powerful retention and frequency tool—and effectively cross-selling users across the expanding array of services. Monetization layers, particularly the high-margin advertising business, provide a powerful lever for continued profit growth.
The most significant barriers to scale are external and regulatory. The ongoing global debate around gig worker classification poses a critical threat to the current cost structure and requires proactive, strategic engagement with policymakers. Intense competition remains a constant, necessitating continuous innovation to avoid commoditization.
The largest growth opportunities lie in leveraging the existing platform and user base. Expanding Uber for Business into a comprehensive enterprise solution for travel and logistics, entering new high-frequency delivery verticals like grocery and retail, and positioning the platform as the primary distribution network for third-party autonomous vehicle technologies are the most promising vectors for long-term value creation.
Recommendation: The growth strategy should be singularly focused on increasing the number of Cross-Platform Weekly Active Consumers. This North Star Metric aligns the entire organization around the core strategic goal of transforming Uber from a series of transactional apps into an indispensable, high-frequency utility for modern life. The immediate priorities are to enhance the Uber One value proposition, build out the B2B enterprise offering, and utilize AI to personalize and deepen the user's journey within the ecosystem.
Legal Compliance
Uber maintains a comprehensive and globally applicable privacy notice that details the types of data collected (e.g., location, transaction, device, and communications data), its usage, and sharing practices. The policy is transparent about data collection from users, through service usage, and from third-party sources. It clearly states that data is used for service provision, safety, customer support, R&D, and marketing. The policy also outlines user rights to access, control, and correct their personal information. However, Uber has faced criticism and legal challenges regarding its data practices, particularly the extent of location data collection, which historically included tracking even when the app was running in the background. The company provides a dedicated privacy center and region-specific information, acknowledging regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Recent significant GDPR fines related to improper data transfers to the US indicate that despite a robust policy, implementation and compliance in complex areas like cross-border data flows remain a major challenge.
Uber's Terms of Service (ToS) strategically positions the company as a technology platform, not a transportation provider. This is a critical legal distinction aimed at mitigating liability for incidents that occur during rides and reinforcing the independent contractor status of drivers. The ToS includes several key clauses that have been the subject of legal scrutiny, most notably a mandatory arbitration clause that limits users' ability to sue the company in court, directing disputes to private arbitration instead. This clause is often presented in a 'take-it-or-leave-it' manner, which some legal experts argue constitutes a contract of adhesion. The ToS also contains disclaimers of liability and governs user conduct on the platform. The enforceability of these terms, particularly the arbitration clause, is a recurring legal battleground for the company.
Based on direct website interaction and available policies, Uber's cookie compliance appears functional but not proactively user-centric. Upon visiting the site, a cookie consent banner is presented, which is a baseline requirement under GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive. However, the mechanism often defaults to an 'accept all' approach, requiring users to navigate to a secondary menu to opt out of non-essential cookies. The policy distinguishes between essential, personalization, analytics, and marketing cookies. While it provides a mechanism for consent, the design may not fully align with the GDPR's strict requirement for explicit, unambiguous, and freely given consent before non-essential cookies are placed. The website also notes that third parties like advertising networks may use cookies over which Uber has no control, which is a standard but important disclosure.
Uber's overall data protection strategy is a clear strength in terms of policy and infrastructure, but a significant risk area in terms of regulatory enforcement. The company has a dedicated Data Protection Officer (DPO) as required by GDPR and has built an internal 'privacy-as-a-service' platform to manage consent architecture. They provide a detailed Privacy Notice with region-specific addendums for jurisdictions like the EEA, Brazil, and various US states, demonstrating a sophisticated approach to global compliance. A dedicated page for US users outlines rights under laws like CCPA/CPRA, including the right to opt-out of the 'sale' or 'sharing' of personal information for targeted advertising. Despite these measures, Uber has been fined hundreds of millions of euros under GDPR for unlawful data transfers, highlighting a critical gap between policy and practice. This indicates that while the external-facing compliance documents are robust, the underlying data handling processes, especially for international transfers, are under intense regulatory scrutiny and pose a high financial risk.
Uber has a public and proactive stance on accessibility, explicitly stating its commitment to meeting Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 Level AA. The website includes features like 'Skip to main content' links, which are a basic tenet of web accessibility. Their dedicated accessibility page details features for riders and drivers with disabilities, including compatibility with screen readers like VoiceOver and TalkBack, and policies for service animals. However, the company faces significant legal challenges regarding the accessibility of its core transportation service. Lawsuits have been filed under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) alleging discrimination due to a lack of wheelchair-accessible vehicles (WAV) in many markets. Uber's defense often hinges on its status as a technology company rather than a transportation provider, a distinction that courts are increasingly challenging in the context of accessibility. Thus, while digital platform accessibility is a strength, physical service accessibility is a major legal and reputational risk.
Uber operates in a complex and evolving regulatory environment with two primary pillars: Transportation Network Company (TNC) regulations and labor laws concerning worker classification. TNC laws, which vary by state and city, impose requirements for driver background checks, vehicle safety, insurance, and operational record-keeping. Uber's website and app are designed to meet these requirements by providing fare estimates, driver information, and safety features. The most significant and persistent legal challenge is the classification of its drivers. Uber's business model is predicated on drivers being independent contractors, a status that is under constant legal and legislative attack globally. The passage of laws like California's AB5, and the subsequent battle over Proposition 22, exemplify this high-stakes conflict. Uber's legal positioning as a technology platform is central to its defense of the independent contractor model. Recent settlements, like a $15 million agreement in Seattle over pay transparency for delivery workers, show that municipal-level regulations are also a significant compliance burden and risk.
Compliance Gaps
- •
International Data Transfers: Repeated, significant GDPR fines indicate a systemic issue with ensuring adequate safeguards for transferring EU user data to the US.
- •
Service Accessibility (ADA): A significant disparity exists between the digital accessibility of the platform and the physical accessibility of the transportation service, with insufficient availability of wheelchair-accessible vehicles (WAV) in many areas, leading to ongoing litigation.
- •
Clarity of Terms of Service: The use of mandatory arbitration clauses and dense legal language in the ToS can be seen as anti-consumer and may be unenforceable in some jurisdictions.
- •
Cookie Consent Mechanism: The cookie banner's design may nudge users toward acceptance, potentially falling short of the 'freely given' consent standard required by GDPR.
- •
Worker Classification Ambiguity: The legal distinction between independent contractor and employee remains a contentious and unresolved issue, creating regulatory uncertainty and legal risk across jurisdictions.
Compliance Strengths
- •
Comprehensive Privacy Documentation: Maintains detailed, accessible, and regionally-specific privacy policies and a central Privacy Center.
- •
Proactive Digital Accessibility Stance: Publicly commits to and builds its digital assets to meet WCAG 2.1 AA standards.
- •
Dedicated Data Protection Governance: Appointment of a Data Protection Officer and development of internal consent management systems show a mature approach to data governance.
- •
Safety Feature Integration: The platform prominently features and promotes safety tools and resources for both riders and drivers, addressing a key regulatory and consumer concern.
- •
Clear Disclosures for TNC Regulations: Provides users with necessary information like driver details and fare estimates as required by most TNC laws.
Risk Assessment
- Risk Area:
Worker Misclassification
Severity:High
Recommendation:Continuously lobby for and adapt business models to new 'third way' worker classifications (like Prop 22). Increase transparency and benefits offered to independent contractors to mitigate legal challenges and public pressure. Diversify business lines to reduce reliance on the rideshare model.
- Risk Area:
GDPR & Data Transfers
Severity:High
Recommendation:Conduct an urgent and complete audit of all EU-US data transfer mechanisms. Re-evaluate reliance on SCCs and explore alternative data localization or anonymization techniques to minimize cross-border flows and reduce the risk of further multi-million euro fines.
- Risk Area:
ADA & Service Accessibility
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Invest significantly in expanding the WAV fleet through partnerships, driver incentives, and direct investment. Publicly report on progress and proactively engage with disability rights organizations to develop more equitable service offerings, moving beyond legal defense to strategic resolution.
- Risk Area:
Antitrust & Competition
Severity:Medium
Recommendation:Ensure pricing algorithms and market practices are regularly reviewed by legal counsel to avoid claims of anti-competitive behavior. Document the pro-competitive aspects of the platform for riders and drivers to counter regulatory scrutiny.
- Risk Area:
Enforceability of Terms of Service
Severity:Low
Recommendation:Review and simplify the language in the Terms of Service. Consider offering a more prominent and simpler opt-out for the arbitration clause to bolster its enforceability and improve consumer trust, even if it results in a small increase in litigation.
High Priority Recommendations
- •
Immediately overhaul EU-US data transfer protocols to align with the latest GDPR enforcement decisions and avoid further catastrophic fines.
- •
Develop and fund a clear, time-bound plan to materially increase the availability of wheelchair-accessible vehicles (WAVs) in key markets to mitigate ADA litigation risk.
- •
Launch a global initiative to enhance driver benefits and earnings transparency, proactively shaping the narrative and legal landscape around gig work rather than reactively defending the independent contractor model.
Uber's legal positioning is a masterclass in strategic risk management, built to enable a disruptive business model within highly regulated transportation and labor markets. The company's core legal strategy is to define itself as a 'technology platform' rather than a 'transportation company.' This distinction is the bedrock of its defense against a wide array of existential threats, from driver classification lawsuits to liability for incidents on the platform and arguments for less stringent accessibility requirements under the ADA.
On the digital front, Uber demonstrates a sophisticated and mature compliance posture. Its privacy policies are comprehensive and tailored to a global audience, with clear acknowledgments of major regulations like GDPR and CCPA. The company has invested in the internal infrastructure, such as a DPO and consent management systems, to support these policies. Similarly, its stated commitment to WCAG 2.1 AA standards for its website and apps shows a proactive approach to digital accessibility.
However, this digital strength contrasts sharply with immense legal risks in its physical operations. The ongoing global battle over driver classification remains the single greatest threat to its business model, with the potential to fundamentally alter its cost structure. Furthermore, massive GDPR fines reveal a critical disconnect between data protection policy and execution, particularly concerning international data transfers. Finally, while the website may be accessible, the core service is not for many individuals with disabilities, creating significant legal and reputational risk under the ADA. Uber's legal strategy is therefore a high-wire act: leveraging sophisticated legal arguments and documentation to navigate a minefield of regulations that were not designed for its business model, while constantly facing challenges that threaten to upend its foundational legal and operational assumptions.
Visual
Design System
Minimalist Corporate
Excellent
Advanced
User Experience
Navigation
Horizontal Top Bar (collapsing to Hamburger on mobile)
Intuitive
Excellent
Information Architecture
Logical
Clear
Light
Conversion Elements
- Element:
Ride Booking/Quotation Widget
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:For new or logged-out users, placeholder text could be more benefit-driven, such as 'Enter destination for a fare estimate' to immediately clarify its function.
- Element:
Primary CTA Buttons ('Get Started', 'Sign Up')
Prominence:High
Effectiveness:Effective
Improvement:On pages with multiple primary CTAs (e.g., for Riders and Drivers), introduce a subtle visual distinction (e.g., a filled vs. outlined button) to guide the majority user segment more strongly.
- Element:
App Download Links ('Download the Uber app')
Prominence:Medium
Effectiveness:Somewhat effective
Improvement:For mobile web visitors, employ a dismissible sticky banner at the top or bottom of the viewport. This would keep the primary business goal of app installation persistently in view without being overly intrusive.
Assessment
Strengths
- Aspect:
Minimalist & Focused Design
Impact:High
Description:The extensive use of white space, a high-contrast monochrome color palette, and clean typography creates a sophisticated and uncluttered aesthetic. This design choice reduces cognitive load, allowing users to focus on primary tasks like booking a ride or signing up.
- Aspect:
Mature & Consistent Design System
Impact:High
Description:Uber employs an advanced design system (Base Web) that ensures remarkable brand and UX consistency across its global website and diverse product lines (Ride, Eats, Freight). This creates a seamless, predictable user experience and reinforces brand identity.
- Aspect:
Persona-Driven Information Architecture
Impact:High
Description:The website's structure is logically segmented around its core user personas: Riders, Drivers, and Businesses. This clarity allows users to self-identify quickly and navigate directly to the most relevant information and user flows, enhancing conversion for each segment.
Weaknesses
- Aspect:
Aesthetic Can Feel Impersonal
Impact:Medium
Description:The minimalist, corporate black-and-white design, while professional and efficient, can lack emotional warmth. This may create a functional but sterile experience that doesn't foster a strong emotional connection with the brand.
- Aspect:
Homepage CTA Hierarchy
Impact:Low
Description:On the main homepage, multiple value propositions (Ride, Drive, Reserve) are presented with similar visual weight. This could slightly diffuse the focus for a first-time user compared to a singularly focused landing page, potentially slowing the primary conversion path.
- Aspect:
Over-reliance on Illustrations
Impact:Low
Description:The stylish, abstract illustrations are on-brand but occasionally can be ambiguous without the accompanying text. While visually pleasing, incorporating more authentic, human-centric photography could build greater trust and relatability.
Priority Recommendations
- Recommendation:
Personalize the Homepage Experience for Returning Users
Effort Level:High
Impact Potential:High
Rationale:For logged-in users, dynamically reorder homepage content based on their usage patterns. A frequent Uber Eats user should see food delivery promotions first. This personalization would increase engagement, cross-sell services effectively, and improve retention by making the platform feel tailored to individual needs.
- Recommendation:
A/B Test 'Warmer' Visuals on Key Conversion Pages
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:Medium
Rationale:On sign-up and landing pages, test versions that incorporate high-quality, authentic photography of people (riders and drivers) instead of abstract illustrations. This can build trust and emotional resonance, potentially improving conversion rates by making the service feel more human and less transactional.
- Recommendation:
Implement a Persistent 'Download App' Smart Banner on Mobile Web
Effort Level:Low
Impact Potential:High
Rationale:Since the app provides the optimal user experience and is a primary business goal, a smart banner on mobile web that prompts users to download or open the app is a critical conversion tool. It keeps the primary call-to-action visible without disrupting the user flow, directly driving more valuable app installs and engagement.
Mobile Responsiveness
Excellent
The layout adapts seamlessly across all viewport sizes. Content reflows logically, typography scales for readability, and touch targets are appropriately sized for mobile interaction.
Mobile Specific Issues
No itemsDesktop Specific Issues
No itemsThe visual design and user experience of Uber.com reflect a mature, world-class technology company. The website is a masterclass in minimalism, leveraging a sophisticated, high-contrast design system to create an experience that is both effortlessly functional and globally scalable. The core strength lies in its clarity and focus. The information architecture is intuitively structured around Uber's key user personas—Riders, Drivers, and Businesses—allowing for targeted messaging and streamlined user flows that efficiently guide visitors toward their goals. This clear segmentation is evident in the distinct landing pages, such as the hyper-focused Swedish homepage which strips away all distractions to prioritize the primary conversion action of getting a fare estimate.
The design system is advanced and impeccably consistent, using the 'Uber Move' typeface, a strict monochrome palette with strategic color accents, and a uniform illustration style. This ensures powerful brand recognition and a predictable, low-friction user journey across all of Uber's verticals. From a UX perspective, the cognitive load is kept remarkably light through generous white space, concise copy, and a clear visual hierarchy, reinforcing the brand's core value proposition of simplicity and convenience.
Mobile responsiveness is flawless, a critical necessity for a mobile-first business. The transition from desktop to mobile is seamless, with navigation collapsing logically into a standard hamburger menu and all content adapting perfectly to smaller screens.
While highly effective, the design's primary weakness is its potential to feel impersonal and sterile. The corporate minimalism, though professional, lacks warmth and could be enhanced with more human-centric visuals to build deeper emotional trust. Key opportunities for strategic improvement lie in personalization and conversion optimization. Dynamically tailoring the homepage for logged-in users based on their activity would significantly increase relevance and cross-platform usage. Furthermore, a more aggressive mobile app download strategy, such as a persistent smart banner, would better align the web experience with the core business objective of driving users to the more feature-rich native app. Overall, Uber.com's visual and UX design is a powerful asset that effectively communicates its brand identity as a modern, reliable, and efficient global mobility platform.
Discoverability
Market Visibility Assessment
Uber has established itself as a category-defining brand in the mobility and on-demand delivery sectors. Its name is synonymous with ridesharing, giving it unparalleled top-of-mind awareness. However, its brand authority is a double-edged sword; historical controversies around corporate culture, driver relations, and regulatory battles have created persistent negative sentiment. While the brand is recognized globally, its perception can be polarized, often valued more for its convenience than for brand affinity. Digital content and PR efforts are actively working to reshape this narrative, focusing on safety, sustainability, and driver success stories to rebuild trust and authority.
Uber maintains a dominant digital presence, reflecting its leading market share in the U.S. ridesharing market over its primary competitor, Lyft. In the highly competitive food delivery space, Uber Eats is a strong second to DoorDash in the U.S., holding a significant portion of the market. This market position is clearly visible in search results, where Uber consistently ranks for high-intent keywords related to both ridesharing and food delivery. Their digital visibility is a direct reflection of their aggressive global expansion and multi-service business model.
The digital presence is highly optimized for multi-sided customer acquisition. The website serves as a primary funnel for both riders and drivers/couriers, with clear, distinct calls-to-action for each segment. The integration of various services (Ride, Eats, Reserve, Business) on a single platform creates significant potential for cross-promotion and increases the lifetime value of an acquired user. The strong emphasis on app downloads indicates a strategy focused on capturing users within their owned ecosystem, leveraging digital channels like social media and search to drive installs.
Uber's digital infrastructure is built for global scale with hyper-local execution. The website architecture, with its country and city-specific pages, demonstrates a sophisticated approach to local SEO and market penetration. This allows Uber to tailor messaging, offerings, and promotions to specific geographic areas, making their services feel local despite being a global brand. This digital strategy is crucial for entering new markets and competing with regional players.
Uber's content strategy covers a broad range of topics that position it as a comprehensive technology platform for movement and logistics. Beyond the core services of rides and food delivery, their digital assets (like their blog and newsroom) touch upon autonomous driving, sustainability, urban mobility, and the future of work. This wide coverage allows them to engage in broader industry conversations and frame themselves as an innovator shaping the future, rather than just a service provider.
Strategic Content Positioning
Uber's website content is heavily weighted towards the consideration and conversion stages of the customer journey. The homepage immediately prompts users to get a price estimate or sign up, targeting high-intent visitors. Content supporting the awareness stage, such as blog posts about travel destinations or city guides, is present but less prominent. There's a strategic opportunity to build more top-of-funnel content that captures users earlier in their planning process, building brand preference before the moment of need.
Uber possesses a wealth of unique data on urban mobility, economic trends, and consumer behavior. There is a significant opportunity to leverage this data to produce high-authority research reports, white papers, and data visualizations. By publishing proprietary insights on topics like traffic patterns, the economic impact of the gig economy, or the adoption of electric vehicles, Uber can solidify its position as a thought leader and become a primary source for media, policymakers, and academics.
Competitors like Lyft have historically focused on building a more community-oriented and driver-friendly brand image. While Uber has made strides, a content gap exists in creating authentic, community-driven content that showcases driver stories and experiences. Furthermore, in the food delivery space, DoorDash often excels in hyper-local restaurant partnerships and content. Uber could create more content celebrating local restaurants and culinary scenes in the cities it serves to close this gap.
Across its primary digital touchpoints, Uber's brand messaging is generally consistent, revolving around convenience, choice, and a seamless user experience. The pivot towards safety and sustainability is also evident. However, consistency can be challenged by the diverse needs of its three core audiences: riders, drivers, and merchants. Messaging tailored to drivers (flexibility, earnings) is distinct from messaging to riders (convenience, safety). The overarching brand narrative of 'reimagining the way the world moves for the better' serves as a unifying theme, but requires careful execution to feel authentic to all segments.
Digital Market Strategy
Market Expansion Opportunities
- •
Develop content hubs around emerging verticals like grocery and package delivery to build organic search authority before major marketing pushes.
- •
Create hyper-local content strategies for new, untapped cities to accelerate market entry and build a user base organically.
- •
Launch a B2B content strategy targeting the logistics and freight industry to grow the 'Uber Freight' service line.
- •
Explore content partnerships with the travel and tourism industry, integrating Uber's booking platform with travel guides and itineraries.
Customer Acquisition Optimization
- •
Increase investment in programmatic SEO for city and airport transportation queries to capture high-intent, low-cost organic traffic.
- •
Develop a robust content-driven referral program that incentivizes sharing through valuable content (e.g., 'share this city guide with a friend and you both get a discount').
- •
Utilize proprietary data to create unique content that attracts high-value backlinks, reducing reliance on paid media for authority building.
- •
Cross-promote Uber One membership benefits through targeted content to Uber Eats users, and vice-versa, to increase customer lifetime value.
Brand Authority Initiatives
- •
Establish an 'Uber Mobility Institute' to publish data-driven reports on urban planning, sustainability, and economic impact, positioning Uber as a key partner to cities.
- •
Launch a high-profile content series featuring the stories and successes of drivers and restaurant partners to humanize the brand.
- •
Partner with academic institutions to research and publish findings on the future of transportation and the gig economy.
- •
Proactively create content addressing tough industry questions (e.g., driver compensation, environmental impact) to lead the narrative rather than react to it.
Competitive Positioning Improvements
- •
Develop content that strongly differentiates Uber on safety features and technology, creating a competitive moat based on trust.
- •
Amplify content related to sustainability initiatives and EV adoption to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
- •
Create a digital experience and content hub for 'Uber for Business' that positions it as a superior solution for corporate travel and meal programs.
- •
Leverage the 'platform advantage' in content, showcasing how the integration of rides, food, and delivery offers a unique value proposition competitors cannot match.
Business Impact Assessment
Market share is directly reflected in digital 'share of voice' for critical keywords like 'rideshare', 'taxi service', 'food delivery', and location-based variations. Tracking branded search volume (Uber vs. Lyft vs. DoorDash) provides a real-time proxy for brand preference and market leadership. App downloads and rankings attributed to web referrals are also a key indicator.
The primary metrics are new user sign-ups (both riders and drivers/couriers) originating from organic and paid digital channels. Success is measured by the Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) and the conversion rate of website visitors to app downloads or first-time users. The ultimate metric is the Lifetime Value (LTV) of customers acquired through these channels.
Brand authority is measured by the volume and quality of media mentions and backlinks from authoritative news, government, and educational domains. Search engine rankings for broad, non-branded industry terms ('future of mobility', 'gig economy impact') serve as a key benchmark. Online sentiment analysis across social media and news can also quantify brand perception over time.
Benchmarking involves continuously tracking keyword rankings against key competitors like Lyft and DoorDash for high-value commercial terms. Analyzing the reach and engagement of competitor content provides insights into their strategic focus. The market is also benchmarked by comparing the feature sets and value propositions highlighted on each competitor's digital properties, such as subscription programs like Uber One vs. DashPass.
Strategic Recommendations
High Impact Initiatives
- Initiative:
Develop a 'Future of Mobility & Delivery' Content Hub
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Solidify Uber's position as the definitive industry thought leader, shaping policy conversations and attracting B2B partnerships. This moves the brand beyond a transactional service to a strategic infrastructure partner for cities and businesses.
Success Metrics
- •
Backlinks from .gov, .edu, and major news domains
- •
Media mentions citing Uber's data/reports
- •
Inbound leads for Uber for Business and Freight
- •
Organic rankings for high-level industry keywords
- Initiative:
Launch a Hyper-Local 'Go/Eat' Content Program
Business Impact:High
Market Opportunity:Capture long-tail search demand and compete more effectively with local-first competitors. This strategy deepens market penetration in existing cities and provides a low-cost acquisition channel in new ones.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in organic traffic for '[city] + [activity/restaurant]' keywords
- •
Growth in new user sign-ups from local content pages
- •
Improved conversion rates on city-specific landing pages
- •
Higher engagement rates on localized social media content
- Initiative:
Create a Platform-Wide 'Uber One' Value Content Series
Business Impact:Medium
Market Opportunity:Increase the adoption of Uber's subscription service, which is critical for customer retention and increasing lifetime value. Clearly articulating the combined value of ride and delivery benefits can create a competitive advantage over single-service competitors.
Success Metrics
- •
Increase in Uber One subscription sign-ups from content
- •
Higher cross-platform usage by Uber One members
- •
Reduction in customer churn rate
- •
Improved LTV-to-CAC ratio
Transition Uber's core market identity from a 'ridesharing app' to an 'integrated global platform for movement'. The digital presence must clearly and consistently articulate the value of a single ecosystem that seamlessly connects transportation, food delivery, grocery, and logistics. This strategy positions Uber not just as a choice for a single transaction, but as an indispensable utility for modern life and business operations.
Competitive Advantage Opportunities
- •
Leverage unparalleled first-party data to create predictive and insightful content that no competitor can replicate.
- •
Promote the cross-platform benefits of the Uber ecosystem (e.g., earn rewards on Eats, spend them on Rides) to build a competitive moat based on integrated value.
- •
Utilize the global brand recognition to build authoritative content partnerships with international organizations, travel brands, and city governments.
- •
Showcase technological superiority in areas like dynamic pricing algorithms, route planning, and safety features through compelling and easily understandable content.
Uber's digital market presence is a direct reflection of its business strategy: aggressive scale, technological innovation, and diversification into a multi-sided platform. The website and broader digital footprint are powerful engines for acquiring both sides of its marketplace—consumers and providers (drivers/couriers). The company's primary strength lies in its dominant brand recognition and its sophisticated, globally-scaled yet locally-targeted digital infrastructure.
However, the analysis reveals a significant strategic opportunity to evolve its digital presence from a purely transactional focus to one that builds deeper brand authority and emotional connection. While highly effective at converting users with immediate needs, the content strategy could be enhanced to engage users earlier in their journey, build community among its drivers and merchants, and more effectively shape public and policy narratives around key industry issues. Competitors often challenge Uber not on scale, but on brand perception and trust.
Strategic recommendations therefore focus on leveraging Uber's greatest untapped asset: its data. By transforming this data into thought leadership, Uber can solidify its position as an indispensable technology partner for the future of urban environments. Furthermore, a hyper-local content strategy can defend against niche competitors and deepen market penetration. The overarching goal is to use its digital presence to transition the brand narrative from a controversial disruptor to an essential, trusted, and integrated platform for global mobility and delivery.
Strategic Priorities
Strategic Priorities
- Title:
Future-Proof the Workforce Model by Establishing a 'Third Way' Framework
Business Rationale:The classification of drivers and couriers as independent contractors is the single greatest existential threat to Uber's business model, creating immense legal, regulatory, and financial risk globally. Proactively developing and advocating for a new framework for gig work is essential for long-term stability and sustainability.
Strategic Impact:This initiative transforms Uber's primary operational risk into a competitive advantage. It de-risks the business from catastrophic legal judgments, improves driver/courier retention and supply stability, enhances brand reputation, and positions Uber as a leader in shaping the future of work.
Success Metrics
- •
Reduction in legal provisions related to worker classification lawsuits
- •
Increase in driver/courier retention rate
- •
Positive shift in public and policymaker sentiment scores
- •
Adoption of new legislative frameworks in key markets
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Long-term Vision
Category:Operations
- Title:
Accelerate 'Super App' Dominance by Expanding the Uber One Ecosystem
Business Rationale:Uber's primary competitive advantage over specialized rivals (Lyft, DoorDash) is its integrated platform. The Uber One membership is the critical flywheel for this ecosystem, driving cross-platform usage and significantly increasing customer lifetime value. Aggressively enhancing and scaling this program is the central lever for growth.
Strategic Impact:This transforms Uber from a set of discrete services into a unified, indispensable utility for daily life. It builds a powerful competitive moat based on ecosystem value, increases user switching costs, reduces churn, and creates a virtuous cycle where each service strengthens the others.
Success Metrics
- •
Growth in 'Cross-Platform Weekly Active Consumers'
- •
Increase in Uber One subscriber penetration rate
- •
Increase in Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)
- •
Reduction in blended Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative
Category:Customer Strategy
- Title:
Establish Market Leadership in Enterprise Mobility & Logistics (Uber for Business)
Business Rationale:The B2B segment offers a high-margin, recurring revenue stream that diversifies the business away from the price-sensitive consumer market. Expanding Uber for Business from a travel/meal solution to a comprehensive enterprise platform for employee commutes, customer transport, and last-mile delivery unlocks a massive new growth vector.
Strategic Impact:This initiative builds a powerful second pillar of growth for the company. It establishes a sticky, high-LTV customer base, creates a defensible position in the corporate market, and leverages the existing network to generate more predictable and profitable revenue streams.
Success Metrics
- •
YoY growth in Uber for Business revenue and gross bookings
- •
Increase in number of active enterprise accounts
- •
Growth in adoption of new U4B products (e.g., Commute Programs, Central)
- •
Improvement in overall company Adjusted EBITDA margin
Priority Level:HIGH
Timeline:Strategic Initiative
Category:Revenue Model
- Title:
Position Uber as the Definitive Global Network for Autonomous Mobility
Business Rationale:Autonomous Vehicle (AV) technology will fundamentally reshape the transportation industry. To avoid being disintermediated by AV manufacturers, Uber must strategically position itself as the indispensable, go-to distribution network for any autonomous fleet, owning the customer relationship and demand generation.
Strategic Impact:This secures Uber's long-term relevance and leadership in the next era of mobility. It transforms the business model by potentially removing the largest variable cost (driver payouts), leading to a step-change in profitability and operational efficiency while solidifying its role as the central hub for Transportation-as-a-Service.
Success Metrics
- •
Number of strategic AV partnerships signed and integrated
- •
Percentage of autonomous miles traveled on the Uber network in key markets
- •
Development of a successful hybrid-fleet (human + AV) management platform
- •
Reduction in network-wide cost per mile
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Long-term Vision
Category:Partnerships
- Title:
Transform Brand Perception from 'Utilitarian App' to 'Essential Infrastructure'
Business Rationale:Uber's current brand is highly functional but lacks the emotional trust and affinity required to become a truly integrated 'super app'. Its transactional nature and legacy of controversy are weaknesses. A strategic shift in brand narrative is needed to build the equity required for deeper user trust and loyalty.
Strategic Impact:A stronger, more trusted brand acts as a force multiplier across the entire business. It improves customer and driver loyalty, creates a more favorable regulatory environment, justifies premium service tiers, and provides a durable competitive advantage beyond mere network effects.
Success Metrics
- •
Improvement in brand trust and sentiment tracking scores
- •
Increase in unaided brand recall for attributes like 'safety' and 'reliability'
- •
Reduction in customer churn rate
- •
Higher NPS scores across rider, driver, and merchant segments
Priority Level:MEDIUM
Timeline:Strategic Initiative
Category:Brand Strategy
Uber must evolve from a transactional, gig-economy disruptor into an indispensable and trusted 'super app' for all movement. This requires proactively reshaping its workforce model to ensure sustainability and leveraging its platform advantage to become the central, integrated network for the next generation of mobility.
The integrated, multi-service platform ('Super App') that combines Mobility, Delivery, and Logistics, creating a powerful ecosystem with high user stickiness and cross-platform network effects, all anchored by the Uber One membership program.
Driving widespread adoption of the Uber One membership to accelerate the cross-platform flywheel, increasing user frequency, retention, and lifetime value across all business segments.